Today we will talk about a fairly well-known error that users of smartphones based on the Android operating system may encounter. When sending USSD requests, the message “Connection problems or incorrect MMI code” may appear on the smartphone screen. The message may also look like “Connection problem or invalid MMI code” or even in English - Connection problem or invalid MMI code.
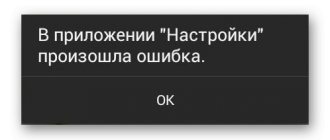
This is what the error looks like on the device screen:
In English:
The question arises - what is MMI? MMI or Man-Machine Interface is a special code used to generate USSD requests, which ensures interaction between the subscriber and the operator’s service applications. Sometimes there is a crash that results in the above error. What to do? There are several possible solutions, we will tell you about them in more detail.
Turn airplane mode on and off
Airplane mode, as you probably know, allows you to turn off all communications of the device. Turn on airplane mode for literally 5-10 seconds, then turn it off again so that your smartphone finds the network.
Then send a USSD request. Most likely everything will work.
If all else fails
If the described methods turned out to be useless, do not despair. Below are methods that are found in discussions of the invalid MMI code error.
Vyacheslav
For several years he worked in mobile phone stores of two large operators. I understand tariffs well and see all the pitfalls. I love gadgets, especially Android ones.
Ask a Question
Problems and solutions
Change basic settings.
It is believed that disabling the default country code setting will resolve the issue.
Android Memory Cleaner
Experts attribute the failure when sending a USSD request to the incorrect installation of some applications or the unreliability of the sources from which they were downloaded. It is enough to remove the suspicious ones for the system to work again “like clockwork”.
Contact your mobile service provider.
By contacting by phone, you can clarify whether any work is being carried out on the server or not.
4.7/5 — (33 votes)
Reboot your smartphone
In general, turning on and off airplane mode should be enough to solve communication problems. However, perhaps the problem is in the smartphone software - say, there was some kind of glitch. In order to return the device to its previous form, simply reboot it. Or turn it off and on again - whichever is more convenient for you.
After turning on, check the device for errors.
JRD MMI TEST - what is this error?
I would like to additionally tell you about a way to eliminate an unpleasant defect associated with the periodic appearance of a notification from an application on the display:
The program on some gadgets is built-in and cannot be completely removed. But it is possible to stop or “freeze” it if you have Root access and special software (Root-Uninstaller, for example).
But the utility itself often does not bother users until the Mobogenie gaming software is installed, which provokes inappropriate behavior and constant display of messages on the screen.
Try removing “Mobogenia” (Mobogina), rebooting the smart phone, and clearing its cache. The problem should be fixed.
So we figured out “connection problem or incorrect MMI code” - what it means and how to fix it. I hope the instructions helped you.
Change network type
Try changing the network type. Let's say you use networks in Auto mode. You need to try changing the network type to 3G or even 2G - for a while, then you can return everything to its original state.
Go to settings.
Find the “Wireless Networks” section (in the example, a Huawei smartphone is used; on devices from other companies, the interface may change slightly).
Tap on the line “Mobile network”.
Click Preferred Network Type.
Change the network type. Ideally, you should use a mixed network type (“Auto”), most likely this is what you have installed. Select a different network type, wait a minute and return to Auto mode.
After that, send a USSD request. If it doesn’t help, select a different network type and try sending a USSD request with it.
If you are using “4G Only”, in which case you will not be able to send USSD requests in any case, switch to the mixed type of network mode (“Auto”).
SIM card wear
Unfortunately, there are situations when, due to mechanical deformation or prolonged use, the SIM card is no longer able to perform its direct function - to maintain communication. In this case, you will have to contact the service center for a new card. In this case, contacts that were recorded only on the card memory will disappear.
If the error appears after the next SIM card change, don’t be upset, you probably just didn’t insert the card all the way. Try removing it and installing it again. Sometimes the contacts become somewhat deformed, so that a gap is created, generating an obstacle to communication. This may also cause the card or battery latches to break. You can check the functionality of the SIM card on another phone.
Replacing the card if you apply with identification documents is a quick procedure, and you will be able to keep your number.
Make sure the operator network is selected
This may be caused by some kind of glitch. You need to select your carrier's coverage. To do this, go to the same “Mobile networks” section and select “Operator”.
Wait for it to download and select your operator's network. Although it is better to use automatic network selection (switch at the top of the screen).
The procedure may help, especially if you are roaming.
general information
To understand the problem, you need to understand what the abbreviation MMI means. It is derived from the phrase man-machine interface, which translated from English means “human-machine interface”. The codes of this interface are responsible for correctly recognizing USSD service requests.
In turn, USSD is unstructured additional service data that provides the interactive part of the interaction between a person and a device. This is an algorithm similar to SMS with one significant difference: while the first is used for communication between the subscriber and the operator or the phone itself, the second ensures the exchange of text messages between cellular users. Due to the fact that modern GSM networks are not designed for letter commands, asterisks and hash marks are still used to enter them.
MMI codes are sometimes called service codes and are used to perform the following operations:
- Checking the current account balance. All modern cellular operators, such as Tele2 or MTS, use exactly this mechanism.
- Top up your balance using scratch card serial numbers.
- Management of additional tariff services.
- Transition to a new tariff and much more.
How to cancel a subscription on Android
It is best to uninstall the application. This is the most effective way to protect yourself from its activity. However, it is possible that it could sign you up for paid subscriptions, so first check your card for unknown charges, and then look at the list of current subscriptions on Google Play:
If you subscribed through Google Play, there is no cost to cancel it.
In principle, if the subscription was purchased through Google Play and payment has already been made, you can demand a refund from Google. We described how this is done in a separate article. But since the developers of such applications usually carefully think through ways to steal money, as a rule, they do not use the payment tool built into Google Play so that they cannot be withdrawn if something happens.
Source
How to find a virus on Android
But, you say, software is installed on smartphones with custom names. Yes it is. Therefore, you will need a small utility that will allow you to effectively identify all the slag software that you have installed for yourself by determining the name of their packages.
The red square shows an example package name
Package Name Viewer is convenient because it allows you not only to find the application you need by the name of its package, but also, if necessary, to go to the settings to remove it. To do this, simply click on the application icon, and you will be taken to the corresponding section of the system, where you can stop, disable, delete accumulated data, revoke privileges, or simply erase the unwanted program.
Be careful!
In almost every publication we warn our readers about various types of virus threats. But also don’t forget about system utilities with names unknown to you. They can perform an extremely important role; stopping them will lead to irreversible consequences. Therefore, before carrying out radical manipulations, it is better to ask Google/Yandex, in the comments on the IT Technician website.
Now let's get closer to the point. MBN test what is this program for Android?
Let us immediately note that not every smartphone owner will find it on their mobile device. This functionality is only available on models that support fourth generation cellular communications (4G LTE). That is, gadgets released more than 5 years ago are unlikely to contain this element in the list of installed system software.
In addition, in the latest versions of Android, developers have completely hidden this item so that users do not try to make their own adjustments and harm the operation of the device.
This is what the MBN test application looks like in the general list:
If you go to the detailed information page, you won’t see anything dangerous or specific. In the internal memory, the object occupies tens of kilobytes, periodically accesses the cellular network (when a data connection is connected), and does not require special permissions or access from the user.
The most interesting thing is that on the Internet (even on foreign resources) a meager description of the program is provided. But from everything we reviewed, we can draw an accurate conclusion: the built-in MBN application is responsible for periodically testing the performance of the 4G communication module. The software exchanges signals with base stations. By the way, the abbreviation itself stands for multi-bearer network .
The author recommends:
[Tips] [Report] [10.1.2.0] Usage report...
Actually, a small report on setting up and using 10.1.2.0 in everyday work life...
In general, the change of Android version went unnoticed for me - there really was an unstressed transition from seven to eight. In the “For Developers” settings, options have been added regarding audio transmission via bluetooth, something else has been added, but otherwise the MIUI interface remains the same. Everything you need works and is in its place. The phone rings, performs all the functionality I need, nothing works, not even adaptive screen brightness. In general, I’m happy with the firmware, and after the “file” it’s absolutely beautiful.
I flashed it via fastboot, after another flashing (I chose full cleaning automatically in TWRP) I used XiaomiADBFastBootTools to remove Google, I didn’t install OpenGApps pico this time...
Then it was time to try and turn off what was unnecessary for me personally. And not only disabling, but also deleting. It's simple: I need maximum autonomy, but with maintaining the functionality of all bands (EDGE/3G/LTE), so that WhatsApp with Viber, SMS, mail, telephone, bluetooth work. And CardDAV synchronization is on par with MiCloud.
Finding the optimal configuration for me took about 10 days. Because before going to bed, you delete the package, clear the battery statistics and caches, and in the evening you look in “Settings → battery and performance” to see who ate the most... And again.
A small but practical tip: in principle, after unlinking from any Google services (play, etc.) and deleting them, autonomy makes an extremely sharp jump. Everything else is “catching fleas” and Just for fun, combined with technological paranoia and the desire to understand what this or that package is and generally what it is for.
The list with 4PDA (also for MIUI10) helped me a lot; if the moderator allows it, I’ll post a direct link here. There is also package parsing.
Malicious Android apps
Found a virus? Remove it
These are mainly applications that are potentially highly in demand by users. Among them are keyboard skins, photo editors, applications for creating ringtones, etc.:
These are the names of application packages, that is, something like their identifiers. Since these are all malicious applications, their creators know that they will be found and dealt with. Therefore, they may well be ready to change the user names of the applications that you and I see. But we can't track it. Therefore, from this point of view, it is much more reliable to track the identifiers and remove malicious software based on them.