Sergey Efimov
October 15, 2021
Comments (0)
A wireless data connection is one of the popular methods of accessing the Internet. To perform tasks, specialized equipment is used - routers. They operate at a certain speed, but they also have other characteristics. Ordinary people rarely understand what Wi-Fi standards are, because knowledge does not affect the conditions for using the device. But sometimes it is necessary to understand this terminology. For example, when purchasing a new device.
Almost everyone needs modern Wi-Fi
What is Wi-Fi signal frequency
Each modem transmits digital streams of information from one point or points to another. The signal is an electrical impulse with 2 basic characteristics - Wi-Fi wavelength and frequency. Since wireless technologies belong to the category of radio waves, they operate according to similar laws as light.
Wi-Fi frequencies are the number of periods of alternating current per second, otherwise the number of waves traveling in a certain place in space. The frequency of the voltage determines the overall length of the radio wave.
So, at what frequencies does Wi-Fi work:
- 2.4 GHz (2412 - 2472 MHz).
- 5 GHz (5160 - 5825 MHz).
There are other ranges - 0.9, 3.6, 10, 24 GHz. They are rarely used when regular frequencies are occupied, and only if the user has a license for them. Each frequency has individual properties. And even a weak signal can travel great distances, but in such a situation you will need a special antenna or Wi-Fi gun to amplify the pulse.
To communicate via wireless technology, you must have an access point (equipment) and at least 1-2 Wi-Fi clients. Sometimes a point-to-point connection occurs, that is, users communicate directly. At the same time, the standard provides for a significant degree of freedom in choosing the adapter and radio channel settings.
Which Wi-Fi channel to use
If you live in an area with no neighbors, you can use any channel without receiving interference. If you happen to be one of the millions of people living in cities where most have wireless Internet access, you need to figure out which Wi-Fi channel to use. When your Wi-Fi channel overlaps with other nearby networks, neither you nor your neighbors get a very good internet connection.
Each of the 14 channels in the frequency band is divided into 5 MHz. The Wi-Fi network signal occupies about 20 MHz of bandwidth, so it overlaps with the two channels on either side of it. When you select a channel for your Wi-Fi network, you are essentially choosing a center from 5 different channels. So if I were to select channel 6 for my Wi-Fi network, I would actually be using channels 4.5, 6 , 7, and 8.
There is only room in the spectrum for three channels that do not overlap each other, channels 1 , 6 and 11 . So if a neighbor decides to start using channel 4 (which actually uses channels 2,3,4,5 and 6), they create and receive interference from your channel 6 network. So, to avoid interference from their channels, you would want I would like to move as far away as possible and set up my Wi-Fi network on channel 11.
Since most people use channels 1,6 and 11, some of you may think that it might be better to choose another channel, such as channel 3 or 4. The answer to this question is no . When wireless routers partially share bandwidth, they cannot communicate well, resulting in significantly reduced Internet performance and data corruption.
It is much better to completely share a channel with a neighbor than to only partially block it. Our routers have channel sharing software built into them that allows our routers to be polite to each other and take turns when another network is completely sharing our bandwidth.
If you have multiple neighbors using different Wi-Fi channels, you can set your network to the channel (1, 6, or 11) that is furthest from them or the one that is used the least. You should also look at the signal strength of surrounding Wi-Fi networks and stay away from those that are the strongest.
What does frequency affect, what are allowed in Russia
The frequency of the network signal directly affects the wavelength and other characteristics:
- Absorption or penetration: higher frequency demonstrates better properties. In buildings with many partitions, thick walls, and coverings, this is a significant indicator.
- Reflective properties - the ability of a signal to pass through soft structures and be reflected from surfaces. In this case, the quality of communication will be lower.
- Degree of information density: high range can process and transmit more information.
- Overcoming obstacles: Wi-Fi's high frequency but short wavelength makes it more difficult to navigate around physical barriers. Therefore, in residential buildings they prefer to use the lowest possible modem operating parameters—2.4 GHz.
- Attenuation is the natural decrease in the level of Wi-Fi electrical impulse. Its strength actively decreases at high frequency.
Thus, the main thing that determines the channel width is the quality and speed of work on the Internet.
Important! In the Russian Federation it is allowed (no license required) to use both 2.4 and 5 GHz frequencies in homes.
So let's start with IEEE standards (Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers) - an international non-profit association of specialists in the field of technology, a world leader in the development of standards for radio electronics and electrical engineering. The main goal of IEEE is standardization in the field of IT. So, in order to distinguish between standards, after the abbreviation IEEE, numbers are written that correspond to a specific group of standards, for example:
- Ethernet is a standard of the IEEE 802.3 group
- WiFi is a standard of the IEEE 802.11 group
- WiMAx is a standard of the IEEE 802.16 group
Moving on, what do the letters after IEEE 802.11 mean? These letters indicate the Wi-Fi network standard.
| IEEE standard | Name of technology in English | Frequency range of networks, GHz | Year of Ratification by the WiFi Alliance | Theoretical throughput, Mbit/s |
| 802.11b | Wireless b | 2,4 | 1999 | 11 |
| 802.11a | Wireless a | 5 | 2001 | 54 |
| 802.11g | Wireless g | 2,4 | 2003 | 54 |
| Super G | 2,4 | 2005 | 108 | |
| 802.11n | Wireless N, 150Mbps | 2,4 | — | 150 |
| Wireless N Speed | 2,4 | — | 270 | |
| Wireless N, 300Mbps | 2,4 | 2006 | 300 | |
| Wireless Dual Band N | 2,4 and 5 | 2009 | 300 | |
| Wireless N, 450Mbps | 2.4/ 2.4 and 5 | — | 450 | |
| 802.11ac | Wireless ac | 5 | — | 1300 |
From this table it can be seen that with each new standard, the speed of the Wi-Fi network is steadily increasing. If you see IEEE 802.11 b/g/n on any device (router, laptop, etc.), this means that the device supports three standards: 802.11b, 802.11g, 802.11n (at the time of writing this is the most popular combinations, since the 802.11a standard is outdated and uses the 5 GHz frequency band, and 802.11ac has not yet gained much popularity).
It's time to understand the frequency ranges in which Wi-Fi networks operate, there are two of them - 2.4 GHz (more precisely, the frequency band 2400 MHz-2483.5 MHz) and 5 GHz (more precisely, the range 5.180-5.240 GHz and 5.745-5.825 GHz).
Most devices operate at 2.4 GHz, which means using the 2400 MHz-2483.5 MHz band with a step frequency of 5 MHz. these stripes form channels, for Russia there are 13 of them
Channel Low frequency Center frequency High frequency 1 2.401 2.412 2.423 2 2.406 2.417 2.428 3 2.422 2.433 4 2.416 2.427 2.438 5 2.421 2.432 2.443 6 2.426 2.4 37 2.448 7 2.431 2.442 2.453 8 2.436 2.447 2.458 9 2.441 2.452 2.463 10 2.446 2.457 2.468 11 2.451 2.462 2.473 12 2.456 2.467 2.478 13 2.461 2.472 2.483
When setting up the router, you can select one of the channels or trust the choice of the router itself and select AUTO. It is worth noting that choosing a channel is a responsible matter, since the more devices (for example, neighboring routers) work on your channel, the lower the speed will be for everyone who uses this channel. To make the right choice, you should use one of the programs for scanning Wi-Fi networks in your home/office, determine the less busy channel and select it when setting up a Wi-Fi router. In more detail how to do this is described in the article How to select/change a wireless channel on a router/router .
Frequency channels in the 5GHz spectral band:
| Channel | Frequency , GHz | Channel | Frequency , GHz | Channel | Frequency , GHz | Channel | Frequency , GHz | |
| 34 | 5,17 | 62 | 5,31 | 149 | 5,745 | 177 | 5,885 | |
| 36 | 5,18 | 64 | 5,32 | 15 | 5,755 | 180 | 5,905 | |
| 38 | 5,19 | 100 | 5,5 | 152 | 5,76 | |||
| 40 | 5,2 | 104 | 5,52 | 153 | 5,765 | |||
| 42 | 5,21 | 108 | 5,54 | 155 | 5,775 | |||
| 44 | 5,22 | 112 | 5,56 | 157 | 5,785 | |||
| 46 | 5,23 | 116 | 5,58 | 159 | 5,795 | |||
| 48 | 5,24 | 120 | 5,6 | 160 | 5,8 | |||
| 50 | 5,25 | 124 | 5,62 | 161 | 5,805 | |||
| 52 | 5,26 | 128 | 5,64 | 163 | 5,815 | |||
| 54 | 5,27 | 132 | 5,66 | 165 | 5,825 | |||
| 56 | 5,28 | 136 | 5,68 | 167 | 5,835 | |||
| 58 | 5,29 | 140 | 5,7 | 171 | 5,855 | |||
| 60 | 5,3 | 147 | 5,735 | 173 | 5,865 | |||
Accordingly, in the Russian Federation we have the following non-overlapping channels with a width of 20 MHz indoors: 1. 5150-5250 MHz 36: 5180 MHz 40: 5200 MHz 44: 5220 MHz 48: 5240 MHz (this channel is effective provided that the next band is used) 2. 5250-5350 MHz (check the possibility of using this band) 52: 5260 MHz 56: 5280 MHz 60: 5300 MHz 64: 5320 MHz
Due to the less frequent use and larger numbers of channels of the Wi-Fi point, the speed of Wi-Fi increases. But to use 5GHz, it is necessary that not only the Wi-Fi source (router) operate at this frequency, but also the device itself (laptop, tablet, phone, TV). The disadvantage of using 5 GHz is the high cost of equipment compared to devices operating at a frequency of 2.4 GHz and the shorter range compared to the frequency of 2.4 GHz.
I really hope my article helped you! Please share the link with your friends:
How to find out what frequency a Wi-Fi router operates at
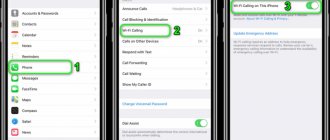
Before making adjustments to the operation of the modem, you need to review the current settings. How to find out the Wi-Fi frequency of the router through the settings:
- Open browser.
- Log in to the panel as administrator: write 192.168.0.1 in the search bar.
- Enter login and password. Standard ones often have the same appearance - Admin.
- Go to Wireless Mode. The window will indicate the frequency and other operating parameters.
There are special utilities that analyze and present in the form of graphs the frequencies of operating devices.
The range can also be found using the WiFiInfoView utility. Using it you can not only determine the frequency, but also change the settings:
- Download a small program.
- If the utility is in the archive, then unpack it.
- Launch the exe file. No installation required on the device.
- The screen displays information about the current channel and frequency. Additionally, there is no need to open the modem parameters.
How to find an open WiFi channel
To find a free WiFi channel among those used by neighboring networks, you will have to use third-party programs. Very often, on various Internet forums it is recommended to use a wireless analyzer - the inSSIDer program.
The program must be downloaded (inSSIDer for XP, inSSIDer for Windows 7 and Windows 8), installed and launched. You will be shown all available active WiFi networks. Look at the “Channel” column. It indicates the radio channels used. Currently in Russia 13 WiFi channels are allowed for use. Of these, 3 channels are non-overlapping - channels 1, 6 and 11. If one of these channels is not busy, great. If everyone is busy, just look for a free one and borrow. Note: Undoubtedly, inSSIDer is an excellent and functional product, but a bit heavy in my opinion. If you need an easier and simpler program, you can use WiFiInfoView.
This is a simple free program that, however, shows all the necessary information and works with most WiFi adapters.
Which one is better, how to change it in the settings
Almost all adapter settings are made in the web interface. Different routers may have different instructions for changing settings. An example of working with TP-Link is given:
- Open browser. Enter the standard set of numbers 192.168.1.1 (or 0.1).
- Click on Settings.
- Write admin in the login and password fields. Sometimes the default may be another word - user.
- Go to the menu, in the left column there will be an item Wireless mode.
- It contains the Channel Width (Bandwidth), select the frequency.
- Save. Reboot the network adapter.
2.4 or 5 GHz
Advantages of the 2.4 GHz frequency:
- Overcoming physical barriers.
- Affordable cost of network device.
Flaws:
- Range is low.
- The number of non-overlapping channels is smaller.
- The likelihood of extraneous noise when devices operate in this range.
Advantages of 5 GHz:
- Large selection of channels that do not overlap with each other.
- Good signal range.
Minuses:
- Poor flexibility when overcoming obstacles.
- Increased price of the modem.
Conclusion: Each frequency has advantages and limitations depending on local conditions and individual tasks. Users living in ordinary apartments can have a high-speed connection at 2.4 GHz, if the network is not too congested. When you need to broadcast a signal over long distances or reduce serious interference, 5 GHz is a priority.
Important! Older router models may not support the transition to 5 GHz. Usually the markings are indicated on the body of the device.
Frequency band categories have their own advantages and limitations
Choice between 20 and 40 MHz
Within the 2.4 GHz frequency, you can also vary the bandwidth: 20 or 40 MHz. At first glance, a larger width is preferable, but it is worth studying their characteristics in more detail:
- The 20 MHz width has three non-overlapping channels. They are independent, so even when connecting 2-3 devices there will be no interference.
- There is one free channel in the 40 MHz band. To have a good connection speed, it is possible to activate Wi-Fi on only 1 device.
- Installing clean modes on outdated equipment provokes incompatibility between devices.
Therefore, the 40 MHz indicator transmits the impulse well, but negatively affects the quality of neighboring connections, that is, the risk of conflict is higher if the band becomes wider. And from a practical point of view it is recommended:
- Leave 20 MHz when using Wi-Fi in residential buildings and buildings with a large number of users.
- Switch to 40 MHz in private premises without neighbors, as well as in the presence of a weak signal and an unstable web connection.
The main advice is to experiment on your own. You can set one frequency or width for a certain period of time, then change it. If the user does not understand the differences in these parameters, it is worth installing an auto-frequency detection function in the modem. Then the router will be able to select the most profitable bandwidth without human intervention.
Note! For phones and tablets, you need to purchase Wi-Fi Analyzer programs, through which you can change channels. Recommended numbers are 1, 6, 11 or other free and non-overlapping numbers.
5 GHz frequency range: high speed, low coverage
The 5 GHz band is used by Wi-Fi 5 and Wi-Fi 6 and is between 5180 MHz and 5825 MHz of the Wi-Fi frequency spectrum. It has a clear improvement over 160MHz channels, even if it's just two 160MHz channels for that frequency band, they incredibly improve the Wi-Fi connection, having twice the real and theoretical speed. It also includes, compared to its predecessor, 80 MHz channels, which also help greatly in reducing congestion on the Wi-Fi network, while still providing very good Wi-Fi speeds. This is a band that supports 25 channels at 20 MHz, 12 channels at 40 MHz, 6 channels at 80 MHz and 2 channels at 160 MHz.
Based on this table, we are going to explain the four channel groups (there are more channel groups in this range, this is the region that determines which channel groups we can use and which channel groups are limited to it), the lower channels, or U-NII-1 . UNII-2A channels, DFS or U-NII-2S channels and UNII-3 channels or high channels .
U-NII-1 channels or low channels
These are channels 36 to 48, these are 20 MHz, 40 MHz or 80 MHz bandwidth channels, they are at the beginning of the 5 GHz band spectrum and are called "low frequency" channels because they are the low frequency channels within the 5 GHz band.
Channels U-NII-2A
These are channels 56 to 64, they are also 20 MHz, 40 MHz and 80 MHz bandwidth channels, we can use them, but they are under two restriction protocols: DFS or dynamic frequency selection (dynamic frequency selector) and TPC or transmit . Power control. The IEEE 802.11 standard allows devices such as routers and access points to share the 5 GHz radio frequency spectrum with radar. Radar signals are vulnerable to interference from other devices using the same spectrum.
The DFS feature allows the router or access point to detect radar signals and change its operating frequency to avoid interference. This process ensures that radar systems can send and receive accurate information. TPC will automatically adjust the channel and output power of the router so as not to interfere with military signals from radar, etc.
If we combine U-NII-1 and U-NII-2A channels, we can use 160 MHz channel width, in particular we will have one channel with 160 MHz bandwidth for routers.
Channels U-NII 2S
These are channels from 100 to 140, also with bandwidths of 20, 40 and 80 MHz and with the same restrictions as the previous ones. They are separated from U-NNI.2A because these frequencies cannot be used in other regions, however in Europe we can enjoy these channels without problems, with the above restrictions but without problems for indoor and outdoor use.
In this frequency band we also have a channel with a channel width of 160 MHz, ideal for achieving the best wireless performance.
Channels U-NII-3 or high channels
These are the channels ranging from 149 to 165, these are the channels from 20, 40 and 80 MHz without any restrictions, and they are called high channels because these are the channels that use the highest frequencies in the 5 GHz band.
Here we can see a table of channels distributed by region to better understand all their zonal restrictions:
As you can see, in Europe we can't use much of the spectrum in the 5 GHz band, but at least we have far fewer restrictions than other regions.
Advantages and disadvantages of the 5 GHz band
Advantage
- His speed is very high.
- Having more bandwidth, devices usually do not overlap
- Compatible with most devices as long as they have at least Wi-Fi 4.
Disadvantages of a no deposit bonus
- Low coverage
- Low penetration
Selecting the optimal Wi-Fi channel on the router
In most cases, the router is able to automatically select the fastest option. However, he is not able to cope in all situations. The situation when you need to choose the desired frequency range yourself, as a rule, arises in the following cases:
- At some point, there is a sharp decrease in the speed of the Internet connection.
- There are a large number of different devices using a WiFi connection. They use channels that are chosen at random and interfere with each other.
- If you are using a high-quality and powerful router, but there is no way to connect to it from a distance of several meters.
In all of these cases, the most likely reason is that multiple devices are occupying the same or overlapping frequency slots, which negatively affects the speed of Internet access.
In order to find the least busy channel, you can use one of the specialized applications. There are programs for this that run on a computer, but you can, for example, use an Android application. WiFi Analyzer is suitable for solving this problem.
After launch, you will be able to see a list of available options. In the list shown, a row of stars will be shown next to each of them. The more there are, the higher the quality of communication will be when working on this channel.