Often users of a popular operating system encounter an unpleasant problem. Programs begin to freeze, and simple applications open very slowly. When you go to the task manager, you notice that several items with the same names svchost load the processor by 50, or even 100 percent.
When you try to remove a process from the manager, you will either cause yourself even more problems, since most often forcing a service shutdown does not end well, or you will simply receive an error that will warn that the administrator does not have access to perform such operations. This article describes why svchost loads the processor and solutions to the problem for each version of Windows.
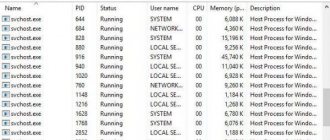
Figure 1. Device Manager window with svhost.exe processes running
- Setting up Windows Update Center
What to do if svchost.exe is loading the processor
The Windows svchost.exe process would hardly have been of particular interest to computer users if its reputation in the heyday of Windows XP, Vista and 7 had not been spoiled by viruses masquerading as this system process. However, a genuine process often brings problems: it can load the processor by 100% and, accordingly, cause terrible slowdown of the computer. Below we will talk about svchost.exe: what it serves, in which cases it can cause the processor to be 100% loaded, and in which cases, being a virus, it can also pose a threat to the computer.
Genuine svchost.exe
The genuine svchost.exe, the Windows host process, is a vital component of the operating system through which important system services are loaded from dynamic link libraries (DLLs). For most of these services, svchost.exe runs as a separate process. Therefore, in the “Details” tab of the Windows 8.1 and 10 task manager, you can detect the activity of several processes at once.
In Windows 7, all active processes can be seen in the Processes tab of the task manager.
Svchost.exe works with updates, Windows Defender, power management, network connections, various devices connected to the computer, and others. In Windows 7 and 8.1 systems, svchost.exe processes are launched under the names “System”, “LOCAL SERVICE” or “Network Service”, and in Windows 10 they can also be launched under the name of the current user. Launched on behalf of the user, it ensures the operation of services responsible for synchronizing mail, calendar, contacts and other data of the account owner.
Why is svchost.exe using 100% CPU?
If we are not talking about constant processor load at 100%, but about individual periods when such a problem occurs, the reason for this may be the execution of background Windows operations. These are, in particular, system updates, automatic maintenance, and indexing of disk contents after reinstalling the system. Low-power processors found in budget or older computer devices are especially vulnerable in this regard. The problem with processor load is solved on its own, respectively, upon completion of the operations. In some cases, you may need to resolve an issue caused by a Windows update installation failure.
Another possible reason for svchost.exe activity with a load on system resources is processor overheating, problems with the hard drive or network card. The computer needs to be cleaned of dust and the hard drive checked for errors. You can exclude or confirm the possibility of damage to the network card by monitoring the activity of svchost.exe with the network cable disconnected.
The reason for the processor load to be 100% may be the incorrect operation of one of the services of the svchost.exe process. This, by the way, often occurs on devices with pirated modified builds of Windows installed. To figure out which of them is causal, you need to track it.
Service Tracking
3.1. Task Manager
You can find out which service is using the CPU in the task manager. Call the context menu on the problematic process and select “Go to services”.
The manager window will switch to the “Services” tab, where they will be highlighted in a block.
In the context menu called on each individual service, Windows 8.1 and 10 systems, in addition to the stop and start commands that Windows 7 is limited to, offer, in particular, a search for information about it on the Internet. On the Internet you can find out what this service is, how problems with it are solved, and if the solution is to disable it, then whether Windows will then be able to function fully. If you need a computer urgently, and there is no time to understand the essence of the problem, you can try to stop the problematic service using the appropriate command in the context menu. If there are several of them, you will have to investigate disabling each one in turn.
Forcibly terminating the svchost.exe process itself in the task manager may result in a blue screen of death. When stopping services, the situation is a little simpler: services that are important for the functioning of the system will not be able to be disabled - either access will be denied, or the service will then start again on its own. Stopped services can then be started using the appropriate command in the context menu, and after rebooting the computer they will start themselves. Some of them, if they do not directly affect the performance of the system, but stopping them in the task manager is impossible, you can try to stop them in the Services snap-in (services.msc). In Windows 8.1 and 10 Task Manager, this snap-in is quickly accessible.
By double-clicking on the desired service, its properties window is called up, in which it is stopped with the button, respectively, “Stop”.
If it is impossible to stop the causative service, you can try to reduce the load on the processor by setting the problematic svchost.exe process to a lower priority in the task manager. In its context menu, you must select “Set priority”, then “Below average” or “Low”. However, such a solution will not be effective in every case.
3.2. AnVir Task Manager program
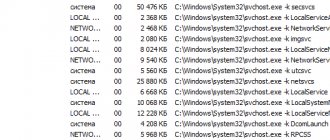
Some may find it more convenient to monitor the services of problematic processes through alternatives to the standard Windows Task Manager. For example, in the AnVir Task Manager program, in the same column of the table with processes, their services are displayed. The description of the service of the selected svchost.exe can be viewed in the block with detailed information, which will appear after double-clicking on the graph of the selected process.
You can go directly to the svchost.exe process services using the program’s context menu by clicking “Go”, then “Go to service”.
And in the context menu for Windows services, you can select either the stopping command “Stop” or “Change startup type”, then “Disabled (Quarantine)” if stopping is impossible. Here, in the context menu for each individual service, you can get online help.
Any kind of experiments with disabling services - either through the standard functionality of Windows or using third-party programs - is best carried out by first creating a system restore point.
Universal Windows troubleshooters
If you do not treat the symptoms, but deal with the problem itself, universal tools for troubleshooting Windows errors, such as disk cleanup, cleaning the system registry, checking the integrity of system files (sfc/scannow), can help. And Windows Clean Boot mode will help determine whether the svchost.exe activity that is loading the processor is actually related to system services. Third party software services may be causing the problem.
Viruses masquerading as svchost.exe
Today, false processes svchost.exe are much less common than in the days of Windows XP, Vista and 7. Virus writers can disguise their malicious programs as it, replacing in the process name, for example, the letter “o” with a zero, the letter “t” with a one, playing with combinations of replacing Latin with Cyrillic, adding some extra characters to the original version of the name. It may be that svchost.exe itself is a genuine process, but its activity, which loads system resources, is associated with a virus that has entered the system. Viruses masquerading as svchost.exe can load not only the processor, but also the disk and RAM, actively absorb Internet traffic, and periodically disconnect the Internet and local network connections. False svchost.exe processes have other signs of the presence of malware in the system - advertising on websites, opening unsolicited web pages in the browser, changing Windows settings, etc. The falsity of svchost.exe can be indicated by the location of the process executable file in a path other than C: \Windows\System32 and C:\Windows\SysWOW64. You can find out the location of the process file in the Windows task manager, in the context menu of each instance of svchost.exe.
In the AnVir Task Manager program, the path to the location of the svchost.exe files is indicated in the “Executable file” table column. In addition, AnVir Task Manager contains a separate column with an indicator of the so-called risk level - the verdict of the program creators, based on behavioral analysis of processes.
AnVir Task Manager works in conjunction with Google’s web service Virustotal.Com, where each active process can be checked directly from the program interface using the “Check on site” context menu option.
The problem with the false svchost.exe process is solved in a universal way for all types of malware - scanning the computer with an antivirus with regularly updated databases and an additional scan using an antivirus utility from another developer (with excellent databases).
WindowsTips.ru
Viruses
True, problems with processes are often the result of infection of the operating system with various viruses. In this case, you will have to permanently disinfect your computer. This is the only way to make the system work. Please note that computer infections are often encrypted under Svchost.exe. It runs as the user, not as System.
You will need to scan your computer with an antivirus and cure everything. Delete anything that cannot be treated. Now clean your computer's registry (CCleaner will help with this) and reboot. That's all the problems are solved. But often a complete reinstallation of the computer is necessary. Only in this case can we hope to eliminate all problems.
Windows 10 - Restore Svchost behavior like previous versions of Windows
In Windows 10 Update Creators, there are many svchost.exe processes running. If you open the Details tab in Windows 10 Creators Update Task Manager, you will be surprised to see a huge number of instances of the svchost.exe process.
Windows has always boasted an abundance of running svchost.exe processes, but in Windows 10, there are many more of them than in previous versions of the operating system, like Windows 7 and Windows 8.1. This happens because the Svchost.exe (host service) executable file is used to run various system services. Each instance groups specific services.
According to Microsoft, this service management model reduces memory consumption.
Starting with Windows 10 Creators Update, services are no longer grouped if your PC has enough memory. Now, for each service, a special process svchost.exe is launched. This dramatically increases the number of svchost.exe processes.
Today we will look at how to configure SVCHOST process grouping in Windows 10 Creators Update. This can be done using the registry.
Grouping Svchost in Windows 10 Creators Update.
To set the Svhost grouping threshold in Windows 10, follow these steps.
Open Registry Editor. Go to the following registry key:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control
Here, create a new or modify an existing 32-bit DWORD value named SvcHostSplitThresholdInKB and change the data value from 380000 to a value equal to or just above the total RAM in kilobytes (KB). ***Svchost Split Default value
Enter a new value in decimal notation. For example, if you have 8 GB of RAM, you would enter the value 8388608 (8 GB = 8192 MB or 83.88.608 kilobytes).
- 6 GB RAM - value 6291456
- 4 GB RAM - value 4194304
- 2 GB RAM - value 2097152
Note: Even if you are running a 64-bit version of Windows 10, you still need to use the 32-bit DWORD value.
Restart Windows 10.
g-ek.com
Waste of RAM: does this really happen?
There is little point in using a pure OS, which has a very meager software arsenal. However, even those who are accustomed to being content with the standard set of built-in Windows tools and do not know that electronics need systematic prevention, there will inevitably come a time when system resources run out and the OS turns into a kind of “turtle”, weighed down by various “digital garbage”.
In the case when a user believes that the physical volume of his RAM is “immense”, that is, more than fits into the system requirements of the version of Windows being used, he is, to put it mildly, mistaken! Since even 32 GB of RAM will not save the OS from slowdowns, which the user himself initiates with his inept actions, ignoring the main question “”.
However, let’s return to the essence of our story, namely, let’s talk about what should be done when you suddenly discovered an “insatiable eater” of RAM in the form of the “Svchost.exe” process, which, among other things, has “HELPERS” of the same name, albeit with less "obvious appetite" in the "Task Manager" window?
Svchost.exe LocalSystemNetworkRestricted is loading the hard drive solution
Particularly curious users when working with Windows can observe the following picture - the Svchost.exe (LocalSystemNetworkRestricted) process heavily loads the hard drive or RAM. Under such a load, the computer can noticeably slow down, and the percentage of memory consumption by this service reaches 50%. For users with a small amount of RAM, this is a big problem. We will figure out what Local System Network Restricted is and how problems with it are solved.
What is this process
The Svchost service itself is a kind of collection that combines a group of other processes. Problems with overloading the Svchost.exe process (LocalSystemNetworkRestricted) can be caused by various reasons - starting Windows update services, failure to connect to servers, system bugs, problems with third-party programs. Often the source of the load is the presence of viruses on the PC. In Windows 10, this process is labeled "Local System Service Host".
Load due to Svchost.exe (LocalSystemNetworkRestricted)
How to disable this process
Simply closing the process itself will not work; it includes several others, and will be constantly activated when Windows boots. Disabling everything one by one is also tedious work. We have collected some practical tips that, if applied, will reduce the load on the system.
- Check the list of active tasks in this Svchost.exe, the user description should only indicate System, NETWORK and LOCAL SERVICE. These files should be located in System32 or SysWOW64. Everything else can be regarded as viruses, and if you have them, then it is better to stop them, and Windows should be urgently scanned for viruses. Use both a pre-installed antivirus and a scanner (AdwCleaner, Dr. Web Cureit!, etc.).
- For more experienced users, I recommend using Process Explorer.
With its help, you can accurately determine many parameters for individual services and their components (load share, location, shutdown commands, etc.). Find out more about its use on the Internet. Process Explorer - You should also disable one of the most problematic services, Windows Update ().
It loads the user at every convenient opportunity. In Windows 7, this is convenient to do through the control panel, and in the top ten, open the list of services. Disable Windows Update service - The same should be done with the Superfetch service. This is a performance improvement application that often only loads the PC.
- It is also advisable to clean and search for problems in the system. Launch the command line (as an administrator) and run two commands in turn: DISM.exe /Online /Cleanup-image /Restorehealth and sfc /scannow. Such operations are very effective in the top ten.
- You should not exclude the possibility of the influence of third-party programs and their background processes. In this case, it is worth checking the stability of the computer with a clean start. If the OS will work without overloads, then remove everything unnecessary. Here is a video instruction on how to download this mode. For seven and ten the process is the same.
Conclusion
The Svchost.exe (LocalSystemNetworkRestricted) service can be a big problem when you have a small amount of RAM. If slowdowns due to Network Restricted begin after starting the PC and continue for some time, then pay more attention to the third point.
talkdevice.ru
Process monitoring: analysis of indicators and the right decision
As mentioned above, the “Svchost.exe” process can be used by various Windows services. Therefore, do not be surprised if in the “Processes” column you see several processes of the same name. When using the Internet and simultaneously using several resource-intensive programs, this fact is the norm.
A deviation can only be considered a discrepancy between the name of the process we are describing (viruses often disguise themselves as “Svchost.exe” by adding various symbols to the process name, or, on the contrary, abbreviating the “character original”). Also a cause for concern is the “fake path” entry (location, directory of the executable file must match the value: windows\system32). Pay attention on whose behalf the process was launched. If “Svchost.exe” is not launched by the system, then it’s time to sound the alarm - it’s a virus (for more details, read)!
Svchost.exe loads windows memory | quick solution to the problem
Programs freeze, the computer slows down, applications do not respond. Almost every PC user has encountered similar problems and still does. There are a huge number of reasons for this, but today we will talk about the svchost.exe file, which consumes most of the computer’s resources.
We will tell you what processes are associated with this file, why it loads the system so much and how to deal with it correctly.
Description of svchost.exe
A similar problem appeared quite a long time ago, but there is still no resource on the Internet that would describe all the nuances and methods of combating it. This article will focus on the solution on Windows 7.
It's worth starting with the fact that svchost.exe is a system process. It should be located at: C:\Windows\System32\
Checking the location of an application called svchost.exe is not difficult at all, just go to the task manager (Ctrl+Alt+Delete – Task Manager), find a process with this name that consumes a lot of RAM, right-click and select “Open location” file storage. The process will be displayed in the manager only if you have the “Display processes of all users” checkbox checked. In the Explorer window, you will see the file and the folder in which it is located.
If the location of the file differs from the above, then we can say with 95% probability that it is a virus, but in this case it can be defeated either by simple deletion or by using a normal antivirus. You should also pay attention to the name. An application can also be considered a virus if it looks like: svch0st.exe, svchost.exe (where “s” and “o” are written in Russian), etc. Another factor that helps determine the authenticity of a file is the username specified in the task manager.
Valid names:
- System
- LOCAL SERVICE
- NETWORK SERVICE
By the way, don’t be alarmed by the fact that there are so many copies of svchost.exe displayed in the task manager. This program is designed to work with various applications that use dll libraries, respectively, sometimes it is very difficult for many programs to use one svchost.exe and its copies are launched, but with different identification numbers.
Disabling Windows 7 Update
So what should you do if, after checking, svchost.exe was not suspected as a malicious file or virus?
The solution turned out to be very simple. By default, every Windows 7 user automatically searches for updates and installs them. Despite choosing the search and installation period, the OS still constantly searches for them, which in some cases leads to a similar problem. On my personal computer, with 4 GB of RAM, only 300 MB were free, svchost.exe consumed 2.5 GB.
To disable updates, you must complete the following steps:
- Go to the “Start” menu - “Control Panel” - “Windows Update” - “Customize settings”;
- Select "Don't check for updates."
Disable the hidden Windows Update feature
It would seem that this is where the story should end, but despite the importance and necessity of these actions, svchost.exe will still consume RAM, since this is not enough to completely disable updates. To finally solve the problem, it is necessary to perform several more actions, namely:
- “Control Panel” - “Administration” - “Services” - “Update Center”;
- In the “Launch type” section, put “Disabled” - “Apply”.
After this, you need to restart your computer. When the system boots, open the task manager and you will see that the svchost.exe process is now consuming a small amount of RAM. If you need to update the system, you can turn on the options described above, and after the update, turn them off again using the same scheme.
voron-xak.ru
Clear Event Viewer logs to fix Svchost process
1. Search for “Event Viewer” using the search box located in the left corner of your system screen and launch the application.
2. In the Event Viewer, click on Windows Logs located in the left sidebar.
3. Once you expand this item, click on “Application”.
4. Now on the right side of the log, in the “Actions” window, click on “Clear log...”, as shown in the picture.
5. When the pop-up menu appears on the screen, click “Clear”.
6. Perform the above step with Security, Installation, System, and Routed Events logs.
7. Restart your computer.
♥ ON TOPIC: How to make Windows 10 look like Windows 7.
Svchost.exe loads the processor and memory at 100%. Virus or not?!
In all versions of Windows without exception, from XP to Windows 10, there is a special service process - svchost.exe. Its full name is Generic Host Process for Win32 Services or, in the latest versions of the OS, Host Process for Windows Services. From the name it is clear that the main role is a kind of universal platform for executing various services in the system. For example, Windows Defender, font service, DNS, SSDP, etc. That is why, when you open the task manager, you can find several svchost lines there at once. And that's completely normal. But various virus writers could not ignore this versatility, disguising malicious executable files as this process, and sometimes simply using it again as a platform for the operation of their virus. A couple of years ago, a similar infection was common. Sometimes even for more experienced users.
So, one fine day your computer started to slow down a lot. You opened the Task Manager and saw that the svchost.exe process is loading Windows to the maximum (the processor and memory can be loaded up to 100%). What to do and how to determine whether it is a virus or not? Let's figure it out together.
Let's start by simply opening the task manager and looking very carefully at the name of the executable file - svchost.exe. It should be called exactly as I wrote. If a virus is disguised as a Generic Host Process, then usually its executable file is named, although very similar, but you can still see the difference - it is lost or, on the contrary, one or more characters have been added to the name. Examples: svchosts.exe svchost32.exe or svchosts32.exe svhost.exe svshost.exe svch0st.exe - zero sign instead of o svcchost.exe
Here's a good example:
The second sign by which you can recognize a virus is the location of the file. The executable file svchost.exe is located in the system directory:
C:\Windows\System32 - for 32-bit systems C:\Windows\SysWOW64 - for Windows x64
In some cases, copies of the file may be located in the following directories: C:\WINDOWS\ServicePackFiles\i386 - usually in Windows 7 after installing the SP1 service pack C:\WINDOWS\winsxs\ - directory with service update files C:\WINDOWS\Prefetch\ — data about programs launched at system startup is stored here. If any other folder is used, as in the screenshot above, it is a virus. Ok, we have decided on the name and location in the system. But what if everything seems to be correct, but the process loads Windows to the fullest. Then you need to look for the culprit in services that use svchost for their work.
Then there, in the Task Manager, right-click on the “svhost” task and select “Go to services”:
A list of services will open. It will highlight those that use the Generic Host Process platform:
Right-click on each of them in turn, select “Stop” from the menu and look at the result.
Attention: keep in mind that by killing a system service, you may disrupt the operation of Windows and will have to reboot.
The same can be done through the Windows command line. To do this, press the Win+R key combination and enter the CMD command in the Run window. Click on “OK”. This way we will launch the Windows command line. Enter the command:
tasklist/svc
And let's look at which services use Host Process for their work:
Pay attention to those lines with svchost.exe where one service is specified. If there are 3 or more of them, we skip them, these are system services with a probability of 99.99%. Then, one by one, we try to end such single processes with the command:
taskkill /F /PID
Example:
taskkill /F /PID 1868
The result should be the message "Success: Process completed."
Thus, through experience, we will be able to find the culprit and the main devourer of system resources and disable it. Now you need to check the system disk with a good antivirus program - DrWeb CureIT or Kaspersky Antivirus for the presence of infection.
Attention! The steps described above assume that you have some experience with Windows operating systems. For inexperienced and novice users, I advise you to immediately proceed to scanning the system with an antivirus program.
Also, I would strongly recommend scanning Windows with the excellent free utility ADWCleaner in order to remove possible adware or spyware modules.
As a rule, after all these steps the problem is successfully resolved.
PS As a postscript, I can’t help but mention the option of a system service failure, after which it can also lead to svchost loading the processor and memory to the maximum. In this case, you should try to roll back the system to an earlier state. If this does not help, then there is only one way out - a complete reinstallation of the operating system.
nastroisam.ru
Reboot
The first scenario is a banal reboot of the computer. This is very important if you haven’t turned off the operating system for a long time. In this case, your memory will be filled not only with Svchost.exe netsvcs, but also with other functions that are important for work. Alternatively, you may simply have experienced a minor system glitch. It does not pose a danger to the data, but it does have a significant impact on the performance of the computer and its memory.
It is in this situation that the most common reboot will help. A complete system restart will occur, after which you will be able to work normally. This is how many users struggle with the problem. But this only helps in the listed cases. If the problem that Svchost.exe netsvcs loads the memory of Windows 7 lies elsewhere, then a different approach is needed to eliminate the “hot spot”. Which one?
So, how do you get rid of the problem where the host process is loading Windows? I recommend doing the following:
- Install all necessary updates for your OS. If there is a chance that the system is installing the necessary updates, then simply wait until the end of the installation process;
- If after a few hours nothing has changed, then restart your computer, if the problem is random, then it will disappear;
- Try to shut down the problematic svchost.exe process yourself. Launch the task manager, go to the “Processes” tab, right-click on the problematic (costly) process and select “End process tree”;
Completing the process tree
Registry
Download and install an application called CCleaner. Run it, and then configure it - in the scan, mark all hard drive partitions, browsers, and the computer registry. Now on the right side of the window, click on “Analysis”, and then on “Cleaning”. Wait a few seconds - the computer's registry will be cleared. As a result, the Svchost.exe netsvcs process will no longer load the system. In addition, you will have free space on your hard drive. True, cases when our process brings a lot of trouble due to the computer’s registry are quite rare. Often you have to fix the problem in other ways.