No matter how trivial it may sound, a Wi-Fi router in the modern world is one of the most important household devices, especially if we are not talking about connecting one workstation, but about organizing Internet access for a series of devices. In addition, an increasing number of users prefer wireless connections due to its simplicity and convenience. And if everything is simple with mobile devices or Smart TV - the corresponding module is built in by default, then to connect a PC you will need a separate Wi-Fi adapter.
What is a Wi-Fi USB adapter and what is it for?
A WiFi USB adapter is a device that connects via USB to our computer be it a desktop or a laptop, and it comes in the form of a Pendrive and allows us to connect to WiFi networks . Typically we have to install the drivers that come with the USB WiFi card itself, although if you are using Windows 10 it is highly likely that it will automatically recognize the WiFi adapter and then install the drivers without user intervention. In just a minute we will have this device in action.
Wireless WiFi adapters will give us the ability to connect via WiFi to our router or WiFi hotspot if our computer did not previously have a WiFi card. In the case of laptops, they all have a Wi-Fi card inside, but mid-range computers usually have very weak Wi-Fi cards and give us poor wireless performance, both in terms of coverage and speed.
How it works and why you need a Wi-Fi adapter
Internal modules - connect to a PC via a PCI slot.
People planning to use this device should learn a lot about the Wi-Fi adapter: how such a device works and why it is used. As you know, it is bought to connect a laptop or personal computer to a wireless network.
The operating principle is quite simple. The adapter is capable of receiving and sending data packets using radio communications. To quickly transmit them, the device converts the signal into a radio wave. While receiving information, it is converted back into a digital signal.
USB Interface Types
There are currently two different types of USB WiFi adapters that support USB 2.0 - the lowest level and the cheapest adapters of this type will not give us too much real-world speed, although we will have better coverage (if they have external antennas). Those that support USB 3.0 will always be the fastest ones, those that will provide us with the best real speed and will not be limited by the maximum speed of the USB 2.0 interface itself. It is logical that adapters using the USB 3.0 interface are the most expensive and expensive.
Nowadays, the most common thing is to find adapters with USB 3.0 interface, but if you buy a low-end device, the most common thing is USB 2.0 to save costs and hence you get lower wireless performance. in terms of speed.
Dual band selectable 2.4 GHz or 5 GHz
With the release of Wi-Fi 4, also known as 802.11n, USB WiFi routers, access points and adapters began to widely use the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands, selecting them simultaneously using built-in software. Today, there are USB Wi-Fi cards that only support 2.4 GHz and other Wi-Fi cards that support 2.4 and 5 GHz.
It is extremely important that when purchasing a USB WiFi adapter, it has support for both frequency bands , 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz. Just because they are dual band doesn't mean you can connect to both bands at the same time in fact, although routers and access points are both dual band (broadcast on both bands at the same time), WiFi adapters are selectable dual band (can connect two bands but one band or the other, but not both at the same time) due to hardware limitations, since they do not have two chipsets inside, but only one is compatible with both bands.
Internal or external antennas
The fundamental aspect of a Wi-Fi adapter is its antennas. The more antennas a WiFi adapter has, the greater the actual speed we will achieve with MIMO technology, so it is recommended that at least one adapter include two antennas.
As for whether they should be internal or external, if we are going to connect in places close to the access point or router, they can be internal without problems and we will get very good wireless performance, usually adapters with internal antennas are very small physically , ideal for connecting them to laptops.
If we are going to connect in places far from the access point or router, it is highly recommended that the antennas be external, otherwise we might have low coverage and therefore real wireless speed. Typically, these types of adapters with external antennas are physically larger than adapters with internal antennas, and in addition, they usually have a USB base for connecting the device to a desk rather than to a rear USB port where it provides less Wi-Fi. Speed Fi. real.
If you don't care about adapter size, you'll always get better performance with WiFi adapters with external antennas, but if you're going to be using it on a laptop all the time, size is likely an issue. However, there are Wi-Fi cards with two antennas, one internal and one external, for cases where we will be connecting very far away, this "hybrid" combination is ideal for not having so many external antennas.
We connect the WiFi adapter to your computer
Now we will show you ways to connect different Wi-Fi adapters to your computer.
Connecting an external module
There should be no difficulties when connecting the external module. The procedure is so simple that any student can quickly cope with it.
- We insert the purchased module into a free USB port on the computer.
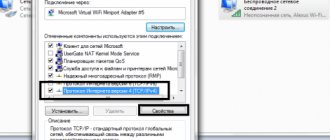
- We take the disk that should be included with the adapter and install the driver from it. If there is no such disk, then download the driver from the Internet.
- After installing the driver, a wireless connection icon should appear in the corner near the clock. Click on it and connect to your network. If you don’t know how to do this, then see our article: how to connect to a Wi-Fi network for the first time.
Indoor module connections
Here the connection process is a little more complicated than with an external module. But it’s still worth trying to insert the Wi-Fi adapter yourself.
- Open the side cover of the system unit.
- Find a free slot and firmly insert the purchased WiFi adapter into the PC.
- Close the side cover and screw in the existing antennas.
- Install drivers either from disk or download from the Internet.
- Restart your PC. Try connecting to your network.
Wi-Fi card connections (PCMCIA)
Everything is simple and easy here. Insert the card into the PC Card slot and install the driver if necessary. Some models will work without installing a driver.
If you are not satisfied with the speed or quality of the wireless Internet, keep in mind that you can always connect with a cable. How to do this correctly, see our previous article: connecting a laptop to the Internet via a cable.
Wi-Fi Versions You Should Use
When we are going to buy a Wi-Fi adapter, the most important thing is to always look at the compatible Wi-Fi version as well as the Wi-Fi class, these two parameters will tell us the maximum performance that we can achieve, that is, the maximum speed that we will achieve .
Today we must buy Wi-Fi USB adapters, at least Wi-Fi 5, this means that it is compatible with the 802.11ac standard and therefore we will have excellent wireless performance. Very soon we will see the first WiFi adapters with Wi-Fi 6, which will allow us to get high wireless transmission speeds, if you have a Wi-Fi router or access point with this standard, some of the improvements we will get with Wi-Fi 6 cards This:
- MU-MIMO support, allowing the router to send information to us along with other devices and optimize the overall performance of the wireless network.
- OFDMA
- Energy saving thanks to TWT (Target Wake Time), ideal for laptops.
- BSS color to reduce interference with other Wi-Fi networks.
Not only the version of Wi-Fi that will be used is very important, but we also have to check whether it supports 802.11b/g/n standards, that is, whether it supports the 2.4 GHz band for connection. There are some Wi-Fi adapter models that do not support this band, but only support the 5 GHz band.
How to choose
An adapter is an electronic device that is selected taking into account technical parameters. Due to inexperience, some users believe that it is the same for a computer and TV. On the one hand, they work using the same protocols, but the operating systems of the computer and the TV are different, which means the software is different.
TV model compatibility
A branded adapter will be more expensive.
As a rule, the manufacturer already indicates on the adapter body which TVs it is compatible with. It is best to take a device from the same company as the equipment at home.
A branded adapter will be more expensive, but it will be a guarantee against possible problems during connection and performance.
There are also Wi-Fi modules positioned as universal. They are easy to connect and, as a rule, function properly.
However, complaints have become more frequent that after reflashing the TV, the device is no longer recognized and then no longer works. And there is no way to restore it.
Transmitter power
The parameter is ambiguous, more relevant for a router than for a TV. Still, there is a recommended value: no less than 17 dBm. If it is lower, the connection will be unstable. The characteristics are indicated on the device packaging.
Operating frequency
For different devices, this parameter varies from 2.5 to 5 GHz. The router and adapter must operate at the same frequency, otherwise they will not be able to connect to each other.
Signal standard
If the router has one standard and the adapter has another, data will be transferred, but at a reduced speed.
This characteristic affects the speed of data transfer between devices. It should be similar to the router. Routers work with different signal standards. The optimal one is IEEE 802.11 n (300 Mbit/s), although there is also “ac”, which provides a maximum speed of 600 Mbit/s, but it is designed for a frequency of 5 GHz.
If, for example, there is one standard on the router and another on the adapter, the data will be transferred, but at a reduced speed.
Also, do not forget about various obstacles that interfere with the passage of the Wi-Fi signal: radiation from microwaves, refrigerators, metal objects in the form of pipes, batteries, and so on. All this prevents the adapter from working at full power.
Radius of action
This is the distance between the receiver and the transmitter - the TV and the router. An important parameter that is worth considering if you want a stable connection. Conventionally, modules are divided into:
- closed;
- open spaces.
The characteristic is indicated on the packaging of the device and is expressed in meters. The greater the range, the farther the TV can be from the router. When choosing an adapter based on this parameter, you should take into account all possible obstacles in the signal path: walls, partitions, furniture.
Encryption
If desired, the connection is hidden from prying eyes
. Who would like it if an unwanted guest connects to his Wi-Fi network. This needs to be stopped immediately, with knowledge of the matter, because the signal is transmitted further, going beyond the boundaries of the home.
Even if the owner does not mind his neighbors using his Internet, he must remember two things: firstly, the speed is reduced, and secondly, not everyone visits legal sites, which in the future can cause litigation.
To create a secure connection, you just need to specify a unique network name and set a strong password for it. If desired, the connection is hidden from prying eyes. You can also set the encryption to WEP, WPA, WPA2 (in the router settings, from the computer).
Wi-Fi Class 5 or Wi-Fi 6 is worth buying
The version of the Wi-Fi adapter is just as important as the Wi-Fi class. Usually we can see nomenclature on the adapter such as “AC1200”, this means the combined speed of two Wi-Fi frequency bands. The higher this number is, the higher the performance (real speed) we will get, if we see "AC" appearing it is Wi-Fi 5 and if we see "AX" it means it is Wi-Fi 6 .
Currently we can find the following classes of Wi-Fi in Wi-Fi adapters, depending on our needs (and budget), it would be advisable to buy one or the other:
- AC433 : This is an antenna adapter capable of reaching 433Mbps on the 5GHz band with Wi-Fi 5 only, it is not dual-band.
- AC600 This is a Wi-Fi adapter with antenna and dual band mode, we can get up to 150 Mbps in the 2.4 GHz band with Wi-Fi 4 and up to 433 Mbps in the 5 GHz band with Wi-Fi 5.
- AC750 This is a Wi-Fi adapter with two antennas and dual band mode, we can get up to 300 Mbps in the 2.4 GHz band with Wi-Fi 4 and up to 433 Mbps in the 5 GHz band with Wi-Fi 5.
- AC867 : This is a dual antenna WiFi adapter capable of reaching 867Mbps on the 5GHz band with Wi-Fi 5 only, it is not dual-band.
- AC1200 This is a Wi-Fi adapter with two antennas and dual band mode, we can get up to 300 Mbps in the 2.4 GHz band with Wi-Fi 4 and up to 867 Mbps in the 5 GHz band with Wi-Fi 5.
- AC1300 This is a Wi-Fi adapter with two antennas and dual band, we can get up to 400 Mbps in the 2.4 GHz band with Wi-Fi 4 and 256QAM and up to 867 Mbps in the 5 GHz band with Wi-Fi 5.
- AC1750: This is a WiFi adapter with three antennas and dual band mode, we can get up to 450 Mbps in the 2.4 GHz band with Wi-Fi 4 and up to 1,300 Mbps in the 5 GHz band with Wi-Fi 5. They are high-end .
- AC1900 : This is a WiFi adapter with three antennas and dual band, we can get up to 600 Mbps in the 2.4 GHz band with Wi-Fi 4 and 256QAM and up to 1,300 Mbps in the 5 GHz band with Wi-Fi 5. They are very high . -end .
Currently, manufacturers have not yet released USB Wi-Fi cards with the Wi-Fi 6 standard, but most likely it is the maximum class AX3000 (2 antennas).