Notice
: Undefined variable: related_to_this_post in
/home/u266276471/domains/mobobzor.com/public_html/wp-content/themes/mobobzor/functions.php
on line
256
There is the easiest way to disable safe mode on a modern PC - a complete restart of the system, but what what to do if, after restarting the computer or laptop system, this mode constantly starts? There are several effective and simple methods that allow you to disable Safe Mode in Windows 7.
Safe mode is useful when it is necessary to solve certain difficulties with a PC by starting the system in this mode - the user will receive a system with a small number of running programs, utilities, and active applications. Which in turn makes it possible to start the system comfortably when it does not start in standard mode.
How to enable or disable Safe Mode
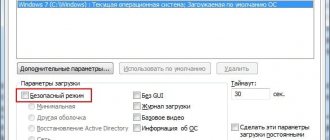
Managing the operation of such a function does not require a large number of actions. When working in one of the programs in which the desktop remains accessible, you need to press the Windows + R key combination (the first key is located at the bottom of the keyboard and is indicated by a flag) to access a small window. In this window you need to enter “msconfig” (without quotes), and then agree with the entered text. A new “System Configuration” window will immediately appear, where in the “Boot” tab all you have to do is find the “Safe Mode” item and check the box (to enable) or uncheck (to disable). Under this label, when turned on, several boot functions are visible that can be configured.
Reference! From this window, the user can also edit the list of programs that start when the laptop is turned on. The applied changes will take effect after the PC is turned off.
If you cannot call up the “System Configuration” window using the buttons for some reason, then as an alternative option in the Start menu search system you need to enter “msconfig” and select the only option offered.
Via "shift reboot"
This is another way to invoke Safe Mode from a running Windows 10 operating system.
- Click on Start
- Click on the Shutdown button
- Hold down the SHIFT key and click on the Reboot menu item
- Next, on the blue screen, we proceed in the same order as in the previous method: Troubleshooting - Additional options - Boot options - Reboot - F4 (or F5/F6).
This method can also be used from the lock screen if you are unable to log into your account.
Why do you need laptop safe mode?
Starting the system in Safe Mode is detrimental to the user experience, but it is necessary to combat problems with Windows. List of some ways to use it:
- Checking the OS for viruses. Autoloading is not used in this mode, so programs that launch immediately and protect viruses from scanning software will not work.
- System Restore. If you have backed up your Windows settings, you can restore them. It is recommended to do this in Safe Mode.
- Reinstalling drivers. If for some reason you can’t do this in the normal state of the computer due to system failures, then you can do it in safe mode.
- Solve a problem with some programs.
Registry Editor
One of the registry keys is responsible for starting safe mode, so you can control the computer startup modes through the registry editor, but to do this you need to work under an administrator account.
- Run “regedit” in the search bar.
- Let's go to the section where global settings for all users are stored - HKLM.
- We follow down the hierarchy, as shown in the screenshot.
- Create the “25000080” section through the context menu of the “Elements” directory.
- Similarly, we add a binary parameter and call it “Element”, following the principle of creating new files and renaming them in Explorer.
- Using the context menu, open the dialog for changing the key value.
- Enter it as shown in the screenshot and save the new settings.
We have considered all the options for calling the safe mode that Microsoft offers.
Why does my laptop only work in safe mode?
If the laptop does not perceive changes in loading parameters, then this can be perceived as a symptom of damage to the computer.
As an additional option, you can try the following: while starting the computer, press the F8 key several times, which will bring the user to the window for selecting startup methods. This menu contains startup options, and at the very bottom, separate from everyone else, is “Windows Normal Boot.” It should be selected for correct startup in normal state.
If the laptop continues to start in safe mode after this, then, most likely, irreversible changes have occurred at the software level. In this case, it is recommended to purchase an installation disk (or dump its data onto a USB flash drive if the laptop does not support a disk drive) for Windows 7, 8, 10, or any other OS of your choice, and install the system again. In this case, there is a chance to save all the files on your computer by selecting the appropriate item in the menu.
Using Windows Automatic Repair
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=y7-xcy0v5xI
If your system won't start and you don't have bootable media or a recovery disk, this method may be useful.
- Turn off the PC (to do this, hold down the power button for several seconds).
- If there is a restart button, restart your PC several times. If there is no reset button, turn on the PC and force it to shut down while it boots by holding the power button for a few seconds. You need to repeat the procedure three times until Preparing automatic recovery for Windows 10 appears on the screen.
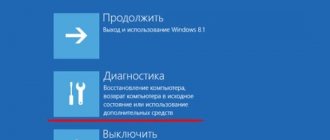
- On the first blue screen, go to Advanced options
- Next, select the action Troubleshooting
- And then proceed the same way as in the second method described in this article.
Exiting Safe Mode by Rebooting the System
With standard settings, Safe Mode is not the default mode, so to exit it, just restart the OS: “ Start ” - “ Shutdown ” - “ Reboot ”.
If the reboot does not give the desired result, then you need to use the system settings utility msconfig
Exiting Safe Mode Using the System Configuration Utility
Let's look at the step-by-step execution of this task:
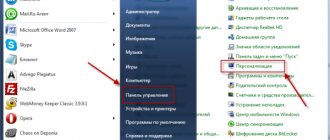
- to the “ System Configuration ” section is through the Command Line, which is called using the hotkey combination Win + R.
- In order to launch the necessary utility, enter the command msconfig (short for Microsoft Configuration) and press Enter.
- As a result, a settings window with several tabs should appear. First of all, you need to refer to the section “ Are common" and activate the option "Normal launch", if it is active, then leave everything as it is.
- Next, you should switch to the “Loading" and remove the checkbox "Safe mode" It is this enabled feature that makes many users think about how to exit Windows 7 safe mode. After this, all that remains is to confirm the changes made by pressing the Apply key.
- The final step will be to reboot the system, which the OS will immediately prompt you to do.
After this, Windows should boot normally. If this does not happen, there is most likely a serious malfunction of the system or physical components of the computer.
Using a Windows boot disk
This is the first of two methods that should be used if the system does not start.
We will need a recovery disk or bootable media with Windows 10.
- Go to Bios
- Specify your boot disk or flash drive as the first boot device.
- On the first screen, click on the Next button
- On the next screen, select System Restore
- On the first blue screen, click Troubleshooting
- Next, click on Command Line
- At the command prompt, enter one of the following commands: bcdedit /set {default} safeboot minimal bcdedit /set {default} safeboot network - to run with network support
- Press ENTER, close Command Prompt and restart your computer
How to get out?
With this method, safe mode must be disabled manually. Therefore, after setting up your computer, go to System Configuration and uncheck the box, as shown in the first method of this article.
You can also run Command Prompt as an administrator, enter the command bcdedit /deletevalue {default} safeboot, press ENTER and restart the computer.
Reasons for permanent operation of the operating system in Safe Mode
If the method described above did not give the desired result, then this indicates that for some reason the system cannot start a particular process or service in normal mode. Most often, the reason lies in the absence or incorrect operation of critical hardware components (motherboard, video card, processor, etc.) or drivers that start and immediately stop working. If the system boots only in safe mode due to a malfunction of certain components, it is unlikely that it will be possible to fix the problem using software methods, and the only option will be their physical replacement or repair.
System logs will help determine the exact causes of the malfunction. To access them, you need to right-click on the “ Computer ” icon, which can be found on the desktop or in the “ Start ” menu, and select “ Manage ” from the drop-down context menu.
Event Viewer option menu , and then “ Windows Logs ”, where all reports about processes occurring in the operating system environment will be sorted into the appropriate categories: when they turn on, how they work, how they turn off, etc.
The second part of the article will be devoted to another important aspect of protection on Windows 7 and other operating systems of this family - security warnings , which sometimes lead to incorrect operation of applications or completely block them.
Disable security warnings for individual files
When launching executable files (formats such as exe, msi, bat, etc.), by default a notification appears in front of the user, requiring confirmation of the action and containing information about the publisher of the program. In general, this is a useful feature that can also serve as an important administration tool, but in some cases, for example, when there are user scripts in autorun, this security measure is redundant and leads to disruption of certain applications.
Fortunately, for any “problem” file this option can be disabled, for which you will need to enter its personal settings: RMB on the file - “ Properties ”.
The required option is located on the “ General ” tab and is activated using the Unblock button.
As a result, all subsequent runs of this executable file will not be accompanied by a security alert.
Disabling security warnings using group policies
It is also possible to completely disable this Windows security component. However, experts do not recommend doing this, since disabling this function means significantly weakening the entire security of Windows 7.
First you need to open the Group Policy Editor, which can be done through Command Prompt , which is called by the key combination Win + R. The command gpedit.msc is entered into it
In the directory that appears, you need to wade through the jungle of many drop-down lists, namely: “ User Configuration ” - “ Administrative Templates ” - “ Windows Components ” - “ Attachment Manager ”.
By clicking on the last item, you will find a small list of options in the left panel. In this case, we will need “ Removing attachment zone of origin information ” and “ List of exceptions for low-risk file types ”.
By double-clicking on each of them, in the settings window that opens, you need to activate the “ Disable ” checkbox and confirm the changes by clicking the Apply button.
At the end, you need to apply the changes, for which you enter the command gpupdate /force in the command line
This concludes our article. It described all the possible ways to disable safe mode and security warnings, which an ordinary user can independently implement.
Video on the topic
Manipulating a system running in “Safe Mode” allows you to eliminate many problems associated with its performance, as well as solve some other problems. But still, this operating procedure cannot be called fully functional, since when using it, a number of services, drivers and other Windows components are disabled. In this regard, after troubleshooting or solving other problems, the question of exiting “Safe Mode” arises. Let's find out how to do this using various action algorithms.
Options for exiting “Safe Mode”
The methods for exiting “Safe Mode” or “Safe Mode” depend directly on how it was activated. Next, we will look at this issue in more detail and explore all the options for possible actions.
Method 1: Restart your computer
In most cases, to exit the test operating mode, it is enough to restart the computer. This option is suitable if you activated “Safe Mode” in the usual way - by pressing the F8 key when starting the computer - and did not use additional tools for this purpose.
- So, click on the Start menu icon. Next, click on the triangular icon located to the right of the “Shutdown” inscription. Select "Reboot".
- After this, the computer restart procedure will begin. During it, you do not need to perform any further actions or keystrokes. The computer will restart normally. The only exceptions are when you have multiple accounts on your PC or have a password set. Then you will need to select a profile or enter a code expression, that is, do the same thing that you always do when you turn on your computer normally.
Method 4: Selecting a mode when turning on the computer
There are also situations when the computer is set to boot “Safe Mode” by default, but the user needs to turn on the PC one-time in normal mode. This happens quite rarely, but it does happen. For example, if the problem with the system’s performance has not yet been completely resolved, but the user wants to test starting the computer in the standard way.
- Restart the computer running in “Safe Mode” as described in Method 1. After BIOS activation, a beep will sound. As soon as the sound is released, you need to press F8 several times. In rare cases, some devices may have a different method. For example, on a number of laptops you need to use the combination Fn F8.
- A list will open with a selection of system startup types. By pressing the Down arrow on your keyboard, highlight the "Start Windows normally" option.
- The computer will start in normal operation mode. But the next time you start it, if you do nothing, the OS will be activated again in “Safe Mode”.
There are several ways to exit Safe Mode. Two of the above output globally, that is, they change the default settings. The last option we studied produces only a one-time output. In addition, there is a normal reboot method that most users use, but it can only be used if “Safe Mode” is not set as the default boot.