Installation files, or executable files, are sometimes called binary files. Because their format is a continuous sequence of binary values. In computing, a setup file causes a computer to perform specified tasks according to coded instructions. This differs from a regular data document, which must only be read. A file with a name ending in .exe is a program that, when opened, causes the operating system to launch an application.
Purpose and execution of files
Such installation files can be written by hand in machine language, although it is much more convenient to develop the software as source code in a high-level language that can be easily understood by the programmer. In some cases, the source code may be in assembly language, which is closely related to machine code instructions. The high-level language is compiled into either a machine code setup file or an object file.
Several of the latter, linked together, can create installation files. They are in container format, in the form of installer and linkable format (ELF). This structures the generated machine code, for example by segmenting it into sections:
- .text — installation code;
- .data - static variables;
- .rodata - static constants.
To be executed by the system, the installation file must conform to the system application binary interface (ABI). It is most simply accomplished by loading into memory and simply jumping to the beginning of the address space and executing it from there. But in more complex interfaces, installation files have additional metadata that defines a separate entry point. For example, in ELF, the entry point is specified in the header in the e_entity field, which specifies the virtual memory address from which execution begins. In GCC (GNU Compiler Collection), this field is set by the linker based on the _start symbol.
Launch structure and functions
Installation files typically include a runtime system that implements language features, as well as task scheduling, exception handling, calling static constructors, and interacting with the operating system. For example, passing arguments, environment, and returning exit status along with other startup and shutdown functions such as releasing resources. For C, this is done by associating a "crt0" object which contains the actual entry point and does the setup and shutdown by calling the runtime library.
Thus, Windows installation files typically contain significant additional machine code beyond that directly generated from the source. In some cases it is desirable to skip it, such as when developing embedded systems or simply learning how compilation, linking, and loading work. In C, this can be done by skipping the normal runtime and instead specifying a linker script that generates the entry point and handles startup and shutdown, for example by calling mainstart and returning the exit status to the kernel at the end of the operation.
How to install a program from disk
If you bought a game or program on disk, or if you downloaded an ISO or MDF file from the Internet, the procedure will be as follows:
The ISO or MDF disk image file must first be mounted on the system, which means mounting the file so that Windows sees it as a disk. You can read in detail about how to do this in the following articles:
- How to open an ISO file
- How to open an MDF file
Note: if you are using Windows 8 or Windows 8.1, then to mount the ISO image, simply right-click on this file and select “Mount”, as a result, you will be able to see the “inserted” virtual disk in Explorer.
Installation from disk (real or virtual)
If the installation does not automatically start when you insert the disk, then simply open its contents and find one of the files: setup.exe, install.exe or autorun.exe and run it. Next, you just need to follow the instructions of the installation program.
Disc contents and installation file
One more note: if you have Windows 7, 8 or another operating system on the disk or in the image, then firstly, this is not really a program, and secondly, they are installed in slightly different ways; detailed instructions can be found here: Windows installation.
Types of extensions
The Windows installation file is also called a binary file. A program is a sequence of instructions, understood by the computer's central processing unit (CPU), that it must execute on a set of data.
Windows file extensions: .EXE, .COM, .BAT, .VB, .VBS, .WSF, .PIF.
Macintosh file extensions: .APP, .SCPT, .APPLESCRIPT.
The installation can be implemented in three formats:
- Custom third-party installation system in EXE file.
- Windows Installer in MSI.
- EXE file that loads the MSI embedded in the EXE.
MSIs can only be installation files, while EXEs, on the other hand, can be literally anything that can run on a computer. Executable files consist of instructions that have been translated from source code into machine code, also called machine language or object code, using a specialized compiled program. The machine's code consists entirely of zeros and ones, which represent the state of the processor's logic circuits and memory cells.
Digital Age
Nowadays, computers are becoming increasingly widespread, many can no longer imagine life without them, and almost all enterprises have switched to electronic document management. But just 15 years ago, not everyone could boast of having a home PC, or high-speed unlimited Internet access. And the development of new software has become a profitable business for many, bringing in billions. If you look at the statistics of in-demand professions on the labor market, every year more and more programmers and other similar specialists are required.
And this is natural, because even the most powerful and modern computer without software is nothing more than a set of expensive chips. Operating systems and programs are a kind of layer between man and machine, which serve for their interaction. But for the programs to work, they must first be installed, since you cannot simply transfer a set of files to your computer and expect everything to work by itself; this is why they need to be installed correctly. So what is installation? What is it like and what is it needed for? We'll figure this out.
Executable EXE files
Installers execute the code or series of instructions contained within them. The two main types are compiled programs and scripts.
On Windows systems, compiled programs have an EXE extension. On Macintosh computers, compiled programs have an APP extension. Both types of executable files are compiled from source code into binary machine code, which is directly executed by the processor. EXE work only on Windows OS, and APP - on Mac OS X. This is due to the fact that the code is executed by the operating system and therefore must be compiled in a format that it understands.
Uncompiled executable files are often called scripts. They are saved in text format, not binary. In other words, you can open the script and view the code in a text editor. Because scripts do not contain executable machine code, they require an interpreter to run. For example, a PHP file can only execute code when run through the PHP interpreter. If it is not available, then the PHP script can only be opened as a text document.
Since executable files run code when opened, the user should not open unknown ones, especially those received as email attachments. These compiled executable files are the most dangerous and can run malicious code. For example, VBScript (.VBS) can run automatically on Windows systems through the built-in Windows Script Host. Similarly, AppleScript (.SCPT) can be run through the AppleScript interpreter included with Mac OS X.
Review [edit | edit code ]
Most programs are supplied for sale and distribution in compressed (packaged, see: Archive) form. To function properly, they must be unpacked and the necessary data placed correctly on the computer, taking into account differences between computers and user settings. During the installation process, various tests are performed to ensure compliance with the specified requirements, and the computer is configured (set up) as necessary to store the files and data necessary for the correct operation of the program.
Installation, as a rule, includes placing all the files necessary for the program in the appropriate places in the file system, as well as modifying and creating configuration files. Package managers also perform dependency control during installation, checking whether the system has the packages necessary for the program to work, and if the installation is successful, registering a new package in the list of available ones.
Because this process is different for every program and computer, many programs (including operating systems themselves) come with a universal or custom installer—a program that automates much of the work required to install them.
Some programs are written in such a way that they are installed by simply copying their files to the desired location, and there is no installation process itself. They say about such programs that they “do not require installation.” This is common among programs for Mac OS X, DOS and Microsoft Windows. There are operating systems that do not require installation, and thus can be directly launched from a boot disk (CD or DVD) without affecting other operating systems installed on the user's computer. An example of such an operating system is Knoppix or Mac OS 1-9.
The term also includes plugins, drivers, and program files that are not programs themselves.
Common operations performed during the software installation process include creating or changing:
- Used and unshared program files.
- Catalogs.
- Records of configuration files used by one program, or jointly.
- Environment variables.
MSI User Interface
MSIs are database files used by Windows Installer. They contain information about the application, which is divided into functions and components, and each component may contain registry information. MSI shortcuts contain the user interface that is used for installation and various other data in the form of prerequisites. It may also contain actual files that must install themselves, which is currently the recommended way to install an MSI on Windows. An alternative is to write a program that does the installation itself.
MSIs are executed by an EXE that is part of Windows and is called MSIEXEC.EXE. This application reads the data in the MSI and executes the process.
Algorithm for launching MSI files:
- Open the Start menu in the lower left corner of the screen.
- Click "Computer" to open Windows 7's own file manager called Windows Explorer. It displays drives and folders in the left pane. If you click on one of the drives or folders, you can see its contents in the right pane.
- Click "Organize" in the top left corner of the manager and select "Folder and Search Options" from the drop-down menu. The Folder Options window will open.
- Click View at the top of the Folder Options window to view viewing options.
- Uncheck "Hide extensions for known types" in the "Files and Folders" section to see all extensions.
- Click Apply and then OK to apply the settings and close the Folder Options window.
- Use an explorer window to find the MSI to run.
- Click "Type" at the top of the right pane to sort files by type so that all MSIs appear together. If Type is not displayed at the top of the right pane, move the view slider in Details to display details including Type. The view slider is in the upper right corner of the Explorer window.
- Double-click MSI to launch the Windows Installer application.
Possible installation options [edit | edit code ]
- Manual installation - Installation is performed without an installer or with significant manual effort by the user.
- A silent installation is an installation during which no messages or windows are displayed. "Silent installation" is not synonymous with "automatic installation", although it is often mistakenly used in this sense.
- Automatic installation is an installation that is performed without user intervention, excluding, of course, the process of launching it. The installation process sometimes requires interaction with the user, who controls the installation process by making choices: accepting the user agreement, configuring settings, specifying passwords, and so on. Graphical environments may use installers that provide a so-called Installation Wizard, but they also often provide command line options that allow for a completely automatic installation.
- Self-installation is an installation that does not require an initial startup process. For example, Vodafone Mobile Connect USB Modem, which is installed from the USB port of a computer when connected to it without the need for manual startup.
- Remote installation is an installation that is performed without using a monitor connected to the user’s computer (in particular, performed on a computer with no video output at all). This can be a controlled installation from another machine connected via a local network or via a serial cable. Unattended and remote installations are common operations performed by system administrators.
- A “clean” installation is an installation performed in the absence of such factors, which may vary from program to program. Due to the complexity of a typical installation, there are many factors that influence its successful outcome. In particular, files remaining from a previous installation of the same program, or an unstable state of the operating system may lead to incorrect installation and operation of the program.
- Direct installation is installation of a program performed from a copy of it on the hard drive (called a flat copy), rather than from the original media itself (usually a CD or DVD). This can be useful in situations where the target machine is unable to handle random read access from optical drives during CPU-intensive tasks, such as installing programs.
Running for DOS system
To run a file from MS-DOS, the executable type is launched, which is .exe, .bat or .com. To check which documents in the current directory are executable, use the "dir" command at the MS-DOS prompt. Using this method, you can define a resource with .exe installation files or replace them with .bat or .com. Once the name of the executable type has been determined, enter its name on the MS-DOS command line. For example, if the executable file is game.exe, enter “game” at the command line.
If the file is not found or you receive an error message such as "invalid command or file name," the file is likely not in the current directory. Go to the executable directory and enter the command again. It's important to remember that if you run it from an MS-DOS shell (in MS-DOS on Windows), the program will still use Windows to run.
Installation
Before answering this question, it's worth diving a little deeper into how programs work. In its pure form, any of them is a set of sequences of ones and zeros that the processor of a computer or other device interprets into certain commands. But such programs were common a long time ago, when PCs did not have a graphical interface and were “fed” programs directly.
But now, if you look at almost any software, then in addition to the interface, you will notice a lot of other things: additional fonts, language packs, help files, online checking for updates and much more. All this is hidden in special system libraries, and they need to be copied correctly. True, the installation can be different, but first things first. So what is installation?
Creating Directives for Windows
Each application must be copied to the PC with a specific directory structure that guarantees its proper functioning. You can use special software, such as Inno Setup, which is very useful in creating executable files (EXE) that act as application installers for Windows.
The main advantages of free software are that it has a large number of features that work on almost all Windows systems (7, 2008 R2, Vista, XP, 2008, 2003, 2000, Me, 98, 95 and NT 4.0. 32 bits and 64 bits). It is recommended to use the wizard first and then the built-in script editor to do advanced compilation of the installation files.
The Inno Setup Example Scripts folder contains many example templates for various application installer models; it is recommended that you try them all first to get an idea of the range of options available.
Experienced users of this software can create their own scripts and modify them to create powerful application files. It is recommended that you review the included help for more information about the available commands.
Definition
Almost all programs are delivered in compressed or packaged form, which is natural, because it is much easier to download one installation archive and get everything you need from it than to download or copy dozens, or even hundreds of different files. For example, just look at the catalog of any software to ask the question: “What is an installation?”
Installation is the process of copying and installing software onto the end user's computer. It cannot be called a regular copying to the file system, since during the installation process a special program (package manager) checks the computer for compatibility, the presence of the necessary accompanying software, etc.
Then the installer places files on the disk in the required sequence, creates additional directories if they are needed, makes entries in the registry, startup, associates files, etc. So now we know what installing a program is.
As you can see, during this process the computer performs many actions, although the user, most often, does not notice any of this. It is also worth noting that we will use this term in relation to plug-ins and drivers, although they themselves are not programs.
There are also several basic installation types. And although they do the same job, their methods are slightly different. And when examining the question of what software installation is, it is worth mentioning the most common ones.
For example, a “silent” installation is performed without displaying pop-ups and other things. The user starts the process and after some time simply receives a program ready to use.
Automatic installation (the most common) occurs without human intervention, of course, except for the launch itself and some settings, for example, instructions on where to unpack the software, whether to create a shortcut to launch, etc.
Manual installation is different in that it requires many complex steps.
There are also programs that do not require installation, and the entire installation consists of simply copying files to the hard drive on their own. So now we know what installing a program is.
Computer games have long ceased to be some kind of childish or primitive entertainment. This is a profitable business, and many large companies spend tens or even hundreds of millions on creating the next toy that brings in profits several times more.
So what is a game installation? Essentially, this is the same as installing another program. During this process, game materials (models, sound, textures, etc.) and executable files are copied to the hard drive, which assemble it all into a three-dimensional controlled image.
Installation
(
installation
) is the process of installing software on the end user's computer. It is performed by a special program (package manager) present in the operating system (for example, RPM and APT in GNU/Linux, Windows Installer in Microsoft Windows), or by the installation tool included in the software itself. In the GNU operating system, it is very common to use the GNU toolchain and its analogues to compile software immediately before installation.
Most programs are supplied for sale and distribution in compressed (packaged) form. To function properly, they must be unpacked and the necessary data placed correctly on the computer, taking into account differences between computers and user settings. During the installation process, various tests are performed to ensure compliance with the specified requirements, and the computer is configured (set up) as necessary to store the files and data necessary for the correct operation of the program.
Finding the location of installation files
In order to determine which files are installation files, the easiest way is to look at the shortcut properties. Sequencing:
- Open the shortcut properties window, for example for Firefox.
- You can use keyboard shortcuts if the shortcut is either in the Start menu or in the Programs list.
- Right-click on the shortcut and select “Properties”.
- Find the full path to the executable file and its name.
- For this example: C: Program Files Mozilla Firefox firefox.exe.
- Go to the EXE through the Mozilla Firefox folder, where the Windows 7 installation file for Firefox will be located.
Software installation programs
In addition to the above method of installing programs, there is another one that involves the use of special software. All you need is to install this software and install other applications using it. There are many such programs, and each of them is good in its own way. We have a special article on our website that contains a list of them and a brief description.
Read more: Programs for installing programs on your computer
We will look at using such software using Npackd as an example. By the way, you can install it using the instructions given above. To install the program, after launching the application you need to do the following:
- Go to the "Packages" tab.
- In the “Status” field, select the “All” option.
- From the Category drop-down list, select the category that the software you are looking for belongs to. If you wish, you can also define a subcategory by selecting it from the list of the same name.
- In the list of all found programs, left-click on the one you are looking for.
Note: If you know the exact name of the program, you can skip all the above steps by entering it in the Search field and pressing Enter.
- Click the "Install" button located on the top panel. You can perform the same action through the context menu or using the hot keys Ctrl+I.
- Wait for the download and installation process of the selected program to complete. By the way, this entire process can be tracked on the “Tasks” tab.
After this, the program you have chosen will be installed on your PC. As you can see, the main advantage of using such a program is that there is no need to go through all the steps that are in the usual installer. You just need to select the application to install and click “Install”, after which everything will happen automatically. The only disadvantage is that some applications may not be on the list, but this is compensated by the ability to add them yourself.
Archiving the game
In order to turn the game into one EXE, use the popular WinRAR archiver, create a new archive and name it. All game data .exe, font file, Unity exe and more are copied there. Click SFX, then additional options. This will turn the entire RAR into a program that will extract itself and then launch the game.
- Add the name of the game installation file to “Run after extraction”. Make sure the extraction process is hidden and goes to a temporary directory.
- Check the “Overwrite all files” checkbox: in case you need to fix an error, it will replace the existing material in the temporary folder with new one.
- Add an icon, if necessary, in the “Text and Icon” section.
- After saving and clicking there should be one .exe that will work.
IExpress creation method
IExpress is a utility that comes bundled with versions of Windows starting with Windows XP and higher. The utility comes with a graphical interface called IExpress Wizard. And it is also possible to create installation files using SED files written manually using a wizard.
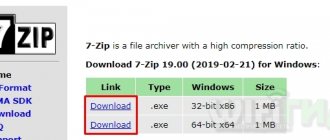
Like 7-Zip above, this method creates a self-extracting archive with two main differences. First, the end user will be taken through a multi-page installation wizard, and second, the end user can specify the target directory where the tool is located and extract the files.
To create an EXE installer using IExpress:
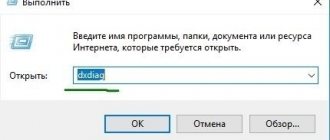
- Open the Run prompt with the Windows key + R and type iexpress.exe to launch the IExpress wizard.
- Select “Create a new self-extract directive file” and click “Next”.
- Select “Extract files only” and click “Next”.
- To confirm the request, select “No request” or “User request using”.
- For a license agreement, display the license if you need the end user to agree to any license agreement (EULA), if not, then it is better to select “Do not display license”.
- In order to add all the files that you need to see installed, click the “Add” button, go to the folder and select them all.
- Continue through the IExpress wizard and select the desired options for the Show Window and Ready Message prompts.
- For the package name, click Browse, navigate to the location where you want to create the installation EXE, and give it a name.
- Click “Next”.
- Select "Save self-healing directive (SED) file" if you want to create a modified installer later. If you select “Do not save”, you will have to go through the entire process from scratch.
- On the “Create a package” page, click “Next” to complete the process.
An application package that combines all the documents into one, called an installation file, makes it easy to deploy and configure them on users' computers. Customization reduces the total cost of ownership by allowing applications to be installed and configured efficiently. The result is a package that provides the product with new capabilities, such as declaring features without installing them, installing products on demand, adding custom settings, and others.
Driver installation programs
In addition to programs for installing other software, there are software solutions for automatically installing drivers. They are good because they are able to independently determine which drivers are missing or outdated and install them. Here is a list of the most popular representatives of this segment:
Using all of the above programs is very simple, you need to run a system scan, and then click the “Install” or “Update” button. We have a guide on how to use such software on our website.
Read more: Update drivers using DriverPack Solution Update drivers using DriverMax
In conclusion, we can say that installing a program on a computer is a simple process. The main thing is to carefully read the descriptions at each stage and choose the right actions. If you don’t want to deal with this every time, programs for installing other software will help. You should also not forget about drivers, because for many users their installation is unusual, and with the help of special programs the entire installation process is reduced to a few mouse clicks.
We are glad that we were able to help you solve the problem. Thank the author and share the article on social networks. Describe what didn't work for you. Our specialists will try to answer as quickly as possible.
Distribution (installation file)
The process of installing a program involves recording various information in different places. What and where to write is already specified in the installation file. They call it a distribution kit. An example of such a file is shown in the figure below, but the file may look different.
Its name may contain: Name and version of the program - Alcohol_120_7
The word that indicates that this is an installation file is
Setup
. It may be that the file will be called Setup
or something else. Don't let this confuse you. The distribution folder most often contains only a few files.
To start the installation process, you just need to double-click on the distribution.
Downloading files to your computer
So, what do we need to do in order to install the necessary program on the computer? First, you need to download its installation file, after running which the program will be installed on your computer. To do this, you need to find the link to download the program and click on it.
An example of such a link:
In your browser, after clicking on the download link, the download process to your hard drive should start. In some browsers, a dialog box may appear asking you to save the file in the specified folder, then specify the folder and remember it.
In most browsers, when downloading a file, a download line should appear at the bottom of the browser. Example for Google Chrome. Please note that we downloaded the MM26_RU.msi file. Now by clicking on it we can begin installing the program:
What to do if there are several links?
Even for one file we try to give 2 links:
- From software developer sites. This ensures that the files are as up-to-date as possible and that the program file is exactly as the developers intended.
- From our website. This means greater security (we scan files with antiviruses) and in many cases excellent download speeds.
There are times when there are different versions of a program for different operating systems. In addition to the operating system version (Vista, XP, 8, 10), there is also a bitness (32 or 64-bit)
To choose the right one in this case, you need to look at what system you have.
You can easily find out by going to the computer properties. In Windows XP or Windows 7, this can be done by clicking on My Computer (right mouse button) → Properties. In Windows 8/10, click on Start (right mouse button) → System.
Program installation process
- Often during installation you are asked to select a language. We choose Russian, there is no Russian, we choose English. And, of course, click OK. (Fig.1)
Various additional programs can often be imposed, such as Yandex bar Sputnik-mail
,
Google search
. There is no need to install them. They are created so that you use their search engine (for example, Yandex or Mail).
To prevent it from being installed, you must not skip this step and uncheck the box to install Yandex bar (or another program). (Fig. 5) And then click next.
Next, we may be asked where to create shortcuts to the program. There is nothing terrible here, no matter what we choose, it will not affect the installation process in any way. I advise you to check the box “create a shortcut on the desktop” and clear everything else. (Fig.6)
In the last step, after installation, we may be asked if we want to automatically launch the program after completion. It's up to you to decide.
They may also suggest reading the readme file or some instructions for use. Feel free to refuse this (you need to uncheck this item).
Well, click the done button. That's it, the process is complete.
- In all other cases, use one wonderful rule: If you don’t know what you are being asked, just click next without changing anything.
Installing applications on your computer
To install a program or game, use an installer or, as it is also called, an installer. It may be on the installation disk, or you can download it from the Internet. The software installation process can be divided into stages, which is what will be done in this article. But unfortunately, depending on the installer, these steps may differ, and some may be completely absent. Therefore, if following the instructions you notice that you do not have a window, then simply move on.
It is also worth saying that the appearance of the installer may vary significantly, but the instructions will apply to everyone equally.
Step 1: Run the installer
Any installation begins by running the application installation file. As already mentioned, you can download it from the Internet or it may already be on disk (local or optical). In the first case, everything is simple - you need to open the folder in Explorer where you downloaded it and double-click on the file.
Note: in some cases, the installation file needs to be opened as an administrator; to do this, right-click on it (RMB) and select the item of the same name.
If the installation will be performed from a disk, then first insert it into the disk drive, and then follow these steps:
- Launch File Explorer by clicking its icon on the taskbar.
- In the sidebar, click on “This PC”.
- In the “Devices and Disks” section, right-click on the drive icon and select “Open”.
- In the folder that opens, double-click on the “Setup” file - this is the application installer.
There are also cases when you download from the Internet not an installation file, but an ISO image, in which case it must be mounted. This is done using special programs such as DAEMON Tools Lite or Alcohol 120%. Now we will provide instructions for mounting the image in DAEMON Tools Lite:
- Launch the program.
- Click on the “Quick Mount” icon, which is located on the bottom panel.
- In the Explorer window that appears, go to the folder in which the ISO image of the application is located, select it and click the Open button.
- Left-click once on the mounted image to launch the installer.
Read more: How to mount an image in DAEMON Tools Lite How to mount an image in Alcohol 120%
After this, the “User Account Control” window will appear on the screen, in which you will need to click “Yes” if you are sure that the program does not contain malicious code.
Step 2: Select Language
In some cases, this step can be skipped; it all depends directly on the installer. You will see a window with a drop-down list in which you need to select the installer language. In some cases, Russian may not be in the list, then select English and click “OK”. Further in the text, examples of two installer localizations will be given.
Step 3: Getting to know the program
After you have selected the language, the first window of the installer itself will appear on the screen. It describes the product that will be installed on your computer, provides installation recommendations, and suggests next steps. There are only two buttons to choose from; you need to click “Next”.
Step 4: Select Installation Type
This stage is not present in all installers. Before proceeding directly to installing the application, you must select its type. Often in this case, the installer has two buttons “Configure” / “Customization” and “Install” / “Install”. After selecting a button for installation, all subsequent steps will be skipped, up to the twelfth. But after selecting the advanced installer settings, you will be given the opportunity to independently specify many parameters, ranging from selecting the folder into which the application files will be copied, and ending with the choice of additional software.
Step 5: Accept the License Agreement
Before you begin setting up the installer, you must accept the license agreement and read it first. Otherwise, you cannot continue installing the application. Different installers perform this action differently. In some, you just need to click “Next”, while in others, before that you will need to put the switch in the position “I accept the terms in the License Agreement” or something similar in content.
Step 6: Selecting a folder for installation
This step is mandatory in every installer. You need to indicate in the appropriate field the path to the folder where the application will be installed. Moreover, you can do this in two different ways. The first is to enter the path manually, the second is to click the “Browse” / “Browse” button and navigate it in “Explorer”. You can also leave the default installation folder, in which case the application will be located on the “C” drive in the “Program Files” folder. Once all the actions have been completed, you need to click the “Next” button.
Note: for some applications to work correctly, it is necessary that there are no Russian letters on the path to the final directory, that is, all folders must have a name written in English.
Step 7: Selecting a Folder from the Start Menu
It’s worth saying right away that this stage is sometimes combined with the previous one.
They are practically no different from each other. You need to specify the name of the folder that will be located in the Start menu, from where you can launch the application. As last time, you can enter the name yourself by changing the name in the corresponding column, or click “Browse” / “Browse” and specify it through “Explorer”. After entering the name, click the “Next” button.
You can also refuse to create this folder by checking the box next to the appropriate item.
Step 8: Selecting Components
When installing programs that contain many components, you will be asked to select them. At this stage you will have a list in front of you. By clicking on the name of one of the elements, you can see its description to understand what it is responsible for. All you need to do is check the boxes next to the components you want to install. If you cannot fully understand what exactly this or that item is responsible for, then leave everything as it is and click “Next”; by default, the optimal configuration is already selected.
Step 9: Selecting File Associations
If the program you are installing interacts with files of various extensions, then you will be asked to select those file formats that will be launched in the installed program by double-clicking LMB. As in the previous step, you also need to check the box next to the items in the list and click the “Next” button.
Step 10: Create Shortcuts
In this step, you can locate the application shortcuts that are required to launch it. Usually it can be placed on the “Desktop” and in the “Start” menu. All you need to do is check the appropriate boxes and click “Next”.
Step 11: Install additional software
It’s worth saying right away that this step can happen either later or earlier. It will prompt you to install additional software. Most often this happens in unlicensed applications. In any case, it is recommended to refuse the proposed option, since in themselves they are useless and will only clog up the computer, and in some cases, viruses will spread in this way. To do this, you need to uncheck all the boxes and click the “Next” button.
Step 12: Review the report
Setting up the installer parameters is almost complete. Now you will see a report of all the actions you have performed previously. At this step, you need to double-check the information provided and if there is a discrepancy, click “Back” to change the settings. If everything is exactly as you indicated, then click “Install”.
Step 13: Application Installation Process
Now you have a bar in front of you that displays the progress of installing the application into the previously specified folder. All you need to do is wait until it is completely filled with green. By the way, at this stage you can click the “Cancel” button if you change your mind about installing the program.
Step 14: Finish installation
A window will appear in front of you, informing you that the application has been installed successfully. As a rule, only one button is active in it - “Finish”, after clicking which the installer window will close and you can start using the newly installed software. But in some cases there is an item “Launch program now”. If there is a mark next to it, then after pressing the previously mentioned button, the application will launch immediately.
There will also sometimes be a "Reboot Now" button. This happens if the installed application requires a computer restart for it to work correctly. It is advisable to complete it, but you can do it later by clicking the appropriate button.
After completing all the steps described above, the selected software will be installed on your computer and you can immediately begin using it. Depending on the actions taken previously, the program shortcut will be located on the “Desktop” or in the “Start” menu. If you refuse to create it, then you must launch it directly from the directory you chose to install the application.
Dictionary
List of English words and expressions that may appear during the installation process