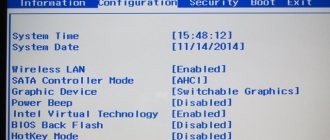
The Boot section is required to specify boot devices and their corresponding boot priorities
TOOLS - used to update the BIOS.
EXIT - exit the BIOS. Has 4 modes:
- Exit & Save Changes (F10) - exit with saving data set directly by the user.
Exit & Discard Changes - exit without saving data (factory setting).
In the Exit menu you can save the changed settings, as well as reset the BIOS to default settings
Almost every user knows how to correctly configure bios in default images. But if you are a novice user, go online. There are many resources on the Internet that have pages “setting up the bios system in pictures.”
Thank me by sharing the link with your friends on social networks:
How to close the BIOS on a laptop?
If your BIOS has an interface with a menu bar at the top, then to exit this program you need to go to the Exit item in the main menu. And at this point, use the commands “Exit Without Sawing” and “Save & Exit Setup”.
Interesting materials:
How to disable automatic computer shutdown? How to turn off the computer without the Start button? How to turn off the computer without a button? How to turn off a computer without a monitor? How to turn off a computer without starting? How to turn off the computer after an hour? How to turn off a computer after a while? How to turn off a friend's computer? How to turn off the computer if the screen does not work? How to turn off a computer if it won't turn off?
What is BIOS.
If we recall history, starting with 286 processors, computers had a built-in BIOS Setup system setup program. BIOS - Basic Input/Output System or Basic input/output system, here are the system settings on which the speed and reliability of the computer depends.
This system stores information about installed hard drives and drives and sets their boot order, which can be useful when installing an operating system from a CD or flash drive and when installing a second hard drive. Information about time and date is also stored here, which can also be changed in the BIOS. The BIOS also stores a very large number of different settings, which there is no point in changing for an ordinary user, but some of them still, albeit rarely, have to be changed.
Such settings are located on a ROM chip - CMOS, which allows it to store its settings regardless of whether the computer is turned on or not. Some motherboards have two BIOS chips installed, one of which is the main one, the other is a backup one, so that if the main one fails, it can be restored from a backup copy.
For different motherboard manufacturers, the BIOS menu may differ in appearance, there may be different names of menu items and their location on the screen. Also, some settings may be hidden and only available when you press a certain key, but the main points are available in all system setup programs. Many novice computer users are simply afraid to go into the system settings and this, to some extent, is correct, because changing them can disrupt the normal operation of the computer. And you need to remember one rule that you must always adhere to when working with the BIOS:
You always need to know exactly what you want to change in the BIOS and what the result should be in the end. Never change anything unless you know why it is needed and what it can lead to.
Why does a computer user need to change BIOS settings?
Here are a few reasons why a user may need to change BIOS settings:
- To change the boot order of hard drives and CD-ROM drives;
- Reset system settings to default settings;
- To change the speed of RAM or processor;
- To enable/disable USB devices;
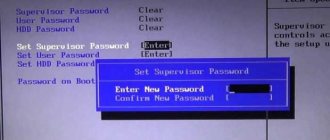
- To set or remove a BIOS password or system password;
So, as you can see, even a simple computer user may need to go into the BIOS and change its settings. There are several points that you need to know in order to enter the BIOS, make the necessary changes in it and exit it correctly. For the most part, these are general rules that apply equally to both desktop computers and laptops, with only a small difference between them.
How to enter BIOS on Windows 7
Among personal computer users, the question of how to enter Bios on Windows 7 is becoming more and more pressing. This is due to the fact that the scheme of this operation has changed. If in early versions of this operating system, in order to enter Bios, you just needed to start the computer and press one button, and it did not matter what OS was installed on the computer, then in new versions it is not so simple.
Let's talk in more detail about how this procedure is performed on Windows 7.
PC won't exit bios
Users have encountered boot problems since the very first version of Windows.
There are various things that can prevent your system from booting normally. For example, system failure, hardware damage, update installation failure, etc.
However, there are some loading issues that are more severe than others. One of these problems is definitely the BIOS problem that prevents users from starting their computer.
If you can't exit the BIOS, your computer is basically useless because you can't start it.
Question details
In fact, the BIOS always boots first, as it recognizes and starts the hardware.
And after that it launches the Windows bootloader, as a result of which a loading bar appears, after which the Windows icon, the “welcome” screen and the desktop window appear.
In this BIOS, you need to set the boot priority from the hard drive so that after loading the BIOS, the Windows bootloader, or the additional system selection window, if you have several of them installed on one computer, automatically starts.
Enter the BIOS in the Boot menu, select Boot Device Pr yiorit y , select the required item (Hard Disk.) and press Enter to select the device.
If you want to save the configuration settings, then you must save the changes when exiting the BIOS, when asked in the dialog box:
"Save. exit setup? - click - “OK”.
Additional menu items
Almost all modern ASUS motherboards contain a Tools
, which grouped options for working with BIOS Setup settings profiles and for calling the built-in BIOS code update utility. Settings for additional features of the motherboard may also be located here.
Mid-level products often have an Ai Tweaker
, which contains most of the options required for overclocking.
On high-end motherboards, another name for this section is used - Extreme Tweaker
- with a corresponding increase in the number of available settings.
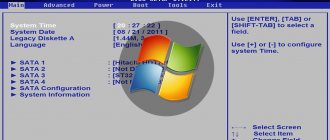
The following conventions are adopted in BIOS Setup on ASUS motherboards. Selecting one or another main menu item is carried out using the cursor keys and . In this case, options specific to this section will be highlighted. Select a specific option: arrow keys and . If an option contains several values at once (say, date or time), you can move between individual fields using the key.
To change the option value, use the and keys on the extended keyboard. If you want to see all the values available for a given option, press: a small menu will open in which you can select the appropriate option using the and keys.
If there is a triangle symbol to the left of an option name, selecting it and pressing a key will take you to a submenu (for example, Figure 6 shows the Primary IDE Master
item
Main
). Exit to the upper level - key.
If there are too many options in a given section or menu and they do not fit on the screen, a vertical scroll bar appears to the right of them, signaling this fact.
The key allows you to save the changes made at any time and exit BIOS Setup; if you are in the top-level menu, you can discard the changes made and exit BIOS Setup. In nested menus, as already mentioned, you can return to the top level.
(the above picture does not exactly match my BIOS, but it is similar enough, that’s why I copied it from the BIOS site).
This is how I make my settings.
If you have a different configuration of this BIOS, then I apologize for the discrepancy with yours.
American Megatrends has a strict OEM business model for AMIBIOS. The company sells the source code to motherboard manufacturers or customizes AMIBIOS for each OEM individually, whatever business model they require. AMI does not sell chips containing BIOS to end users. As a result, AMI does not produce end-user documentation for BIOS firmware, or provide direct technical support, leaving that to patent holders. However, the company has published two books on its BIOS, written by its engineers.
What to do if a password is required to enter the BIOS
A password is usually not set when entering the BIOS, but some manufacturers or repair companies protect the entrance in this way. The easiest way is to enter the required combination, but often it is lost or completely unknown. In such cases, you have to turn off the computer, remove the system unit cover and remove the battery that powers the CMOS memory. It contains the password. After removing the battery, you need to close the contacts of its socket for 15 seconds. This will clear the CMOS and reset the password. After this, the battery is installed in place, the computer is assembled, turned on and logged in without a password.
It must be remembered that all changes made to the BIOS can damage the computer. Without an idea of what will happen when you change a particular parameter, you should not do anything. Attempts to act on the principle of “what will happen if...” in this case are completely unacceptable. If you are not sure that everything is being done correctly, it is better to turn to specialists. This will help solve the problem while maintaining the functionality of the computer, in particular its hardware.
What is BIOS and what is it for?
BIOS (BIOS, English BasicInput/Output System) is an information input/output system that communicates between the hardware and the computer’s operating system. It contains information about the composition, configuration and current state of all elements of the computer, determines the boot order of the operating system, and performs dispatch functions for monitoring systems and security. The BIOS code is located on a special chip with corresponding markings located on the motherboard. It can be updated, i.e. re-record, but this undertaking is complex and risky.
To change the system boot order (used when reinstalling the OS installed on your PC), go to the Boot tab
The most common way a user accesses the BIOS is to change the system boot order. When installing an OS from a flash drive, you must set USB boot as the first number, otherwise after the first reboot the computer will install the old system and the process will go in an endless circle. In addition, other actions can be performed:
- Change or return to factory (optimal) settings.
- Changing the processor operating mode.
- Obtaining information about the processor temperature.
- Fan operation mode control.
- Enable/disable some ports or functions, etc.
After the changes have been made, the program will offer the choice of saving them or leaving the setting unchanged. To do this, you will need to press the appropriate keys.
Attention! Making changes to the BIOS settings can radically change the operating mode of the motherboard and processor. For an unprepared user, such a step is fraught with undesirable consequences, including the complete failure of the components. Without precise knowledge and understanding of the essence of your actions, nothing should be changed.