Author of the article
Maxim aka WisH
Higher education with a degree in Information Systems. Experience as a system administrator - 5 years.
If the router does not provide Wi-Fi, but there is wired Internet on the computer, the problem is most often in the router settings. But there may be other reasons. Let’s figure out why the router doesn’t distribute the Internet via wi-fi, even though we can connect via cable. If there is no Internet at all, then this is a different case, although it will be partially touched upon in the article.
Causes of failures
Before you start to deal with the problem, you should check whether the Internet works in principle. Plug the cable from your provider into your computer and make all the settings for a direct Internet connection. If everything works on the computer, but the router does not distribute the Internet, then look for the reason in it. If the router distributes Wi-Fi, but the Internet does not work, then the reason is the unavailability of the Internet on the part of the provider.
So, possible reasons for the lack of Wi-Fi:
- errors in the router that have accumulated from long and continuous operation;
- problem in the device settings;
- hardware failure;
- The problem is with the provider.
To find the reason, you will have to carry out several actions. Let's start with the simplest and move on to cover the entire possible range of problems.
You cannot save settings in the router control panel
Sometimes, users want to set some settings for the router, for example, for the initial installation, they click on the save button in the control panel, but nothing happens. Some users claim that the Control Panel may also occasionally show an error when saving new settings.
Why is this happening? Well, most often, the problem lies in the browser through which you are trying to configure the router settings. For example, if you are trying to access the control panel through Google Chrome, then try accessing it in Internet Explorer or Mozilla Firefox. You can also try saving the settings on a completely different device.
However, if you are still encountering this problem, it is most likely due to the faulty firmware on the router. You need to try flashing it and then do the setup again. However, it may also be that the router has already outlived its usefulness - and even flashing it won’t help.
Reboot your router
First of all, if the router works but does not distribute Wi-Fi, reboot it. During long-term operation, when the router does not turn off for weeks, errors accumulate in it. Minor failures resolve themselves or do not affect operation, but when a certain critical number accumulates, one of the functions may fail. For prevention, it is recommended to turn off the router when it is not needed and turn it on only when you are using it. There is no need to always turn it off and on, but if you leave for work or go to bed, and Wi-Fi is not needed to connect to home devices, then you should turn it off. The next time you start the device, it will load the standard firmware and perform self-diagnosis, so that failures will not accumulate, which will affect the speed of operation.
If the Tp-link router (or any other brand) does not distribute Wi-Fi, but there is Internet, reboot the router. Rebooting can be done by simply unplugging it from the outlet, but it’s better to do it right. To restart the device, use the special button. Some have a large button to turn it on and off.
Press the button and hold it a little. When you release it, make sure that the router has stopped working and all the lights have gone out. Wait about another minute and then turn it back on. The system will boot with no accumulated errors in its memory, but all settings will be saved.
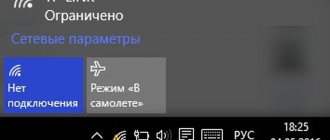
The Wi-Fi router does not distribute the wireless network. Or the network is present, but Internet access is not
Sometimes, a situation may arise when your router seems to be configured as it should, but it doesn’t want to distribute a wireless network. For example, the router is working, the indicators on the device body confirm this, but your additional devices, for example, a smartphone or tablet, cannot find the distributed network. It is worth noting that this sometimes happens - and the reason for this is the router software, which began to fail. All you need to do is restart your router, which will, in most cases, fix the problem.
If there is still no wireless network, even after rebooting, then try going to the control panel and check if the router settings were reset by accidentally pressing the reset button. Also inspect the router case for the presence of a button to activate wireless network distribution (wireless) - it could also have been accidentally pressed.
However, what to do if the Wi-Fi router distributes a wireless network, it is detected by all user devices, and you can even connect to it, but there is no access to the Internet itself? Well, in this case, the device itself may again be to blame - restart the router and see if anything changes. It’s also worth checking whether there is any access to the provider’s network and the Internet at all. Sometimes we blame the router for the problem, but the provider is to blame.
Checking the router and cable
If your router stops providing Wi-Fi, first check the cable for damage.
If there is visible damage, you need to cut off the problem area and splice the wire. If the length allows, you need to crimp the twisted pair, cutting off the part with the old connector.
Next, you should check that the connection to the device itself is correct. Typically, each manufacturer highlights in color the connector into which the cable from the provider itself is plugged in (usually labeled WAN/Internet).
Check the indicator with a globe icon or WAN. If it is not lit, then the problem is in the connection or on the provider’s side.
Pull out the cable, check if the port is correct, and insert it until it clicks into the correct connector.
Wait a bit and check the internet indicator. If it lights up, then the wireless network should work.
There are other devices where you can plug a connector into any port. In them, the configuration is carried out in the system itself, setting all the parameters for connecting to the Internet there. Typically, such devices belong to the professional segment and are rarely seen in homes. Still, it’s better to check this and read the instructions for your router. The name and model are written on a label on the bottom. Also look at the settings login information there, this will be useful in the next steps.
It also happens that a modem is used instead of wired Internet. In this case, remove it from the router connector and check the contacts on it and in the router.
Modems are configured separately in the router itself, so you will have to check that the settings are correct. It happens that they go wrong or the mobile operator changes something in its parameters, and they stop working correctly with the old settings.
Reinstall your wireless device and drivers
Damaged drivers or other problems with the wireless device may be the reason why the Wi-Fi router does not work. Make sure you don't have any driver issues by following these steps.
- Open Windows Device Manager (right-click Start and select Device Manager).
- In Device Manager, expand Network Adapters to view all network devices.
- Highlight the Wi-Fi or wireless network adapter and press the Delete key on your keyboard to remove the device.
- Once the device is removed, close all windows and restart your computer.
After the computer is booted, the Windows operating system will automatically install the necessary drivers on the network card.
Network adapter settings
Wi-Fi may be distributed, but the problem lies in the receiving device itself. Usually such problems happen with laptops and tablets.
- To check, click on “Start” and enter ncpa.cpl in the bottom line.
- A window will open containing all types of connections to all networks that were available on this device.
- Here, find your active wireless network connection, right-click on it and select Properties. Check if it is disabled. Do not confuse the virtual wireless network setting in Windows, which serves other purposes.
- In the window that opens, find “TCP/IPv4 protocol” and double-click on it. Another window with parameters will open.
- Here, set automatic receipt of everything. If the settings are already in the required form, then you can try changing the DNS server acquisition to manual; to do this, in the “Preferred server” line, enter Google DNS – 8.8.8.8.
When using the Internet on a phone or tablet, go to settings and go to the wireless networks section. Here, find your Wi-Fi and remove it. To do this, click on it and hold it for a while until another window appears with available options. Select Delete or Forget. After that, try to connect.
You constantly need to restart the router for it to work properly
There are cases when users are forced to restart their routers without stopping, since they constantly cut off the connection speed, cut off connections for some or all devices, block Internet access on a computer connected via a local network, and much more. In general, the router can cause a lot of problems and therefore it is restarted without stopping. It happens several times a day.
It is worth noting that a problem of this nature most often occurs on routers that are no longer new, which have served for about two to three years. However, there are also exceptions in the form of some new routers, but they are usually in the extremely cheap segment.
So why do problems like this arise? The answer is the following: from extremely severe overload of the router. The device simply cannot bear the load that the user places on it, as a result of which it begins to fail in every possible way or even break connections. If you encounter this problem on your router, then try the following:
- Perform a firmware update on your router.
- Try disabling programs on devices connected to the wireless network that may create a load, for example, uTorrent and the like.
- Reset your router and then configure the settings. Perhaps you went through the settings in the control panel and set something that theoretically could interfere with correct operation.
- During operation, the router should be checked for severe overheating. If it heats up like a kettle under load, that’s the reason. Either put it in a cooler place (especially if it is in the sun) or replace it.
- Cheap routers will almost never cope with heavy loads. Do you like to watch streaming videos in ultra-high quality or constantly download a ton of content from the Internet? A budget router probably won’t cope with such tasks.
Checking Wi-Fi settings, changing channel
The next step is to check the router settings. They rarely go astray just like that, but sometimes it happens. There are too many options here to describe them in one section, so we will have to describe a general algorithm that will work for most models.
Take your device, turn it over and look at the bottom label. It contains the username and password to log in, as well as the address. Usually the address is 192.168.1.1, and enter it in the address bar of the browser. The login and password are most often admin.
If you have already changed the login/password combination or the device address, you will have to remember the specified parameters.
After entering the required data, a window will open containing all the information about the device and its settings. In the upper or left part of the window there are sections through which you can navigate to different tabs. Select your wireless network or Wi-Fi there and go to the tab. Here, check that the wireless module is not disabled, the name is set correctly, and the password is correct. Using Tp-Link as an example, these parameters are configured on the first and second tabs of the “Wireless Mode” section.
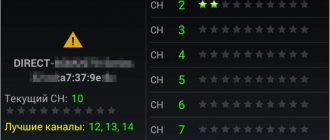
There is an option here called channel. There are several of them and automatic selection is required. The problem is that if there are many devices around you distributing a wireless network, then the channels will be clogged. Some devices have built-in programs to scan and display the situation, but most do not. Try changing the channel on the router, saving the settings and trying to connect again. If it worked, it means that in the past there were so many routers busy with distribution that the signal simply could not get through. In some cases, it helps to purchase devices that operate not only at frequencies of 2.4 Hz, but also at 5 Hz, then the number of available channels will increase.
Indicator operation: constant “burning”, flashing
If access to the Internet is lost or the computer has lost connection to Wi-Fi, inspect the indicators located on the router body. They usually reflect the reasons why the device is not working properly.
If no indicator lights up, make sure that the power supply plug is inserted into the connector on the case. Check the plug - sometimes it becomes dislodged and the power is interrupted. This is also possible during voltage surges and short-term power outages.
If the lights are on or flashing, determine what each one means. The number and arrangement on the body differs, depending on the manufacturer and model of the device.
Standard set of indicators using the example of TP-Link TL-WR720N:
- Power. Lights up only when the router is turned on. If there is no power, the other indicators cannot light up.
- SYS. Signals that system settings are in progress. On most models it is indicated by a gear. Normally this indicator should blink. If not, there was a malfunction. If the light blinks, the modem is being configured. This process usually does not take more than a minute.
- WLAN. The light indicates the current Wi-Fi status. If the indicator is not lit, the wireless network is not working. When the light is constantly on, the router is distributing WiFi, but no external devices are connected to it yet. If the device is working properly, the WLAN blinks, which indicates data exchange between the router and another gadget.
- LAN Indicates that there is a network connection via cable. The display principle is the same as for WLAN. If an external device is connected, the light will blink. Otherwise it won't light up.
- Second LAN. Most routers have several connectors for cable connection of devices. There are 2 of them on the TP-Link TL-WR720N. Many devices have 4 LAN outputs, which is convenient if you need to simultaneously connect a computer, TV, and other gadgets.
- WAN. Displays the status of the Internet connection. Usually the indicator symbol is applied in the form of a globe or planet. If the WAN is off, there is no Internet. If the light is on, the connection is established and there is access to the network. The blinking indicator indicates that the Internet is working and the data exchange process is normal. This can be observed, for example, when loading pages in the browser.
- WPS. Wi-Fi Protected Setup technology allows you to quickly connect devices to a secure router without entering a password. The indicator only works when trying to make a quick connection to the modem. If the light flickers frequently, a connection is in progress. If the operation is successful, the indicator lights up and does not blink. Slow flashing indicates a failure.
When the router starts, POWER should be lit and SYS should be blinking. Then WAN and WLAN light up. The remaining lights may not light if the devices are not connected via a LAN cable or using WPS.
Resetting the router and reconfiguring
If none of the above helped, the router does not want to distribute Wi-Fi, then all that remains is to reset the settings to factory settings. In this case, all settings will be erased, the router will be as clean as it was just purchased. You will have to re-enter all the parameters, but be sure not to install any tricky and unnecessary option that could block the network.
The reset button is hidden in a recess so that it cannot be pressed accidentally. Use a thin, but not sharp object to press on it. Hold it for ten seconds, the indicators on the router should blink and then the reboot will begin. After turning on, the login information that is written on the bottom of the router will be suitable. You will have to configure the router yourself, because each model has its own. It’s better to go to the provider’s website and download instructions for your model there, so everything will be correct.
Other options
If the router is connected, the updates are in order, you definitely installed the Internet and paid for it, but Wi-Fi still doesn’t work, we’ll dig further.
There is a connection, but no internet
If the Internet does not work, there may be several reasons. From non-payment for the Internet to mechanical damage to the router or cable.
- Look at the router. If the Internet icon is red or goes out, it means you do not have access to the network. Contact your provider. Perhaps they are undergoing renovation work.
- Check if all wires are connected. If the wires do not fit tightly, return them to their original position in their sockets.
- If this does not solve the problem, then inspect the cable responsible for the Internet. Assess the condition. An outdated or damaged cable will not transmit a signal.
- Wires may be damaged in other places. Experience shows that cables lying in the attic or anywhere else can be bitten by mice and rats.
- The reason may be a faulty WAN or LAN port. This often occurs on older devices that have been handled carelessly.
- If you are using a 4G modem and your Wi-Fi is not working, the problem may be with the device itself. Check whether the SIM card fits tightly in the port. The problem may be a faulty USB port.
Constantly obtaining an IP address when trying to connect
It is rare, but such a problem does occur. A gadget or PC cannot connect to the network unless it receives at least a temporary IP address. The problem here is in the router settings themselves.
- Go to the router remote control page. The address is written on the back of the device.
- Go to the “DHCP” tab. The checkbox should be “Enable”. Check the range of available addresses for devices.
- Go to the “Wireless” tab.
- Make sure WPA2 encryption is enabled.
- In the same tab, go to “Wireless MAC filtering”.
- MAC address filtering needs to be disabled.
- Check the “Allow the stations specified by any enabled entries in the list to access” option. Translated, this means: “Accept requests from devices whose MAC addresses are not listed.” That is, the router will accept authorization from all devices, and not just from those whose addresses were pre-registered. This option is usually used by corporate users.
- Click on “Save” and reboot the router.
The smartphone does not see the network
A frequent case and quite ordinary. The point is to update the software of the smartphone itself. When the manufacturer releases updates, your smartphone automatically downloads and installs them (unless you have disabled auto-updates). Due to shortcomings by engineers, the algorithm for connecting to a wireless network may be incorrectly written in the new firmware.
The laptop does not see the network
The keyboard of a laptop and a PC are different. Not fundamental, but they exist. For example, a laptop has a hotkey. Hotkeys. By pressing any key combination, we can decrease or increase the brightness of the monitor, control the volume of the speakers, etc.
Take a closer look at the keyboard. An interesting icon in the form of an antenna is drawn on the F2 or F8 button. And the combination FN + F2 (or F8) disables network adapters. It is likely that you accidentally pressed this combination, which is why the network disappeared.
Closed Wi-fi network
Large corporations, companies and firms use a closed Wi-Fi network for computers. This is done for security purposes, since a good hacker with skillful hands can easily access secret files and folders via Wi-Fi. All he needs to do is connect to the network.
Therefore, the exact MAC addresses of employee devices and computers are registered on the server. It's like entry by invitation only. You can connect to such a network only by registering your MAC address.
Power Saving Mode
Modern laptops, tablets and smartphones are equipped with a task optimization and energy saving system. This is done to ensure that the battery charge lasts as long as possible.
Some devices give you the option to choose which systems to turn off, and some do it themselves. For example, if you set the maximum energy saving level, the system will disable all network connection protocols via GSM and Wi-Fi. A laptop works on the same principle. If the battery charge is low, the system can automatically turn on power saving mode and turn off all connections.
PS Your battery charge directly affects the Internet speed on your device. Guess how?
Network without Internet access
In order not to hurt your eyes with long stories about what protocols, IPv4 connections and a DHCP server are, let’s get straight to the problem. Right-click on the “Internet connection” icon on the taskbar. Click on “Network and Sharing Center”. We open our connection and see “IPv4 - without Internet access.” In the same control center we find “Change adapter settings”.
You will see icons for local network connections. We look for the one that says “wireless connections”, right-click and go to “Properties”. You should check the “Obtain an IP address automatically” and “Obtain a DNS server address automatically” checkboxes. "OK". You have transferred the burden of solving the problem of finding addresses to the computer itself.
If it doesn’t help, then there is plan B. We register the network addresses ourselves.
For D-link and Netgear routers, the following is relevant: IP address: 192.168.0.2, mask: 255.255.255.0, gateway: 192.168.0.1 and DNS address: 192.168.0.1
What should you do if every time you turn on your computer, a network without access is detected? Watch the following video:
Error 651
It comes when you decide to tinker with the Internet settings or when you have just installed an Internet cable. Some providers still use this system. Nobody knows exactly why this is done, but Internet providers like to do it.
How timely Dial Up! Click “Start”, go to “Control Panel”, go to “Network and Sharing Center”.
Click on “Set up a new network connection”, “Connect to the Internet”, “Create a high-speed connection”.
Here you need to enter your personal information and click “Connect”.
If the magic doesn't happen, call your suppliers and scold them.
Hardware faults
If resetting the settings does not help, then there are not many options left. After checking the cable from the provider by connecting it to the computer, you need to check one more thing. Take your phone or laptop to a different wireless network and try connecting to it. If everything works here, then there are only a couple of options left:
- hardware failure;
- The problem is with the provider.
To eliminate the first point, try taking the router to someone you know who definitely has everything working, and install it there. If nothing works, then the wireless communication module may have stopped working. In this case, all that remains is to take it for repairs or buy a new one. It is unknown what will be more expensive.
When Wi-Fi does not work (connection using a network cable)
Look for a section called Wireless (other names include Wi-Fi, Wireless Network, etc.). In the picture this section is marked with a green frame. Once there, find the checkbox to enable wireless communication and check it, then again set the network name and password for authentication in it, remove possible MAC address filters.
The Advanced options section should have approximately the same parameters as in the figure below:
· Channel selection: automatic;
· Bandwidth (20/40 MHz);
· Router operating mode: “access point” (or AP, access point);
· Mode: bgn for modern devices, or g for older PC models.
Reboot your Wi-Fi router and try connecting to the network again. Having trouble connecting? Try changing the name (SSID) and password, playing with the channel selection, choosing a different bandwidth. Reboot every time after changing the next setting if the interface requires it.
Problems on the provider side
When resetting the settings did not help, but the device works fine elsewhere , you can only think about the provider. Call technical support, describe all the actions taken and their results. It could be a faulty server or router in your home or area. Usually the entire Internet disappears at once, but it also happens that it goes through the cable, but there is no wireless network. Tell your technical support specialist about these problems. He will tell you what to check and what the problem is.
Problem with network equipment or computer
If there is no Wi-Fi, the source of the problem may not only be the network equipment, but also the computer itself. To find out, just connect to the remote access point from another device, such as a laptop, tablet, smartphone or TV. If you cannot connect, the reason is the router or lack of Internet supply from the provider. If you can safely surf the Internet from other devices, you need to pay attention to the performance of the computer.
The principle of building a wireless network at home
Note! People's homes contain a large amount of different equipment - phones, smart TVs, computers, tablets, etc. To organize a high-speed and uninterrupted home wireless network, you need to purchase high-quality routers. Routers from TP-Link, Keenetic, Samsung, Xiaomi and Zyxel are popular.
Routers from TP-Link
Temporary glitches
If the devices were just connected and there were no problems, then this is a temporary failure. There are not many ways to eliminate it. Rebooting the router and resetting the settings will help if the problem was in the router. If the router still does not distribute Wi-Fi, although there is wired Internet on the computer, then the provider is to blame. He is carrying out repair work or errors have accumulated in the main dispenser. Wait a little, usually this is fixed quickly. If the Internet does not appear, call technical support. The provider has diagnostic tools for all devices on the line.
After all the stages of diagnostics, resetting the settings and calling the provider, the problem will probably be solved. In rare cases, it happens that the receiver breaks down in the devices themselves, such as a laptop or phone. You can eliminate this by connecting to any other network.
External obstacles to the signal
Why does the Internet not work on the computer, but Wi-Fi works?
As practice shows, it doesn’t matter what kind of phone a person has - an iPhone or Xiaomi, an iPad or Samsung tablet, a laptop from HP or no-name, everyone without exception can lose their wireless Internet.
Often the problem is caused by improper placement of network equipment in an apartment or house. If the router is located far from the receiver, the signal quality decreases noticeably. If the user is confident that his network equipment covers the entire area of his home, then he will need to additionally ensure that there is no interference in the place where the signal is propagated.
One of the biggest obstacles in the way is cabinets with mirrored elements. It is precisely inside such cabinet furniture that network equipment is often installed. Mirror surfaces simply reflect the signal and it is lost.
There is also one obstacle to the signal path - reinforced walls. They absorb part of the signal rather than simply mirror it.
An example of an unsuccessful router location in an apartment
Note! Network equipment may not operate correctly if installed near an electrical panel.