5
(2)
Inexperienced users don't come across Task Manager very often, but this system utility is actually very useful. For example, through it you can close a frozen process or see which program is so zealously “biting off” RAM and laying claim to processor resources, or find out the IP address of a computer on the local network. Today we’ll talk about how exactly you can open the dispatcher. There are many ways - we will try to consider them all.
Using keyboard shortcuts
First, let's talk about what “hot keys” or “hotkeys” are, which are often mentioned in instructions. This term may be unclear to inexperienced users.
“Hot” are standard keyboard shortcuts. They were named that way because of their frequent use. The combinations can be either general, i.e. act both in system applications and in application applications, as well as specific ones, working in a specific program. In this case, we are talking about a combination that always works in Windows, regardless of the type of program running and the type of device - PC or laptop.
When using “hot” combinations, the buttons must be pressed simultaneously! This is the main condition, since otherwise the combination may not work, or will lead to a result different from what was originally expected!
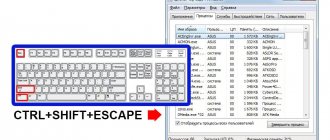
Ctrl + Shift + Esc
Everything is very simple. Press and hold the keys indicated in the title.
After this, you can look at the task manager window.
More experienced users can immediately ask a completely logical question: “Why use this particular combination at all - after all, it’s much more common to use Ctrl + Alt + Del”?!
It’s simple - this combination is universal, and works not only in the case of a “physical” machine, but also in the case of a virtual machine.
For reference: “virtual” is a system that runs in the “parent” OS in a separate window. You can come up with many scenarios for its use - for example, on a virtual machine they often test potentially suspicious applications that are undesirable to run in a working environment.
The same combination works when working with a remote desktop. This is the name of a special access mode in which the user can use the resources of a remote device by working with it directly.
In a word, if you always want to launch the dispatcher in any situation, it won’t hurt to learn the combinations of these three keys.
Ctrl + Alt + Del
The most common and well-known combination, a sort of “holy trinity” of every self-respecting Windows user.
After pressing these buttons simultaneously, the same “Dispatcher” will appear in front of the user. But... Not in all cases. If you try to use this method in the OS, starting from Windows 8 onwards, you will see something not quite familiar...
But if you look closely, you can see an item with the desired name below.
To launch the Manager, you just need to left-click on it.
Or you can simply use the combination Ctrl + Shift + Esc suggested above. Well, or continue reading the article further, because hotkeys are far from the only way to launch this application! Although you will agree that they are very convenient to use, for this case we have an article about hot keys in Windows 10.
What is it for?
In general, the question arises: why does the average user need to know how to work with the task manager?
Task Manager is a standalone program installed by default in any version of Windows. The manager is needed to view processes, services and programs running in the system, and manage them (restart or close unstable system elements).
To put it simply, you can see what is “loading” your device’s processor and forcefully stop the program.
More experienced users also use the task manager to analyze the distribution of system resources between processes and services.
Video: how to configure task manager on Windows 7
The video describes the basic techniques for working with the task manager. For those who do not have the opportunity to view it, we will describe all this below.
What operations with processes and services are available
So, we found and opened the task manager. What's next?
We see 6 tabs in the window, but most often the user accesses the first two.
In the manager window we see 6 tabs
The first tab displays a list of currently running applications. In the "Status" column you can check whether the application is running. In case of problems, the “Not responding” entry appears. As you can see, the user has 3 actions available: “Cancel task”, “Switch” and “New task”. The “End task” button forcibly stops the application, the “Switch” button switches it to the active state and redirects the window of the selected utility to the foreground. And finally, “New task...” allows you to create a new process.
The Processes tab provides information about running processes and allows you to force them to terminate if necessary.
The remaining tabs, as a rule, are not needed by the average user.
When there are many processes
What should you do if you think there are too many processes in the Task Manager window?
The more applications are installed on your computer, the more entries there will be in the manager window. Too many tasks often overload the processor and cause the computer to freeze. To reduce the running list, most of the processes can be stopped, but some should not be touched.
Basically, in the application manager, all processes are divided into system and user. Which of the two groups the process belongs to can be seen in the “User” column. In the future, we advise you to perform all operations only with non-system processes in order to avoid malfunctions in Windows.
Unnecessary processes
Let's give an example of tasks the deletion of which will be painless for your system.
| Process name | Process description |
| AdobeARM | Adobe Software Updates |
| Juiced | Java Utilities Updates |
| Hkcmd | Process accompanying Intel hardware |
| NeroCheck | Process for finding conflicting drivers |
| RaVCpl64 | Audio manager for Realtek card |
| Nwiz | NVIDIA NView support |
Again, these are just examples of processes. They may or may not be on your computer. It all depends on the configuration of your equipment.
Using the taskbar
Perhaps a real lifesaver for inexperienced users, allowing them to call the dispatcher without using any keyboard shortcuts at all. You just need to move the mouse cursor to the panel, right-click over it and select the appropriate item in the context window that appears.
In the "seven" everything looks similar.
Everything ingenious is simple! But there are situations when the taskbar is jam-packed with open application windows, and there is basically no free space on it. In this case, such a simple and convenient method may not work. But, as you might have guessed, there will still be a solution!
Using “Windows Search”
Everything is very simple. In Windows 10, there is a magnifying glass icon near the Start button. Click on it, and in the input field that appears, we begin to write “Dispatcher...”. Since the search system in the “top ten” is really “smart”, it will quickly suggest the desired option. All you have to do is left-click on the appropriate item. And by the way, the search can be changed; read about this in the article on how to remove search in Windows 10.
In Windows 8/8.1 everything is similar, but in Windows 7 it’s a little different. Click on the “Start” button and find the input field.
In it, enter “Dispatcher” again, after which we click on the appropriate item with the left mouse button.
In this case, the required item is called “View running processes in the task manager.”
Still, searching in the top ten is much more intelligent - this is one of the clear advantages of this system.
However, this is not relevant to the point, and we continue to analyze ways to launch the “Dispatcher”.
Option #2. The most common
This is the fastest and most universal way. It works anytime, anywhere, which is why everyone loves it so much. I use this method myself all the time and recommend it to you.
- Press the keys together on your keyboard “Ctrl+Alt+Delete”».
- Click on the “Launch Task Manager” button».
Standard utility “Run”
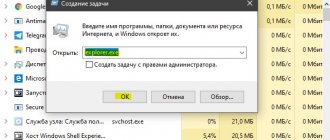
If you are not yet tired of flexing your fingers on the “hot keys”, you can use the combination of the Win and R buttons (the latter button will work regardless of the layout).
After clicking them, the standard “Run” utility window will appear.
Copy and paste the taskmgr.exe command into it, and then click “OK”.
Option number 4. Thanks to the special team
With this method, you will need to repeat it once, after which the computer itself will remember which command you entered last time and will automatically enter it all subsequent times. All you have to do is confirm your choice.
- Win + R together .
- In the window that appears, enter “ taskmgr ”.
- Click on the OK button.
Using the command line
Do you want to feel like a “hacker” from Hollywood movies? No question - to do this, try calling “Dispatcher” using the command line. It’s easy to find it - in the search field, which we already talked about above, start typing “Command...”.
We click on this item with the left mouse button, after which the good old runtime environment opens...
We copy the same taskmgr.exe command. Right-click on any free space in the “black window” and... the command is automatically inserted.
All you have to do is press Enter!
Owners of Windows 8/8.1 will do the same thing, but Windows 7 users are out of luck - Microsoft did not introduce the implementation of the “Paste” command via the right mouse button into this system. So you will have to enter the phrase taskmgr.exe manually...
If you make a mistake, it's okay. In this case, the system will write “Command not found.”
Power User Menu
Starting with Windows 8, Microsoft hid some of the system software in the corners of the Metro interface, but left the ability to launch it from the “Advanced User Menu”. You can launch it in two ways.
First, press the key combination Win + X (here the last letter is the Latin “X”)
The second method is even simpler - click on the “Start” button with the right mouse button. In both cases, a window will open on a black background, where you need to select the item you are interested in by clicking on it with the left mouse button.
An attentive user, by the way, may have already noticed that from the same menu you can call up the Command Prompt (and you can do it with administrator rights), open the “Run” utility window and do a number of other necessary things. You can experiment at your leisure!
Let us repeat once again - Windows 7 and earlier versions of Windows do not have this function!
Startup problems
If the task manager does not start, the message “Task manager has been disabled by the administrator” is displayed, you can assume that it has disappeared from the computer. There may be several reasons why access is denied by the administrator. The blocking may be due to the accidental deletion of the program launch file, but in most cases this is the result of viruses. When starting the Windows operating system, they can block some programs, in particular the task manager. If anti-virus treatment does not help, you need to perform the following steps to restore the dispatcher.
Let's look at how to open it in Windows 7. Call up the “Run” window using Win + R. We type the command “gpedit.msc”, which transfers it to the “Local Group Policy Editor” window. Here we click in turn on the tabs “User Configuration” → “Administrative Templates” → “System” → “Action options after pressing CTRL+ALT+DEL” → “Delete task manager” and here we select “disable”.
After such actions, the error that is disabled by the administrator usually disappears, the task manager is restored and will start when called by the command.
Task Manager executable file on the system
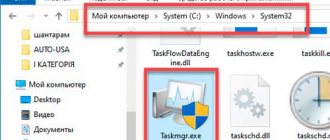
Again we go to the search field, which has already been mentioned several times above, and paste there (Ctrl + V or right mouse button - “Paste” command) the line taskmgr.exe.
On the right side of the window that opens, select “Open folder with file.”
An Explorer window will open, where the system utility file itself is located.
Or you can cheat and, bypassing all these points, open any Explorer window (even “My Computer”) and, right-clicking in the address bar, use the “Paste” command to enter the following path there:
C:\Windows\System32
Then press Enter and immediately go to the desired folder. And if you don’t want to search among a scattering of files for the one you need, immediately enter in the same line:
C:\Windows\System32\taskmgr.exe
And press Enter again. The task manager you are looking for will open immediately!
RegtickPro and AVZ programs
I myself have been successfully using for many years a simple and free program that does not require installation and consists of a single RegtickPro file.
Download the program from me and run it from the archive.
In the program, go to the “System” menu, uncheck “Disable Task Manager” and click “OK”. That's it, the task manager should become available!
To unlock the registry editor, additionally uncheck “Disable MS Registry Tools”.
For the same purposes, you can use the AVZ program, but it is more heavyweight and complex than this (in Regtick a couple of clicks and the problem is solved). In the AVZ program, the following points are used for this: “11. Unlocking the task manager" and "17. Unlocking the registry editor."
Create a shortcut on the taskbar
In order not to break your fingers with hotkeys and not constantly copy commands, you can make it even simpler - add the desired shortcut to quickly call the utility directly to the Taskbar. Make it easier than ever!
First, open the “Dispatcher” using any of the methods described above. It is necessary for its window to appear on the Taskbar.
After that, right-click on it and select “Pin to panel...” from the context menu that appears.
Create a shortcut on the desktop
If there is simply no free space on the Taskbar, you can do it even simpler and create a shortcut to launch the utility directly on the Desktop.
To do this, you need to right-click on any free space on the table (if there is one), and select “Create-Shortcut” in the context menu that appears.
A settings window will open where you need to enter the path to the object... The attentive reader already knows what this item is:
C:\Windows\System32\taskmgr.exe
Paste this value into the appropriate field and click on the “Next” button.
After this, the system will offer to somehow “name” the created shortcut. You can enter something of your own, you can leave the proposed option - the performance of the solution will not be affected in any way.
Click “Done” and admire the ready-made shortcut for quick access!
That's all! From now on, by simply clicking on it with the left mouse button, you can always launch the “Dispatcher”.
We also suggest that you read the article on how to create a shortcut on the Desktop.