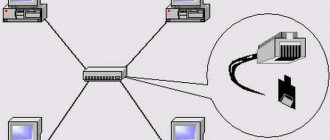
Anyone who has ever set up a router on their own from a computer/laptop via wifi or via a wire has come across such concepts as “WAN” and “LAN”. It is to these ports that the provider cable (twisted pair) is connected to access the global Internet or from a router, after which you can open any http address in the browser and establish a connection to sites. The WAN interface, or as it is also called Ethernet Port, and LAN are present on all routers, regardless of the manufacturer - TP-Link, Asus, D-Link, Mikrotik and so on. For some, their number can vary from 2 to 5. We have repeatedly published on the pages of wifika.ru instructions for setting up various types of Internet via wireless - Dynamic IP (DHCP), Static IP, PPPoE and so on. Today I would like to dwell on the very concept of “WAN Network” - how this term is translated, what it means and how it differs from LAN or Wireless LAN.
How WAN and LAN are translated - definition of the term
WAN (VAN) in decoding sounds like “Wide Area Network” - translated into Russian it is a global computer network. We simply call it the Internet. That’s why one of the connectors on the wifi router is marked with the “WAN” icon - this is where the cable for accessing the Internet, which the provider laid into the apartment, is connected to.
LAN (LAN) is by analogy “Local Area Network”, that is, in our opinion, a local network. That is, this is a connection between different devices within a connection to one router. Over such a network, you can transfer files or broadcast video and music from one media to another.
Read more about the difference between a local and global network in a separate article.
How to setup
Let's look at the procedure for setting up a WAN using TP-Link routers as an example. To begin with, we note that providers require different network settings. Which ones are there:
- Dynamic IP - dynamic (issued automatically);
- Static IP - the user enters data manually;
- PPPoE - each time to gain access to the network, you must enter a login/password.
Instructions on how to set up on Windows 7:
- Click "Start".
- Select Control Panel.
- Go to Network and Sharing Center.
- Click "Change adapter settings."
- You will see a computer icon with a red cross - right-click on it and select “Properties”.
- Click on the item highlighted in blue in the picture and click “Properties”.
- If the checkbox is checked opposite: “Use the following IP address,” then static settings are used. Rewrite all the numbers.
- Select “Obtain an IP address automatically” and click “OK”.
So, all wires are connected - let's move on to setting up the router:
- To get started, open your browser and enter “192.168.1.1” (the address of your network equipment) into the address bar.
- In the window, enter your login/password (usually the word admin).
- Click “Quick Setup” in the menu on the left.
- After reading the information, click “Next”.
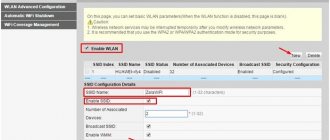
- If the settings from the provider come automatically, then select “Dynamic IP” and click “Next”.
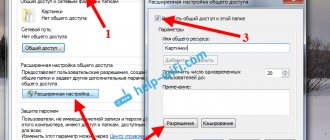
- Next, indicate everything as in the picture. Change the fields "SSID" - this is the name of the access point, and "PSK Password" - the password for the network. Click “Next” and “Finish”.
- If network settings need to be entered manually, select “Static IP”.
- In the next window, enter the settings that you previously overwrote in the connection properties. The remaining fields are filled in by analogy with a dynamic connection.
WAN port - connector on the router
So, in the broad sense of the word “WAN” is simply the Internet. In the narrow one that we encounter when setting up a network, this is a port on a wifi router for connecting to a wire. It can be indicated by an abbreviation or the words “Internet”, “Ethernet”.
Or just a globe icon
Also, to make it more difficult to confuse it with the LAN interface, it is often distinguished in a different color from other RJ-45 connectors.
Technical points
The main differences between these formats:
- The first type helps to create an internal network; WAN is used to connect users globally.
- A local group has a limit on the number of clients and territory, while a global group does not.
- The ports have different data transfer protocols - Ethernet and 802.11 for local and PPP, HDLC, Frame Relay for external.
The user needs to know the difference between these ports when connecting a home router for the Internet. Remember that a LAN socket is necessary to connect computers if there are several of them, and the WAN allows you to receive a signal from the provider.
LAN connector on your router or computer
Through the LAN connector on the router we connect other devices to it via cable. There are usually many LAN ports for connecting multiple devices at the same time. Most often these are desktop computers or old TVs without a wifi adapter. They are designated by numbers and are always marked with the same color within the same router.
Today, in the wireless era, it is rare to see computers and laptops connected to the router via LAN ports with cables. More often this is done via WiFi, that is, via “Wireless LAN”. To do this, use an 802.11n or ac adapter, which is inserted into the PCI connector on the motherboard or an external USB port. After installing the drivers in Windows, a regular cable signal turns into a wireless signal.
How to connect the Internet via LAN?
To set up direct access to the Internet on a computer, just insert a previously crimped LAN cable from your Internet provider with an RJ-45 plug into the Ethernet port of the PC. Then right-click on the “Start” icon and select “Network Connections” from the context menu.
Interesting materials:
How to remove sound volume limit on Android? How to remove Google Play error on Android? How to remove Google panel on Android? How to remove the floating keyboard on Android? How to remove hints on the Android keyboard? How to remove the Yandex search bar in Android? How to remove full screen mode on Android? How to remove the frame on Android? How to remove Facebook ads on Android? How to remove ads on Android Samsung?
What is the difference between WAN and LAN connection on a router?
A logical question immediately follows: what is the difference between the WAN and LAN ports on a router, if an RJ-45 cable is connected to both? LAN connectors, unlike WAN, are designed to connect other devices to a local network via cable - computers, laptops, printers, IP cameras, and so on.
What is your opinion: is WiFi harmful?
Yes
22.91%
No
77.09%
Voted: 36470
- There is a cable in the WAN that the provider pulled into the apartment to supply the Internet to the router itself
- In LAN - a wire from another device that needs to be connected to the Internet and local network
As I already said, many of them do not have a wireless adapter (WiFi 802.11ac or 802.11n), and they can only be connected to the Internet using a network cable. Therefore, there are often more LAN ports than WAN ports - usually from 2 to 4.
The speed of the interface may also differ. For example, in inexpensive router models, the Internet speed via WAN will be limited to 100 Mbit/s, although the local network (via LAN) can be gigabyte, that is, reach 1 Gbit/s.
The same applies to the Wireless LAN wireless interface, where the speed depends on the frequency range. At 2.4 GHz (WiFi standard 802.11n) it is usually limited to 150 or 300 Mbit/s, and at 5 GHz (802.11ac) it can reach 900 Mbit/s and higher.
Indication
In order to find out which connections are active, routers use indicators. These are the lights on the front or top of the device.
The indicator for the WAN network is indicated by the letter “I” or may have a globe on it. If nothing is connected to the corresponding connector, the LED is not active. It may also be inactive if the wire is damaged or there is a problem on the provider's switch. In general, if the WAN interface indicator is not active, this means that the signal is not reaching the router.
If the indicator blinks yellow, this means that the signal is being received, but there is no Internet on the device. Either the settings on the router are incorrect, or there are problems with the provider’s equipment. In this case, a cable malfunction is excluded.
If the LED is on or blinking green, then the WAN connection is active and you can use the Internet.
LAN ports also have an indication. Usually these are numbers corresponding to the serial numbers of connectors, or monitor icons. Each connector has its own LED, which shows which ports are currently connected. However, models appear without LAN port indication or with one LED for all ports.
If the indicator is not active, this means that nothing is connected to the port or the connected device is disconnected from the network. It could also indicate a problem with the cable.
If you connect a cable from any device, for example, a laptop, to the WAN port, nothing will break, just like if you connect a cable from the Internet to the LAN. The indicator of the connected port will also light up, indicating a connected device, but the network will not work.
WAN port error on router
If you connect another computer through the WAN port on the router, an error will occur and it will not work on the local network. It’s the same thing and vice versa - if you insert an Internet cable into the LAN connector of the router, it will not be connected to the Internet. This will look like an icon with an exclamation mark in the Windows panel and a notification in the browser that “network without Internet access” or “disconnected state”.
Moreover, the WAN or LAN indicator on the router’s LED panel will light up - after all, the cable is connected. But the Internet will of course not work.
However, in some devices, Internet WAN and Ethernet LAN interfaces can be combined due to their specific nature. The simplest example is on the PCI network card of a computer, laptop or TV. After installing the native driver through this connector, we can connect it either to the router or insert the Internet cable from the provider directly.
Another example is the PowerLine adapter, which can simultaneously work to receive an Internet signal via cable and distribute it to other devices.
What is a LAN port?
“LAN” stands for “Local Area Networks” or “Local Area Network”. It connects nodes located at a short distance from each other. An example of such a network would be a network in an office or university. In other words, computers can be connected directly to each other via a LAN.
There are specially created devices for this – hubs and switches. These are switches with network connectors that help create huge local networks. Also, if you use a router, you can give such a private network access to the global Internet.
WAN IP
Accordingly, the definition of WAN IP follows from all of the above. This is an external address that does not belong to each individual device individually, but to the entire local network, hidden behind the wifi router’s gateway.
Roughly speaking, this is the address of the router - yours, if a channel in a dedicated white IP is installed in your apartment. Or a provider, which in turn already assigns other internal gray addresses to its subscribers. Sometimes you need to know it to remotely access the router via the Internet.
Pinout
Power cords, like other accessories, break down over time. If you have crimping skills, an extra connector and a suitable tool, then you can solve the situation quickly - with pinouts.
The twisted pair (Internet cable) is crimped following the following diagram.
Instructions:
- Remove the braid.
- Arrange the wiring according to the diagram.
- Cut the wires so that they are at the same level.
- Insert the wires into the connector - each into its own core. They must reach metal parts. It is recommended that the braid is also “inside” as deep as possible.
- Now all that remains is to crimp with special pliers.
- Do similar actions with the other end of the wire.
What are WANs and MANs
Wide area networks (WANs) and metropolitan area networks (MANs) are actually very similar. They all overlap somewhat and have no clear differences. Essentially, these are networks that connect multiple local networks together.
For people who like differences, MAN is a network consisting of several local networks that are connected together via high-speed connections and all located in the same city or region. A WAN also consists of several local area networks, but has an area larger than one city and can be connected by different types of technologies, including the Internet.
For a classic WAN example, think of a company that has branches in three different locations around the country (or the world). Each location has its own local network. These LANs are connected together as part of the same overall network. Maybe they're connected via dedicated, private connections, or maybe they're connected together over the Internet.
In fact, the Internet itself is the world's largest WAN, connecting many thousands of LANs around the world together.
WAN Services
PSTN
The public switched telephone network is the oldest and largest WAN communication network available. PSTN features include:
- It is a dial-up network with global coverage
- The interface with PSTN is similar, so computers use a modem to connect to PSTN
- Speeds on the PSTN are typically limited to 56 Kbps.
- You can use PSTN whenever you need it (upon request) or rent a separate channel
Figure 8: PSTN Telephone Network
Leased line
For some companies, the benefits of a private leased line can be much greater than the costs. A leased line is an independent road and has a higher speed than the regular public telephone network. However, it is quite expensive, so only large companies usually use it. Other leased line features include:
- Ensure regular connection, stable quality
- You may pay extra to upgrade your leased line
X.25
X.25 was born in the 1970s. Its original purpose was to connect large servers (mainframes) to remote workstations. The advantage of X.25 over other WAN solutions is that it has a built-in error checking mechanism. Choose X.25 if you need to use the same line or the quality is not high.
X.25 is an ITU-T standard for wide area network communications using packet switching over the telephone network. The term X.25 is also used for the physical layer and data link layer protocols to create an X.25 network. According to the original design, X.25 uses the same line to create a packet-switched network, although X.25 can also be built over a digital network. Currently, the X.25 protocol is a set of rules that define how to establish and maintain connections between DTEs and DCEs on a public data network (PDN). It specifies how DTE/DCE and PSE (packet exchange) devices will transmit data.
- You need to pay a subscription fee when using the X.25 network
- When using an X.25 network, you can connect to the PDN via a leased line.
- X.25 network operates at 64 Kbps (on the same line)
- The size of a packet (called a frame) in an X.25 network is not fixed
- The X.25 protocol has very strong error checking and correction mechanisms, so it can operate relatively reliably on low-quality analog telephone lines.
- X.25 is now widely used in many parts of the world where numbers are not popular and line quality is still poor.
Frame Relay
Frame Relay is more efficient than X.25 and is gradually replacing this standard. With Frame Relay, you pay to rent a line to the nearest node on the Frame Relay network. You send data on your line, and the Frame Relay network routes it to the closest node to the recipient and transmits the data to the recipient's line. Frame Relay is faster than X.25
Frame Relay is a standard for packet-switched WAN communications over high-quality digital lines. A Frame Relay network has the following characteristics:
- There are many similarities when deploying an X.25 network
- There is an error checking mechanism, but no error correction mechanism
- Data transfer speed can reach 1.54Mbps
- Allow different packet sizes
- Can be connected as a backbone connection to a local network
- Can be deployed over many different connection types (56K, T-1, T-3)
- Work at the physical layer and data link layer in the OSI model.
WAN Data Encapsulation Methods
WAN physical layer protocols define the hardware and how bit signals are transmitted. Link layer protocols control the following functions:
- Check and correct errors
- Establishing a link
- Organize Data Frame Fields
- Perform point-to-point flow control
Physical communication layer protocols also define the data packaging method or data frame format. The method of encapsulating data in a wide area network is often called HDLC (High Level Data Link Control).
This term is both a generic name for data link protocols and a protocol name in the WAN protocol and service suite. Depending on the WAN service and connection method, you can use one of the following data packaging methods:
- Cisco HDLC for seamless point-to-point connectivity with other Cisco routers.
- LAPB for X.25 network
- LAPD, used in combination with other protocols for B channels in the ISDN network.
- Cisco/IETF for Frame Relay Networks
The figure shows the most common data encapsulation methods and how they are used for typical types of WAN connections. As you can see in the figure, PPP is a flexible method that can be used for many types of WAN connections. In general, which method to use will depend on the type of WAN service, such as Frame Relay or ISDN, and the network service provider's data packaging method.