The reason why Wi-Fi turns off on an Android phone by itself may be a problem with both the mobile device and the router. In this article, we will look at options for correctly placing, configuring, resetting and flashing the router to restore the wireless connection. We will also pay attention to possible problems in the “mobile phone” itself.
Please note that Wi-Fi connection may be lost constantly or periodically due to inept user actions, interference from other electrical appliances, or damage to equipment due to a power surge.
How often do you update the firmware of your router?
What version of Android is installed on your phone?
Why WiFi turns off: list of main reasons
There are many reasons why an Android mobile device may lose its access point. To better understand the problem and localize the “culprit,” it is better to start the search in this order.
- Incorrect network setup . A WiFi router provides network coverage and determines the quality and security of wireless communications in almost every modern apartment. Although progress has been made in recent years in developing an intuitive, self-explanatory interface, the router remains a complex network device that requires basic knowledge to configure. It often happens that after an inept attempt to change the password of an access point, the entire network crashes due to the fault of the user himself.
- Router malfunction . Routers (aka routers, aka modems) are “afraid” of power surges in the network. They are also easy to damage by hand and tear off the non-removable antenna, which is guaranteed to lead to problems in the form of network disconnection on client devices. The “capriciousness” of the firmware and other reasons can lead to a short-term loss of connection or the inability to connect via Wi-Fi. Frequent symptoms of a router malfunction include network crashes and its recovery after rebooting the device, high latency (“ping”), and a sharply reduced coverage radius. If 10 or more phones are connected to one router, then crashes, slowdowns and delays are normal.
- Problems with the phone . Most often, the smartphone is to blame for disconnecting the Wi-Fi connection. If the device is ultra-low-cost, then the router may not “make friends” with its wireless module or work correctly with the firmware. The phone may lose connection due to an outdated OS, viruses and programs of dubious origin. The antenna in the Android device may have come loose, or it might have a case with a shielding metal layer on it.
Beware of passwordless networks
We always need to be careful when we go to a network without a password, such as in a restaurant or shopping mall, which is public and anyone can easily access. And it is possible that an attacker could monitor these connections and collect various data from users who choose to connect, which can even be done using passwords.
Although you will not only have access to all the information we send through this Internet connection, such as emails, messages, etc., it can even be done through our credit card information or other passwords.
Additionally, these users will also be able to use a public and unsecured wireless connection to distribute any type of malware. Thus, if we exchange files over the network, this user can easily insert infected software into our mobile device. For this reason, we must not only make sure to use secure HTTPS connections , but it is always recommended to use a VPN connection, with which we can encrypt all our data and prevent anyone from accessing it. In this way, we will be able to keep any information and data from our mobile phone safe and will also avoid the entry of possible viruses when connecting to the network without any password and security.
Determining the culprit
The easiest way to localize the problem that causes the Internet to disappear is by eliminating network links. If the Wi-Fi connection on your Android device disappears, then try connecting to a neighbor’s router. If there are none, then visit a cafe or other public places with hot spots. If you still have problems, then the problem is most likely in the phone.
Also, many Android phones can work as a router; just enable the “Access Point” function in the curtain or network settings.
Try connecting to your home router from another device. This could be a smartphone or laptop. A PC with a Wi-Fi adapter is also suitable for the experiment. If you can’t connect from other devices, then the problem is on the router’s side.
Android engineering menu settings
If your device is powered by a MediaTek processor (most devices with a Qualcomm processor do not have this option), you can go to the engineering menu and set the Wi-Fi settings directly through it. You can open it using the command “*#*#3646633#*#*” entered in the dial pad. For some tablets that do not have this panel, you can install special utilities to enter engineering mode. The settings are checked and set in the “connection” tab.
You should only configure something through the engineering mode if you are an advanced user of the Android platform. This is a mode for developers; any changes at random can lead to unpleasant consequences.
Quick solutions
It is better to solve wireless communication problems with simple actions that do not require special skills.
Rebooting devices
Many connections and constant load can lead to the router's RAM memory becoming full. To return it to normal operation, reboot the device using the button on the case or remove the power supply from the outlet. Do the same with your phone.
Specifying the correct login and password for the WiFi network
In 90% of cases, you cannot connect to Wi-Fi due to an incorrectly entered network password. The standard WLAN password is located on a sticker on the back of the router. If the character set for logging into the network has been changed and you don’t remember it, then share it from your Android smartphone via a QR code from the “Network Information” menu settings.
Now there is no particular point in specifying the hotspot login, since there is an automatic search for all available connections. When searching for a specific network from a large list of available ones, make sure that you enter the characters of its name correctly.
Changing the location of the router if the phone constantly loses WiFi
Radio waves emanating from the router are absorbed and reflected by the walls of the room. The thicker they are, and the more of them, the lower the signal quality and the higher the ping. To equalize the strength of the coverage area throughout the apartment, it is advisable to mount the router in its central part on the wall. As a last resort, move it to those rooms where the network is most often used.
Influence of other devices: microwave, radiotelephone
Interference is caused not only by neighboring networks, but also by household appliances operating in a house or apartment. These include a microwave oven, a home radiotelephone, and even a washing machine motor. To prevent them from affecting the quality of the Wi-Fi signal, place the router away from the kitchen or bathroom.
What to do if there is a weak signal or sources of strong interference?
This factor is a fairly common reason for Wi-Fi connection disconnection. Needless to say, this coverage is based on radio signals that can be shaken. It’s worth saying directly about the signal level that it is not always stable. It is influenced by several factors, the most significant of which is the voltage in the electrical network. A wide variety of electrical devices are involved in creating interference, which can sometimes be so strong that it prevents the Wi-Fi signal from spreading.
The presence of metal objects between the portable device and the router can be even more disruptive. If the laptop is located at a fairly large distance from the signal propagation point, it may periodically disappear. Therefore Wi-Fi turns off. As already noted, the signal is not stable.
When a laptop, phone or tablet is placed close to the router, the vibrations are unnoticeable, but when moving away they begin to become more pronounced, and eventually the Wi-Fi connection is interrupted. Mobile phones or microwave ovens have a particularly negative impact on communications. You can fix the problem by moving the laptop closer to the wireless router.
Router
If all of the above did not help set up a wireless network, then let’s move on to a detailed analysis and solution to problems with the configuration and malfunctions of the router.
Checking the indicators on the body: correct operation
Each router model has status and operation indicators. Using them, you can determine whether the device is receiving power, whether Wi-Fi distribution is turned on, and whether it is receiving traffic from the Internet provider.
For wireless Internet operation, pay attention to the WLAN LED indicator. It should be lit or flash continuously. If this is not observed, hold down the button of the same name on the end of the case (if there is one) or reboot the device.
WAN Connector: Check Status
Through the WAN port, the router receives the signal from the Internet cable and redirects it as a radio signal to users. The status of its operation is usually displayed on the body by a corresponding indicator. If the indicator does not blink or is not lit, then the connection with the server is lost. The cause may be a malfunction of the device: the port is loose due to frequent switching, the lock of the RJ-45 twisted pair plug is broken, the microcontroller is broken due to a thunderstorm. If the provider suspended the service for non-payment, the result will be the same.
DHCP server
DHCP server (aka dynamic IP) is a function that assigns a network address to newly connected Android devices and everything else. If it does not work correctly, then a laptop, computer or any gadget will not be able to enter the network. DHCP settings “fail” due to the user’s inexperience in administering the router or after flashing it.
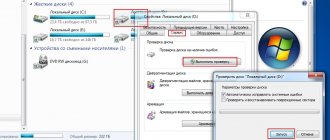
To return IP distribution back, you need to go to the router settings:
- Using the TP-Link router as an example, go to its menu by entering 192.168.0.1 (or 192.168.1.1) in the address bar of the browser.
- Enter your login and password (by default - “admin”), click “Login”;
- On the left side of the window, look for the DHCP tab and enable the functions with a checkbox, save the actions and exit the settings.
Now you can reboot and try to connect to the modem.
Setting the mode, encryption type, channel, strength, region
These steps are similar to the initial setup of the router after purchasing it. Reconfiguration consists of specifying the operating mode, the method of encoding information from intruders, and selecting a wireless communication channel or region of location. Pay attention to these settings if your problem is frequent short-term connection loss.
For this:
- We go to the router menu in the already known way;
- In the “Wireless Mode” tab, select the mixed operating mode “11bgn mixed” and set the channel parameters to “Auto”. We leave the remaining settings as in the screenshot.
- We set up network encryption by selecting the “Personal” mode, the WPA2 protocol, the AES algorithm and selecting a login password (write it down on a piece of paper) and click “Save”.
- In the advanced settings, set the power of the Wi-Fi radio transmitter to “High”.
- We set the operating mode to “Standard Wi-Fi router”
- You can select your home region in the Quick Setup section.
After saving, reboot the router.
Lots of Wi-Fi connections
The main problem of public networks is the multitude of users. Not only is the speed divided between them, but the delays of information packets will grow exponentially. If you have a lot of guests surfing the Internet from your router, then new Android devices will not be connected until one of the previous ones quits. This is due to the overflow of free frequencies for data transmission. We recommend not connecting more than 6–10 smartphones at the same time.
In the admin panel of network equipment, you always have the opportunity to disable and block unwanted “clients”.
Firmware update
The router software is regularly updated by developers. If it has vulnerabilities or errors, you need to update the software from a special section of system tools:
- Download the current firmware version for your model from the official website (www.tp-link.com).
- Go to the TP-Link “System Tools” menu, and to the “Firmware Update” section.
- Select the file with the firmware and start the update.
Under no circumstances should we disconnect the modem from the network until it is rebooted.
Reset
Resetting the settings will return the router to its factory state, allowing you to configure it from scratch. All saved profiles and settings will be lost. To reset them, look for the “Factory settings” section in the main menu and click “Restore”.
A similar action can be performed with a button on the case.
Installing the wrong firmware
The cause of problems with the operation of the Wi-Fi module may be custom firmware that blocks the connection. Manufacturers recommend installing only official versions of the firmware: custom versions are not always reliable. If problems arise after flashing, you should roll back the device to factory default or flash it again. Only now on the official one.
What good is a smartphone if it doesn't connect to the Internet? Even the best Android smartphones sometimes have problems with the Internet. If you have problems with your Wi-Fi network, we offer several methods to solve them.
Smartphone
Having dealt with the router, it's time to move on to Android-based mobile devices. The quality and performance of the Wi-Fi connection depends on their correct configuration.
It is possible to turn off WiFi in “Sleep mode”
Phones can disconnect from the network in sleep mode. Android devices “knock out” unused background processes, including the Wi-Fi module. To prevent this from happening, you need to turn off the function in the network settings.
Viruses and third party software
By downloading everything from the Play Market (or worse, installing third-party “.apk” files), Android device owners risk catching a ransomware virus or adware that interferes with normal operation. There are also pests that intercept control of individual system functions. A sure sign of this is excessive heating of the smartphone, rapid battery consumption, slow operation of the interface, and loss of the Internet.
To return your phone to normal, remove all unlicensed applications, and also scan the system with an antivirus. We recommend clearing the cache and internal memory of debris using official utilities, for example, Clean Master.
The Internet suddenly disappeared, and then appears: remove VPN applications
To bypass regional and personal blocks, many use a VPN server to redirect traffic to other countries. This utility can configure the Wi-Fi module of a smartphone to suit itself, leading to data transfer failures and periodic disconnection from the router. To return your Android phone to its previous settings, remove all software that uses VPN servers and reboot the system.
Problematic antivirus: try to disable it
An antivirus created to protect Android OS can harm it by mistaking standard system executable files for unwanted software. This happens when the heuristic analyzer, an analogue of the human immune system, is highly sensitive. This antivirus does more harm than good, so we disable or delete it along with the settings. If this is not possible, then a factory reset will be required.
Problems with the operating system: reset to factory settings
An antivirus that cannot be removed, hidden viruses, and a slow system clogged with files are good reasons to reset Android to factory settings. But remember - all files, logins and passwords, settings, contacts will be irretrievably lost. Therefore, take care of transferring them to cloud storage or physical media. We also recommend charging your phone to 100% and not interrupting the reset process.
To return Android to its default state:
- Go to “Settings” and tap on “System”;
- Select “Reset settings” from the list;
- We delete all data using the same function;
We wait for the reset to complete and log in to the smartphone using our Google account.
Why does Wi-Fi keep connecting and disconnecting?
It is worth remembering that a radio or microwave can jam the signal; the phone may not see the router. This happens if you are sitting in the kitchen, the microwave is running, and the router is in another room.
Why does Wi-Fi sometimes connect and then disconnect:
- When a microwave oven operates, it produces waves that interfere with normal signal acquisition. They are a kind of source of interference. In the kitchen, interference can often occur, unlike other rooms where there are no radio devices, as well as equipment that operates thanks to waves of different frequencies.
- If all else fails, try to reflash the router, changing the channel and coverage radius. In this case, all systems will be updated, and the equipment will begin to work on a different line, wave. This will significantly simplify the situation and improve the performance of the router. In this case, the phone will connect to it without any problems.
Network data