If you're seeing a lot of svchost.exe items hogging your CPU, you're not alone. Many Windows 10 users are reporting this issue. Don't worry, this can be fixed. Here are 4 fixes to help you sort it out.
What is svchost.exe?
According to Microsoft, svchost.exe is:
"shared host process. name for services that are launched from dynamic link libraries."
Simply put, it is a legitimate Windows process while performing a specific Windows operation. But in some cases, you may see the svchost.exe consuming CPU or memory resources in the Task Manager for no apparent reason.
How to fix it?
Here are 4 solutions you can try. You may not have to try them all; just work your way down until you find the one that suits you.
1: Scan your computer for viruses
2: disable certain svchost.exe services
3: Empty Event Viewer Log
4: Troubleshooting Windows Updates
Why are there several svchost.exe processes on the system?
Precisely because many services operate simultaneously.
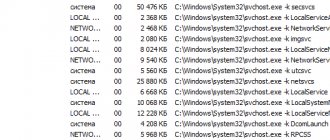
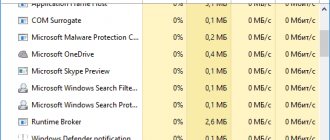
Multiple svchost.exe processes
If the processes are not displayed, in the task manager, click the “Show processes of all users” button, because all these processes run on behalf of other users (for example, “NT_AUTHORITY\system”). And also pay attention to the command line from which the process was launched - there is a full path there. If there is something different from \Windows\System32\svchost.exe, this is a reason to pay more attention to such a process, because Various malicious software is often disguised as this process.
PS If you don’t see the “command line” or other column, click on the “View -> Select Columns” menu and check the necessary boxes next to the column names.
3: Empty Event Viewer log
Large log files in Windows Event Viewer can cause excessive CPU or memory usage. To fix this, you can clear the Event Viewer log:
1) On your keyboard, press the Windows and press R , then type eventvwr and press Enter .
2) On the left side of the panel, click Application under Windows Logs . On the right side of the panel, click Clear History ....
3) Repeat the same procedures to clear the Security, Setup and System .
4) After this, restart your computer.
Is svchost.exe a virus or not?
Let's do this, below there will be a series of questions - if you answered “no” to any of them, then you should pay close attention. And the more such answers, the more attention needs to be paid.
- Can you launch Task Manager and go to the Processes tab?
- Do you see multiple svchost.exe processes when displaying all user processes?
- The names of all these processes look the same (exactly “svchost.exe” without any “0” instead of “o”, etc.)?
- Are their launch parameters similar? “-k LocalService” or something like that...
- Are all processes running from the same directory? “\Windows\system32\” by default.
- Are all svchost.exe processes running under system accounts?
svchost virus or not
Of course, these are not all possible cases, but most Trojans can be weeded out this way. Go ahead.
Equipment setup
In all versions of Windows without exception, from XP to Windows 10, there is a special service process - svchost.exe . Its full name is Generic Host Process for Win32 Services or, in the latest versions of the OS, Host Process for Windows Services. From the name it is clear that the main role is a kind of universal platform for executing various services in the system. For example, Windows Defender, font service, DNS, SSDP, etc. That is why, when you open the task manager, you can find several svchost lines there at once. And that's completely normal. But various virus writers could not ignore this versatility, disguising malicious executable files as this process, and sometimes simply using it again as a platform for the operation of their virus. A couple of years ago, a similar infection was common. Sometimes even for more experienced users. So, one fine day your computer started to slow down a lot. You opened the Task Manager and saw that the svchost.exe process is loading Windows to the maximum (the processor and memory can be loaded up to 100%). What to do and how to determine whether it is a virus or not? Let's figure it out together.
Let's start by simply opening the task manager and looking very carefully at the name of the executable file - svchost.exe. It should be called exactly as I wrote. If a virus is disguised as a Generic Host Process, then usually its executable file is named, although very similar, but you can still see the difference - it is lost or, on the contrary, one or more characters have been added to the name. Examples: svchosts.exe svchost32.exe or svchosts32.exe svhost.exe svshost.exe svch0st.exe - zero sign instead of o svcchost.exe
Here's a good example:
The second sign by which you can recognize a virus is the location of the file. The executable file svchost.exe is located in the system directory:
C:\Windows\System32 - for 32-bit systems C:\Windows\SysWOW64 - for Windows x64
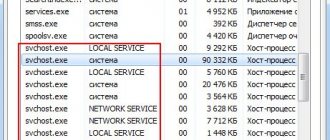
In some cases, copies of the file may be located in the following directories: C:\WINDOWS\ServicePackFiles\i386 - usually in Windows 7 after installing the SP1 service pack C:\WINDOWS\winsxs\ - directory with service update files C:\WINDOWS\Prefetch\ — data about programs launched at system startup is stored here. If any other folder is used, as in the screenshot above, it is a virus. Ok, we have decided on the name and location in the system. But what if everything seems to be correct, but the process loads Windows to the fullest. Then you need to look for the culprit in services that use svchost for their work. Then there, in the Task Manager, right-click on the “svhost” task and select “Go to services”:
A list of services will open. It will highlight those that use the Generic Host Process platform:
Right-click on each of them in turn, select “Stop” from the menu and look at the result.
Attention: keep in mind that by killing a system service, you may disrupt the operation of Windows and will have to reboot.
The same can be done through the Windows command line. CMD in the Run window . Click on “OK”. This way we will launch the Windows command line. Enter the command:
tasklist/svc
And let's look at which services use Host Process for their work:
Pay attention to those lines with svchost.exe where one service is specified. If there are 3 or more of them, we skip them, these are system services with a probability of 99.99%. Then, one by one, we try to end such single processes with the command:
taskkill /F /PID <
er:
taskkill /F /PID 1868
The result should be the message "Success: Process completed."
Thus, through experience, we will be able to find the culprit and the main devourer of system resources and disable it. Now you need to check the system disk with a good antivirus program - DrWeb CureIT or Kaspersky Antivirus for the presence of infection.
Attention! The steps described above assume that you have some experience with Windows operating systems. For inexperienced and novice users, I advise you to immediately proceed to scanning the system with an antivirus program.
Also, I would strongly recommend scanning Windows with the excellent free utility ADWCleaner in order to remove possible adware or spyware modules.
As a rule, after all these steps the problem is successfully resolved.
PS As a postscript, I can’t help but mention the option of a system service failure, after which it can also lead to svchost loading the processor and memory to the maximum. In this case, you should try to roll back the system to an earlier state. If this does not help, then there is only one way out - a complete reinstallation of the operating system.
svchost.exe is using up CPU or memory
This is a very common problem. And the course of action here is very interesting.
- You need to determine the name of the service that consumes system resources. So, let's go step by step. For Windows 7, you need to display the process “Process ID” or “pID” - will display the process identifier in the task manager so that you can uniquely identify and distinguish one svchost.exe from another. For Windows 8, for example, in the manager all processes are already grouped by PIDs.
Processes are grouped by PID - We remember the PID and for Windows 7 go to the “Services” tab.
Services by PID of processes
There we sort by PID and look for our ill-fated PID, study the list of services... - If you don’t need the service, you can safely disable it. If necessary, try setting it up. The age-old question “Which services are needed and which can be safely disabled?” – There are a million instructions on the Internet, my answer is – if you are firmly convinced that you don’t need it – stop, work. Make a note of what you disabled. All configurations are different, someone working without a network at all can turn off a lot. Someone without a printer, file search, design - turns off the other. From my personal experience, the computer began to breathe more freely when I disabled the update service, firewall, Windows Defender (since I use a third-party antivirus solution), indexing service and themes. You can also safely disable others, but it’s better to read the corresponding manuals. The list of services is not so large - you only need to look at those that relate to a given process, which consumes a lot of resources.
- PROFIT. That's all.
Practice has shown that such optimization is quite effective. Well, some services can not be disabled, but switched to manual start.
Disable BITS (Background Intelligent Transfer Service)
You can resolve the high network load issue caused by svchost.exe by disabling BITS (Background Intelligent Transfer Service). It is a native Windows service that helps your system receive and install automatic updates. This service requires network resources to check for new updates and download their files directly to your system. If you can live without automatic updates, we recommend that you try disabling this service, at least for experimental purposes. If you ever want to reactivate this service, you can easily do so.
To disable BITS:
- Press Windows Key + R buttons simultaneously, paste services.msc and press Enter .
- Now you can see the entire list of services that are on your PC. Look for a service called Background Intelligent Transfer Service .
- Right-click and select Properties . Then change the value next to Startup Type to Disabled .
- Click on the Stop button to stop the service.
- Finally, click Apply and OK to save the changes.
You should now see a clear difference in your network usage. If nothing has changed, try rebooting your system to be sure.
Viruses masquerading as svchost
Shost is a process that is very often exposed to viruses and Trojans. Virus software developers “disguise” their Trojans, and when we try to find an unwanted file, we encounter a fake process.
Detecting a virus may seem like a difficult task, but in reality everything is simple. To distinguish a virus from a real program, you need to look at who started the process. We go to the dispatcher. The “User” column displays the addresses of the files that are opened and controlled by svchost. Opposite each line the svhost should be:
- SYSTEM.
- LOCAL.
- NETWORK SERVICES.
If the column contains one of the items above, don’t worry, it’s not a virus. The fact is that the svhost is launched only by the system. Even though we know for sure whether the process is infected, for safety reasons it is still better to scan the entire computer.
If instead of SYSTEMS, LOCAL or NETWORK there is “User” or any other names, we scan the system (Figure 3). You most likely will not have to remove programs, but individual suspicious folders and files should be scanned by an antivirus program.
Also, we can go to the msconfig path by entering this command in “Run”. There should be nothing similar to this process in Autoload.
If you notice folders of the following types: “Net-Worm.Win32.Welchia.a”, “Trojan-Clicker.Win32.Delf.cn” or similar - check them and delete them VIA ANTI-VIRUS. Our website has a wide selection of different antivirus programs.
Figure 3. Device Manager window for searching for viruses masquerading as svchostk
Main conclusions
Thus, when the svchost process loads Windows 7 memory, the solution in more than 90% of cases is right on this page. From my own experience I can say that most often the culprit is:
- Viral activity;
- Hard drive problems.
The rest is everything I listed above. But there are also reasons among hardware malfunctions of other equipment. Only here everything is much more difficult to calculate and the situation must be analyzed individually.
You can write to me in the comments below and we will try to solve the problem together. If I helped you, please also write a comment indicating the solution method. Or perhaps you have already dealt with the svchost problem yourself in some other way. It will be interesting and extremely useful for me to learn about other options and I will be grateful if you share it here with me and other readers