Hello friends! Today I will tell you about how to view the characteristics of a computer on Windows 7. The post is short and, in principle, there is nothing interesting here. I think everyone knows and understands how to get the necessary information about their computer. Specifically in this post, I will consider all the standard ways to obtain the characteristics of a computer running Windows 7, although they are also suitable for others. Well, shall we get started?
System window
What can you find out? You can find out the name of the processor that is installed in your system unit. The amount of RAM, also known as RAM. System type 32 or 64 bit, as well as processor bit size, respectively. By the way, I recently wrote a post about this, I highlighted the link. Next come other characteristics, I have listed the main ones. So how do you open the “System” window? This information is given below, which consists of several ways. You can use any of them and see the characteristics of your computer.
First: I think absolutely everyone has a “My Computer” shortcut on their desktop. Using it, you can literally open the “System” window in 3-5 seconds and find out some characteristics. To do this, right-click on it, thereby calling up the context menu. Then click "Properties" and you're good to go!
By the way, if the shortcut is created artificially, then the window that you would like to see will not open. How to determine? It’s easy to determine: if the shortcut actually has a shortcut icon, then, alas, nothing will work. If the shortcut is displayed as *.exe files, then everything will work out. To create such a shortcut not a shortcut, use the fourth method. There I described a little what and how it’s done.
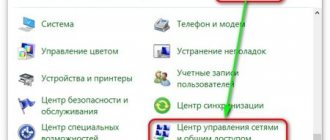
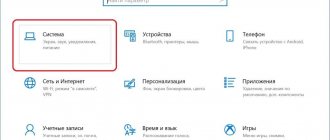
Second: you can open it using the “Control Panel”. There are several ways to open the Control Panel. For example, through the Start menu or enter the control in cmd. After opening, you need to click on “System and Security” and click on “System”. This is if you have a display in the form of “Categories”, but if there are “Large” or “Small” icons, then immediately find and click on “System”. This will open the properties window.
Third: Through search in Start. Open and write the word “System” and select the desired search result.
Fourth: Again through the Start menu. You need to open and right-click on the word “Computer” and select “Properties”. By the way, there is a “Display on desktop” option, if the “My Computer” shortcut is created artificially, then click. A new icon will appear on the desktop, and the old one can be deleted. This is the same information that I promised in the first paragraph.
Using third-party applications to determine laptop characteristics
A good quality small application that can determine many laptop parameters - CPU-Z. With its help, you can view the technical characteristics of your processor, motherboard (model and chipset), size and type of RAM, and video chip performance. Information about each component is provided in separate tabs - CPU, Mainboard, Memory and Graphics, respectively.
Even more detailed information about installed system components is provided by the AIDA64 application. It is true that it is paid, but with a trial period during which the functionality is not limited, therefore, you can use the program completely free of charge.
Unlike many similar utilities, AIDA64 provides information not only about the processor, video adapter, etc., but even about the monitor, including its size. You can view them in the following way:
- Launch AIDA64 and click on the “Display” tab.
- Open the "Monitor" item.
All available information about the display will appear in the application work area - its name, size in inches, maximum resolution. Information that allows you to determine the release date of your monitor may also be useful - the program indicates the year and week of its manufacture.
device Manager
Device Manager is a Windows component that includes information about connected devices. Using it, you can update or remove the drivers of these devices, determine and change the operating parameters of any device. You can also find out whether the connected components are working correctly. In a word, good stuff.
How to start? This is almost a rhetorical question, since I answered it in the first paragraph. That is, you will need an open “System” window in which you need to click on the “Device Manager” link on the left. You can also open it using the Start menu by searching for “Device Manager.” This component can also be launched using the command mmc devmgmt.msc in cmd or in “Run” (Win + R).
Other information about the laptop that cannot be found out from diagnostic programs
While data such as the type and amount of memory, the diagonal size of the laptop display in inches can be viewed in some diagnostic programs, for example, AIDA64, these applications do not show the date of manufacture of the laptop itself or, for example, its weight. But the label that should be stuck on the back cover of the device can tell you how to find out the year of manufacture of the laptop:
Another characteristic that is interesting to many is the weight of the laptop. No diagnostic utilities display it in any way. In the absence of scales, it is possible to determine how much a laptop weighs only approximately, focusing on its dimensions and characteristics. Thus, large-format laptops with a diagonal of 17'' can weigh more than three kg. Gaming and multimedia devices often weigh even more, exceeding 4 kg. Basically, laptops with a diagonal of 11-13'' weigh 1.3-1.5 kg, 15-inch laptops - 2-2.5 kg.
The stability and performance of a computer depend on the selection of hardware and software components and their compliance with the tasks being solved. An outdated or incorrect driver, a device that is incompatible with the motherboard, or an insufficient video card speed can make it impossible for the operating system to function properly. To avoid such errors, you should know exactly what is inside the case. How can you view the parameters of a computer running Windows 7?
System Information
System Information is a Windows component (msinfo32.exe) that includes information about software (including drivers) and system components. You can also see hardware configuration information.
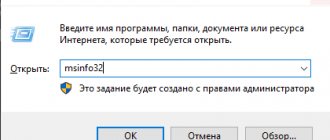
How to start? I answer. As always, through the “Start” menu by typing “System Information” into the search bar. Via the command line by typing the command msinfo32 or in “Run” (Win + R) by entering the same command there.
When may you need information about the characteristics of a computer running Windows 7?
Not only ordinary curiosity or a thirst for knowledge causes the need for information about the technical characteristics of a computer; there are also more serious circumstances:
- Failure in work. Computer freezes and random errors require a comprehensive study of the reasons, including analysis of the operation of the hardware.
- Installing drivers and updates. When new versions of drivers and installed programs are released, you must select those that match the characteristics of your computer. And for this you need to know them.
- Overheat. If the temperature of the processor or hard drive is too high, this is a serious cause for concern and finding out all possible causes, including hardware ones.
- Selection of components. Replacing, upgrading or expanding hardware requires information about the compatibility of various devices.
- Software requirements. Many resource-intensive programs will not run on a computer that does not have sufficient power. Therefore, before starting installation, you should check the hardware requirements of the program with the characteristics of the system.
DirectX Diagnostic Tool
Also a good option, and most importantly standard. What does standard mean? I use this word often. If we are talking about Windows, then standard means already available. In this case it concerns programs. They are already available and you don’t need to go online and download anything.
So how to launch? Very simple! In the command line, also known as cmd, or in “Run” (Win + R). Command to run: dxdiag . I will not describe what information can be obtained, since everything is visible in the screenshot above. Besides, you can run in and look there yourself.
Method 1: Open the System panel using the Win + Pause/Break hotkeys.
This is perhaps the easiest way. For those who often need to use the System panel , this is the ideal tool.
So, on the keyboard, press and hold the Win key (bottom row, left corner of the keyboard). And press the Pause/Break key (upper right corner of the keyboard).
Using third-party programs and more
I like this option better because it gives better results. The methods above can also be useful. For example, if you need to look at the characteristics of the computer at your work place, but there are no programs at hand. Although who’s stopping you from downloading a portable version of a program in advance and putting it on a flash drive for later use. Also not a bad option, but I think no one carries storage drives with them. Although if the work requires it, then of course yes, but if not, then I don’t think so.
I will not talk about this or that program. I’ve already given up because it’s easier to give a link. Therefore, if anyone is interested, look here. There I reviewed 3 programs, namely: Aida64, Speccy, CPU-Z. Although I considered it rather rudely, I rather mentioned them and provided download links. Follow the link that I indicated just above in this paragraph. You will get right where you need to go and there will be no need to go down the article. What you need will open.
There is another way to get information, but only specifically about Windows 7. I didn’t highlight a whole point on it, since there’s nothing there at all. In general, launch the command line (cmd.exe) and enter this command there: systeminfo . I screenshotted the result, see below. Perhaps this will be useful to someone.
This is where I will end my post. Thank you for reading to the end. If you have any questions or want to add anything, be sure to write in the comments. No one will be left without an answer. If you don’t want to miss the news from my blog, you can subscribe to it.
Alexey Antropov was with you, bye everyone.
How to find out computer parameters using standard methods
You can find out the characteristics of your computer and system using Windows 7 tools, special programs or BIOS.
Hotkeys
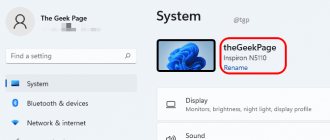
The fastest way to get a brief report on your computer’s configuration is to call up the “System” window using a combination of the Win (with the Windows icon) and PauseBreak (function key next to PrintScreen) hotkeys.
The window that opens with the title “View basic information about your computer” contains information about the installed version of Windows 7, the manufacturer and model of the computer, the characteristics of the processor and RAM. The overall performance index is also located here, and more detailed data on the operation of individual hardware components can be viewed by clicking on the active line next to it or by clicking on the tabs on the left side of the window.
System utility "System Information"
Detailed information can be obtained using a special Windows 7 utility. To launch it, use the combination Win + R, then in the input line of the “Run” window that appears, type the command msinfo32 and press the “OK” on-screen button.
The main window of the utility contains a lot of useful information, which is divided into several groups. By moving through the tabs on the left side, you can find all the necessary data about the hardware capabilities of your computer.
Another way to get to the same window is to use the search bar. Click the “Start” button and type “System Information” in the search bar. All that remains is to go to the active line in the list of results.
DirectX Diagnostic Tool
More detailed information about the characteristics of the video card and sound devices of the computer can be obtained using DirectX. Call up the familiar “Run” menu and type the command dxdiag.exe in the input line.
The DirectX Diagnostic Tool window contains several tabs with system information, as well as screen, sound, and input information.
A special feature of the DirectX Diagnostic Tool information window is a reduced amount of general information and more detailed information about the screen and sound devices.
Control Panel
You can also get to the “System” window we already know using the “Control Panel”.
- Click “Start”.
- Then in the right column of the menu that appears, select “Control Panel”.
- In the large “All Control Panel Items” window, find the “System” tab.
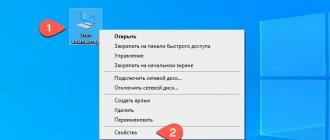
- Clicking on the tab, we find ourselves in a familiar window. You can also get to it if, after the “Start” button, select the “Computer” line, right-click on it and select “Properties” in the context menu that opens.
device Manager
Device Manager contains a list of all hardware components of your computer and basic information about them: model, status, conflicts, drivers, manufacturer, and much more. Having selected the item of interest, you need to click on it with the mouse and get all the necessary information.
If any of the devices has problems (or is not recognized by the system), it will be marked with a special yellow or red icon with an exclamation mark.
There are several ways to call the utility.
Open via search bar
- Click the “Start” button.
- Enter “Device Manager” in the search bar.
- We move along the found active line.
Login from the “System” window
Find using Run window
- Press Win+R.
- Enter the command devmgmt.msc.
- Click on the “OK” on-screen button.
Command line
Basic information about your computer can also be found using the command line.
The undoubted advantage of this method is its versatility; it is equally applicable to both older versions of Windows and the newest ones.
BIOS
Basic information about the computer can be viewed when it starts, while the BIOS is running, by pressing the Del (Delete) key.
The main advantage of this method is its independence from the installed operating system, so the data can be seen even if Windows 7 does not start for some reason. In addition, the BIOS will be the first to report problems with the hardware, for example, a burnt-out RAM stick.