Many people ask what a wifi signal amplifier for a router is and what it is needed for. This device can often also be found under the name of a wireless communication repeater, as well as a Wi-Fi repeater or repeater. Such a variety of names is not surprising. There are a huge number of models on the market, because wireless signal repeaters are produced by the same companies as other network equipment - TP-Link, Asus, Zyxel, Keenetic, Tenda, D-Link and others. In this article, we will understand what a wifi repeater is, what it is needed for, and how to choose a signal repeater for your router.
Why do you need a WiFi repeater - signal repeater?
The very idea of a wireless network is that the Internet should not be limited to one room, but spread throughout the entire apartment, office or even a garden plot. But the greater the distance from the wireless distribution source, the worse its speed.
In order to strengthen the existing signal coming from the access point, they came up with a wifi repeater, which is also called a repeater, repeater or simply amplifier. It “picks up” the main network and distributes it further, thereby improving the quality of communication and increasing the range of wifi.
The wifi repeater does not provide any other functions. Therefore, apparently, it is in the shadow of the more famous wireless device - the router. The latter, by the way, can also work in amplifier mode. But for the function of extending the reception area, it is simply irreplaceable, both for home and in the office.
Types of amplifiers
Like any other gadget, wireless network amplifiers vary in power and design qualities. There are several types of repeaters on the domestic market:
- Portable or personal. This option is suitable for strengthening the signal when using one or two mobile devices. They are compact and low-power Can be connected via a USB port;
- Homemade. A similar technique is used at home to strengthen wireless networks to which up to 5 devices are connected. In this case, the range can reach 20 meters;
- Office. This category includes powerful repeaters that can be used as a full-fledged access point. The key advantage is a wide range of antennas that provide a stable signal when using up to 50 connected devices.
When might you need to connect a wifi signal amplifier to your router?
Situations in which it may be necessary to install a WiFi repeater occur very often.
The most common is due to incorrect initial installation of the main router. For example, you were lucky and your grandmother left behind a large five-room apartment in a Stalinist high-rise building. You decided to organize a wireless network in it, but did not install the router in the “geographical” center of the apartment. Let’s say, in your room with a desktop computer (because it is connected via cable, and you don’t want to drag it across the entire apartment). Or in the hallway immediately above the front door, as Internet providers like to do today. Then it turns out that there is not enough wifi to the far room and it is not possible to access the Internet from a laptop or smartphone.
Another option is when you organize wifi in a private home. Here it is even more difficult to guess the optimal location for installing the router - distance, thick walls and who knows what else. I had a case where the dacha plot was located next to some military facility, so the antennas there were jamming everything that was possible and impossible with interference. Therefore, God himself ordered the use of a Wi-Fi repeater.
What is a Wi-Fi signal booster?
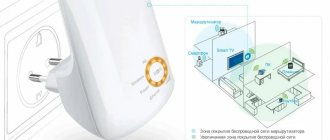
First, let's look at the essence of a WiFi signal repeater, what it is. This is a universal amplifier used to increase the operating area of a wireless network and eliminate the “dead zones” characteristic of the operation of a router (if installed incorrectly). The device has a compact body with a built-in circuit and antennas for receiving and transmitting a WiFi signal. If necessary, the repeater can be installed in any convenient place and moved to any point. You only need to configure the Wi-Fi signal amplifier once. If the router position is changed, all settings are saved.
How to choose a wifi signal repeater for a router?
The photo below shows the TP-Link TL-WA850RE repeater model, which the company kindly provided to us. It works with all routers regardless of brand.
Most models of wifi repeaters from different manufacturers look very similar to this TP-Link. This is a small “box” that has a plug on its body for direct connection to an outlet. Often the electrical point occupied in this way is compensated by the presence on the repeater itself of an outlet for connecting any other device.
But there can be several amplifying antennas. They can be hidden in the case, like WavLink
and external, for example, like the Mercusys MW300RE
The technical characteristics also differ. The main thing you need to pay attention to when choosing is the supported frequency ranges. If you want to expand your 5 GHz wifi network, then the repeater must be able to work in this range.
So which one is better to choose?
But here everything is simple - choose whichever one you like) There is no difference between them. I have an 850RE, but somehow I don’t feel like changing it – it copes with its tasks with a bang. By the way, you can take a look at the video with his participation:
If you have a cool fast router and you need the same repeater for it, look at the support for the 802.11ac standard, modern repeaters only differ in standards. Everything else is design. But even if you take a cheap Xiaomi, there’s nothing to worry about. People use it successfully too.
All proposed models are perfect for an apartment. If you have a huge area or a large country house, it is recommended to consider purchasing several repeaters and think over a scheme for proper signal coverage over the area.
I would especially highlight dual-channel models - they can intelligently unload the network by transmitting data on one frequency and receiving it on another - you can see the speed increases in the characteristics above.
When choosing, do not pay attention to the speed of the Ethernet port - in 99% of cases no one uses it.
Conclusions about the operation of the wifi repeater
Summarize. As you can see, the presence of another link within the local network between two computers in a video wifi repeater still reduces the overall speed, which was not a surprise to us, since the presence of any additional device, be it a repeater, powerline or some other adapter, will influence her. The most interesting thing was to see in which mode these losses would be the least.
As it turned out, the highest average speed was with the scheme (No. 4), when the computers were connected to each other through a repeater, bypassing the router - 4800 Kbps compared to 2200 that WiFi without a repeater gave. This is quite logical, since between them there was not that extra “knee” in the chain, in the form of a router, whose role in this case was played by today’s hero. Although the spread between the largest and smallest values is a little annoying - the connection is not stable.
But the most questions from this test arose for my ASUS RT-N10U router - why does it output only 2 MB per second?? It turns out that in my network it is he who is the weakest link - it’s worth thinking about, as in one famous program, saying “goodbye” to him and looking at another model.
The second place in speed went to scheme No. 2, in which one of the computers was connected to the router using a patch cord, and our repeater distributed a signal to the laptop. Although, as we found out, the router played a disservice to us here, this does not affect the overall picture in any way, since after that we tried to use TP-LINK as an adapter (No. 3), receiving a wireless signal and sharing it on the PC - with this he did the worst job.
What to look for when choosing a repeater?
There are several key points to consider when choosing a Wi-Fi signal booster. I will try to briefly, but as informatively as possible, talk about each of them.
Supported band (2.4 GHz and 5 GHz)
Repeaters, like routers, are single-band (operate only at 2.4 GHz) and dual-band (supporting 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz). On the box, or in the description, it is usually written “Dual Band”, “AC”. Amplifiers that support the 5 GHz frequency have support for the Wi-Fi 802.11ac standard. A dual-band repeater can connect to the router in two bands at once. At 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz. Or, for example, connect to the router only at a frequency of 2.4 GHz, and distribute two Wi-Fi networks: at a frequency of 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz.
It makes sense to choose a dual-band Wi-Fi signal amplifier, even if you currently have a single-band router (works only at 2.4 GHz). Since at the output you will be able to get a network in the 5 GHz band (in which the speed may be higher). Well, when you change your router to a dual-band one, you don’t have to change the repeater.
In 2022 - 2022, I recommend buying dual-band Wi-Fi signal repeaters. Single-band can only be purchased if your budget for purchasing this device is very limited.
Transmission speed
The technical specifications of the amplifier indicate the maximum transmission speed for each range (Wi-Fi network standard). For example, at 2.4 GHz (802.11n) up to 300 Mbit/s, at 5 GHz (802.11ac) up to 867 Mbit/s. This is the maximum theoretically possible speed. Not real. But the higher it is, the higher the amplifier’s throughput, and the higher the actual Internet connection speed will be.
Availability and speed of LAN ports
The repeater can be equipped with Ethernet ports. Usually this is 1-2 ports. Most often one. There are models without Ethernet ports at all.
They are needed in two cases:
- To connect devices to the repeater using a network cable. For example, you can connect a desktop computer or a TV that does not have Wi-Fi to the Internet. That is, the repeater distributes the Internet not only via Wi-Fi, but also via cable.
- To work in access point mode. This is when the repeater is connected to the router using a network cable. The main advantage of such a connection is higher stability and speed (compared to a wireless connection). There must be support for the “Access Point” operating mode. This mode is available on most devices.
As for the speed of LAN ports, on more budget options the ports are not gigabit (up to 100 Mbit/s), but on more expensive models the ports are gigabit (up to 1000 Mbit/s).
Mesh technology support
If you thought that dual-band repeaters were the newest and most modern, then I will disappoint you. The newest and most modern ones support Wi-Fi Mesh technology. With their help, you can build a seamless Wi-Fi network, which will solve the main problem of signal amplifiers - switching devices between the router and the amplifier. All devices (except old ones that do not support fast roaming on a Wi-Fi network) in such a network will switch very quickly (fast roaming) and without losing the connection.
But Mesh support is needed from all devices (router, amplifier, client). There are very few such devices on the market now. TP-Link has a line of devices (routers and amplifiers) called OneMesh. If you have a router that supports Wi-Fi Mesh technology, you simply buy a signal amplifier (in the case of Mesh, most likely, it should be from the same manufacturer as the router), configure it, and get a seamless Wi-Fi network. One network throughout the house. As with the Wi-Fi Mesh system. In the article linked above, I showed how to set up such a network using the example of a TP-Link RE300 amplifier and a TP-Link Archer A7 v5 router.
So far I have not seen such devices from other manufacturers. Keenetic and ASUS have something similar. But there you can combine several routers with this technology into one network. There seem to be no separate Wi-Fi repeaters. But this is at the time of writing. I think they will appear.
Antennas and their number
As for the number of antennas, there are usually two. Four antennas can only be found on expensive models, which usually support MU-MIMO technology. Otherwise, these four antennas are simply not needed there.
The range of the network does not depend on the number of antennas. There is not even much difference in whether the antennas are internal or external. The range of the relayed Wi-Fi network will be approximately the same for all models. Moreover, you do not need to focus on the length of these antennas.
Access point mode support
This is when a Wi-Fi signal amplifier can be connected to a router using a network cable and it will distribute the Internet via Wi-Fi while receiving it via cable. It is not recommended to use them instead of routers (connect a cable from your provider). And in most cases this cannot be done at all.
This scheme can be used in the case when you have a network cable laid in another room, and when connecting the amplifier via Wi-Fi, it greatly reduces the speed. There will be insignificant speed losses along the cable.
Most modern amplifiers support access point mode.
And further:
- Possibility of control via an application from your phone. This feature is not available on all devices. Typically, configuration and management is carried out via a web interface (via a browser).
- If, for example, you choose a repeater on AliExpress, then make sure that the seller offers the product with a suitable plug for you. The socket type must be “European (EU)”. Otherwise, you can only connect it through an adapter.
- The presence of a WPS button (or similar) simplifies the process of setting up the device.
- Support for MU-MIMO and Beamforming technologies can only be found on top models of Wi-Fi amplifiers. If you have an expensive and powerful router, you need a fast network, and you can’t do without an amplifier, then it is advisable to choose a model that supports these technologies.
Tip: if you have a new router, I advise you to check whether it supports Wi-Fi Mesh technology. You can look at the specifications on the official website. You can also update the firmware to the latest version, since Mesh support may depend on the firmware. If it does, then it’s much better to choose a repeater that supports Wi-Fi Mesh, or another similar router, and combine them into one seamless Wi-Fi network. I wrote about this in more detail above.
Range of wifi amplifier
As for the distance over which this repeater model expanded the signal from the main source and strengthened WiFi. I connected it in the room farthest from the access point in an ordinary “Brezhnev” three-ruble note - it turned out that it directly passed through 3 plasterboard walls at a distance of about 10 meters. In this room, even the iPad Air couldn’t connect to the Internet, the wireless module of which has no complaints - it sees wifi even where it is no longer available on other smartphones. Our Extender from TP-LINK also caught it (two antennas make themselves felt). And without any problems I began to extend it all the way up the staircase. I agree that the initial location of the Point is not very good, but for our experience it was just right.
Numerically, this is expressed as follows. When there was no repeater, in the far corner of the apartment the Internet speed from the router was as follows:
When we connected the amplifier, this is what we got for the wifi signal zone:
Of course, these results are relevant only for my network - they were influenced by the characteristics of the PC’s network card, the laptop’s wireless module, the router’s hardware, and even the radiomagnetic environment in the room, which we brought as close as possible to a quiet everyday one. But they certainly represent the overall picture, so you can safely use these conclusions in your practice when designing your networks.
Well, the TL-WA850RE did its job perfectly, and I can recommend it to my subscribers as an effective way to expand your WiFi reception area.
What is it for?
One router is often not enough to cover the entire apartment or house. The reason may be a large area of the room (exceeding the range of the router) and other factors:
- Obstacles. A WiFi signal repeater helps eliminate the problem associated with deteriorating network quality due to a large number of walls or partitions.
- Interference. The presence of other Wi-Fi networks in the router's operating area can lead to problems with the network. To reduce the negative impact, it is recommended to connect a wireless signal amplifier.
- Wrong choice of location. It is recommended to install the router at the central point of the serviced premises. But this is not always possible, so the signal is distributed unevenly. If it is not possible to install the device correctly, you can use a WiFi amplifier.
After connecting the repeater, the router transmits the signal as usual, and the repeater will only receive it and forward it further.
Who needs a repeater?
If the Wi-Fi signal does not reach part of your apartment (house, office) or it is very weak and its speed is unsatisfactory, you cannot do without a repeater. Despite the fact that on the Internet such devices are often called a WiFi signal amplifier, in fact this box just repeats it, essentially passing it on through itself. In other words, this is a signal extender.
However, buying a Wi-Fi repeater is not always justified. As a rule, it is used as a last resort when all other methods have failed.
SETUP AND CONNECTION
There are two main options for setting up a wireless repeater:
- using WPS button;
- or web interface.
The first setting method is not always available and depends on the model. With WPS support, you should proceed as follows - turn on the repeater, wait a certain time before it loads and press the WPS button on the amplifier and WiFi router. In this case, the repeater automatically detects the network and goes into operating mode.
If there is no WPS or if there are problems with automatic connection, you can proceed to the second option - configuration using the web interface. The repeater has a special Ethernet connector, and the device comes with a patch cord that allows you to connect to a laptop or PC.
How to set up a repeater without WPS?
To do this, the repeater is connected to a computer. In the address bar of the browser, the IP address of the device is entered, which is usually indicated on its case, after which the user is taken to the settings menu.
The essence of further settings for the repeater is to specify the MAC address (BSSID) of the main access point, as well as its security parameters. Since the procedure for different models may vary, it is better to use the instructions for a specific device. Once the repeater setup is completed, the device reboots and operates in normal mode.
Before installing a WiFi repeater, it is advisable to check the range of the amplifier in the room. The easiest and most accessible way is to use a smartphone with installed software (WiFi Analyzer). The program allows you to check the signal strength at each desired point and accurately determine the location for connecting the repeater. The latter is installed in the area of the most stable reception.
If there are antennas on a WiFi repeater, it is important to choose their position correctly, taking into account the subtleties of the signal distribution in the room. If the router and repeater are on the same floor, vertical orientation is optimal. When installed on different floors - in a horizontal plane.
The number of amplifiers required to create a stable signal is determined individually. As a rule, one repeater is enough for a house or apartment.
To the begining
How to make a repeater with your own hands?
Despite the variety of repeater models, you can make the device yourself from scrap materials. Let's look at several options for making a WiFi passive repeater with your own hands.
Method No. 1
The easy way is to make your own antenna in the shape of a diamond. The material you will need is a coaxial cable, a sheet of aluminum, a plastic box, wire and soldering equipment.
The algorithm of actions is as follows:
- Make two rhombuses out of wire so that each side is 3.1 cm long. One of the corners of the rhombus must be soldered.
- Solder the top edges together to form a triangle.
- Solder a 0.5 cm long wire to the bottom edges.
- Connect the copper core of the coaxial wire at the top of the solder, and the braid at the bottom.
- Protect the product from adverse weather conditions using a plastic box (if it will be placed outside).
For better amplification, you can use a foil screen.
Method No. 2
To implement another way to make a WiFi repeater, prepare a backing (cardboard or foam), side cutters, wire (copper), pen, ruler and scissors.
The following is the algorithm:
- Cut a nozzle 0.15 m long. There should be a thickening on one side for attaching to the router.
- Install 5 cm long pins horizontally to each other.
- Place the attachment on the router's antenna.
If there are several antennas, it is advisable to prepare an appropriate number of amplifiers.
Method No. 3
Another option is to convert a regular router into a signal amplifier. If you don’t have time to figure out how to choose a repeater, you can find an old router and adapt it as a repeater. You need to know that not all routers have this feature. For example, problems are possible with TP-Link and D-Link.
For example, consider the algorithm for the ZyXel router:
- Go to settings, enter your username and password.
- Go to the control panel and change the mode to “Amplifier”.
- Apply the settings and reboot the device.
- On two routers, press the Wi-Fi (WPS) button.
- Wait for connection.
In the future, to return to normal mode, just change it in the settings as the main one.
Alternatively, you can use an Android WiFi signal repeater using your phone. To do this, the FQRouter2 application is installed on the device. Next, you need to enable the corresponding function. It is worth considering that this option is not available for all devices.
If the repeater doesn't help
Repeaters are quite interesting devices, but they are not universal enough. If you need to transmit a signal through a couple of solid walls, or to a remote room, the wireless signal may not cope. In this case, transmitting data over ordinary electrical wires can help. We have done a large review of such devices, describing in detail the pros and cons. In addition, we recorded a short video repeating this text:
Myths about strengthening Wi-Fi signal or what not to do
- One of the frequently repeated search queries is the phrase “download WiFi signal booster.” This is impossible. The maximum that can be done is to download drivers for the computer’s network card and update the router’s firmware. All other advice will be harmless at best. At worst, they will end up infected with the virus.
- Another myth is more powerful antennas. As practice shows, replacing the antenna with a longer (and supposedly more powerful) one does not lead to anything. Why: firstly, some of the antennas in modern routers are built into the case. Secondly, they are specially designed for a specific model and lengthening them and increasing the number does not change anything. A funny thing - the Chinese really like to stick a bunch of antennas, so the router looks like a spider. As practice shows, these decorations are of little use. Third, if you disassemble a particular plastic antenna, it often turns out that the metal core in it reaches well up to a third of the length.
Everything else is purely a design trick to make the router seem powerful. The Chinese are especially guilty of this. By the way, there are special attachments for turning the omnidirectional antennas of the router into highly directional ones. But their installation has many nuances to recommend them to most users.