What is the system capacity - pros and cons
Almost most users have seen and heard about this word more than once. On the Internet, programs are always labeled with what system it is intended for - x64 or x32 . But few people know what exactly bitness means.
So, there are two bit depths - 64x and 32x (the latter is also designated 86x, but does not change the essence, it is still the same 32-x).
Let's turn to the great Wikipedia and see a clear definition of bit depth:
depth is the amount of information that can be simultaneously processed by a device or bus.
There is a bit depth not only of the operating system, but also of the processor, data bus, video card, etc.
From the above we can conclude that the higher the bit depth, the better. Unfortunately, this is not always the case. Firstly, each Windows bit level has its own disadvantages, which we will now look at.
Disadvantages of 32 bits
- When using a 32x-bit system or processor, the computer will not be able to use more than 4 GB of RAM. If it costs more, the system simply won’t see it.
- A 32-bit OS only supports programs written for this bit depth. 64-bit applications will not launch.
Disadvantages of 64 bits
- The requirements for a 64-bit system are much greater. It requires more disk space and RAM.
- Inability to find drivers for old equipment.
Now all software and hardware are new and support 64x technology. I don't think anyone still has computers from the 2000s or earlier.
The advantage of 64-bit is that the computer will be able to use more RAM (the maximum amount depends on the system, processor or motherboard). The work efficiency will be slightly higher. Also, 64-bit technology has a system of protection against kernel exploits - the Kernel Patch Protection system.
Additionally
For example, you have installation media, but you don't know what version is installed there. What to do in this case?
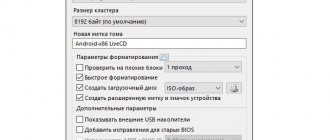
To do this, the DISM command will help us, which will show which editions the distribution contains and help us find out the version number of the Windows 10 distribution.
Mount the image or connect the installation media. Remember the letter of the mounted image or media. For example, this is the letter F:
- Open the distribution, go to the sources folder
- Find the file install. Its extension can be .wim or .esd.
- Launch Command Prompt (as Administrator)
- Depending on the file type (install.wim or install.esd), enter
dism /get-wiminfo /wimfile:Image letter:\sources\install.esd (or .wim)
The window will display information about the image and distribution editions. In the latest distributions, the image includes not only different types of system (x86, x64), but also all editions (Home, Pro, Educational and others).
To get information about the assembly, add /index to the previous command:
You can find out the version number of Windows 10, its release, size, creation date, etc.
How to find out the bitness of the Windows operating system
Let's start with the fact that there are simply a bunch of ways to determine the bitness of an OS. This category includes not only system capabilities, documentation for a computer or laptop, but also various kinds of utilities.
Let's find out which system is currently installed on your computer.
Using System Properties Windows 7 and 10
I have Windows 10 installed, so I will show it as an example. For the “seven” this process is practically no different.
- Open the Computer or This PC directory.
- Right-click on any empty space and go to “Properties”.
- We are looking for the “System Type” item.
I have it listed here as “64-bit operating system, x64 processor.” I note that if you try to install such an OS on an x32 processor, you will encounter failure, but the opposite is possible.
Windows 10 Settings
If you have Windows 10 installed, then here is another way to find out the bitness of the OS. Here's what you need to do:
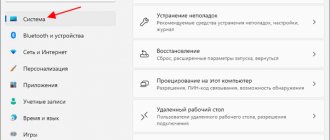
- On the desktop, press the key combination Win+I.
- The “Settings” window will open, where we go to the “System” section.
- In the left column, scroll down and select the “About the system” subsection.
- System and processor bit information will be displayed on the right.
There is also other useful information regarding the current release of Windows.
Using the System Information tool
Any modern Windows operating system has a search feature. In seven it is located in the Start menu, and in ten it is on the taskbar and also in Start.
- Click on search and enter the following phrase “System information”.
- Find the “Type” item.
It will say “x64-based computer” or another value.
In Windows 8, the above points work exactly the same.
How to find out the bitness of Windows XP
If anyone is interested in this, then I’m not too lazy to mention the old lady XP. Yes, it can support both 32 and 64 bits.
- Right-click on the “My Computer” icon.
- Go to Properties.
- A small window will open containing useful information.
- If information about the bit depth is not indicated, then the system is 32-bit, otherwise it will be written 64-Bit Edition.
Using the DirectX Diagnostic Tool
This is also a very simple way to find out the bitness of the Windows system.
- Open the Run window using the Win+R keys.
- Enter the dxdiag .
- The DirectX Diagnostic Tool will open.
- Find the item “Operating system”. Everything is listed there.
AIDA64 program
The AIDA64 utility provides just a ton of information about your computer. To find out information about the bitness of the Windows system, you need to open the “Computer” tab and visit the “Summary information” . On the right, in the “Computer Type” section, it will be indicated on what base it is built.
Approximately the same information is available in the “Operating System” section. On the right there will be an item “OS Kernel Type” . I have "Multiprocessor Free (64-bit)" listed.
To find out the bit size of the processor, open the “Motherboard” tab and select the “CPU” section. Information will be displayed on the right. We are looking for the sub-item “Instruction sets” , where x86, x64 or all together + other sets should be indicated.
Checking your configuration using the Options tool
If you want a basic overview of your PC's configuration, the Settings app can provide a variety of information about your hardware and software. You can also define a performance score.
Follow these steps:
- Right-click the Start menu, then open Settings
- "System".
- "About the program".
On this settings page you can find the exact version of Windows, as well as the build number, which changes every time new updates or feature updates are released (for example, Anniversary Update). You can also see the OS type, processor model, and memory installed in your computer.
How to find out the bit depth of a computer and laptop processor
Everything is quite simple. Firstly, above we considered a method with system properties. The system bit size is indicated there, and the processor bit size is indicated, separated by commas. But there are several other methods that we will now check.
This is interesting: How to find out the number of processor cores
Using the Command Line
To launch the command line in Windows 7, find it in the Start menu - All Programs - Accessories or simply enter “CMD” in the search. For Windows 10, press the Win+X key combination and select the appropriate option. Instead of the command line, PowerShell may be written, if so, use this utility (analogous to the command line).
In the window that opens, write the command – systeminfo .
We are looking for the item “Processors” or “Processor(s)”, opposite which the processor bit capacity will be indicated. But for some reason this designation is not indicated on my HP laptop, for an unknown reason.
Check the processor bit rate in the BIOS
To enter the BIOS from your computer or laptop, you need to know the model of the motherboard / laptop. Next, we find the information using the key that can be used to get there. I have already given the link, so you won’t have to search for long.
- Restart the computer and press the key that is responsible for entering the BIOS (for example, F8, F2, ESC, etc.).
- Typically the information is listed on the Main or Advanced tab.
- The item will most likely be called Processor Type.
Video instruction
y http-equiv=»Content-Type» content=»text/html;″>le=»text-align: justify;»>Well, a video on how to view the release, build, version and bitness (x86 or x64) systems in several simple ways.
Note: If you want to know which version of Windows 10 you need to upgrade from the current 8.1 or 7, the easiest way to do this is by downloading the official Media Creation Tool updater (see How to download the original Windows 10 ISO). In the utility, select “Create installation media for another computer.” In the next window you will see the system version recommended for you (only works for Home and Professional editions).
And maybe this will be interesting:
Which is better to use, 64 or 32 bit system?
We have already discussed the disadvantages and advantages of each system above. Nowadays, a lot of software is written specifically for 64-bit systems. It also uses more than 4 GB of RAM, which is simply necessary for running highly demanding programs.
Simply put, if you only use Word or a similar text editor on your computer and browse the Internet, then a 32-bit system is suitable for you. When working in heavy graphics programs, video editors and gaming, it is better to use 64-bit systems.
Detailed definition of 64 bit and 32 bit processors
Whether your computer's architecture is 32-bit or 64-bit depends on the processor (CPU) of your computer. Most computer processors fall into one of these two categories, but 64-bit systems have replaced 32-bit systems over the past few years. 64-bit processors have more powerful functionality than 32-bit processors because they can store and process more information.
To understand the difference between 32-bit and 64-bit, you need to understand a little about binary computing. We must know that in binary form there are two numbers - 0 or 1. Thus, a 32-bit number has 2³² possible addresses, or 4,294,967,296. By comparison, the capacity of a 64-bit number is 2⁶⁴, or 18,446,744,073,709,551,616. Comparing roughly 4 billion bytes (about 4 gigabytes) with 18 quintillion bytes, or about 18 billion gigabytes or 16 exabytes, shows the very large difference between the two.
What is the difference between x64 and x86?
x86 is a 32-bit architecture. x64 is an architecture corresponding to 64-bit bits.
Interesting materials:
What does lemon balm affect? What week do you go on maternity leave? On what platform is the East European Plain located? To what account are accounts payable written off? To what account are general business expenses written off? For how long is sick leave granted? For what period is the order issued? For what period is the cash balance limit set? For how long are job descriptions approved? For how long is sick leave issued?
Why there are no 128-bit operating systems
Currently, there are 32- and 64-bit processors, operating systems, and programs. Before their appearance, programmers worked with 8- and 16-bit systems. Therefore, it is logical to assume that with the development of technology, new devices and programs with greater bit depth will appear. The logical next step would be 128-bit systems. But does this make sense? Let's figure it out.
Bit capacity in computer science is the number of bits that a device can simultaneously process. Exists:
- The processor bit capacity is the bit capacity of its machine word.
- The data bus width is the operating system width.
- Capacity of programs and applications.
All these concepts overlap and may partially depend on each other. At the lowest level is processor performance.
We must consider several important points related to 128-bit technology:
- Bit depth issues.
- Processor capacity and OS capacity and how they are related to each other.
- The growth of bit depth has happened historically and why it has stopped now.
- Increasing the system bit capacity beyond 64 may currently be of interest only for a narrow range of applied tasks.
As the bit depth increases, the accuracy of the calculations also increases.
128-bit (or higher) architecture is useful for mathematically intensive operations such as graphics, cryptography, complex system modeling, but not for operating systems.
Based on the text above, we can conclude that for the majority of users a system with a 64-bit processor is now sufficient. A 64-bit system provides sufficient computer performance for most professional applications, such as:
- Mathematics
- Physics
- Geodesy
- Cartography
- Cryptography
- Database
64 or even 32 bits are large enough for most practical calculations. A wider memory bus allows for faster loading of instructions and data. However, each instruction also requires more memory and processing power if it uses more bits. A higher operating system bit depth does not directly mean higher speed. Increasing the system capacity, contrary to expectations, does not provide a performance increase in proportion to the increase in capacity. On the contrary, it will slow down due to the need to process longer addresses.
So, 128-bit operating systems won't be coming to your local computer store anytime soon. But perhaps you will be able to work with such a bit OS in 10 years.
128 bit operating systems
In computer science and engineering, 128 bits is used to refer to structures and data types that occupy 128 bits of memory in a computer, or 16 bytes of memory.
In 128-bit computer architectures, all fundamentals such as registers, address buses, or data buses are 128-bit. Researchers described a 128-bit multicomparator in 1976. The design of a central processing unit (CPU) with a 128-bit multicomparator appeared in 1999. Without realizing it, many of us are already using 128-bit modes. Yes, there are no mainstream general purpose processors that can process 16 bytes at a time. However, 128-bit capabilities have been on the general market in limited form for at least fifteen years. In addition, there were experimental and commercial developments even earlier, the most famous modifications being the DEC VAX.
The beginning was made by the “multimedia” instructions MMX/SSE in the late 90s, manipulating 128-bits, although not as a single integer, but divisible by several numbers.
Today, the latest version of the most popular Windows OS will refuse to work on a computer whose processor and motherboard do not support the CMPXCHG16B assembler instruction, which operates on a 128-bit number.
Finally, many supporting technologies in mainstream computers use 16-byte math: memory in video cards, IPv6 addressing, ZFS (zettabyte file system). They will all benefit if central microprocessors move to 128 bits.
Do you need a 128-bit operating system
64-bit programs give programs direct access to about a billion times more memory space than modern PCs. However, even for dedicated supercomputers, this limitation can be overcome by other architectural changes than simply increasing the number of bits.
Most numbers rarely exceed a few million in a typical computer program, much less than 64-bit numbers, which is billions of billions (18,446,744,073,709,551,616). Computer programs also often use what are called floating point numbers, which are fractional numbers. Here the number of bits improves the accuracy. However, floating point bit precision has little to do with operating system bits or memory size.