Hi all!!!
The Windows operating system has a whole package of standard programs installed that the user is not even aware of. Some programs can be found in the Start menu => All programs => Maintenance or Standard => Utilities or Accessibility. Another part of the programs is accessible only through the command line and the “ Run”
».
How to run the Run Command on Windows7 or where is it located? 1. To open the “Run” command, do the following: Start menu => All programs => Accessories => Run
2. You can open the Run command directly from the Start menu bar
Start menu =>Run
If the Run command is not in the Start menu bar , then you need to enable it. To do this, right-click on the Start menu and select “Properties”:
A new window will open, where in the “Start” Menu tab, click on the “Customize ...” button
check the box next to the item → “Run” command and click “OK”
After this procedure, you will have the “Run” command right in the Start menu bar
3. The fastest way to invoke the Run command is to press the key combination “Win + R”
That's all, all that remains is to enter the desired command in the “Open” field and click “OK”
List of commands that can be called
| Russian element name | English element name | Team |
| Ftp protocol (command line) | Ftp-protocol (command prompt) | ftp |
| Iexpress Wizard (not translated) | Iexpress Wizard | iexpress |
| Internet Explorer | Internet Explorer | iexplore |
| Paint | Paint | mspaint |
| Windows Firewall | Windows Firewall | firewall.cpl |
| Wordpad | Wordpad | write |
| ODBC Data Source Administrator | ODBC Data Source Administrator | odbcad32 |
| Administration | Administrative Tools | control admintools |
| Backup and recovery | Backup and Restore | sdclt |
| Notebook | Notepad | notepad |
| Turn Windows features on or off | Turn Windows features on or off | OptionalFeatures.exe |
| System Restore | System Restore | rstrui |
| Logout | Log Out Of Windows | logoff |
| Date and time | Date and Time | timedate.cpl |
| Disk Defragmenter | Disk Defragmenter | dfrgui |
| Authorization Manager | Authorization Manager | azman.msc |
| Windows Task Manager | Windows Task Manager | taskmgr |
| Driver Verification Manager | Driver Verifier Manager | verifier |
| device Manager | Device Manager | devmgmt.msc |
| device Manager | Device Manager | hdwwiz.cpl |
| Additional hours | Additional Clocks | control timedate.cpl,,1 |
| Shut down Windows | Shut Down Windows | shutdown /s |
| Notes | Sticky Note | StickyNot |
| Windows account database protection | Securing the Windows Account Database | syskey |
| Sound | Sound | mmsys.cpl |
| Sounds (sound scheme) | Sounds (sound theme) | control mmsys.cpl,,2 |
| Sound recording | Sound Recorder | soundrecorder |
| Gaming devices | Game Controllers | joy.cpl |
| Initializing Security Hardware for TPM | Initialize the TMP security hardware | TpmInit |
| Screen color calibration | Display Color Calibration | dccw |
| Calculator | Calculator | calc |
| Command line | Command Prompt | cmd |
| Windows components | Windows Features | OptionalFeatures |
| Management Console (MMC) | Microsoft Management Console | mmc |
| system configuration | System Configuration | msconfig |
| Local security policy | Local Security Policy | secpol.msc |
| Local users and groups | Local Users and Groups | lusrmgr.msc |
| Windows Image Download Wizard | Windows Picture Acquisition Wizard | wiaacmgr |
| Create Share Wizard | Create A Shared Folder Wizard | shrpubw |
| Device Driver Installation Wizard | Driver Package Installer | dpinst |
| Hardware Installation Wizard | Add Hardware Wizard | hdwwiz |
| Volume mixer | Sound Volume | sndvol |
| Resource Monitor | Resource Monitor | resmon |
| Configuring program access and defaults | Set Program Access and Computer Defaults | control appwiz.cpl,,3 |
| Setting up Account Control | User Account Control Settings | UserAccountControlSettings |
| Scissors | Snipping Tool | snippingtool |
| Shared folders | Shared Folders | fsmgmt.msc |
| Disk Cleanup | Disk Cleanup Utility | cleanmgr |
| Control Panel | Control Panel | control |
| Folder "Fonts" | Fonts Folder | fonts |
| Downloads folder | "Downloads" Folder | Downloads |
| Folders settings | Folder Options | control folders |
| Reboot | Restart Windows | shutdown /r |
| Transferring Printers | Printer Migration | PrintBrmUi |
| Pen and touch devices | Pen and Touch | TabletPC.cpl |
| Personalization | Personalization | control desktop |
| Task Scheduler | Task Scheduler | control scheduled tasks |
| Remote Desktop Connection | Remote Desktop Connection | mstsc |
| Getting programs | Get Programs | control appwiz.cpl,,1 |
| Disk check | Check Disk Utility | chkdsk |
| Checking and restoring system files | System File Checker (Scan and Repair) | sfc /scannow |
| File signature verification | File Signature Verification | sigverif |
| Conductor | Windows Explorer | explorer |
| Explorer: C:\ | Windows Explorer: C:\ | \ |
| Explorer: C:\Users\Your_name | Windows Explorer: C:\Users\Your_name | . |
| Explorer: C:\Users\ | Windows Explorer: C:\Users\ | … |
| DiskPart program | Disk Partition Manager | diskpart |
| Programs and components | Programs and Features | appwiz.cpl |
| Event Viewer | Event Viewer | eventvwr.msc |
| Screen resolution | Screen Resolution | desk.cpl |
| Personal Sign Editor | Private Character Editor | eudcedit |
| Local Group Policy Editor | Local Group Policy Editor | gpedit.msc |
| Registry Editor | Registry Editor | regedit |
| Registry Editor | Registry Editor | regedt32 |
| Fax cover page editor | Fax Cover Sheet Editor | fxscover |
| Resulting Policy | Resultant Set of Policy | rsop.msc |
| System Information | System Information | msinfo32 |
| Properties of the system | System Properties | sysdm.cpl |
| System Properties: Advanced | System Properties: Advanced | SystemPropertiesAdvanced |
| System Properties: System Protection | System Properties: System Protection | SystemPropertiesProtection |
| System Properties: Hardware | System Properties: Hardware | SystemPropertiesHardware |
| System Properties: Remote Access | System Properties: Remote | SystemPropertiesRemote |
| Properties: iSCSI Initiator | iSCSI Initiator Properties | iscsicpl |
| Properties: Internet | Internet Properties | inetcpl.cpl |
| Properties: Keyboard | Keyboard Properties | control keyboard |
| Properties: Mouse | Mouse Properties | control mouse |
| Properties: Mouse | Mouse Properties | main.cpl |
| Properties: Mouse: Pointer Options | Mouse Properties: Pointer Options | control main.cpl,,2 |
| Properties: Mouse: Pointers (Scheme) | Mouse Properties: Pointers | control main.cpl,,1 |
| Certificates | Certificates | certmgr.msc |
| Network connections | Network Connections | control netconnections |
| Network connections | Network Connections | ncpa.cpl |
| System Monitor | Performance Monitor | perfmon |
| Indexing Service | Indexing Service | ciadv.msc |
| Component Services | Component Services | dcomcnfg |
| Component Services | Component Services | comexp.msc |
| Program compatibility | Program Compatibility | msdt.exe -id PCWDiagnostic |
| Create a system repair disk | Create a system repair disk | recdisc |
| Nearby users | People Near Me | collab.cpl |
| Saving usernames and passwords | Stored User Names and Passwords | credwiz |
| DirectX Diagnostic Tool | Direct X Troubleshooter | dxdiag |
| Help Desk Diagnostic Tool | Microsoft Support Diagnostic Tool | msdt |
| Digitizer Calibration Tool | Ditilizer Calibration Tool | tabcal |
| ClearType Text Adjuster | ClearType Text Tuner | cttune |
| XPS Viewer | XPS Viewer | xpsrchvw |
| Problem Reproduction Action Recorder | Problem Steps Recorder | psr |
| symbol table | Character Map | charmap |
| Phone and modem | Phone and Modem | telephon.cpl |
| Windows Remote Assistance | Windows Remote Assistance | msra |
| Disk Management | Disk Management | diskmgmt.msc |
| Computer management | Computer Management | compmgmt.msc |
| Print management | Print Management | printmanagement.msc |
| Color management | Color Management | colorcpl |
| Installing or removing interface languages | Install or uninstall display languages | lpksetup |
| Devices and Printers | Devices and Printers | control printers |
| user accounts | User Accounts | Netplwiz |
| Window color and appearance | Window Color and Appearance | control color |
| Windows Mobility Center | Windows Mobility Center | mblctr |
| Support Center | Action Center | wscui.cpl |
| Sync Center | Sync Center | mobsync |
| Accessibility Center | Ease of Access Center | utilman |
| Encrypting File System (EFS) | Encryption File System | rekeywiz |
| Fonts (adding or removing) | Fonts | control fonts |
| Screen (text size) | Display (size of text) | dpiscaling |
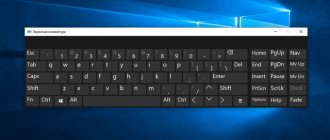
| Screen keyboard | On-Screen Keyboard | osk |
| Magnifier | Magnifier | magnify |
| Narrator | Microsoft Narrator | reporter |
| Power supply | Power Options | powercfg.cpl |
| Power Options: Advanced Options | Power Options: Advanced Settings | control powercfg.cpl,,1 |
| WMI Control | Windows Management Infrastructure | wmimgmt.msc |
| language and regional standards | Region and Language | intl.cpl |
| Region and Language: Optional | Region and Language: Administrative | control intl.cpl,,3 |
| Region and Language: Languages and Keyboards | Region and Language: Keyboards and Languages | control intl.cpl,,2 |
That's all I have for today!!! Good luck to you!
Did you like the post? Help others learn about this article by clicking on the social media button ↓↓↓
Second option with keys
Where is Run in Windows 8? Let's look at the second key combination, which allows you to open the Start menu in this version of the system software. As in the previous case, the specified combination includes the “Windows” button. But the second of them is the English letter “X”. Therefore, the order of issuing the “Run” command in this case is as follows:
- We hold down the key with the Windows logo in the bottom row of the keyboard and, without releasing it, press the English letter “X”.
- In response, the Start menu will appear in the lower right corner of the screen. In it you need to select the item labeled “Run”. After this, the required command will be executed.
What commands are there for the Run menu?
A
C
- calc - calculator
- certmgr.msc - certificates
- charmap - symbol table
- chkdsk - disk check
- ciadv.msc - Indexing Service
- cleanmgr - disk cleaning
- cliconfg - SQL network client program
- cmd - console
- collab.cpl - Neighboring users
- compmgmt.msc - computer management
- control - control panel
- colorcpl — Color management
- control admintools - administration
- control appwiz.cpl,,3 — Setting up program access and defaults
- control appwiz.cpl,,1 - Receiving programs
- control folders - folder properties
- control desktop - Personalization
- control color — Window color and appearance
- control fonts — Fonts (adding or removing)
- control netconnections - network connections
- control intl.cpl,,3—Region and Language: Advanced
- control intl.cpl,,2 - Regional and Language Options: Languages and Keyboards
- control keyboard — Properties: Keyboard
- control mouse — Properties: Mouse
- control main.cpl,,2 - Properties: Mouse: Pointer Options
- control main.cpl,,1 - Properties: Mouse: Pointers (scheme)
- control mmsys.cpl,,2 - Sounds (sound scheme)
- control printers — Devices and printers
- control powercfg.cpl,,1 — Power supply: Additional parameters
- control userpasswords2 – user accounts (whether to require passwords or not)
- control schedtasks – scheduled tasks
- control timedate.cpl,,1 - Additional clocks
- comexp.msc - Component Services
- compmgmt.msc - Computer management
- credwiz - Saving usernames and passwords
- cttune - ClearType text tuner
How to access the Windows 7 menu?
In the Windows 7 menu (Fig. ... Methods for calling the Main Menu:
- click on the Start button in the taskbar;
- key press – Windows>;
- keyboard shortcut +.
Interesting materials:
How to bleach a yellowed blouse? How to bleach yellowed nylon tulle? How to bleach a yellowed sweater? How to bleach a yellowed mink coat? How to bleach yellowed plastic on a refrigerator? How to bleach yellowed soles of white sneakers? How to bleach yellowed soles on sandals? How to bleach yellowed soles on sneakers? How to whiten yellowed soles? How to bleach yellowed sheets?
Methods for calling a tool
Despite the seeming limited options for solving the problem posed in this article, in fact, you can call the “Run” tool in quite a few ways. Let's look at each of them in detail.
Method 1: Hotkeys
The easiest and fastest way to open the Run window is to use hotkeys.
- Type the combination Win+R. If someone doesn’t know where the Win button we need is located, it is located on the left side of the keyboard between the Ctrl and Alt keys. Most often it shows the Windows logo in the form of windows, but it can also have other images.
- After typing the specified combination, the “Run” window will be launched and ready to enter the command.
This method is good for its simplicity and speed. But still, not every user is used to keeping various combinations of “hot” keys in memory. Therefore, for those users who rarely activate “Run”, this option may be inconvenient. In addition, if for some reason the explorer.exe process, which is responsible for the operation of Explorer, was crashed or forcibly terminated, then it will not always be possible to launch the tool we need using the above combination.
Method 2: "Task Manager"
You can also activate “Run” using the “Task Manager”. This method is good because it will work even if Explorer crashes.
- The fastest method to launch Task Manager in Windows 7 is to type Ctrl+Shift+Esc. This option is exactly what is suitable in case of failure of the Explorer. If everything is fine with the built-in file manager and you are used to performing actions not using hot keys, but using more traditional methods, then in this case, right-click (RMB) on the “Taskbar” and select the option "Start Task Manager."
Regardless of which section the “Task Manager” starts in, click on the “File” item. Next, select the “New task (Run...)” option.
Method 3: Start Menu
You can activate “Run” through the “Start” menu.
- Click the Start button and select All Programs.
Navigate to the "Standard" folder.
In the list of standard applications, look for “Run” and click on this name.
How to use the command line
Due to the fact that there are quite a large number of teams, their entire list cannot be displayed in one article. For this reason, we will look at the simplest commands that can be executed without administrator rights. Let's begin.
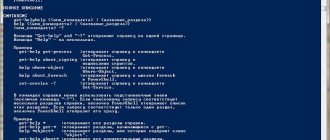
After launching the command line, you will see a window similar to this:
The address line preceding the blinking cursor is the address of the current folder on the hard drive (or on any other connected device). Navigating through folders (changing the current folder) is one of the simplest actions. Let's run this command. To do this, you need to enter the cd command into the window and specify the full path to the name of the folder we need, and then press Enter to start execution. For example, if you want to go to the address “ C:Program Files ”, just enter cd C:”Program Files”
List of Run window commands
To quickly use the “execute” commands, I present the 10 most frequently used ones, which will be difficult to open using other methods. See the table for a brief description.
| What opens | Team |
| registry editor | regedit |
| system configuration settings | msconfig |
| command line (cmd) | cmd |
| group policy editor | gpedit.msc |
| device Manager | devmgmt.msc |
| task manager | taskmgr |
| disk defragmentation | dfrgui |
| system recovery tools | rstrui |
| task Scheduler | taskschd.msc |
| Windows Firewall Control Window | firewall.cpl |
You can download an extended list of “execute” commands here, unzip and place the file, for example, on your desktop. This list should always be at hand, it’s more convenient and you won’t always be able to view it on the Internet if there is no connection.
Ways to solve the problem
You can open the Run window in Windows 8 in the following ways:
- Using a special combination of keys on the keyboard (“Win” and the English letter “R”).
- Using the "Programs" menu.
- Using the combination of the “Win” keys and the English letter “X”.
Each of the above methods will be discussed in detail within the framework of this review material. We will also give recommendations regarding their use in practice.
Using special keyboard shortcuts
The easiest way to open the Run window in Windows 8 is to use key combinations specially reserved for this purpose. This method also works on earlier versions of Microsoft system software. That is, it is universal, unlike those that will be described below. They are tied to the specified OS, and it is impossible to use them on other modifications of Windows.
As with most operations in this version of system software, “Windows” is used as one of the keys (the OS logo is drawn on it) for the “Run” command in Windows 8. Hot keys in this version of the OS are simply tied to it.
The second key is the English letter “R”. In this case, there is no strict connection to the active language. That is, a similar combination can be used when Russian or any other language is enabled. The procedure for launching the “Run” window is as follows: hold down “Windows” and, without releasing it, press the English letter “R”. Then we release them. The window we need immediately appears.
Benefits of the Run command
- Saving effort and time. This dialog is considered a multifunctional tool for significantly speeding up work. Just imagine how much effort it takes to launch the Device Manager window. First, we will open “Start”, go to “Control Panel”, find “System” in the extensive list and then select “Device Manager”. If you don’t know this algorithm at all, it will take a good ten minutes just to find this window.
- Hard to reach commands. There are commands that cannot be detected even with the help of Windows Assistant. This is where the urgent need for the “Run” function appears.
- Fine-tuning the system. It should be noted that this tool provides the user with the opportunity for more detailed and specialized configuration of the system, which is impossible to implement without the “Run” dialog.
- Say goodbye to Start. Finally, you will no longer need to wander through the vastness of the Start menu. All you need is to enter the word into the tool window using the keys.
Why does the average user need the command line?
Surely, each of you has come across various articles on the Internet in which the authors urge you to use one or another command to solve a certain problem. For example, through the command line you can manage files stored on any media, change system operating parameters, or even create an Internet connection . However, the above can be easily accomplished using a regular mouse and keyboard.
Working with the command line in Windows 7 and how to call it
The earliest operating systems did not have the graphical interface familiar to modern users. Previously, only text commands .
However, today, despite the variety of possibilities that provide easy and convenient communication between the user and the PC, they are still used. There are also operating systems that work only by entering text commands into them. They are commonly used by database administrators, programmers, and other IT professionals.
An excellent example of controlling an operating system using text commands is the Windows 7 command line. It is present in any distribution of this OS and can be run on any PC running this operating system. You don't need to be an administrator or any kind of IT specialist to learn how to use it. Let's look at this issue in more detail.