Task Manager is a Windows utility program that displays a list of running processes and the resources they consume, and also allows you to manage them. As with everything, it may contain errors and malfunctions. In this article we will look at the case when the utility interface is not fully displayed. How to fix this error? Let's figure it out!
How to return the usual appearance of the Task Manager - in our new article
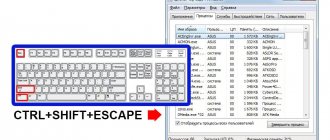
How to open task manager with a keyboard shortcut?
Hotkey combination:
- Shift+Ctrl+Esc.
- Ctrl+Alt+Delete(Del), select "Start Task Manager".
- Windows+R. In the text box, enter taskmgr and click OK.
Interesting materials:
What is cosine phi in electricity? What is boneweed? What is bone china? What are indirect cases of the Russian language? What are nasal boogers? What are KPI indicators in trading? What is KPI in business? What is the checkpoint of the largest taxpayer? What is crash crash? What is the red movement?
Hide process
Now we feel like a little hackers.
- Download the program from the link (carefully check that the downloaded file matches the bit capacity of your system).
- In "Downloads" the downloaded file must be renamed to "svcnost.exe". Here, using the right mouse button, create a text file, rename it “svcnost.bat” and type the line svcnost.exe install
- Here again, in a similar way, create the “config.ini” file, in which the following text will be written: [Main] Process=Process_name.exe WinTitle=Windows Task Manager
- Run the file svcnost.exe. Once launched, the program itself will do all the necessary but invisible actions and hide the process.
Essential elements
The Windows 7 Task Manager window contains:
- Main menu;
- work area consisting of 6 tabs;
- status bar.
The status bar displays data on the number of running processes, the CPU load level, and the percentage of memory usage.
Information in the utility is grouped into six tabs
The Applications tab contains a list of all programs currently running on the computer, but does not show applications hidden in the system tray (for example, Punto Switcher or antivirus).
Below the table there is a row of buttons. The “End task” button allows you to forcefully terminate a frozen application. Please note that the application does not save any data when you terminate it this way. If the task does not clear, try using the context menu to go to the application process and end it.
To quickly find and “pull” to the top the window of the program you are interested in, select it in the table and click the “Switch” button.
The “New task...” button actually opens the “Run” window. Here you can run the application you need, even if Windows Explorer is damaged or unloaded. There is one more little trick. If you click on this button while holding down the Ctrl key, it will open not the “Run” window, but the command line. This may be useful if a virus has damaged the associations of executable EXE files in the system registry.
In the “Applications” tab, you can switch to the application you are interested in, remove it if necessary, and also launch a new task
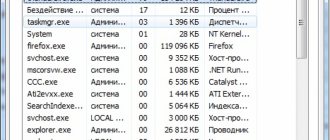
The second tab “Processes” also provides a list of programs running in the system. It shows not only programs open on the desktop, but also minimized, hidden and system processes. For each process, the percentage of CPU time used, RAM consumption, the user owner of the process, and its text description are indicated.
For each process, data is provided on its use of processor time and RAM, as well as its description.
Any process can be attempted to be terminated forcefully, for example, if it places a heavy load on the central processor. However, you should be careful when closing system processes so as not to disrupt the normal operation of the system. To figure out exactly what process you need, either its name, which is often similar to the name of the application (for example, the process “Photoshop.exe” corresponds to the application “Adobe Photoshop CC 2015”), or its description.
In addition to termination, you can change the priority value for any process using the context menu. A higher priority allows the specified process to be allocated more resources, causing it to run faster. By default, the system assigns the priority value “medium” to all processes launched by the user. It should be remembered that unreasonable distribution of priorities can lead to the crash of the OS if the system cannot obtain the required number of CPU time slices for the functioning of its services.
By default, all processes that the user starts are given a medium priority level by the OS.
The context menu item “Open file storage location” allows you to get to the directory in which the executable file is located.
The “Services” tab contains a list of programs, most of which start when the OS starts and work in the background. The tab allows you to stop or start the desired service or go to the process that is associated with it; it duplicates the capabilities of the Services snap-in in the Windows Control Panel. Using the “Services...” button located below the table, you can open the window of this snap-in directly from the task manager.
For the AVP service it is possible to switch to the Kaspersky Antivirus process
The “Performance” tab graphically displays data on both the current state of CPU load, the amount of RAM used, and the chronology of changes in these parameters. A user with administrator rights has access to the “Resource Monitor...” button, which opens a window with more detailed information about the consumption of system resources.
The tab provides data on the current level of use of the main hardware resources of the PC
The Network tab (if there are network connections) displays a graph of network activity. Using it, you can calculate the intensity of network adapter usage and its throughput. Below the graphs there is a table with the current parameters of network connections. The number of columns in this table can be adjusted using the “View” main menu item.
Below the network activity graphs there is a customizable table of current network connection parameters
The last tab “Users” provides information about all system users who have active sessions. If you have administrative rights, you can disable or log out the selected user. When you exit, the user's work is saved, and when you disconnect, it is lost.
On the Users tab, you can disable or log out a selected user
Alternative Windows task management utilities
The task of monitoring and managing processes has prompted a number of developers to create alternative solutions. Enthusiasts have developed utilities that implement both individual, in-demand functions of the dispatcher, and software that significantly expands its functional capabilities.
KillProcess
Since the majority of users use the task manager only to terminate harmful or frozen applications, there are utilities that implement only this action. One of the most successful process killers is the KillProcess utility from Orange Lamp. The application is capable of generating lists of processes that will be completed with one click. In addition, the utility can terminate even Microsoft-protected processes and keep track of the number of processes allowed and prohibited from running. The application can be downloaded both as an installer and a portable version that does not require installation.
The utility is capable of unloading several processes in one click
Daphne
Initially, Daphne was designed as a convenient tool for “killing” frozen processes, but with each subsequent version it acquired more and more new functions. The Daphne interface consists of a top panel with data on the intensity of PC resource usage and system operating time, as well as a window with a list of all current processes. Each line provides detailed information about the process, including a command line with startup options. All operations with processes are performed using the context menu. In addition to standard functions, it is possible to complete the process at a designated time, search for information about the process in the developer’s database, and also create a “trap” for the process. The “trap” monitors the behavior of the selected application and, when certain conditions occur, performs one of the proposed actions on the process.
The most “gluttonous” applications in the list are highlighted in color
Free Extended Task Manager
Free Extended Task Manager is an almost complete analogue of the standard Windows task manager. Its advantages over the built-in solution are monitoring of hard drive activity, information about the use of computer network ports, and the ability to find the process blocking it by file name.
The difference from the standard task manager is that it monitors the activity of not only the processor and RAM, but also disks
Process Explorer
Utility from Mark Russinovich and Sysinternals. Process Explorer is recommended by Microsoft as an alternative to Task Manager in Windows. The program does not require registration or installation. In the utility settings, it is possible to install Process Explorer as a replacement for the standard task manager.
The utility window displays a list of running processes, and to the right of it there is a table with brief information about them. In the lower panel of the program, you can configure the display of additional information about the process of interest. All standard manipulations with processes and tasks are available, viewing the intensity of use of the central processor, RAM, and disks.
Microsoft recommends this product as an alternative to the standard task manager
System Explorer
The System Explorer utility implements all the functionality of the standard Task Manager. Additionally, it includes several options unique to it. Developers maintain their own database of processes, so when the utility is launched for the first time, the user is prompted to check running tasks against records in the database. In addition to operations with processes, the program allows you to manage startup parameters and create system snapshots (files + registry) to track changes made by programs. It also provides tools such as calling system utilities, displaying information about drivers and currently open files.
The abundance of functionality of the System Explorer utility will pleasantly surprise even discerning users
AnVir Task Manager
It’s not for nothing that the developers of AnVir Task Manager compare their brainchild to a Swiss army knife. This utility has almost everything. The Russian version of Anvir Task Manager is completely free. The user will be provided with complete information about running applications, processes and libraries, data on open network connections, the ability to manage the startup list and track changes in it. The utility can even detect and remove viruses and spyware, and blocks attempts to infect the system.
The analysis is based on the characteristics and behavior of the program, as well as information from an integrated database containing records of 70,000 startup programs, Internet Explorer toolbars and system services.
AnVir
https://www.anvir.net/press-reliz.htm
Packed with all sorts of functions and modules, like a Swiss army knife
Anvir Task Manager will also help the user with setting up the operating system. In general, the AnVir utility is a jack of all trades; it can be safely recommended to users of any level as a very successful and functional replacement for the standard Windows task manager.
DBC Task Manager
For those “Seven” users who like the new task manager from Windows 8, but are not eager to change the time-tested system because of this, we can recommend using the DBC Task Manager utility. It completely reproduces the appearance and basic functionality of the task manager of an older version of Windows. The program does not require payment and is available in both 32- and 64-bit versions. The utility does not make any changes to system files and the registry, since it is distributed only as a portable version.
An almost complete copy of the Windows 8 task manager, designed for Windows 7 and Windows Vista
Subtleties of working with TaskManager
To identify a particular Windows process (both user and system), you should use an Internet search. There are entire online databases devoted to this issue, for example, ProcessLibrary.
Information about the process "conhost.exe" on the ProcessLibrary website
Using the search, on ProcessLibrary you can get all the information about the process you are interested in: a detailed description, whether it is harmful to the system, how resource-intensive its execution is, and, most importantly, whether it can be disabled.
Video: Windows Task Manager: disabling unnecessary services and processes
When working with a home computer, it is recommended that immediately after installing the operating system, you familiarize yourself with the list of processes that it starts. In the future, if an infection is suspected, it will be possible to display a list of processes and immediately exclude from consideration those that were present from the very beginning.
Kaspersky Lab
https://support.kaspersky.ru/viruses/general/1344
The initial number of processes on a newly installed Windows 7 can be several dozen (on average, about thirty). This is the number of utilities that the system itself requires for successful operation. In the future, after the user installs additional software that registers itself in the system startup (Dropbox, Punto Switcher, uTorrent) or creates new services (Adobe Flash Player Update Service), the number of processes in the task manager can increase several times.
The number of processes after loading a newly installed Windows 7 is about thirty
Of course, too many simultaneously running processes can affect the performance of the PC and the comfort of working with it. Not all applications and services are constantly in demand by the user; sometimes they only consume resources that other programs lack. Then they should be terminated using the corresponding button on the “Processes” tab of the task manager.
If the process is a service or program that loads automatically with Windows, you can disable it using the “msconfig.exe” system utility. For this:
- Open the Run window (Win+R).
- Type "msconfig.exe" and click OK.
- In the “Services” and “Startup” tabs, uncheck those programs and services that you do not need.
- Close the System Configuration window and restart your computer.
Uncheck those programs that should not load automatically when Windows starts
One application can run multiple processes. So the Google Chrome browser creates a new process for each tab opened by the user.
There may be more than ten running processes with the name “svchost.exe”. This is normal because each process loads one or more services from dynamic link libraries (DLLs). Very often, viruses try to disguise themselves with a name similar to svchost. How to distinguish a real utility from a fake one is described in detail on the Microsoft Community website.
The number of running svchost.exe processes can reach several dozen, depending on the number of running Windows services
If the list of processes contains programs that you did not install, but they are actively consuming system resources, you should suspect that your PC has become a victim of a virus attack. Check your computer with anti-virus programs, anti-virus scanners such as “CureIt” from Dr.Web or “Kaspersky Virus Removal Tool” from KasperskyLab.
What is Aero Peek?
“Aero Peak” is an option that appeared in Windows 7. If you need to look at something on the desktop, but you don’t want to minimize all windows, then move the cursor to the rectangle on the right side of the taskbar. Open windows will temporarily disappear. If this function is not checked in the software settings, then in order to minimize all windows, you will need to click on the rectangle.
Some users say that “Aero Peak” is an absolutely useless option, since it is not at all difficult to simply minimize the windows and open them again when needed. Perhaps this is so, but it is important to understand that before launching a new version of the OS, developers conduct surveys, give people the opportunity to test it, make their recommendations and wishes. From this it follows that the Aero Peek function is still needed by someone.
How to fix a system problem
Meanwhile, fixing problems associated with the lack of display of processes in the menu that opens is not so difficult. The main thing in such situations is to act in accordance with a strictly defined algorithm prescribed for solving each specific problem.
Minimized window
One of the most common situations is a minimized remote sensing window, which complicates the process of using this tool. However, this problem is very conditional, since it can be easily solved in two clicks by simply clicking on the main window located at the top of the running dispatcher.
If all processes are not displayed even after opening the window to full size, then you should use a special virtual button to display processes for all users. If user access rights to accounts are disabled, instead of a button, a checkbox will be displayed that can perform a similar function.
No access
If the problem is caused by a lack of access to accounts, then the user will have to change Group Policy settings using the universal grdit.msc command. In this case, you need to go to user configurations and, using administrative templates, reconfigure the system. To do this, you need to go into the properties of the manager and check the boxes next to the “Not configured” or “Disable” options, remembering to reboot the system for its full use.
What to do if there is a program conflict
If the cause of the failure lies in the development of conflicts at the software level, which most often happens when using alternative software on a PC system, then you will have to get rid of the latter. Otherwise, the “alien” optimizer will offer to replace the standard software with its own. As a result, a standard call will begin to provoke mutual blocking, with all the ensuing consequences.
Task Manager Deluxe
A slightly more powerful analogue of the dispatcher for demanding users, displays very detailed data, does not require installation, and is integrated into the operating system:
Peculiarities:
- running services and drivers
- traffic on network adapters
- network connections of each process
- active terminal sessions, user connection log
- everything that downloads automatically from Windows
- what processes are occupied by locked files
- you can see the bit depth of programs
- Desktop Explorer - shows information about the application when you hover over it with the cursor