Probably, many users of computers, laptops and mobile gadgets would at least once like to watch their favorite films, photographs, TV shows, say, on a large screen television panel or, conversely, synchronize the Internet broadcast of the same TV, radio with a mobile device, and also listen to music on a good sound system. For this we need a so-called UPnP media server. What it is and how to configure it, we will now look at. There's nothing complicated.
UPnP - what is it?
In general, UPnP is an abbreviation of the term Universal Plug & Play. In other words, this is a kind of virtual system that unites connections of smart devices located on the same network with each other based on TCP/IP, UDP, HTTP, etc. protocols.
Understanding the topic “UPnP: what is it?”, in simple terms we can describe this as creating the ability to transmit and receive data by all devices that support this standard. The simplest example is, say, viewing photos on the same TV instead of a smartphone. As is already clear, it is enough to simply synchronize devices with each other to provide mutual access to data.
Why Universal Plug and Play is Unsafe
Computer technologies are designed to facilitate the work of various modern gadgets. But there are risks when using them:
- Global network access.
Initially, it was planned to use this smart service to connect home computer gadgets only at the local level within the same network. This system has taken root in the IT world, but many modified routers now include UPnP in the default firmware, thereby giving access to the router itself and all Internet devices connected to it. Computer hackers can take advantage of this (gain access to someone else’s PC, use connected devices to send spam and viruses).
- Device programming errors.
Not all electronic gadgets keep up with software updates. UPnP is improved by developers every year, but scammers find vulnerabilities in the programs of connected devices and thereby bypass UPnP protection and connect to the user’s personal devices from his local network.
Windows Presets
Before you begin to consider how to set up and enable a UPnP home media server, you should make some preliminary settings in the operating system itself.
In Windows OS, depending on the version, this is done in slightly different ways, but the general principle is the same.
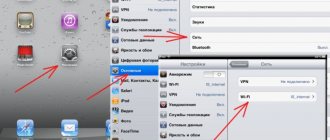
So, you need to activate the UPnP server (Windows 7). How to enable it? Nothing could be simpler. You just need to go to the programs and features section (in previous versions of Windows, the add/remove programs menu) located in the standard Control Panel, and then select the Windows feature installation options. Here you select the network services item, check it, and on the right you use their composition item. When entering this menu, be sure to enable the discovery and management client and check the UPnP user interface. Then the changes are simply saved and take effect without a reboot. This applies equally to XP, Vista, 8 or 10 systems.
It’s worth noting that in some cases you may need a Windows installation disc.
MediaTomb (Mac, Linux, FreeBSD) [no longer available]
MediaTomb is another completely free DLNA server with transcoding capabilities. It is an extensible UPnP solution with binaries for OS X, FreeBSD and a large number of Linux distributions. One of the best features of MediaTomb is the documentation with detailed instructions on how to operate devices like PS3 and DLNA TVs.
The server is configured via a web interface, which provides an easy way to manage media. If you run into problems that the Wiki or FAQ can't solve, then there is an active forum where you can ask for help.
How to enable UPnP on a router
But that's not all. If the network connection between devices is supposed to be carried out using a wireless connection using a router (router), you will have to check the UPnP settings on it as well.
Although, as a rule, almost all the most common router models come with the UPnP service already enabled, it is nevertheless better to check the settings. For most models, you can enter the router menu by entering the address 192.168.1.1 in any Internet browser. Depending on the model, menus may differ in names or location of individual controls. But in any case, you need to find the “Enable UPnP” option or make it available (in the English version - the Enable UPnP Protocol or Enable UPnP Settings menu).
NAT Traversal
One solution for NAT Traversal, called Internet Gateway Protocol (IGD Protocol), is implemented through UPnP. Many routers and firewalls present themselves as Internet gateway devices, allowing any local UPnP control point to perform various actions, including obtaining the device's external IP address, enumerating existing port mappings, and adding or removing port mappings. By adding port mapping, the UPnP controller behind the IGD can allow IGD bypass from the external address to the internal client.
Enable UPnP in Skype
Now let's look at an example of the popular program for communicating using IP telephony Skype. UPnP technology is also used here. What is this in relation to the application itself? This is the same port forwarding system for establishing communication with another device. It is much more pleasant to communicate with friends, seeing their image, say, on a large TV screen.
Enabling UPnP is very simple. Here you need to go to the main settings of the program and select additional parameters, and then use the “Connection” menu. It has a special field for enabling UPnP, opposite which you need to check the box and then save the changes.
Recommendations
- "Using the UPnP Control Point API." Microsoft Developer Network. Retrieved September 11, 2014.
- "The ISO/IEC standard for UPnP device architecture makes networking easier and easier." International Organization for Standardization. December 10, 2008. Retrieved September 11, 2014.
- “The UPnP specification is designated as the international device interoperability standard for IP-based network devices” (PDF). UPnP Forum. February 5, 2009. Retrieved September 11, 2014.
- Goland, Yaron Y.; Schlimmer, Jeffrey K. (October 2, 2000). "Multicast and Unicast UDP HTTP Messages." UPnP Forum Technical Committee. Archived from the original on December 30, 2006. Retrieved September 11, 2014.
- "UPnP V1.0 Device Architecture" (PDF). UPnP Forum Technical Committee. October 15, 2008. Retrieved September 11, 2014.
- "How Windows Firewall Affects the UPnP Design in Windows XP SP2." Microsoft. May 23, 2014. Retrieved September 11, 2014.
- "UPnP Device Architecture Version 1.0" (PDF). UPnP Forum. October 15, 2008. Retrieved September 11, 2014.
- "UPnP Device Architecture Version 1.1" (PDF). UPnP Forum. October 15, 2008. Retrieved September 11, 2014.
- ^ a b
"UPnP AV Architecture" (PDF). UPnP Forum. March 31, 2013. Retrieved September 11, 2014. - “UPnP Forum Unveils Advanced AV Specifications Taking Home Networking to the Next Level” (PDF). UPnP Forum. July 12, 2006. Retrieved September 11, 2014.
- "Device control protocols." UPnP Forum. Retrieved September 11, 2014.
- "DLNA Network Device Compatibility Guidelines." Digital Living Network Alliance. March 2014. Retrieved September 11, 2014.
- "Digital Living Network Alliance (DLNA) Home Network Device Compatibility Guidelines - Part 1: Architecture and Protocols." International Electrotechnical Commission. October 23, 2013. Retrieved September 11, 2014.
- “OpenCable Home Networking 2.0 Specifications - Home Networking Protocol 2.0 Revision 10” (PDF). Cable television laboratories. May 30, 2013. Retrieved September 11, 2014.
- "CEA-2014-B (ANSI) - Web Protocol and Framework for Remote User Interface over UPnP Networks and the Internet (Web4CE)." CEA R7 Home Network Committee. January 1, 2011. Retrieved September 11, 2014.
- "Device Protection V 1.0". UPnP Forum. Retrieved September 11, 2014.
- “Device Security and Security Console V 1.0.” UPnP Forum. Retrieved September 11, 2014.
- "UPnP-UP - Universal Plug and Play - User Profile."
- Sales, Thiago; Sales, Leandro; Almeida, Higgo; Perkusic, Angelo (November 2010). "Extending UPnP to provide user authentication and authorization in widespread systems." Journal of the Brazilian Computer Society
.
16
(4): 261–277. Doi:10.1007/s13173-010-0022-2. - Eastep, Thomas M. (4 June 2014). "Shorewall and UPnP". Retrieved September 11, 2014.
- "Linux UPnP Internet Gateway Device - Documentation - Security." Retrieved September 11, 2014.
- "Network hacking." January 12, 2008. Retrieved September 11, 2014.
- ^ a b
"Internet Gateway Device (IGD) V 1.0". UPnP Forum. November 12, 2001. Archived from the original on February 22, 2011. - Garcia, Daniel. "UPnP Mapping" (PDF). Retrieved September 11, 2014.
- "US-CERT Vulnerability Note, VU #357851." CERT/CC. November 30, 2012. Retrieved September 11, 2014.
- "Millions of Devices Vulnerable via UPnP - Update." The H. January 30, 2013. Archived from the original on August 29, 2014. Retrieved September 11, 2014.
- Moore, H. D. (29 January 2013). "Whitepaper: Security Flaws in Universal Plug and Play: Disconnect, Don't Play." Retrieved September 11, 2014.
- "UPnP Forum Responds to Newly Discovered LibUPnP/MiniUPnP Security Flaw" (PDF). UPnP Forum. February 8, 2013. Retrieved September 11, 2014.
- https://kb.cert.org/vuls/id/339275
- https://callstranger.com/
- https://openconnectivity.org/developer/specifications/upnp-resources/upnp/#architectural
- https://www.tenable.com/blog/cve-2020-12695-callstranger-vulnerability-in-universal-plug-and-play-upnp-puts-billions-of
- "Disable UPnP on your wireless router already." Life hacker
. Retrieved June 14, 2022. - Bodlander, M. (February 2005). "UPnP™ 1.1 - Designed for Performance and Compatibility." IEEE Transactions on Consumer Electronics
.
51
(1):69–75. doi:10.1109/TCE.2005.1405701. - "UPnP Forum Gateway Working Committee: IGD: 2 improvements from IGD: 1" (PDF). UPnP Forum. March 10, 2009. Retrieved September 11, 2014.
The simplest utility for creating a home media server
Actually, here we come to the main issue of setting up and enabling a UPnP server. To begin with, as is already clear, you need to decide on the program (UPnP client). As the simplest utility that does not require manual configuration, we can recommend Samsung PC Share Manager.
In this program, almost all settings are automated; determining devices and connection methods does not require user participation, but the only thing that is required is specifying shared folders with multimedia files stored in them. By default, the application selects its own parameters, but directories preferred by the program can be deleted or you can set your own instead.
Here it is important to check whether the same general access is open to them. This is done from the properties menu, which is called up by right-clicking on the directory. Well, after starting, the UPnP server will turn on automatically, and all devices currently present on the home network will be synchronized. Sometimes you may need to add a program to the firewall exclusion list.
The only drawback of the application, perhaps, is the inability to watch online television or listen to the radio. You can only play content stored in shared folders.
Which devices support DLNA
All certified devices that support DLNA are divided into three main classes:
- Networked devices for household use are televisions, media and music centers, DVD players, network storage devices, home theaters and others.
- Mobile devices – this group includes smartphones and tablet PCs, portable players, video cameras and others.
- Multifunctional household appliances - this niche includes devices that support a variety of communication standards and are able to convert different file formats among themselves. They are required to ensure compatibility between the first and second class.
Despite the large number of different types of equipment, the main thing that immediately comes to mind when mentioning DLNA technology is modern LCD TVs. Moreover, it was precisely with the promotion and total distribution of televisions with the Smart TV function that there was an increase in the demand for the standard. The fact is that, in essence, a “smart” TV is a multimedia entertainment center in modern “Smart Home” systems. For this reason, DLNA is most often used to transfer video content from PCs to TVs.
All electronics that support the presented technology are marked with a “DLNA Certified” sticker on their housing. And although it uses open standards, devices must undergo a pre-certification process to qualify for such labeling. To date, more than 20 thousand different electrical appliances have already received DLNA certification. Regarding the volume of their sales, the figures have long exceeded a hundred million.
To use DLNA, you need an established home network. It can be created either wired, via Ethernet, or wirelessly, using a Wi-Fi network. To use the second method, a sufficient level of bandwidth is required. Comfortable work is only possible with a protocol not lower than the Wi-Fi 802.11n standard.
Using Home Media Server
Another thing is to use the more serious Home Media Server application (Russian development). Here, however, you will have to delve into the settings.
Although automatic detection is enabled, in some cases you will have to add devices manually. For example, the program clearly identifies the desired computer terminal on which it is installed, as well as the router responsible for the connection. If you need to transmit a signal, say, to an IPTV set-top box with subsequent broadcast to a television panel, you will have to enter the IP or MAC address of the device yourself.
Next is the issue of transcoding. In most cases, the “Movies (main)” mode is selected, but if a special utility Ace Stream (one of the Ace Player components) is installed on the system, it is better to use it.
With shared folders, everything is also simple here, but on the issue of television broadcasting you will again have to strain your brains. So, for example, to watch torrent television, you will need to register on a certain resource, and then download so-called podcasts from it, which must be added to the list and then updated. Only after this will it be possible to watch television programs.
Along the way, it is worth noting that on the set-top box you will also have to manually enable the use of the UPnP server. Most often, LAN mode is used to enable it. It may be different, it all depends on the modification of the console itself.
In general, there are a lot of settings in the program. The main ones can be dealt with without problems. But if you need to use any additional parameters, you will have to spend some time. But then the user gets at his disposal a powerful tool for synchronizing devices of any type. In passing, we note that for mobile devices you may need to install special applications and activate UPnP. Without this, there can be no talk of any synchronization.
Yes, and pay attention to one more thing. Unlike the previous utility, the server can only be turned on manually using a special start button or, if required, a restart.
Content
- 1 Review
- 2 Protocol 2.1 Appeal
- 2.2 Opening
- 2.3 Description
- 2.4 Control
- 2.5 Event Notification
- 2.6 Presentation
- 4.1 Media server
- 6.1 Authentication