In Windows 10, Autorun programs and applications, as the name suggests, controls the automatic launch of programs along with the system, thereby making them easier to work with, but slowing down the overall time it takes for the system to fully boot. The more applications you run on the OS, the slower it will load. In this article, we will look at all the possible options for setting up Windows 10 programs to start automatically, how to add and change programs, as well as third-party applications to control this setting.
View and disable startup programs in Windows 10 settings
In Windows 10, the startup settings for programs are located in Windows settings at this path:
- Press two keys Win+i
- In the menu that opens, go to “Applications”
- Next, find “Startup”
- Next to each name there is an On/Off key. Use them to remove a program or add it to startup on Windows 10 1803 series. Versions 1709 and older do not have such a menu.
Here you will see a list of all utilities and applications that start with the OS when you turn on the computer. You can also familiarize yourself with their effect on system performance.
Third-party startup management programs
In addition to the tools built into Windows, there are third-party programs that allow you to manage the startup list. They are worth using if for some reason standard methods do not work. Also, external applications are more functional, that is, they can not only edit the list of self-launching applications, but also work with other computer parameters.
CCleaner
CCleaner is a fairly popular application known for its ability to clean your computer and registry of junk. But he also has one more ability that we need. Download and install the free version, which can be accessed on the official website - https://www.ccleaner.com.
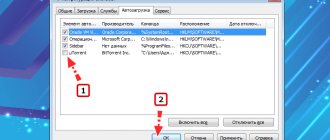
After launching the utility, expand the “Service” block - you will see programs that are currently starting on their own. Here you can remove the application from the list using the button of the same name, or temporarily disable it using the “Turn off” button.
In the “Service” tab we manage autorun
Startup programs in task manager
Now let's find where Startup programs are located in Windows 10. Click:
- Combination Ctrl+Shift+Esc
- If the shortcut is hidden, click More details.
- Go to the “Startup” section, disable rarely used ones with the key of the same name.
Setting up and changing startup
As mentioned above, you can customize the list of applications that automatically launch when you start your computer yourself by adding or excluding programs.
How to add a program to Windows 10 startup?
If necessary, you can include user-selected programs in the startup list using several methods:
- Through the already mentioned startup folder. Copy the program shortcut there.
- Using Registry Editor
- To launch the Registry Editor, hold down the Win + R , the “Run” window will appear, in it in the “Open” line you need to enter the command regedit ;
- Follow the branch that suits you: To configure autorun for the selected account: HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run
- If you need to edit general autorun: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run
- Launch Scheduler: Using the search located in the Start menu, find the application by name. Another way: hold down the Win + R , write the command askschd.msc and press Enter or “OK”;
Important. You should not add unnecessary programs to startup, for example, games or your favorite video player. They can slow down your computer's startup and performance. If you want to optimize your device's performance and restore it to its former speed, excluding such applications from the startup list is a good start.
How to disable autorun programs in Windows 10?
If you realize that your startup contains too many programs and want to reduce their number, you can choose one of several methods.
Important. Do not rush to remove an unknown program from startup. Unknowingly, you can disable an application necessary for the normal functioning of the system or any device and disrupt the operation of the computer. Try to find a description of the program you are interested in on the Internet or consult with a specialist.
- Startup folder. Find the shortcut of the unnecessary application and remove it from the folder;
- Registry Editor
- To launch the registry editor, hold down the Win + R and enter the command regedit ;
- Open the “Run” folder in the appropriate branch for your case: To remove a program from startup of the selected account: HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run
- To adjust the list of general startup programs: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run
- Call the manager: open the context menu of the “Start” button, you need the “Task Manager” item in it. Another way: hold down the Ctrl + Shift + Esc ;
Important. You can quickly and easily find out the current version of Windows 10 on a given computer. To do this, hold down Win + R winver command in the “Open” line and press OK or Enter. A window will appear containing the necessary information.
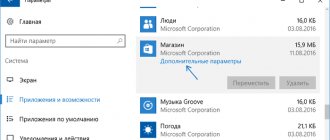
- Go to the Start menu and click on the gear icon;
- Select “Applications”, then “Startup”;
- You will see a picture very similar to the Task Manager: a list of automatically downloaded applications, their status (On/Off) and the degree of influence on the download. Switch applications you don't need into disabled status.
As already mentioned, it is very important to control programs that start automatically, because they can additionally load your computer, reduce its speed and even harm it. Now you know where the Startup folder is located in Windows 10, how and what it can be used for, and what you need to do if you need to add an application to the startup group or exclude it from there.
Startup programs folder in Windows 10
In Windows 10, startup programs are located in the Startup folder. It is enough to add a shortcut to the folder for the program that should be launched along with the system, and it will automatically launch when the PC starts.
Access to the Startup folder is located in the following path:
- Launch File Explorer from the taskbar
- Open the User Folder.
- Next, open the folder with the name of the specific user
- Then follow the subfolders AppData/Roaming/Microsoft/Windows/Main Menu/Start Menu/Programs/Programs/Startup/Startup. You may not see some objects. This means that the folder has been assigned the “Hidden” attribute. You need to expand the “View” tab at the top of the explorer and check the “Hidden” items checkbox so that the objects are displayed.
Going through a series of laid out folders is not very convenient. Therefore, you can master another method, which is described below.
AnVir Task Manager
AnVir Task Manager is a free tool for managing Windows startup, processes and services with an emphasis on security. Helps fight active virus infection, prevents malware from trying to block the system, and also speeds up the boot and operation of the computer.
This is interesting: New hardware and old Windows: can they work together? Do I need to reinstall Windows after replacing the processor?
The application does not require a deep understanding of system processes and security principles, therefore it is recommended for ordinary users.
You must run AnVir Task Manager (as well as other similar utilities) as an administrator.
All startup elements are displayed on the first tab of AnVir Task Manager with the same name. The left side of the top half of the window lists registry keys and folders; on the right - their contents - shortcuts and parameters indicating detailed information: what launches, where the file is located in the system, which application it belongs to.
The most interesting thing here is the percentage assessment of the risk (potential harmfulness) of each object. But keep in mind that a high risk (red zone) does not always indicate that you have a virus. This is rather done to attract the user's attention.
The reason why AnVir Task Manager considered the object suspicious is given at the bottom of the window on the Properties .
In my example, a harmless component of the Intel video driver, igfxpers.exe, was targeted. To make sure that the file is really clean and harmless, I will check it on the service - select it in the list and press the button shown in the screenshot.
Other autorun controls are collected on the same panel where the Virustotal , and in the context menu of each item. Among them:
- Shutdown (quarantine).
- Jump to the process started by the object.
- Opening a file in Explorer.
- Restart and stop the process.
- Adding a program to autorun.
- Editing an entry in the registry.
- Setting up delayed startup (a few minutes after Windows starts).
- Deleting an entry (without a file).
- Search for information about an object on Google.
With a little experimentation, you'll figure out what's what. And then, perhaps, AnVir Task Manager will become your constant assistant.
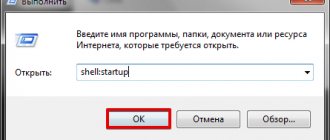
Autoloading programs via shell startup
- Press Win+R keys or use the “Run” command
- A window will appear where you need to type shell:startup and confirm the action with “OK” or “Enter”.
- The shell startup command will open access to the folder with Startup programs, and all you have to do is drag the shortcuts of the target applications here.
Startup programs in the registry
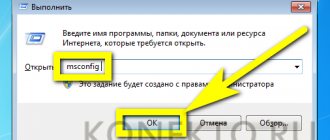
Now let's look at how startup works in the Windows 10 registry. To do this:
- Press Win+R and type regedit
- In the expanded editor window, follow the following path: Computer\HKEY_CURRENT_USER\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run. At the final point, right-click on an empty space in the window, select “Create” then “String parameter”
- Now add the name of the target program for autorun and click “Enter”. The last step is to double-click on the name you just entered and specify in the “Values” line the path to the file storage location, then confirm OK.
The next time you start the PC, the program launch from autorun is activated.
Startup Delayer
Startup Delayer is not an ordinary startup manager. And that's why.
By default, all applications registered in autorun start at the same time. If the computer is not very powerful, this causes overload of hardware resources and slows down Windows startup. The purpose of Startup Delayer is to create a delay when starting individual applications, so that they start working not together, but in turn. Thanks to this time distribution, the desktop appears much faster than usual.
Like the previous one, this program is designed for the average user. There is nothing in it that could confuse you. There are three areas in the Startup Applications window:
- Delayed launch.
- Normal launch.
- Startup prohibited.
This is interesting: How to edit the Windows registry, do you need to do it and when?
Immediately after installing Startup Delayer, the first and third areas are empty, and the second lists all auto-starting programs. To create lazy loading, drag applications from the second area to the first and arrange them in the desired order. So - one after another, they will be launched.
In the third - lower area, move what you want to disable autoloading.
Startup Delayer allows you to create several startup profiles, including for each PC user.
Setting up startup programs in the Windows 10 task scheduler
Autostart of programs in Windows 10 is configured using the Task Scheduler utility.
- Start typing the name into “Task Scheduler” in the “Search” line (bottom of the screen, left)
- Expand the scheduler window, open “Actions” among the found tabs and select “Create a simple task”.
- The Simple Task Creation Wizard will appear and ask you to fill in the name line - enter the name of your task, click Next.
- In the next task trigger item, note that you need to start when you log into Windows
- Assign the action “Run program”.
- All you have to do is click the “Browse” button and specify the path to the storage location of the program file for autorun.
What is AutoRuns?
AutoRuns is a Microsoft tool that identifies software that is configured to run when a device boots up or a user logs into their account. When you turn on your computer, trusted software often starts. Outlook is a prime example, as checking your email is often the first action you take after logging into your account.
If the device has been hacked, then the malware that has landed on it must “withstand” a reboot. After the computer is turned off, the malware requires a certain mechanism to continue running on the device. This can be done using built-in Windows features that allow programs to run on boot.
AutoRuns: Basics
In the image below we can see that AutoRuns has a number of tabs, each of which contains information about the autorun mechanism.
Logon tab provides information about standard download locations for all device users. In particular, the places where programs are launched, as well as the corresponding launch keys, are indicated here. The startup key is part of the device's registry: malware often creates a key so that when the device boots, the malware will launch automatically.
Explorer tab displays information about the following elements:
- Shell extensions are separate plugins for Windows Explorer (for example, for previewing PDF files).
- Browser Helper Objects (browser helper objects) are DLL modules that act as plugins for Internet Explorer.
- Explorer Toolbars are third-party plugins for Internet Explorer; The toolbar provides access to a third-party platform.
- Active Setup Executions (executing tasks through Active Setup) is a mechanism for executing commands once for each user during login.
The Internet Explorer tab displays browser helper objects, Internet Explorer toolbars, and extensions.
Scheduled Tasks tab shows tasks that are configured to run on boot or login (this is often used by various malware families).
The Services tab displays all Windows services that are scheduled to start automatically when the device boots.
Drivers allow hardware to communicate with the device's operating system. The Drivers tab in AutoRuns displays all drivers registered on the device, except those that are disabled.
Image Hijacking is a rather insidious method in which the key to start a certain process in the Windows registry actually starts another, malicious, process.
The AppInit DLL shows the DLLs registered as application initialization DLLs.
Boot Execute tab displays startup locations associated with the session manager subsystem (smss.exe).
Well-known DLLs (Known DLLs) in Windows - kernel32.dll, ntdll.dll - allow the software to import certain functions. Some viruses install malicious DLLs created by the virus's developer in places where you are unlikely to look for legitimate Windows DLLs, such as temporary folders.
Winlogon is used when the user logs into Windows. This tab displays the DLLs that log Winlogon event notifications.
Winsock Providers tab displays registered Winsock protocols. Winsock, or Windows Sockets, allows programs to connect to the Internet. Malware can install itself as a Winsock provider to make it difficult to remove. AutoRuns can disable the provider, but not remove it.
The Print Monitors tab displays the DLLs that are loaded into the print spooling service. Malware can install a malicious DLL here.
Windows Local Security Providers (LSA Providers) support processes related to security and authentication.
How to add a program to startup through third-party applications
Let's look at where the startup folder is using free utilities.
Third-party programs are a good way to manage startup for new users. The utilities have a simple interface, a minimum of buttons. They are much easier to use than standard Windows applications and especially the registry.
Add a program to startup via CCleaner
Using CCleaner, you can find in 2 clicks where the startup folder is located in Windows 10. Accordingly, enable/disable autostart software.
Download the official version of CCleaner. When starting for the first time, follow the commands of the installer wizard. Next follow the steps:
- Open the main CCleaner window.
- Go to “Tools”.
- Open the “Launch” subsection.
Now edit the autorun options to suit your needs. Plan tasks, use the option to add software and the ability to remove a program from startup. Connect and remove supporting programs.
What can be removed from autorun, and what is better left untouched
In order to speed up the startup of Windows and increase the performance of your PC, it is advisable to remove from startup what you (and the operating system!) do not use all the time and what is more rational to start manually.
However, you can’t clean everything up. It is important to leave:
- Antivirus and other security programs.
- Hardware monitoring and backup tools (if you use them).
- Device driver components (otherwise there may be problems with the operation of the equipment).
- Programs that you have been using since the system booted.
- Application update utilities (important for security).
- Anything whose purpose you don’t know. If you suspect that an element included in autorun is malicious, check its file with an antivirus. And if it is safe, leave it in place.
The rest can be disabled. If no problems arise after restarting the PC, the disabled items can be deleted (the files they launch will remain in place).
And now – about the programs.