Windows XP Recovery Console
Often problems that arise with Windows XP are related to failures in its operation, the inability to load the operating system, or errors during its operation.
If loading the Last Known Good Configuration, rolling back to a previous restore point, or activating Safe Mode does not fix the OS problem, you do not need to reinstall it immediately.
You can use a more serious system troubleshooting tool - the recovery console. To operate this tool, you must use administrator rights and a set of special commands (operators) built into the console.
How to recognize a broken Windows XP boot area
You don’t have to do much with this, since it’s all done on an intuitive level, that is, you just turn on your computer, and it doesn’t go further than loading the BIOS. At best, it will show an error on the screen that the MBR area is damaged.
Recently, viruses have appeared that deliberately change this area and instruct this area to load itself instead of loading the operating system. The next time they load, they demand money from the poor user. As it turns out, this MBRLock virus can be treated using the method described below.
Installing the Console
In Windows XP, it is possible to directly include the specified tool in the selection of system startup modes. To do this, you must use the original OS distribution.
To perform this setup you must:
- Insert the CD with the Windows distribution into the drive, or use a bootable USB drive by inserting it into the appropriate slot.
Reference! The letter D (or another in this line) is the letter designation of the drive or bootable USB drive with the OS distribution.
Comments
myr4ik07
, 11/08/11 18:18 A good method, but as practice shows, it does not always work.
Dmitriy
, 02/13/12 06:20 Thank you, everything works for me without problems!
Eugene
, 01/07/16 22:01 what to do if you don’t know the password
old man
, 02/17/17 05:00 the commands MUST be swapped: first we edit the MBR (fixmbr) then write BOOT (fixboot). I wonder how this can work for someone without problems, if you first need to correct errors and then set the boot direction for the system, and not vice versa? ))
Running from installation disk
If, after performing the operations to enable the console to start the OS, the required item does not appear in the menu, you must activate this tool directly from the Windows distribution.
In this case, to start it you need:
- Insert the CD with the OS distribution into the drive, or use a bootable USB.
Reference! When you enter the “help” command in the specified line and press “Enter,” a list of all operators used to interact with this tool will appear.
Option 1: Recover another OS entry
Description of the task
Let's consider the first variant of the problem, in case the bootloader was damaged due to incorrect installation of another operating system on the system disk.
This situation is most likely today, since the main operating system, of course, is a more modern version: Windows 7, 8 or 10.
If you had 2 operating systems installed: for example, one on the system drive “C:\”, and the other on “D:\”, “E:\” or another drive. If you incorrectly reinstall the system on drive C, you may find that you now only have one Windows running and during the startup process no offers to start another OS appear on your computer.
The decision depends on the situation. For the described case, the simplest and most effective recovery method is the recovery method using the EasyBCD program.
Why EasyBCD
- At the time of writing this article, the program is free and can be downloaded from the developer's official website.
- EasyBCD's interface is very simple and intuitive. It will take few words to describe how it works.
- You have a running OS on the system disk, and performing various shamanic actions by rebooting into the command line does not seem rational.
- To restore using EasyBCD, you do not need to remember the OS “Administrator” password, which, as a rule, many do not remember.
- The program supports all the latest OS versions.
Algorithm of actions
- Download the program from the official website. To do this, select the “Non-commercial” option. Click REGISTER.
Next you will be asked to register.
And what do you want? The program is free! - Install.
- Launch it. The program will analyze the bootloader and show the entries. In this example, the bootloader was destroyed by an incorrect installation of Windows 10, so EasyBCD shows only one entry in the boot partition "C:\"
- Select the system type, "Auto search for a disk with a working OS" Click the Add button.
- The lost OS appears. In the “Edit Boot Menu” menu we can configure the interface for selecting the OS when the computer boots. In addition, we select the default OS, i.e. one that will start downloading automatically if the user does not select another option. The Metro style menu is more modern with big, beautiful turquoise buttons. Timeout is the time it takes for the user to select an operating system when turning on the PC. After clicking Save, the changes will take effect.
- Check that the steps were performed correctly by restarting the computer: “Tools", Further "To restart a computer».
It is worth noting that the EasyBCD program has many other capabilities, in particular, the ability to restore bootloaders of other versions of Windows and operating systems: Linux, Mac and others.
Recovering Windows XP using the Recovery Console
An example of the operation of the “fixmbr” operators, which rewrites the OS bootloader (MBR), and “fixboot,” which writes a new boot sector to the OS system partition; their launch is one of the most popular actions when restoring the working state of Windows.
To run "fixmbr":
- Type the command “fixmbr” in the “C:WINDOWS>” line and press “Enter”.
Reference! Executing the “fixmbr” and “fixboot” operators in the vast majority of cases allows you to restore the operating system.
If using these commands does not solve your OS problems, you can use other console operations to get Windows XP back up and running.
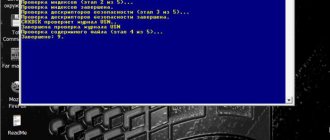
One of these operations is the “chkdsk” command, which checks for errors on the HDD and restores its sectors.
To run chkdsk you need to:
- Open the management console again and enter the “chkdsk” operator with the “/r” parameter, which restores HDD sectors.
Reference! The “chkdsk /r” key also includes the “/p” key, which allows the “chkdsk” operator to simultaneously correct possible errors on the HDD.
Copying download files via the command line
How to remove .Net Framework in Windows 10 - description of methods
If creating and rewriting the MBR does not help, and restoring the boot sector does not give the desired results, then the only way to fix the error is to move the files called NTLDR, boot.ini and NTDETECT.COM to the root of the system hard drive. To do this you need:
- Insert the media into a special port on your personal computer or laptop.
- Restart and boot from the installation media, as was done in the previous instructions. You will need to press the F11 key to get to the boot location selection window.
- Press the key with the Latin letter “R” to launch the recovery console.
- Select which operating system you want to log into. If there is only one on the disk, then by default press one (“1”).
- Write the new MBR code and boot sector as shown in the two previous instructions.
- Without leaving the console, type the “map” command, which will display information about all drives connected to the PC.
- Search for a disk that will contain the Windows distribution.
- Enter the name of the Windows drive and folder to start working with them. Don't forget to press "Enter".
- Write the command “cd i386” to open the folder, and then “copy NTLDR C:\” to copy the file.
- The same is done for NTDETECT.COM (“copy NTDETECT.COM C:\”).
- For boot.ini the process is different - enter the command “Bootcfg /add” and select the desired system.
- Enter the name “XP Professional RU” and specify the parameter “/fastdetect”.
After this, the OS should start correctly and without any errors or failures.
Copying files
Thus, returning the OS to its previous appearance is quite easy. Sometimes the loading of Windows XP is disrupted due to various glitches or viruses, but by following step-by-step instructions you can be one hundred percent likely to restore Windows without installing or reinstalling a new copy of it.
Windows XP Recovery Console Commands
Most used commands:
- “help”: a list of all operators used in this tool;
- command “_help”: information on the operator;
- "map": drive mapping;
- "diskpart": work with disks;
- "chkdsk": HDD check;
- "fixmbr": create a boot entry;
- "fixboot": creating a boot sector;
- “bootcfg:” editing Boot.ini to start the OS;
- "format": formats the HDD in the required file system.
On a note! The above list includes only a small group of operators focused on working with the presented tool.
To view all operators, you must enter the “help” parameter and press “Enter”.
Using the presented software, you can:
- start and disable services that manage the registry when the OS starts;
- present, delete, copy and change file names;
- create and delete directories;
- restore boot file, MBR volume;
- unpack compressed files from the OS distribution;
- format partitions and scan your hard drive for errors.
Using the console often helps out with difficulties that arise with Windows XP without the inevitable reinstallation of the OS. This tool is especially useful in cases where the system cannot boot to the user interface, providing access to the hard drive in this difficult case.
Video - MBR recovery on Windows XP, all commands in the recovery console
Did you like the article? Save so you don't lose!
Recovering the Linux bootloader
Grub 2 bootloader
This instruction will help when:
- We reinstalled Windows and besides it there was also Linux, which became invisible
- Linux stopped booting even when it was the only OS
1)
Booting from LiveCD (LiveDVD, LiveUSB)
2)
We look at the partition table:
$ sudo fdisk -l Device Load Start End Blocks Id System /dev/sda1 * 1 13 102400 7 HPFS/NTFS Partition 1 does not end at the cylinder boundary.
/dev/sda2 14 7749 62139420 7 HPFS/NTFS /dev/sda3 7750 23607 127377020 7 HPFS/NTFS /dev/sda4 23607 30402 54577153 5 Extended /dev/sda5 23607 30119 52301824 83 Linux /dev/sda6 30119 30402 2274304 82 Linux swap / Solaris /dev/sdb1 * 1 5099 40957686 7 HPFS/NTFS /dev/sdb2 5100 16142 88701952 7 HPFS/NTFS /dev/sdb3 16143 19457 26627737+ 83 Linux /dev/sdc1 1 30401 2441960 01 7 HPFS/NTFS Command response shortened for visibility. It can be seen that the system has three disks. The first two have boot areas and several partitions for both Linux and Windows (HPFS/NTFS). You need to decide which of them will restore (you can take turns, temporarily disconnecting the remaining disks). In the case of one hard drive, the situation is simpler. This will be /dev/sda
3)
We mount the Linux partition (here sda5, but if there is a separate boot partition, then you need to mount it), add devices and processes to it, go to it, thus getting into the environment of the OS that is installed on the computer:
$ sudo mount /dev/ sda5 /mnt $ sudo mount —bind /dev /mnt/dev $ sudo mount —bind /proc /mnt/proc $ sudo chroot /mnt
After the transition, you won't have to use sudo because Now all commands are executed as root:
4)
Install the bootloader
# grub-install /dev/sda
If you receive an error message, then update the information about the device /dev/sda and try to install again:
# grub-install --recheck /dev/sda # grub-install /dev/sda
5)
Exit to the LiveCD OS environment, unmount the partitions and reboot the computer:
# exit $ sudo umount /mnt/dev $ sudo umount /mnt/proc $ sudo umount /mnt $ sudo reboot
The last command can be replaced with an alternative:
$ sudo shutdown -r now
Footnotes
- BCDboot
is a tool that is used to create a system partition or restore the boot environment located on a system partition. The system partition is created by copying a small set of boot environment files from an installed Windows® image. The BCDboot tool creates a boot configuration data (BCD) store on the system partition with a new boot entry that allows the installed Windows image to boot... (read more on the official Microsoft website) - Bootsect.exe
updates the primary boot code of disk partitions to enable switching between Bootmgr and the NT boot loader (NTLDR) . You can use this tool to repair your computer's boot sector. This tool replaces FixFAT and FixNTFS. - DiskPart
- This tool allows you to manage objects (disks, partitions or volumes) using scripts or commands entered from the command line (more details on the official Microsoft website)
Restoring the Windows XP bootloader
Tell me how to properly restore the Windows XP bootloader, I had two operating systems installed and the Acronis OS Selector boot manager. I uninstalled one system and Acronis, now I have problems, first in the initial boot phase the message Bootmgr is missing appeared, I applied the Fixmbr and FixBOOT commands in the recovery console, now another NTLDR is missing error appears. I spent two days studying this console, but Win XP still won’t load, what did I do wrong? DRIVE.
Recovering the boot sector from a flash drive
How to speed up boot time on Windows 7 - description of methods
Sometimes errors can occur with the boot sector of the operating system. In this case, a flash drive or disk with the Windows XP installation package will also help. If the message “NTLDR is missing” appears on the display during the OS startup process, then it is 100% likely that there are problems with the boot record.
Such errors can also occur if the MBR is damaged, so you should restore both one and the second fragment so as not to make a mistake. The general step-by-step instructions that will allow you to recover boot records from installation flash drives are as follows:
- Insert the media into a special port on your personal computer or laptop.
- Restart and boot from the installation media, as was done in the previous instructions. You will need to press the F11 key to get to the boot location selection window.
- Press the key with the Latin letter “R” to launch the recovery console.
- Again, select which operating system you want to log into. If there is only one on the disk, then by default press one (“1”).
- Enter the command “fixmbr” (without quotes) in the same way as the previous instructions. It is needed to rewrite the boot record. If the OS asks you to agree to the operation, then you must press the key with the Latin letter “Y”, which means “Yes”.
- Run the “fixboot” command, which will rewrite the boot sector code and also agree to the operation by pressing the “Y” key, meaning “Yes”.
- Exit the recovery console by entering the "exit" command.
Finally, you need to restart your personal computer or laptop to check that the system boots correctly.
Working with boot.ini
If setting and rewriting the boot sector and MBR code did not help, then you should fix the Boot.ini file. To do this, follow these step-by-step instructions:
- Restart and boot from installation media. This process has been described in previous instructions. You will need to press the F11 key to get to the boot location selection window.
- Press the key with the Latin letter “R” to launch the recovery console.
- Select which operating system you want to log into. If there is only one on the disk, then by default press one (“1”).
- Once in the console, enter the command “bootcfg /rebuild”.
- Wait for the scan to finish and confirm the use of the found copy of Windows.
Then reboot the personal computer and observe the changes.
Important! During the scanning process, the PC will check all sectors of the hard drive in search of a copy of Windows. When it is found, the system will prompt the person to write it to the configuration file, which directly affects the correct start of the OS.
Restoring the Windows XP bootloader
You, dear DRIVE, were two steps away from victory, you didn’t have enough patience, but it doesn’t matter, next time everything will work out. It is very important to know that the Bootmgr is missing error indicates damage to the master boot record or partition table of the hard drive, which is located in the first sector of the hard drive. By the way, you have successfully started restoring the Windows XP boot loader
and solved half of the problems, namely, they overwrote the master boot record in the recovery console with the Fixmbr command and wrote a new boot sector with the FixBOOT command, so another error began to appear and the only thing left to do was to copy it to the root directory of the partition with the operating system (mainly drive C ) three files boot.ini, NTDETECT.COM, ntldr. Let's start from the very beginning and get Windows XP to boot.
- We consider possible causes of damage to the Windows XP boot loader, check the BIOS settings in the Boot Device Priority item.
- Using the Fixmbr and FixBOOT commands in the recovery console.
- Copying the boot.ini, NTDETECT.COM, ntldr files from the Windows XP installation disk into the recovery console and loading successfully.
- If after reading the article you still cannot restore the boot of Windows XP, then read our other article “Restoring the system through the Windows XP installation menu or Restoring a damaged copy of Windows XP”
After turning on the computer, friends, it self-tests, then control is transferred to the master boot record of the hard drive, it contains a partition table of the hard drive and a small bootloader program that reads in this table information from which hard drive (if there are several of them) and which partition of the hard drive to produce loading the OS. Subsequently, the operating system kernel is loaded into RAM and Windows XP actually starts. You also need to know that loading the operating system also involves a group of files located in the root directory of drive C, namely boot.ini, NTDETECT.COM, ntldr. The presence of all of the above eliminates the presence of the Bootmgr is missing error when loading XP and ensures successful startup of the system.
By the way, it is not always necessary to restore the Windows XP bootloader in case of such problems, let's look at some of the reasons for this error that I personally encountered. The first is the simplest, if there are several hard drives in the system, the Bios settings have been violated, namely, for example, in AMI Bios, in the BOOT tab, Boot Device Priority, then Hard Disk Drives, the hard drive from which you want to boot is set to the wrong one, which is needed. Troubleshooting this problem and the reasons for its occurrence are well described in our article Bootmgr is missing in Windows 7.
The use of third-party programs in the master boot record, so-called boot managers, for example Acronis OS Selector, is used mainly when there are several operating systems on the computer; the manager displays a convenient OS selection menu at the beginning of boot. You need to use such programs very carefully; if you incorrectly remove the Acronis OS Seletor program from your computer, there is a very high chance of restoring the Windows XP bootloader. The same applies to the GRUB bootloader, which allows you to use Linux and Windows XP on one computer; when you remove GRUB, you will leave your computer alone with an incomprehensible boot record and without hesitation it will show you Bootmgr is missing. In this case, we will correct the situation in the Windows XP recovery console, first we will enter the FIXMBR command and rewrite the master boot record, and with the second FIXBOOT command we will write a new boot sector. But that’s not all, after correcting the boot record, as well as recording a new boot sector in the console, the situation with the error output may remain unchanged and there may be other errors, for example: NTLDR is missing. In this case, you need to once again make sure that there are boot sector files directly involved in loading Windows XP: boot.ini, NTDETECT.COM, ntldr, in the root directory of the disk (C:), in principle, three of these files are enough to boot Windows XP . The easiest way is to use a Live CD, boot from it, then go to the root directory of drive C and make sure that these files are present; if they are not there, then you need to copy them from any working XP and upload them to yourself, having previously checked and, if necessary, edited boot.ini file, a simple text file that contains the path to the Windows XP system files, you must do this, otherwise you will get another error, you can read Editing BOOT.INI. But I like another way: restoring the Windows XP bootloader using the recovery console. If you have an XP distribution, let's use it and copy our three files boot.ini, NTDETECT.COM, NTLDR to the root directory of drive C. I assure you it’s very simple, and you don’t need to edit the boot.ini file, the console will do everything itself. We boot from the Windows XP installation disk, select restore R. If we have one operating system, set the number 1.
Error five. Damage to the system registry
This problem occurs infrequently, but still. The system registry, which contains data about the launch of drivers, affects the start of the Windows XP operating system. If the SYSTEM partition becomes damaged, NTLDR pauses the computer and displays an error message. The files in the registry are unique. Therefore, restoring them by transferring them from another version of the operating system is an impossible task. The output is as follows:
- When logging into Windows XP, type: rename c:windowssystem32configsystem system.old, ending with “Enter.” The damaged registry key will receive a different name, after which it can be replaced with another one.
- After that, run: copy c:windowsrepairsystem c:windowssystem32configsystem to repair the partition. The system should boot.
Restoring Windows XP via the console
Restoring Windows XP via the console
can be considered using a simple example, a damaged boot record (MBR) and the second option: editing the BOOT.INI file from the recovery console. The Master Boot Record is the first sector of the boot partition on the hard drive. The sector contains a partition table and a program tasked with loading the operating system. If the master boot record is damaged or missing, you and I will never boot the operating system. And sometimes this damage or absence still occurs at the most inopportune moment.
For example, one user decided to install 20 operating systems on his computer, and set about creating the corresponding partitions on his hard drive (and sometimes they even create them), and then installing them accordingly. Naturally, all this stops loading at some point and we need to get out of the situation with dignity.
Why won't Windows XP boot?
The reason why Windows XP won't boot could be any failure in the boot process, such as one or more components being missing or damaged. This can be the boot code in the first partition of the hard drive or active partition, the NTLDR bootloader itself, files responsible for starting Windows XP, as well as the system registry, which contains information about what to run and in what order.
Loading problems most often result from:
- unqualified installation of several operating systems on a hard drive, when instead of creating a dual-boot configuration, the boot code of a later installed system overwrites the code of a previously installed one;
- viral infection, mainly ransomware blockers, which can modify the launch parameters of files important for loading in the system registry, the files themselves and boot sectors on the disk.
- defects in the surface of the hard drive, leading to damage and loss of data on it;
- interruptions in the computer's power supply during read-write operations of files responsible for loading (if an unexpected shutdown occurs during Windows startup or shutdown, the likelihood that the system will no longer boot is quite significant).
Restoring Windows XP via the console
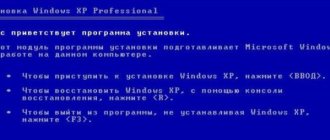
We insert the Windows XP installation disk into the drive and reboot, in the BIOS we set the disk drive as the first boot device, if you don’t know how, read our BIOS: Boot from disk. Next, the Windows XP installation program is loaded and after loading a menu appears, in it you need to select item No. 2. To restore Windows XP using the Recovery Console, press R
.
Press R
and enter the Recovery Console, by the way, you can read the Windows XP Recovery Console.
We have one operating system installed on drive C
and when asked which copy of Windows you should log into, put the number
1
and press Enter.
If you did not have an administrator password, simply press Enter; if you did, enter a password.
- This computer has a non-standard or invalid Master Boot Record. Using FIXMBR
may damage your existing partition table.
This will result in loss of access to all partitions of the current hard drive. If there are no disk access problems, it is recommended that you abort the FIXMBR command. Are you confirming the new MBR entry? We agree - enter y
(which means
yes
) and Enter. The hard disk partition table will be overwritten.
That's all Restoring Windows XP through the console
should complete successfully, enter exit and reboot.
What may not work for us, when entering the FIXMBR command, an error message appears, this means that writing to the partition table (MBR) is blocked by settings in the BIOS, you need to go into the BIOS and find the Boot Virus Detection parameter there (the Enabled value) this option blocks overwriting the boot sector of the hard drive, which is what happens in our case.
Windows XP operating system boot process
Booting Windows XP is a complex and multi-step process that begins from the moment the computer is turned on and ends after the desktop appears on the screen. During these few minutes, many operations are performed hidden from the user’s eyes, each of which lasts from a fraction of a second to several seconds. The process of starting the system itself can be compared to a relay race, where each participant goes through his part of the path and solves his own, strictly defined tasks, after which he passes the “baton” on. If at least one participating component falls out of this chain, the boot process stops and an error message is usually displayed on the screen.
To have an idea of how Windows XP boots, let's briefly look at its sequence. We will not consider the pre-system stages of turning on the computer (self-testing, initialization and the start of BIOS code execution, etc.), and we will conditionally take the moment the BIOS program reads the first sector of the hard drive, where the master boot record (MBR), containing the boot code, is located. and a partition table (logical disks). So:
- The BIOS reads the MBR (Master Boot Code) and transfers control to it.
- The MBR boot code checks the partition table and finds a partition marked as active, reads its first (boot) sector (Boot Sector), and passes control to the code written there.
- The boot sector code transfers control to the Windows NT bootloader - the NTLDR (NT Loader) file, which is located in the root directory of the disk where the operating system is installed.
- The Windows boot loader puts the processor into 32-bit safe mode, checks for the presence of the hiberfil.sys file (the hibernation image), and if it finds it, loads it. If there is no such image, NTLDR reads the Boot.INI boot configuration file. If more than one operating system is listed in this file, a menu is displayed for the user to choose which system to boot.
- When the user presses the F8 key before starting the system, NTLDR opens a menu of additional boot options:
- Next, the ntdetect.com program is loaded to determine the configuration of the computer’s hardware devices.
- Following this, the Windows XP kernel (ntoskrnl.exe file) and the Hal.dll (Hardware Abstraction Layer) library are loaded, the task of which is to hide differences in computer hardware from the kernel code.
- The NTLDR loader then loads the drivers marked as bootable and passes control to the kernel (ntoskrnl.exe).
- HAL initializes the hardware and prepares the interrupt controller.
- Next, the input/output system is turned on and the remaining drivers are loaded, which are assigned the “auto” startup type.
- The kernel loads the Windows session management subsystem - the Smss.exe file, which creates the user environment and continues loading - starts the graphics subsystem (win32k.sys driver), the client-server subsystem (Csrss.exe) and the user logon program (Winlogon.exe and Lsass.exe) .
- After the user logs in, Userinit.exe is launched, which launches the system shell (Explorer.exe) and network connections. Meanwhile, the desktop appears on the screen.