Execution Methods
Understanding will come only after considering each case separately. There are several ways to perform a quick or full format in Windows:
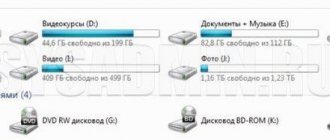
- Through the context menu (right click on the desired disk), select “Format” and see the following window:
By the way, here is a useful instruction in case an error appears related to the inability to complete the procedure.
- The second way is through Disk Management. There, select the required section and use the right-click menu to indicate the desired action:
- Using the format command at the command prompt after running the diskpart tool;
- During a clean OS installation.
Formatting
After this type of formatting, erased data is easily restored. During quick formatting, sectors remain the same size, so sometimes hard disk space is lost.
With this formatting, only the information about the initial record of the placed files is reset.
For example, in a FAT32 system the root directory is reset, in NTFS this is the MFT area. The remaining areas of the disk do not undergo any changes or checks.
Full formatting slowly erases all information from the disk. Once the full formatting is completed, it will be much more difficult to recover any data on the storage medium. This type of formatting allows you to find bad sectors on the disk and fix them.
This procedure can increase free disk space.
A full format overwrites the physical sectors on the disk. On modern storage media, the full formatting process performs the function of checking the entire surface for the health of sectors without overwriting them. This feature is useful, but can take several hours to complete with large disks.
Therefore, in most cases you can get by with a quick formatting process. But if the reliability of the disk is in doubt, then it is better to do a full formatting.
We can add that if the installation of a new operating system is carried out on the same partition where the previous version of the OS was installed, then you can easily get by with quick formatting. And if the OS is installed on a newly purchased disk, then it is better to do a full formatting of the disk. When reassigning a partition, it is also recommended to completely format the drive.
Many users often have a question: why format a hard drive at all? You can explain for a long time and persistently in complex terms why this process is necessary.
But it’s better to consider and explain everything using a simple example. An unformatted hard drive can be compared to a crumpled piece of white paper.
Is it possible to write any long text on such a sheet? The answer is no. And if you straighten out this sheet of paper, you can write anything on it. It’s the same with a hard drive: before you write anything to it, you need to format it. That is, a straightened sheet of paper is, figuratively, a formatted disk.
Perhaps that’s all for now, and until new interesting meetings with you, dear readers...
This entry was posted on Saturday, April 21st, 2012 at 23:47 and is filled under: USEFUL TIPS
Main differences
The difference between quick and full formatting is as follows:
Fast processing involves superficially wiping the disk, creating a boot sector, and creating an empty file table of the specified type (FAT/NTFS). The procedure is completed in a few minutes (and sometimes seconds). After it is completed, recovering deleted data will not be difficult if you use the appropriate software.
Complete includes the procedures listed above + total cleaning of all sectors of the flash drive or HDD. In addition, the drive is scanned for damage. If any are found, a correction is made. If “treatment” is impossible, unsuitable sectors are marked so that no further information is recorded on them. The duration of such a process is tens, hundreds of times longer than with the fast method (the time is affected by the disk volume).
When should you use quick formatting and when should you use full formatting?
It’s difficult to give any clear recommendations here, but usually they do this: if you need to delete all data from a hard drive partition or from a removable storage medium, for example, a flash drive, then use quick formatting, since it is completed in a matter of seconds.
If there is a suspicion that bad sectors have appeared on the disk, or that the file system has been damaged (as a result of a virus or due to incorrect removal of the storage medium from the computer), then use full formatting.
The formatting process does not harm your hard drive or removable storage device in any way and you can format it without fear of damaging it.
Which method should I use?
In most cases, you should choose shallow processing, but there are situations when you should give preference to a deeper algorithm:
- If you intend to sell/give your storage medium to someone, then it is important to clear it without the possibility of subsequent data recovery (you never know what important files were stored on your PC).
- During Windows installation, errors occur during the file copying stage. Most likely, the disk contains bad sectors that can only be "repaired" by a full format. But I would advise you to first check the HDD for errors before installing the OS.
Deleting files
The main task of the file system is to write and read information stored in it. Normally deleting a document clears only the directory, but it still remains on the disk shelves. If, after deleting one of the files, you want to install another, the old files will be replaced by the new ones.
Taking into account this paragraph, you may be interested in learning how you can recover deleted documents that cannot be returned using the Recycle Bin.
Recovering files from a RAW disk
What about SSD?
What is the difference between quick formatting and full formatting? Let's now look at this issue from the point of view of SSD compatibility.
It is recommended to use only the fast one, which will delete all data and no one will be able to “resurrect” it (thanks to the special TRIM command). But a total format can damage the SSD structure. You can find confirmation of this on various computer forums.
I am sure that the topic has been covered to the maximum. If you think that some aspects were not covered in the publication, write to me in the comments. I will definitely answer as soon as possible.
Sincerely, Victor!
exFAT
exFAT is a format that replaced FAT32. Its main difference from its predecessor is that it has no restrictions regarding file sizes. In other words, it is practically the same NTFS, but with some differences. Firstly, the cluster volume has been increased to 32 KB, secondly, the data transfer speed is much higher, and thirdly, exFAT uses space more economically.
The main disadvantage of this format is that it is not yet very widespread and has poor compatibility with other operating systems. Drives with such a file system work correctly only on Windows 7 and higher operating systems. Performance on devices other than computers is also low.
If you choose which format to format the flash drive in from the three presented above, then perhaps you should opt for NTFS if your drive has a capacity of more than 8 GB. If less, then the choice is obvious - FAT32. For those who like experimenting, we can recommend exFAT, but you need to be extremely careful with it.
How is formatting different from deleting?
The only difference between the two is that deletion requires the user to manually delete individual data or select only part of the data he/she wants to delete, but formatting will take all the data on the hard drive and delete it.
Interesting materials:
How to clear cache in Internet Explorer 11? How to clear the cache in Chrome for one site? How to clear cache in HP printer? How to clear cache in Safari on iPad? How to clear the cache on the system? How to clear cache in Sony? How to clear the cache in Viber on iPhone? How to clear WhatsApp cache? How to clear iPhone WhatsApp cache? How to clean the coffee machine holder?
Erasing a memory card
If necessary, the gadget’s memory card is also formatted, but separately. This can be done via a computer or laptop in the standard way. For this:
- Insert the MicroSD card into the SD adapter. Make sure that writing on it is enabled - the switch should be at the top.
- Insert the SD into the card reader, make sure that the system recognizes it as a drive.
- Right-click on the map icon to open the context menu and select the desired command.
You can format the SD card in the phone itself. For this.
Deleting almost all data from a smartphone (except for OS files) is a procedure that is sometimes necessary for any Android device. In other words, this process is called Hard Reset. We will tell you how to format a Lenovo phone in our article.
- Virus inside the system.
- The Lenovo smartphone is very slow and glitchy.
- Selling a gadget (the reset is carried out so that it is “clean”, without your photos or videos, and functions only using factory settings).
- A cleaned Flash card is required.
How to format a partition or flash drive using the windows operating system
ATTENTION!
all data that was stored on a particular partition or flash drive will be lost after the formatting procedure.
1.Go to Start
>
My computer
2. Right-click on the partition icon or flash drive that needs to be formatted, select the item from the drop-down list ( Format...
).
3. Select from the list ( File system
) the system in which you need to format; you can read about the file system in the article
When formatting internal disk partitions and USB
-Windows media offers a choice of two types of implementation of this procedure -
quick
and
complete
.
Quick physically
delete information on the disk. The disk space is simply marked as unused at the software level. And the data access structure is re-formed on it in accordance with the selected file system.
With a visual interface, this functionality is implemented in the Explorer context menu and disk management.
The system itself gives preference to the fast type, the checkbox for its selection is preset. The full type is launched when this checkbox is unchecked. Many programs for writing bootable media work on this principle: quick formatting
, but complete operation is possible if the user deliberately selects this operation.
Why is the fast type preferred? What is the difference between it and the full type? Which is best to use in what situations?
We will try to understand these questions below.
This operation occurs very quickly, and after it it is possible to recover HDD
and
flash drives
using a special type of software.
With SSD
in terms of data recovery, the situation is different: information is physically deleted from the storage cells after any formatting - be it quick or complete, if this procedure is performed using
Windows 7, 8.1
and
10
with the
Trim
.
And it will no longer be possible to save valuable data deleted by mistake after this procedure. This is due to the specifics of data rewriting: if new information is recorded simultaneously with the old one being physically removed from the SSD
, in general the speed of this operation will decrease.
Taking care of the performance of solid-state drives, the Trim
provides physical erasure of data regardless of the method of software deletion.
Quick formatting, due to its efficiency, as mentioned, is offered by default in the Windows environment. It is also provided without alternatives during the installation of the operating system.
Choosing the full type of this procedure can lead to an infinitely long wait for its completion.