To begin with, you should know that there are 2 types of network adapters, built-in and discrete (coming as a separate module). The advantage of these is their independence from the motherboard, which allows you not to spend extra money if your computer is repaired.
As some users recommend, to buy a good adapter, just take a well-known brand; you shouldn’t even pay attention to little-known ones. But there are still a few pitfalls that will make the purchase in vain. We'll talk about these below.
What is a network adapter?
Before introducing the definition of NIC, you need to know that there are quite a few names for network interface based on habits in different regions, such as Network Adapter Controller, Ethernet Card, LAN Card, Network Adapter or Network Adapter Card (NAC). It's a little confusing, but no matter what names NICs have, they all refer to the circuit board that allows devices like computers and network servers to connect over the network. Nowadays, a NIC adapter designed as an embedded style is commonly found on most computers and some network servers. Additionally, network adapters, such as the server network adapter, can also be inserted into device expansion slots.
Why is it necessary?
An adapter is equipment that ensures the functioning of the network at the data link and physical levels. It is classified as a peripheral device. It directly interacts with the data transmission medium.
The adapter successfully solves the problem of reliable transfer of binary data over external communication lines. Since it is a computer controller, it carries out its work under the control of the driver installed in the operating system. The network adapter is mounted in the motherboard socket. It converts the parallel codes used in a computer into a stream of powerful signals that transmit data over a network. Therefore, they are required to be compatible with the network operating system and the information bus of the PC itself. How to install a network adapter on the motherboard?
Functions
We looked at what a network adapter is and how it is configured, and now let's talk about the tasks that are solved when sending or receiving messages. There are nine in total:
- Galvanic isolation is carried out with twisted pair or coaxial cable. Pulse transformers are mainly used for this purpose, although optocouplers can also be used.
- Transmission (reception) of data. They come from RAM to the adapter or from it to the computer's memory thanks to input/output and direct access channels.
- Buffering. Used to match the speed at which data is transferred from or to the adapter with how it is transmitted over the network. Also, while information is being processed, it is stored in a buffer. It allows the adapter to work with the entire package of information. Also, thanks to the adapter, the data processing speeds of various LAN components are coordinated with each other.
- Package formation. The network adapter must divide the data into separate blocks in transmission mode (or they are collected during reception) in order to then format them as a frame of a certain format. It will be composed of several service fields, which indicate the address of the recipient’s computer, as well as the frame checksum, which is used by the device to conclude whether the delivered information is correct.
- Access to the communication channel. Also within its “jurisdiction” is a set of rules with the help of which you can get the opportunity to work with the transmission medium. In addition, the adapter detects conflict situations and monitors the state of the network.
- Identification of your address in the package that is accepted. It can be determined by the setting of switches, flashed into the PROM, or stored in a special register.
- Converts parallel code into serial code when transmitting data, and it converts it back when receiving it. There is a small exception to this. When the data transmission mode is active, information is transmitted over the communication channel in serial code.
- Data encoding/decoding. At this stage, electrical signals are generated and used to represent information. In most cases, Manchester encoding is used. This method does not require a clock signal to be transmitted to recognize 1s and 0s. In this case, polarity reversal is used.
- Reception or transmission of data pulses.
Also, network adapters, when working with the necessary software, can recognize and process an error that occurs due to poor hardware performance, collisions, or electrical interference.
Design features and operating principle
What does such a device consist of? Even the simplest design should contain the following elements:
- Input and output buffers;
- Encoder and decoder;
- Transmitting and receiving shift registers;
- Physical interface;
- Counting block;
- Control logic.
If we explain the principle of operation of the adapter in simple words, we should remember that information is exchanged frame by frame. When transmitting, the PC places the packet in the input buffer and issues a command to send. After waiting for a transmission window, the logic copies the data to the transmit register, where the parallel data is transformed into a serial bit stream.
The encoder converts this bipolar code into a code for transmission (in the case of Ethernet, this is the so-called “Manchester code”, which is already sent “to walk along the wires” until it reaches the addressee. Reception of information from the network occurs according to the same principle, but in the reverse order .
It is important to know that any network card has a unique MAC address, by which it can be identified among millions of similar devices. And if for an advanced user a ban by IP does not cause any difficulties (it is enough to launch a VPN and log in under a different address), then blocking by MAC is a much more serious problem.
It is necessary to change the configuration of the network card at the hardware level, which implies a complete re-flashing. So, if you are banned somewhere by MAC, the least expensive way to bypass the block is to install an additional network adapter.
Among IT specialists, there was once a joke about an even more serious blocking method - the so-called superban. Its essence is that one of the administrators of the forum or site personally visits the user and hits him in the face, once and for all discouraging flooding and other ways of violating the terms of the user agreement.
However, the coin also has a downside: the owner of a Wi-Fi router can only allow certain devices to access the network by MAC address. This is relevant if your technically advanced neighbor, not wanting to pay for the Internet, uses your channel.
Network adapter components
Traditionally, a NIC mainly consists of a controller, a boot ROM socket, one or more NIC ports, a motherboard connection interface, LED indicators, a profile bracket, and some other electronic components. Each network card component has its own unique function:
Controller:
The controller is similar to a mini-processor and processes the received data. As the core part of the network adapter, the controller directly determines the performance of the network adapter.
Boot ROM connector:
This connector on the board provides the ability to load ROM. Boot ROM allows diskless workstations to connect to the network, increasing security and reducing hardware costs.
NIC port for cable/module:
Typically this port connects directly to an Ethernet cable or module that can generate and receive electronic signals that are superimposed on the network cable or fiber optic cable.
Bus interface:
this interface is located on the side of the circuit board, which serves as a connection between the network card and the computer or server through a connection to its expansion slot.
LED indicators:
The indicators help users determine the operating status of the network adapter, whether the network is connected, and whether data is being transferred.
Bracket for profile:
There are two types of profile brackets on the market. One is called the 12cm long full height bracket and the other is called the 8cm long low profile bracket. This bracket can help users secure the network adapter into the expansion slot of a computer or server.
Good producers
The advantage of choosing discrete devices is that they are produced by dozens of popular manufacturers. On the store shelf there are models manufactured by companies such as:
- Intel;
- ZyXEL;
- Apple;
- DELL;
- Lenovo;
- D-Link.
It is important to understand that each manufacturer focuses on its buyer. For example, Acorp and D-Link produce devices intended for a wide audience. While Intel is more focused on creating models that are used on powerful servers. This is why the cost of the final product is different everywhere.
The advantages of budget manufacturers include:
- Low cost, so almost all users can buy their devices;
- The quality of work is much higher than that of built-in modules;
- No complex care required. It will only require occasional dusting. Otherwise, overheating will occur.
How does he work
Let me tell you with a simple example. Here you have two reception devices at home: a laptop and a personal desktop computer. The provider has installed a wire into your apartment through which the Internet flows. Usually, in order for several devices to use the Internet at once, they buy a router or router (these are the same thing).
It receives a signal from the Internet and must send it to connected devices. They are connected by addressing and a routing table. After all, the router must know where exactly to send this or that data. Therefore, each device has its own address. Currently, the most popular addressing standard is IP version 4. You have probably already seen these numbers - 192.168.1.45.
The network adapter receives the signal and sets its address. The address is most often issued by the router itself if it has a DHCP server configured. This feature allows the router to issue addresses itself. Otherwise, you need to drive them in manually.
The computer is connected to the network card. It is usually built into the motherboard. A special internet cable is used for connection. When connected, if there is a signal from another device, which may be a home router, the connector begins to blink or light up. What signals the transfer of information on the network.
If the network card burns out or does not meet certain user requirements, he can buy an additional built-in card. Now let's move on to the laptop. As you probably know, it also has a similar wire connection, with a similar connector.
But more often laptops, tablets, phones and even TVs are connected via Wi-Fi. Therefore, the laptop also has a WiFi adapter. It receives a signal from the router in the form of radio waves according to the IEEE 802.11 standard. Then he converts the signal into something understandable for a laptop.
That is, the adapter helps a computer or laptop connect to any network – both local and global. The Wi-Fi module, if you remove the cover from the laptop, looks like the picture above. But a computer can also be connected wirelessly.
Since most often the computer motherboard does not have an additional built-in Wi-Fi module, it must be purchased separately. They come in two types:
- Internal – connects to the PCI Express bus;
- External – connection goes to any free USB port.
As you may have noticed, to improve the signal, each such module has an antenna. It can be removable or built-in. Similar antennas can usually be seen on a home router. They allow improved communication between two devices.
It's too early to say goodbye
We could have ended it here. But no. After all, external network cards are so diverse that it’s worth talking about more.
There is such a type of network card as a server one. It can only be used in advanced and high-performance systems. Of course, we compare it with a regular network adapter. They still have a standard interface. This is enhanced PCI-X or regular PCI.
The picture below shows an example of a server network card.
Server network card
Server network card
It is clearly visible that there are four network adapters here. But they are all in one device. And each connector has its own twelve-digit identifier, that is, a MAC address. Although one IP address can be assigned for the entire group of adapters. And the operating system perceives this group of cards as a single whole.
What is a MAC address? This, Media Access Control, translates as media access control. An address is always unique and, of course, there cannot be two identical addresses.
Port aggregation is not easy, and it is possible thanks to Port Aggregation technology. The name stands for the association. And this means that several network segments can be combined into one. This increases productivity. Well, accordingly, when all network pots are combined into one, then we are talking about the performance of one, that is, a single port. And its power is equal to the number multiplied by the number of these ports.
There are two modes for operation of server network cards. Let's get to know them now. Each card comes with software included. With its help, each of the present ports can be made active or standby.
There is also a mode when network traffic is distributed evenly across active segments. This is a distribution mode and it allows you to reduce the overall load on the adapter. In recovery mode, when the connection suddenly disappears, it restores. That is, the mode ensures uninterrupted communication between the network and the card.
Is it convenient to use the server card on a computer?
It all depends on how complex your PC is. If there are a lot of bells and whistles, then, in order not to load the central processor, the server card can take on some of the functions, for example, counting the sums of data frames. This data is transmitted over the network. It can also generate data.
Such adapters are equipped with large integrated circuits. Short abbreviation BIS. They are the ones who perform certain functions. For example, they collect and parse data packets, detect collisions, and so on.
The processor is unloaded due to the activity of the server card. However, he already has a lot of problems.
Where is it located in the operating system?
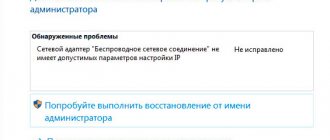
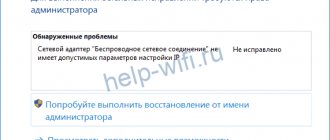
You can view the adapter and its settings in the “Network Connections” section. Just press two keys “R” and “Win” at the same time and enter the command “ncpa.cpl”.
Now you will see all your physical and even virtual adapters. But most often there are from 1 to 2 pieces. If computers have a ladder icon, this is a Wi-Fi module. And if you see a “connector” from a wire, then this is a physical network connection or the same network card for a wired connection.
Divide the number of wires in half
Everything discussed above is related to the “1 Gbit/s” (1000Base-T) standard. If you need a 100-megabit local network, you can safely crimp 4 wires instead of eight. The first and second pair are used:
Pinout of the “100 Mbit/s” connector
Both plugs should look the same when viewed from below - as in the picture. Actually, we only eliminated 4 “extra” conductors, but nothing else changes compared to the “1 Gbit/s” patch cord.
The RJ-45 connector looks like this in real life:
RJ-45 plug with contacts
If the connector is positioned with the top side facing you (and the bottom side towards the table), and then the contacts are directed upward, then the numbering of the wires will go from left to right. Summarizing all the information, we can say that the plugs of a 100 Mbit patch cord should look like this:
See how simple it is?
Now let's talk about what is best to use as a cable. We forgot to say that, in general, connectors can be shielded or without a shield, so the former must be used in conjunction with a shielded cable:
RJ-45 + screen, without screen
The classification of twisted pairs looks like this:
- UTP-2 – 4 conductors twisted into 2 pairs
- UTP-4 – 8 conductors (4 pairs)
- FTP-4 – 8 conductors (4 pairs) + common foil shield
- STP-4 – 8 conductors (4 pairs, each in a separate shield).
Everything else is not suitable for our purposes, and if you still decide to use a shielded cord, take care of purchasing suitable plugs. The “screen” usually has to be soldered, and patch cords, even with an FTP cable, are rare in practice. Here everything looks logical: if the distance does not exceed twenty meters, you don’t need any “screen” in principle.
Purpose and features of network cards
Thanks to the network adapter, a local network is created and maintained. This happens both at the physical and software levels. The network adapter is responsible for transmitting binary data in the form of electromagnetic pulses over a configured LAN channel. A network card is a type of controller, which is controlled using a driver that is installed programmatically in the operating system.
The features of network cards include a list of functions that they perform when receiving or transmitting information.
Firstly, we are talking directly about receiving and transmitting data. Information comes from the computer to the network card or vice versa. This operation occurs through a programmed I/O channel, direct access line, or shared memory.
Secondly, data generation occurs. When receiving, the procedure of connecting data blocks occurs, and when transmitting, on the contrary, the data is separated into separate blocks. This is issued in the form of a frame of the established format.
The frame contains a number of fields necessary to transmit information. One of these service fields indicates the address of the user's computer, and the other field contains the frame checksum. A checksum is a necessary indicator that indicates the correctness and authenticity of information delivered over a network channel.
Thirdly, another feature is the encryption of transmitted data. Electrical signals that will be transmitted over communication channels are usually encoded (a popular type of encoding is Manchester encoding). When data is received, it must be decoded.
Basic parameters of the network card
Different models of network adapters may differ in a number of parameters:
- Data packet transmission speed.
- Type and speed of the bus.
- Methods of access to the environment.
- Availability of compatibility options with numerous microprocessors.
- Transfer protocols.
- Connectors.
Network adapters are an integral part of the life of any modern person. As a rule, the average user does not even notice the use of network cards if they are built into the motherboard of a computer or laptop, and the drivers were installed automatically. Often, problems with network access can largely be attributed to a faulty network card or the use of drivers incompatible with the operating system.
Signal lights
There are usually information LEDs nearby. They are located near the twisted pair connector. These diodes also indicate whether there is a network and whether there is a connection to it.
In addition, these same diodes can signal the operating status of the device. That is, if the same twisted pair or network cable is connected, then the LED will blink, and it blinks rhythmically, just like information data packets arrive.
If the network adapter is not working, the indicators may show other signals. For example,
- The LED does not blink, but is constantly on,
- blinks, but the rhythm is monotonous,
- doesn't light up at all.
You need to know about this in order to observe and notice problems in time. Not only life consists of little things, but also the work of a computer.
Let's see what the built-in network card looks like when the case cover is opened. We find a familiar connector and a chip not far from it. It is soldered onto the motherboard and it performs the function of a network adapter.
It must be said that integrated network cards are not a reliable device. Very often they fail. And this happens with enviable regularity even on new computers. Therefore, all attention switches to the external network card.
Types of network cards and their characteristics
Several types of slots are used to connect external devices:
- 8P8C (which we often mistakenly call RJ-45) - eight-core twisted pair;
- BNC – thin coaxial cable;
- 15-pin AUI - thick coaxial cable;
- Optical connectors.
Of course, you can connect several cables to one network adapter at once, but only one of them will transmit data at a given time. It is worth noting that the presence of all slots is not necessary. The most popular option is 8P8C, which is found in almost every network card.
For user convenience, this slot is equipped with LEDs that light up when a LAN cable is connected.
Based on the type of connection, devices are divided into external and internal. The integrated chip is built into the motherboard (keep in mind that in modern models it is almost always present).
You should also remember that for the network card to work correctly, it requires installation of the appropriate driver, so I recommend keeping a disk with drivers for the motherboard or making a backup copy of important data.
Why, you might ask? When you reinstall Windows (and many users do this at least once a year), all drivers are removed. You can download them on the Internet, but without drivers, the network connection does not work.
If there is only one computer at home and there is no mobile phone with Internet access, you will have to use another device to download the required drivers.
Discrete cards are most often connected via a PCI slot (in the system unit) or via USB (can also be used with a laptop). They can connect to the network using a cable or have additional wireless interfaces - Wi-Fi and/or Bluetooth. Why is "Blue Tooth" in a modern computer?
For connecting wireless headphones and manipulators, this is one of the most convenient options, and the basic transmitter that comes with the kit tends to get lost.
You can also use two network interfaces in one computer - for example, built-in and external. However, as is the case with different connection ports, at a given time, only one of them will transmit data.
How much such a device costs depends on its technical characteristics, one of the key ones being speed (100 Mbit and 1000 Mbit).
The average price range is from $4 for the simplest device equipped with an 8P8C port and connected via PCI, to a high-speed card with wireless data transfer, equipped with a powerful antenna and a long USB cable, which costs $80.
You will find devices with any necessary characteristics at the best prices in this popular online store. I also recommend reading about expansion cards for computers and network cards with Wi-Fi.
Thank you for your attention and see you next time on the pages of my blog! Don't forget to subscribe to the newsletter and share this post on social networks.
Built-in card replacements
If the built-in card in a laptop suddenly fails, then there is no need to bite your elbows; in the photo below you see an excellent solution to the problem.
Or this is a solution, this device will be useful not only for a laptop, but also for a desktop PC.
These devices are called “USB network cards”. Despite the decision of the external design, their essence as a whole does not change. Other examples of devices can be seen below.
What does the price depend on?
The final cost of the equipment is influenced not only by the brand that produced it, but also by some technological solutions:
- Maximum Internet access speed;
- Ability to diagnose problems with the connection cable;
- Availability of auxiliary functions;
- SNMP v1 support;
- Turning on the computer via a local network. This option is called Wake-on-LAN;
- Declared service life.
Based on these characteristics, the price of a network card varies: from 270 to 20,000 rubles. But it is important to understand that buying cheap models will not bring any practical benefit, and may even break down after a couple of months of active use. Therefore, you should be careful here and try to take a critical approach to budget execution.
If a person plans to buy a device only for home use, it is best to focus on integrated options rather than try to buy the device separately. This solution has two undeniable advantages:
- Hardware and motherboard drivers are located on the same hard drive. Therefore, if a problem arises, he will not have to search the Internet for software separately, and this will save a lot of time.
- The second advantage is that you don’t have to spend money. On all modern computers and laptops, a network adapter is present initially and is included in the price. In addition, versions with good throughput are often sold.
How to install and configure the adapter?
Installing a USB module in a PC or laptop is extremely simple - you just need to connect it to the appropriate port. Installing the internal card is a little more complicated - to do this, you need to remove the cover from the system unit, insert the card into the appropriate slot and screw the mounting plate. All manipulations are carried out with the PC turned off. Setting up a wireless adapter usually involves entering a network access code. Sometimes you may need to install drivers. This can be done by using the software disc included with the device, or by downloading the software from the manufacturer’s official website, following the instructions that can usually be found here. Setting up a wired card involves obtaining an IP address. This can be done either manually or automatically. Manual configuration when installing a new card, as a rule, is not required; in this case, the automatic option is preferable:
- To auto-configure the network card, go to the “Control Panel” (you can do this through the “Start” menu). Find and launch Network and Sharing Center. Click on the network connection icon and in the new window click on the “Properties” button.
- In the next window, select “Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4)” and click the “Properties” button again.
- In the next window, check o and “Obtain DNS server address automatically” if they are not there by default. Click OK.
To connect to the Internet, the steps discussed are enough, and you don’t have to configure anything additional. Setting up a local network is more complicated and requires experience in network administration, but if desired, an ordinary user can handle this using instructions, for example, from our website.
Radiation harm: truth or myth
Yes, this technology uses radio frequency. But the popular belief that Wi-Fi is harmful is largely a myth. From the same mobile phone (with the Internet turned off) the radiation is much stronger. Radiation from routers is not capable of causing serious changes in the human body. Exceptions may be confined spaces where there are many simultaneously operating routers.
In this case, Wi-Fi may pose a health hazard. However, routers installed in apartments, offices and public places, firstly, are not so close to each other, and secondly, they are not so powerful as to have a significant impact on human health.
Answering the question whether radiation from a Wi-Fi router is harmful or not, we can say that it will not cause significant harm to health. In normal conditions, for example, an apartment, it is harmless.
By what parameters can network adapters be classified?
In addition to the above, the following can also be used:
- Tire type.
- Buffer size for the packet.
- Transmission speed.
- Compatible with different microprocessors.
- Bus performance.
- Based on the presence/absence of direct memory access.
- Connector design.
- Addressing output/input ports and interrupt requests.
Types of Ethernet devices by connection method
All modern network adapters can be divided into three types according to the connection method: integrated, internal and external. Let's look at each category separately.
Integrated Modules
Today, it is probably impossible to find a motherboard for a personal computer device without an integrated network controller. Depending on the device, the integrated module may have an Ethernet port (connector type - RJ-45) for cable connection or contain a Wi-Fi module for wireless communication. An undoubted advantage of the built-in card is its good compatibility with other hardware, in particular with motherboard components. Other positive aspects of the integrated network controller include the absence of driver problems, and the fact that it does not occupy expansion slots on the motherboard and USB ports. A significant disadvantage of the built-in adapter is its virtual non-repairability in the event of a breakdown. Even if the service department undertakes to replace the controller, the repair can cost a hefty sum. The way out of the situation is to use built-in internal and external modules.
Embedded boards
Just like integrated modules, embedded network cards can be designed for both wired and wireless connections. In the first case, the adapter usually contains one RJ-45 connector; in the second, it is distinguished by the presence of an antenna. There are network cards with outdated PCI and more modern PCI-E interfaces. Both options are designed for installation in the corresponding slots of the computer motherboard. It should be kept in mind that these two standards are not compatible with each other, that is, a card with a PCI connector will not fit a PC with a PCI-E slot, and vice versa.
As for laptops, even in relatively new models there is no provision for replacing the network card; the chip is soldered into the motherboard. If the latter breaks down, the only alternative is an external USB adapter.
Among the advantages of built-in internal modules are the presence of an option for automatic detection and activation of Plug and Play, a large database of drivers, a wide selection of devices on the market and their low cost. Among the disadvantages is that some knowledge is required for installation and configuration; in addition, the drivers for many embedded cards are written by programmers exclusively for Windows.
External Ethernet adapter
An external network adapter is a separate device in a case that connects to the USB ports of a PC or laptop. Such modules come with a standard Ethernet port for a wired connection and a Wi-Fi unit for a wireless connection. USB network cards with Wi-Fi have become very popular among users in recent years due to their portability, versatility and ease of use.
Apple computer users are less fortunate. Their devices use a proprietary standard of Ethernet adapters with a Thunderbolt interface for external connection, which is incompatible with other devices.
In modern operating systems, setting up an external adapter for a wired connection occurs automatically, which is a definite advantage of such cards. The situation with Wi-Fi adapters is less rosy, especially in the Linux environment. Users are often required to take additional steps to configure them. However, external network cards are an indispensable solution in many cases. For example, when the module integrated into the device has burned out, and all the slots in the system unit are already occupied, or an over-the-air connection is simply necessary.
Classification by access methods to protocols and environment
There are three main types of adapter used in network technology:
- Ethernet.
- FDDI.
- Token Ring.
Typically, a certain model only works on its own network technology. But at the same time they can usually support several different data transmission media.
For example, Ethernet works with:
- Fiber optic cable.
- Unshielded twisted pair cable.
- Coaxial cable.
When a device must work with an environment for which it was not originally intended, converters and transceivers are used. Network adapters are also distinguished by their internal data bus:
- PCI.
- EISA.
- ISA.
- MCA.
Classification based on network connections
Depending on how the network adapter accesses the network, there are wired network adapters and wireless network adapters. As the name suggests, a wired network adapter typically must connect the host to the network using a cable, such as an Ethernet cable and a fiber optic cable. A wireless network adapter often comes with a small antenna that uses radio waves to communicate with an access point to connect to a wireless network.
Bus classification based on interfaces
ISA (Industry Standard Architecture) network adapter:
The ISA bus was developed in 1981 and was a standard bus architecture for IBM-compatible devices. Due to the low transfer speed of the cards (9 Mbit/s), the ISA bus interface is no longer a generally accepted type and is difficult to find in modern stores.
PCI (Peripheral Component Interconnect) network adapter:
The PCI bus was developed in 1990 to replace the previous ISA standard. It has a fixed width of 32 bits (133 MB/s data transfer) and 64 bits (266 MB/s data transfer). This type of network adapter was first used on servers and then gradually applied to PCs. Today, most PCs do not have expansion cards, but rather devices integrated into the motherboard. As a result, the PCI network adapter has been replaced by other bus interfaces such as the PCI-X or USB interface.
PCI-X (Peripheral Component Interconnect eXtended) network adapter:
PCI-X is an advanced technology of the PCI bus. It runs at 64-bit speed and is capable of speeds up to 1064 MB/s. In many cases, PCI-X is backward compatible with PCI NIC cards.
PCIe (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express) network adapter:
is the latest standard and is now popular on computer and server motherboards.
The PCIe NIC adapter is available in five versions, and each version supports five types of lanes at different speeds. To learn more about PCIe network adapter, read the text :
PCIe Tutorial: Everything you need to know about the PCI Express card.
USB (Universal Serial Bus) Network Adapter:
The USB bus is an external bus standard. It has three versions with different data rates and can work together with different devices. Additionally, a wireless network adapter is also a type of NIC network adapter that is designed for Wi-Fi connectivity.
Port classification based on type
According to the different connected cables, there are four types of NIC ports that can be found in the market. The RJ-45 port is used for connections using twisted pair cable (such as Cat5 and Cat6), the AUI port is used for thick coaxial cable (such as AUI cable for modules), the BNC port is for thin coaxial cable (such as BNC cable), and optical port for the module (for example, 10G/25G module).
Classification based on transmission speed
Based on the different speeds, there are 10 Mbps, 100 Mbps, 10/100 Mbps, 1000 Mbps, 10 Gbps, 25 Gbps or even higher speed adaptive cards on the market. 10 Mbps, 100 Mbps and 10/100 Mbps Adaptive NICs are suitable for small LANs, home use or everyday offices. The 1000 Mbps network adapter provides higher throughput on a Gigabit network. As for 10 Gbps and 25 Gbps NICs or even higher speed ones, they are welcomed by large enterprises or data centers.
Classifications by application
Computer NIC: Most new computers these days have a built-in network card, so a separate network adapter is not required. It typically comes in 10/100 Mbps and 1 Gbps speeds and allows one computer to communicate with other computers or networks.
Server Network Adapter: The main function of a server network adapter is to manage and process network traffic. Compared to a regular computer network adapter, server adapters usually require higher data transfer speeds, such as 10G, 25G, 40G, and even 100G. Additionally, server adapters have low CPU usage because they have a dedicated network controller that can perform many tasks from the CPU. To meet different user speed requirements for server adapters, FS has released 10G PCIe adapters and 25G/40G NIC cards. Based on the Intel controller, these PCIe adapters support multi-core processors and optimize server and network virtualization.
Reliable models with 4 RJ-45 connectors
HP 366T (811546-B21)
A high-quality model that has 4 ports and is suitable for use in servers or large companies. Only high-quality components were used in production. In addition, the chip has a heatsink that prevents overheating. The product has good throughput and will last a long time.
The average cost is 25,000 rubles.
HP 366T (811546-B21)
Advantages:
- High quality manufacturing;
- Easy installation;
- 4 ports;
- Cooling radiator.
Flaws:
- Not found.
Intel E1G44HT
One of the best options that attracts most buyers with its affordable price and good throughput. The model is made with high quality and has good protection against overheating. The maximum speed is 1000 Mbit per second, which is a good indicator for such a product.
The average price is 14,000 rubles.
Intel E1G44HT
Advantages:
- Value for money;
- Doesn't take up space;
- Good chip;
- Overheat protection;
- Convenient connection.
Flaws:
- Not found.
Silicom PE310G4I40-T
A high-quality device that is made on a reliable chip and has 4 convenient Ethernet ports. Therefore, the product can be used on servers. There is support for all modern functions. The maximum data transfer speed is 10,000 Mbit per second.
Sold at a price: from 40,000 rubles.
Silicom PE310G4I40-T
Advantages:
- High-quality execution;
- Efficiency;
- Long service life;
- Information transfer speed.
Flaws:
- Price.
Top 10 popular adapters
An article about network cards would be incomplete without considering the best representatives of this category of devices. The information below will allow you to navigate the popular models, their characteristics and approximate cost.
Table: popular Ethernet card models
| Model | Device characteristics | Price |
| Intel EXPI9301CT | Low-profile network card with PCI-E interface, speed 10/100/1000 Mbps, Intel 82574L chip and 1 RJ-45 connector. Suitable for most PCs with the appropriate interface. | 2000 rub. |
| TP-Link TG-3468 | Low-profile network card with PCI-E interface, speed 10/100/1000 Mbps, Intel 82574L chip and 1 RJ-45 connector. For computers with PCI-E slots. | 600 rub. |
| D-Link DUB-E100 | External Ethernet adapter with USB 2.0 interface, speed 10/100 Mbit/s and 1 RJ-45 connector. For PCs, laptops and other devices with USB 2.0 ports. | 900 rub. |
| 3COM 3C905C-TX-M | Network card with PCI 2.2 interface, speed 10/100 Mbit/s and 1 RJ-45 connector. Suitable for most computer models with PCI 2.2 slots. | 700 rub. |
| ASUS NX1101 | Network card with PCI 2.2 interface, speed 10/100/1000 Mbit/s, 32 KB buffer, 1 RJ-45 connector and automatic MDI/MDIX detection. For PCs with PCI 2.2 slots. | 650 rub. |
| Apple MD463ZM/A | Ethernet adapter with Thunderbolt interface, speed 10/100/1000 Mbit/s and 1 RJ-45 connector. For external connection to Apple devices. | 2500 rub. |
| Acorp L-1000S | Low-profile network card with PCI 2.3 interface, speed 10/100/1000 Mbps, Realtek RTL8169SC chip, 8 KB buffer, 1 RJ-45 connector and automatic MDI/MDIX detection. For computers. | 850 rub. |
| ST Lab U-790 | External Ethernet adapter with USB 3.0 interface, speed 10/100/1000 Mbit/s and 1 RJ-45 connector. For PCs, laptops and other devices with the appropriate interface. | 1700 rub. |
| Zyxel GN680-T | Network card with PCI 2.2 interface, speed 10/100/1000 Mbit/s, 32 KB buffer, 1 RJ-45 connector and automatic MDI/MDIX detection. Suitable for computers. | 1300 rub. |
| 5Bites UA2-45-02 | External Ethernet adapter with USB 2.0 interface, speed 10/100 Mbit/s and 1 RJ-45 connector. Suitable for computers, laptops and other devices with the appropriate interface. | 500 rub. |
In the age of the Internet, it is difficult to imagine a computer or laptop without such a node as a network card. Among the most important characteristics of the module that you should pay attention to when choosing are the speed of data reception/transmission, the connection interface, as well as the possibility of wireless connection if mobility is a priority.
Mini-test: “Local network”
Time limit: 0
Navigation (job numbers only)
0 out of 5 tasks completed
Questions:
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
Information
Online test to test your knowledge of the basics of computer networks.
You have already taken the test before. You can't start it again.
The test is loading...
You must log in or register in order to begin the test.
You must complete the following tests to start this one:
results
Correct answers: 0 out of 5
Your time:
Time is over
You scored 0 out of 0 points (0)
| Average result |
| Your result |
Instead of a total
As you can see, there is nothing particularly complicated in setting up the program and additional network adapter parameters here. All this will take a maximum of a couple of minutes after the first start of the application. Of course, problems with the created connection may also arise, but this issue can be resolved quite easily.
But here’s the main thing: the user of the same laptop with a built-in Wi-Fi adapter or the owner of a computer with a wired connection or an external USB controller does not need to buy additional equipment, which can sometimes be quite expensive. The program will turn the desired terminal into a virtual router without any problems.