By default, the first user account created in Windows 10 (for example, during installation) has administrator rights, but subsequent accounts created have standard user rights. This beginner's guide will show you step-by-step how to give administrator rights to created users in several ways, as well as how to become a Windows 10 administrator if you don't have access to an administrator account, plus a video that shows the whole process clearly. See also: How to create a Windows 10 user, Built-in Administrator account in Windows 10.
How to enable admin rights for a user in Windows 10 Settings
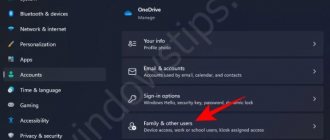
Windows 10 has a new interface for managing user accounts - in the corresponding section of Settings.
To make a user an administrator in Settings, simply follow these simple steps (these steps must be performed from an account that already has administrator rights)
- Go to Settings (Win + I keys) - Accounts - Family and other people.
- In the "Other People" section, click on the user account you want to make an administrator and click the "Change Account Type" button.
- In the next window, in the “Account Type” field, select “Administrator” and click “OK”.
Done, now the user will have the necessary rights the next time he logs in.
device Manager
A very useful utility that many people know about. Here we can manage installations of new hardware and resolve some driver issues. For example, you inserted a new mouse, it will immediately appear in the device manager in the “Mice and other pointing devices” section.
In addition to the above, we can also disable some devices. You can find out some information about the device.
Using the control panel
To change the account rights from a simple user to an administrator in the control panel, follow these steps:
- Open Control Panel (you can do this by searching in the taskbar).
- Open "User Accounts".
- Click Manage Another Account.
- Select the user whose rights you want to change and click “Change account type.”
- Select "Administrator" and click the "Change Account Type" button.
Done, the user is now a Windows 10 administrator.
Conclusion
As you can see, the Windows 10 operating system is equipped with a fairly powerful set of administration tools.
I use some of them, especially in terms of monitoring resources and components, regularly. This allows you to keep control over the main indicators of the system and eliminate most failures and problems. Others are somewhat limited and use third-party applications for additional checks and improvements. But before installing and running someone else’s utility, it is recommended to try the developer’s native applications. I hope my article will be useful in solving problems of optimizing the operation of OS Windows on your computers. Post Views: 348
Using the Local Users and Groups utility
Another way to make a user an administrator is to use the built-in Local Users and Groups tool:
- Press the Win+R keys on your keyboard, type lusrmgr.msc and press Enter.
- In the window that opens, open the “Users” folder, then double-click on the user you want to make an administrator.
- On the Group Memberships tab, click Add.
- Type "Administrators" (without quotes) and click OK.
- In the list of groups, select "Users" and click "Delete".
- Click OK.
The next time you sign in, the user who was added to the Administrators group will have the appropriate rights in Windows 10.
Task Manager
The well-known task manager tool. It has many capabilities, for example, you can find malicious programs and suspicious processes. Under Windows 8 and 10, you can use the Startup tab in the task manager and disable unnecessary applications that are usually loaded with the system.
How to make a user an administrator using the command line
There is also a way to give administrator rights to a user using the command line. The procedure will be as follows.
- Remote Server Administration Tools for Windows 10
- Run Command Prompt as Administrator (see How to Run Command Prompt in Windows 10).
- Type net users and press Enter. As a result, you will see a list of user accounts and system accounts. Remember the exact name of the account whose permissions you want to change.
- Type net localgroup Administrators username /add and press Enter.
- Type net localgroup Users username /delete and press Enter.
- The user will be added to the list of system administrators and removed from the list of regular users.
Command Notes: On some systems based on English versions of Windows 10, you should use "Administrators" instead of "Administrators" and "Users" instead of "Users". Also, if the username is multiple words, put it in quotes.
Available tools
The RSAT support matrix on the Windows 10 platform can be found here. The key point is that Hyper-V tools are not part of RSAT for Windows 10, unlike earlier versions. Hyper-V comes as part of Windows 10 and can be used without installing RSAT. Other tools that are not available in this release:
- BitLocker Drive Encryption Administration Utilities;
- Direct Access;
- Routing and Remote Access;
- Remote Desktop Services;
- Windows PowerShell cmdlets for Cluster Aware Updating;
- Windows PowerShell cmdlets for Best Practices Analyzer.
Opening the "Administration" section
There are several ways to access the specified directory; let’s look at the two simplest ones.
Method 1: "Control Panel"
The first way to open the section in question involves using the “Control Panel”. The algorithm is like this:
- Open the “Control Panel” using any suitable method - for example, using “Search”.
Professional advice
Sometimes you have to work on different clients, and you need to be able to control the remote server from them. But re-tuning can take a long time. If the versions of Server Manager on different clients are similar, you can copy the files from the following locations on the original client to the same locations on the new client. This way, the next time you launch Server Manager on a new client, you will find the configuration that was set on the previous client.
Copy the files from the following locations:
%appdata%MicrosoftWindowsServerManagerServerList.xml %appdata%LocalMicrosoft_CorporationServerManager.exe_StrongName_GUID6.2.0.0user.config
Remember that the versions of Server Manager on the original and new clients must be identical.
Windows 10 Administration Tools Overview
The “Administration” catalog contains a set of 20 utilities for various purposes. Let's look at them briefly.
“ODBC Data Sources (32-bit)” This utility allows you to manage connections to databases, monitor connections, configure database management system (DBMS) drivers and check access to certain sources. The tool is intended for system administrators, and the average user, even an advanced one, will not find it useful.
“Recovery Disk” This tool is a wizard for creating a recovery disk - a tool for restoring the functionality of the OS, recorded on external media (flash drive or optical disk). We described this tool in more detail in a separate guide.
Lesson: Creating a Windows 10 Recovery Disc
iSCSI Initiator This application allows you to connect to external storage arrays based on the iSCSI protocol through a LAN network adapter. This tool is also used to enable block storage networks. The tool is also more focused on system administrators, so it is of little interest to ordinary users.
“ODBC Data Sources (64-bit version)” This application is identical in functionality to the ODBC Data Sources discussed above, and differs only in that it is designed to work with a 64-bit DBMS.
“System Configuration” This is nothing more than the msconfig utility, known to Windows users for a long time. This tool is designed to control the loading of the OS, and allows, among other things, to enable and disable “Safe Mode”.
How to find out the system capacity?
Admin Pack comes in two versions - for 32- and 64-bit OS. To find out which version you have:
- Right-click on the “My Computer” icon.
- Item "System".
- The “Type” line will indicate the bit depth.
Operating system bit size
Do not try to install programs that are designed for another type of OS. They won't work properly.
Basic concepts encountered during work
During the process of activating tools, the following terms are encountered:
- forests - elements of the AD structure containing domains;
- DNS - domain name resolved in AD;
- server - a computer (performing certain functions in the domain);
- Domain Controller - domain controller (server within which the Data Store is located - the directory to which requests from users are received);
- domain is an AD element that includes objects (PCs, printers, user profiles) of the network.
What is AD delegation
Delegation itself is the transfer of some permissions and control from a parent to another responsible party.
It is known that every organization has several system administrators. Different tasks should be assigned to different shoulders. To apply changes, you need to have rights and permissions, which are divided into standard and special. Specific: These apply to a specific object, and a standard is a set of existing permissions that make certain features available or unavailable.
Sources
- https://it-tehnik.ru/windows10/ispolzovanie/kak-vklyuchit-active-directory.html
- https://brit03.ru/programmy/active-directory.html
- https://ru.wikipedia.org/wiki/Active_Directory
- https://zen.yandex.ru/media/tehnichka/kak-ustanovit-rsat-v-windows-10-5fe1f45c230da257b7b5db07
- https://MyComp.su/operacionka/admin-pack-windows-10-x64.html
- https://lumpics.ru/the-printer-does-not-work-active-directory-domain-services-are-not-available-now/
Finding the problem
In most cases, installing RSAT goes smoothly. However, there are two problems you may encounter.
The first is the inability to install RSAT. If this happens, make sure Windows Firewall is turned on. RSAT uses the standard Windows Update backend and requires the firewall to be up and running. If it's off, turn it back on and try installing RSAT again.
The second problem may occur after installation. Some users are missing tabs or experiencing other problems. The only solution to problems after installation is to uninstall and install RSAT again.
If you have problems with ADUC, you should check if its shortcut is connected correctly. This should lead to %SystemRoot%\system32\dsa.msc. If this is not the case, reinstall the program.