Quite often, the user needs to find out exactly the model of the router. For example, for flashing firmware or fine-tuning a device. Due to the different micro parts from which seemingly identical devices are made, it is necessary to know the exact model.
In most cases, you can find out the router model by looking at the device itself. You can usually find a sticker or engraving describing the main characteristics of the device, including the model. It is indicated by the inscription Model or Model No. You also need to install the version, it is marked with the inscription “Ver”, or is written immediately after the model number.
But there are times when this sticker is damaged or there is no physical access to the router. Then you will have to look for other ways. And there is nothing difficult to determine the device number through a computer. Even the most inexperienced personal computer user can handle this.
What is a network SSID and how can I find it on my phone?
SSID term
stands for Service Set Identifier. It shows the WiFi name so that the user or equipment can connect to the Internet without error. The name Wi-Fi can be seen in PCs, smartphones, tablets and other devices that connect to the World Wide Web.
Interesting materials:
How much can you import into Russia from Ukraine? What amount must be declared when entering Russia? Who is in charge of civil defense in the Russian Federation? Who accepts the National Standard of the Russian Federation? When do they give a deferment from the army in Russia? When is Pharmacist Day in 2022 in Russia? When is an agreement considered concluded by the Civil Code of the Russian Federation? When will ECG be available in Russia? When and how was the Constitution of the Russian Federation adopted? When and by whom was the Constitution of the Russian Federation adopted?
How to determine the router model in your home
To determine the model, you should use the above methods. If not one of them does not give results, then you will have to take the unidentified box to the service center. There, with the help of specialized equipment, they will be able to recognize the model for certain.
It is worth saying that you should not disassemble the case yourself and look for information under the cover of the device. Although sometimes the manufacturer writes the number on the board, these are rather exceptions to the rule. Such actions carry serious risks of physically damaging the device, which will lead to loss of its performance. There are many markings on the board, but they refer to specific components. For example, a memory chip or a PWM voltage controller. Unfortunately, it is almost impossible to set the necessary parameters yourself. This will require specialized diagnostic equipment. Which is not in every home.
Even if the treasured inscription is discovered, they often use the same board for different models, simply changing the microcontrollers. And if you install the wrong firmware, it will be much more difficult to fix it. He will come to unsolder the chip and place it in a special programmer. But before that, you will still have to somehow determine the correct device model, and doing this with a faulty chip will be much more difficult.
Niasilil
In principle, everything is clear exactly how data about the exact model leaks from the router. Moreover, unlike the MAC address, which can be changed in some models, I have never come across settings for changing data for Vendor Specific: Microsof: WPS. Those. here you can get more reliable information about the router manufacturer and its model than from the MAC address.
The logical conclusion of the study should be a utility for automatically retrieving this data for all affected access points within the accessibility radius. It is quite possible that a Bash script with tshark and tcpdump can handle this.
The necessary frames from the capture file can be extracted something like this:
tshark -r wpstest.pcapng -R 'wps.device_name != "" || wps.model_name != ""' -2
While there is no ready-made solution, you can view information about the model from Windows using , or manually in Wireshark, as shown above.
By the way. Perhaps experts in tshark and tcpdump or something similar will suggest an elegant way to extract strings with “Device Name”, “Model Name”, etc.
Traffic interception
This is perhaps the most reliable, but at the same time quite difficult method. To use it, you need not only to have an understanding of a wireless network, but also to understand the principle of operation of the router and password encryption.
Initially, the Internet signal is transmitted via cable. The cable transmitting the signal is connected to the router. And the router already distributes the signal “through the air”. The password is set in the router itself and when we enter it from our device, a signal with the password is sent to the router. A response is received from the router with the password set, and if the password is entered correctly, a connection occurs. If not, no connection occurs.
Traffic interception scheme
One way or another, the router gave us a response with the password set on it. Once connected, it exchanges information with all connected devices. They are called data packets. If you wish and have enough computer literacy, these data packets can be intercepted and, by decrypting them, you can obtain the password that was set on the router.
But as mentioned earlier, this method is quite complicated, because to implement it you will need a high level of knowledge in the field of computer technology. But you can simply use the special CommView program, the instructions for which were described above.
Determining the IP address programmatically
In some cases, it is not possible to find out the router’s IP on the sticker (for example, the data has been erased or the sticker has come off). You can check the address through a computer connected to the device. To connect, use Wi-Fi or Ethernet cable. When the connection is established, open the Control Panel, select “Network and Sharing Center”. In the “View active networks -> Connections” item, click on the name of your network.
In the window with connection information, click the “Details” button.
The setting we need is called “IPv4 Default Gateway”. It is at this point that the IP address of the router will be written.
To use an alternative way to clarify the router’s IP, press the key combination “Win + R” and enter the name of the program: cmd. If the run window does not open, select Run by right-clicking the Start menu.
After launching the text interface, enter the ipconfig command and press Enter. The window will display all data about your network devices and active connections. The router's IP can be found in the "Default gateway" line. Typically it is in the format "192.168.XX" or "10.10.X.X" since these IP ranges are reserved for internal addressing.
If after running the command the statistics are not available or you cannot find the required network adapter, use an alternative command: tracert. Unlike the previous one, it does not display network statistics, but shows the entire path that a request to access a specific site or IP address takes. Therefore, after the command itself, you must specify any network address separated by a space. For example, in the screenshot ya.ru is used. The first step in routing (redirecting a request) is to contact the router. Therefore, you can find out the router’s IP in the first line of the route trace.
For other operating systems, the steps to determine the router address may differ. But in most cases, the router’s IP can be checked in the properties of the current connection.
Where is the Wi-Fi password, IP address, MAC address, login and password written on the router?
It’s not uncommon for comments to appear asking me where on the router you can see the password for the Wi-Fi network, the factory login and password, the router address, or the MAC address. Almost every network device has a lot of useful factory information. And if you decide to configure the router yourself, then this information will definitely be useful to you.
Most often, there is a need to look at the Wi-Fi password that was set on the router from the factory. It is also a security key, or PIN code. And all because now most manufacturers set a password for Wi-Fi from the factory. When you buy a new router, or reset the settings, to connect to the wireless network (which has a factory name), you need to specify a password (PIN code). At least to go into the router settings and change the factory security key. True, there are models whose wireless network is not protected by default.
On almost all routers and modems, the factory information is written on the body of the device itself. Most often, this is a sticker with information on the bottom of the router.
Now we will take a closer look at the information on devices from the most popular manufacturers.
Marking sticker
The device model is indicated on the identification sticker on the back of your device.
Example 1 : NAS540
Example 2 : VMG8324-B10A
Example 3 : PLA5405
Router name, board revision
Sometimes users ask the question of how to find out the model of the router used on the network. There are two options: either you can look at the bottom of the router case to read the inscription on the sticker, or you open the web interface and the model name will be printed in the authorization request.
To update the firmware, you need to know not only the name of the device, but also the hardware revision number. Devices of different revisions are always (in 99% of cases) built on different chipsets. Otherwise, the very concept of “hardware revision” would simply not exist.
See what the sticker of a network device called “TL-MR3220” looks like. This name, as we see, is in the “Model” line. Sometimes the combination “Model No.” is used, although the revision number is not printed here. We will find this number after the following sequences of letters:
Now you can find out the full name of the device in question: “TL-MR3220, hardware revision 2.0.”
Archer and Touch routers with 802.11ac support
The TP link Archer router is a dual-band model and supports the established AC standard. The name of the models means the following - AC (supporting the standard) and numbers in the model (for example, AC750) the amount of device bandwidth, which divides the Wi-Fi signal into two bands. The official line is represented by an assortment of gadgets that are distinguished by their design - a classic, rounded body and a large number of built-in antennas, up to 5 pieces.
Among the powerful models, we can highlight a small rating based on the throughput of the TP router, additional ports and functions:
- Archer C7 AC1750 is a 5 GHz device, has 2 USB inputs and 5 built-in ports, and speeds up to 1 Gbps.
- Archer C8 AC1750 – bandwidth up to 1300Mbps, 5 ports and 2 USB inputs.
- Archer C58 AC1350 – model with 5 built-in ports, but no inputs for a USB cable.
- Touch P5 – this model features a built-in touch screen control, 8 built-in input ports and a bandwidth of 1300Mbps.
Driver
It is quite possible that there is a software failure in the operation of the router.
The firmware (driver) may be either damaged or outdated. Therefore, the driver needs to be updated. Or roll back to the previous state if a new version is not found. For this process the sequence of actions will be as follows:
- Go to “Device Manager”.
- We are looking for the “Network adapters” section.
- From the context menu of your router, select the line “Update driver”.
- In a new pop-up window, select the location to search for it and wait for this operation to complete.
But the best option is to contact the official website of the device manufacturer. It is there that you can find the necessary and more recent versions of drivers for your equipment in order to change them. For example, as for TP-Link is shown in the figure below.
Additional communication skills
Regardless of WiFi characteristics, the router provides maximum speed and connection reliability with a wired or optical connection. If some clients (laptops, desktop computers) have an RJ-45 connector, it is better to choose a router with LAN ports and connect the clients to them using patch cords. Most routers have 4 LAN ports in addition to the WAN port for connecting to a cable from your ISP. But you can find a router with a different number of LAN ports - from 1 to 10.
Some high-speed routers are equipped with SFP ports , into which (with the appropriate adapter module) you can connect both twisted pair and optical cable. Routers with SFP ports are usually used to organize high-speed networks, but ordinary household routers with SFP ports are also appearing on sale. If your provider provides Internet access using P2P Active Ethernet technology, you can connect such a router to fiber directly, without an expensive media converter.
It is not always possible to connect to the Internet via a wired or fiber optic line, so many routers are capable of connecting to the Internet using mobile networks. You just need to make sure that the selected model a wireless Internet connection Most routers require a USB modem to connect, some are already equipped with one.
WiFi support . Sometimes it is necessary to “distribute” the Internet only over wired connections, without organizing a wireless network. For example, the security rules of some organizations require the complete absence of wireless access points in the enterprise local network. In such a case, you can use a router without WiFi support to provide workgroup computers with Internet access. However, in most routers with WiFi support it can be disabled in the device settings.
Network structure
Before you begin explaining how to log into the router, you need to understand the very basis of building networks in order to understand why this is needed at all and what the practical benefits of such actions are.
Actually, despite all the “smartness” of the router, it is just a limited robot that needs to be given initial information on connecting to the operator, where to get device addresses from, and which ones to distribute within the network. Of course, all functions of the router are not limited to the specified data, but this is the basis that is used to connect client equipment with each other and external servers or personal computers.
The exchange of information between network clients occurs in a machine “communication language”, which in the presented case is called a protocol. These are specific sequences of digital signals that enable communication between devices. The Internet uses TCP/IP data transmission format.
It’s worth dwelling a little on the structure of a computer network to make it clear what a router is used for. In essence, the global Internet and local connections between computers or any other “highly intelligent” devices are built on combining them into unique circles called networks. Each one, relatively small, is a part (unit) of a larger one. All such structures have their own address, represented by a sequence of four numbers separated by dots. The specified identifier determines the level of nesting of networks in the direction from largest to smallest. That is, the last digit numbers the subnet included in the network with the index specified before the point, which in turn belongs to a group of associations with an even earlier designation in the address. The interconnection of various computer networks is shown in the figure below.
Actually, devices on one network do not know anything about the other devices located in them. The purpose of routers is to switch interactions between different networks.
You probably noticed that routers are called differently. This is no accident. The original name is the English word “Router” or translated into Russian - router. And the familiar “router” is just a poor transcription of the English word, which has taken root and entered the lexicon of our language. In addition to those listed, you may find the name “switch”, from the foreign “switch” - switch or “switch”. This is what similar devices are called based on their functional characteristics - after all, they perform connection switching. All the names given are officially accepted and widely used.
Let's return to networks. Each of them, belonging to the last digit in the address (4 levels), can contain many computers, devices, printers, smart TVs and other highly intelligent devices. And everyone is assigned a unique number, different for each device. It is by this that the access end point is determined, freely visible to everyone else within its subnet. This number is the same sequence of four digits separated by dots as the common association identifier. Complete with the network, it is called an IP address and looks something like this for devices located on the same network: 192.168.0.1. The numbers can be any, but their issuance is carried out according to certain rules, the description of which is too extensive and beyond the scope of the article. The only thing worth emphasizing is that for end-user local networks, addressing of the form 10.xyz and 192.168.yz is accepted, where x, y and z are unique numbers for each device. There is also a limitation - service IPs 127.0.0.1 and 0.0.0.0 are never used for connections. The first is that on any equipment it is always the address of itself, the second is access to all devices within the subnet.
Thus, the connection structure can be represented in one of the forms shown in the figure below.
The router, as a unifying system, has its own separate identifier, which is indicated on all client devices, informing them that this router is a kind of bridge between them and other networks, and all TCP/IP packets must move through it. For home options, the router often uses IP 192.168.0.1 or 192.168.1.1. It is this address that will be used as the basis for the setup procedure. The router itself has two of them - internal and external. We are only interested in the first one. You can find it out either from the documentation for the switch, or it will be written on a label attached to the case. Information about the default username and password is also taken there.
How to disconnect a client from WiFi
We have identified all connected devices - great! But what if one of them is an attacker, for example?! How to disconnect a user from WiFi without disturbing others?! There is nothing complicated here either. You just need to blacklist this user. I’ll show you again using TP-Link as an example.
Right in the list of wireless network clients there is a “Deny” button - click it to add the device to the black list. The same can be done by opening the MAC Address Filtering . First, you need to enable this very filtering:
Secondly, we need to create a rule to block and add to the list the hardware MAC address of the unwanted user, whose WiFi we need to disconnect from:
You need to add a description and enable the rule. We save it and reboot the router so that everyone connected to it reconnects again.
Advice:
If your WiFi has been hacked and is being used illegally, this is a reason to check your router’s security settings. It must have a WiFi password protected using the WPA2 or WPA3 . Never use outdated WPA or earlier standards. Disable WPS technology in the Wi-Fi settings and be sure to change the factory password to enter the router settings. In addition, I would advise you to update its firmware if there is an updated version on the manufacturer’s website.
Wi-Fi security key (PIN) and other factory information
What information can be found on the router:
- Network name , or SSID, is the factory name of the Wi-Fi network. It can be useful in order to find your network among neighboring networks. As a rule, it looks something like this: “TP-LINK_3Ao8”. Of course, on devices from TP-Link.
- Wi-Fi Password , Wireless Password, PIN, WPS/PIN is the factory key to access the wireless network. It usually consists of 8 digits. But it can be more complex. After entering the router settings, I advise you to change the factory password, as well as the network name.
- Router address (IP, web address) – this address is needed to enter the router settings. It can be either an IP address, usually 192.168.1.1, or 192.168.0.1, or a hostname (made up of letters). For example: tplinkwifi.net, my.keenetic.net, miwifi.com. At the same time, access by IP address also works.
- Username and password (Username, Password) – the factory login and password that must be specified on the authorization page when entering the settings of the router or modem. Usually, during the process of setting up the router, we change them.
- MAC address – may also come in handy. Especially if your provider binds by MAC address.
- Router model and hardware version (Rev, H/W Ver) - may be useful, for example, for searching for firmware or other information.
- F/W Ver – firmware version installed at the factory. Not available on all devices.
Virus
We have somehow become accustomed to computer viruses and have learned to fight them. But the fact that the router can be infected and break down!?
If you were going to check the router for functionality, and it stopped functioning, then what do viruses have to do with this, you might think.
Symptoms
Yes, there are viruses for the router and they work differently:
- They can significantly reduce the speed of data exchange. They interfere with the router settings, significantly reducing the speed or completely disrupting the signal level.
- They can change website addresses. How is it shown? Well, for example, you go to a familiar resource, but the malicious code written in the modem forcibly changes the DNS and you are redirected to some advertising site. Or those ad blocks that were previously successfully blocked now begin to pop up whenever and wherever they want. Moreover, this type of virus can redirect to another malicious site and your computer is already at risk.
Check network equipment for infection
Let's look at how to test an infected router for functionality. First you need to make sure that the virus is definitely there. Let's figure out how to find out about this.
To do this, the Internet cable must be connected directly to the computer.
Now you need to do the following:
- We launch any browser and open different sites one by one. You need to make sure that their content is correct and that the site is not being replaced. We recommend opening those resources where you are absolutely sure that there were no advertisements there before.
- Launch the antivirus program. You need to completely scan your computer. Such diagnostics will show that the infection is not coming from the computer. Although if infection has already occurred, then viruses can also be detected on the computer.
Virus removal
If you are now sure that the router is infected, then move on to the next step:
- Reset the device settings to factory settings. To do this, look for a small button labeled “Reset”. To press it, you will need a needle or toothpick. Press the button and hold for 5-10 seconds. After this procedure, you will need to configure the device again.
- If the software is damaged, then it's time to update to a more recent version.
Software glitch
You can double-check the functionality of the router using a computer via a direct LAN connection. In the command line, enter the command “ping (router address)” and press Enter. The address can be found on the back of the device on a sticker.
The system should respond. The waiting time for a response from the device is no more than ten seconds. If more, the computer will respond that the response timeout has been exceeded. If this operation, performed again, gives a similar result, then there is a clear problem with the device.
The only way out is to flash the device. If it is not possible to perform this operation yourself, then it is better to contact a specialist at the service center.
Find out the router model, web interface
Let's say a computer or other device is connected to the router, and a local connection is configured on it. Then, open the “Status” of this connection, click the “Details” button:
You need to look for the line “Default Gateway”, that is, “Main Gateway”. Windows XP doesn't have an Information button, but it does have a Support tab. The main gateway line contains an address that you need to remember in order to open it in the browser.
Where can I find the model name?
If, when you go to an address that looks like “192.168...”, the browser does not display anything, press “F5”. An authorization request should appear, and by the appearance of the request window you can recognize the name:
We will see an inscription with the name of the device. And if you also know the password, then great! The name of the router, as well as the hardware revision number, are displayed on the first page of the interface.
The password admin is usually used; 1234 is suitable for ZyXEL, but in principle, the user can change the value. We want to open the web interface to see its start page. Here's what it looks like, for example, if we're talking about TP-Link:
In the “Hardware Version” line we see the full name of the model: “WR842ND, revision 1”. Note that the hardware revision itself can be indicated not by a number, but by a letter and a number.
Why a web interface? There is telnet!
In the console, that is, in a telnet or SSH session, the name of the router model is available using the following command: cat /etc/versions. This is true for D-Link devices, but most likely for others too, since the Linux command given here is the same everywhere.
So, open the command line with administrator rights and write: ping “router address”. Instead of the combination “router address”, substitute the required numbers.
It will be good if the ping command shows the result. We are looking for the name under the lid
It would seem that nothing could be simpler - you can open the plastic case of the device and look at the printed circuit board on which letters and numbers are printed. Well, let’s immediately note that the letters are really there, but they have nothing to do with the name of the model. Sometimes you can read the revision number (after the letters "V" or "Ver"), but this is the exception, not the rule. There are different bar codes on the top side:
On the bottom side, as you can see, nothing is written:
Conclusion: you should not open the case to get any information at all.
The worst thing is if the unknown device is in recovery mode and cannot be managed via telnet or web interface.
Actually, in this case, there is only one thing left to do - take the “signet” along with the case to a service center. And finding out the full name of the model in the service center costs money. By the way, it will be very bad if they make a mistake with the revision number and you start installing the wrong firmware. Then the device will have to be restored using a special cable. Or you will have to completely unsolder the FLASH chip in order to install it in the programmer. Do you need this?
Many people cannot figure out which power supply to connect: 5 Volts or 12. There is widespread advice that you should take and try all standard voltages. The standard ones are: 5, 9, 12 V. The problem is that some companies still sometimes use a different value. For example, it could be 7.5 Volts. The printed circuit board does not have any “stabilizers”; turn on the wrong thing and everything will burn out.
Almost all routers and access points have a step-down pulse converter in the form of a PWM controller, inductor, diode and capacitor (in the simplest version). Thus, the input voltage range depends primarily on the installed PWM and wiring. Thank you, Ivan, for your comment.
Connection
It doesn’t matter your computer, laptop, phone, tablet or even TV, you can access the router settings from all of these devices. For this purpose, the Internet center has a Web interface. Therefore, you do not need to install any programs or cleverly try to get into it. Everything is done much easier.
First, you need to make sure that your device from which you want to log into the router is connected to it. You must be connected to the device’s network, otherwise nothing will work. This can be done in two ways:
- Via cable - you can connect a computer or laptop. We simply take the wire, if it is not already connected, and insert one end into the transmitter, and the other into the network card of the computer or laptop.
- By Wi-Fi - in a device that has a Wi-Fi module, turn on the search for wireless networks, find the one you need and connect.
View Wi-Fi devices connected to the TP-Link router
Now let’s use a specific example to demonstrate how to see who is connected to WiFi, for which we’ll take one of the most popular brands of wireless routers - TP-Link. On models with the old web interface such as TL-WR740N, TL-WR741ND,TL-WR841N, etc. you need to open the “Wireless Mode” section and find the “Wireless Mode Statistics” item there:
Here you will see the number of devices connected to the router and their MAC addresses.
In newer modern TP-Link routers of the Archer family:
Right on the start page of the web interface there is an icon Wireless clients . We click on it and a sign with currently working Wi-Fi clients appears below. Here you will see the total number of devices, their IP address and network names. This will help you determine as accurately as possible which gadget it is specifically.
Looking at WiFi clients on D-Link
Another equally popular manufacturer of network equipment in Russia is D-Link. I will show you how to find out who is connected to WiFi using the example of the most popular routers - DIR-300 and DIR-615. For other models, the web interface should be identical, but may differ slightly.
On older D-Link firmware version 1.XX, you need to open the advanced settings of the router. On the Wi-Fi tile, use the right arrow to scroll through the parameters until the List of WiFi Clients - click on it.
On newer firmware version 2.X.X, you can view devices connected via Wi-Fi by opening the Wi-Fi section and selecting “List of WiFi clients”:
Well, on the most modern version of the D-Link firmware series 3.XX and 4.X.X, in order to see the devices on the wireless network, you need to open the Wi-Fi settings section and select “Client Management”:
Despite the fact that the software versions collected here cover a time period of approximately 10 years, the procedure has not changed fundamentally.
Main problems
So. Let's start to figure out where the Internet disappeared. Let's rank the reasons from simple to more complex:
- The Wi-Fi router module is disabled or the device itself is not turned on.
- Checking connections. It could be:
- loose plug;
- the cable itself is damaged or the wire;
- The device has been dropped before - there should be traces of impact.
- Is there any debt for the services of the provider? It seems trivial, but people often forget to pay for Internet services on time. And even if you have paid, it would be a good idea to check whether the payment was successful.
- Device settings. They can also go astray. How can I check this? Open any browser and enter the request in the search bar: IP address of your router. It can be found on the back of the device.
- Changes in work on the provider side. We contact the service provider and find out whether repairs are being carried out on the line or whether the traffic speed has changed. Alternatively, you can check this yourself using third-party resources.
Disabling foreign devices from Wi-Fi
Once you have found out who is connected to my WiFi, you should move on. Now we have to take action without harming other users connected to the network. Or be able to freely connect to it. In theory, everything looks simple: just turn off the device. But in practice this is not enough. After all, a banal disconnect will allow a third-party “client” to reconnect to the network almost immediately. This means a more radical solution will be required.
When analyzing the question of how to determine who is connecting to our network, we already looked at the router control panel. But it serves not only to see active connections on the computer. Also, using the web interface (this is essentially the same thing), it is possible to make changes to the router settings. This will allow you to find out and see who is connected to the network, as well as block further access for “left” users. The following steps need to be taken:
- Log in to the router control panel (see above). This feature has previously been used to check connections.
- In the Wireless section, find the Mac Filtering item. The necessary operations are performed through it. It is also possible to configure a Firewall on the router. But it's a little more complicated than setting up access rules through address filtering:
- Select the rule to use. The difference is that in the first case, access is blocked for all devices except those specified in the list. In the second case, “listed” devices will be blocked. Which solution to apply depends on the user.
- Having made your choice, click Add new so that the following window appears:
Now you need to configure filtering. We look at the devices currently connected to the router. Here the user will be interested in the MAC address of the “parasite”. It will be used for further blocking. Enter it in the appropriate field. Anything can be used as a description. In the Privilege section, set deny. That is, deny access. And Status concerns the use of the rule itself. If the status is changed to Enable, the rule works. And vice versa.
After this setup, you can instantly disconnect the unwanted subscriber from wi-fi. Of course, this method is very complicated and it is easier to change the password. But this does not mean that the “freeloader” is not able to learn a new one and connect again.
In general, the access denial method is imperfect. If you simply change the MAC address, there is a chance that you will be connected to someone else's network again. Which means we should move on. And the next logical action is to change the wireless network password. And this leads to the next question.
Additional options
The times of the “free Internet” are already in the past - now every client of the World Wide Web is constantly under close surveillance by search engines and is constrained by various restrictions. This quite naturally led to the growing popularity of VPN technology, which allows you to hide from annoying attention on the Internet and bypass some of the restrictions.
Router manufacturers have not stood aside and most models have support for one or more VPN protocols. If the list of VPN functions of the selected router includes a PPTP client, OpenVPN client, IPSec client or L2TP client, then it is prepared to create a secure network using the appropriate VPN service. If you plan to use a VPN, it makes sense to first understand this technology, choose a suitable service and, when choosing a router, pay attention to the availability of the required VPN function.
Many routers have a number of USB ports for connecting peripheral devices. USB ports on a router can have very useful functions:
- A DLNA server allows the router to provide media resources (photos, videos and music) to other DLNA devices on your network: TVs, media players, stereo systems, etc.
- A torrent client allows you to assign tasks to the router to download files from torrent networks.
- a file server (Samba server) provides local network clients with access to files on a connected external drive.
- The print server (Samba server) allows you to connect a printer to the router and print to it from local network clients.
The USB port can also be used as a DC power source for charging smartphones and other mobile devices.
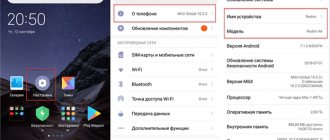
From an Android phone
Unfortunately, you don’t always have a laptop or PC at hand to determine the IP address. Then a smartphone can come to the rescue.
- Let's go to settings.
- “Network and Internet” section
- Turn on Wi-Fi. Now click here to view available connections. If the router is new and there is no connection, then you need to enable WPS. We go to the router and look for this button on the back. On Zyxel routers it is located on the top cover and is indicated by a wave or key icon. After this, the phone should catch the network.
- Select our network. If a password is required, look at the factory password on the label. If there is no password, then press the WPS button again to access.
- In the "Gateway"
you will see the address.
Typical problems for beginners
There are several ways to determine whether your router is to blame for Internet problems.
Checking indicators
When power is supplied, the Internet appears, or the Wi-Fi module is activated, the corresponding indicator on the front panel of the device lights up. So, how to check whether the Wi-Fi router is working or not?
- The first thing to start checking the router is the glow of the LEDs. Perhaps the device was left without power or the Wi-Fi module turned off after a reboot. It is also worth checking the presence of an incoming signal: there is a possibility that the cable introduced into the apartment is damaged (broken, problem with crimping).
The following video will help you check if the network cable is working properly:
- The second step is to connect to the Internet from a second device using the same interface. If you need to check the operation of Wi-Fi, connect via a wireless channel.
- Devices equipped with a radio module will help you check the presence of a Wi-Fi connection. You can also learn about connecting a wireless connection from the web interface for configuring the router. The main page provides the necessary information. Let's show it using a router from TP-Link as an example.
Software problems
A virus can also cause a router to malfunction. Watch the video on the topic:
If the previous tips did not help, reboot the device using the software method. Usually we go to settings, call “System Tools” and click “Restart”. We look at the status of the router in the web interface for its settings through the browser.
If rebooting does not help, and the router also does not work, you can try resetting the previous settings to factory settings. For this purpose, there is a hardware “Reset” button, usually recessed into the case to prevent accidental pressing. You need to get to it using a thin object (needle, toothpick, ampoule). Some models from Asus have another algorithm for protecting against accidental pressing - the button will have to be held in the clamped position for about 10 seconds.
You can also try the following. In the settings of the protocol used, usually IPv4, we indicate the method of IP distribution. Sometimes the settings for the method of obtaining physical addresses are changed by third-party software.
We go to the “Network Sharing Center”, open the “Properties” of the network card and double-click on the protocol version (most likely it is TCP/IPv4). We select the automatic method of obtaining the IP address and DNS server.