When a computer program stops responding to user actions, including an attempt to close it in the standard way, it is said to be frozen. In such cases, you can see “Not responding” at the top of the window. Randomly pressing keys, pulling the cord out of the socket, or turning it off using the power button are not the best solutions in such a situation.
Considering that this kind of thing happens quite often, all computer users should know what to do in such situations and how to properly force close a frozen program. Let's say right away that this problem can have several solutions.
How to cancel a task if the program is frozen
So, when we have found out that it is the program itself that is hanging, and not the OS, we need to try to close it.
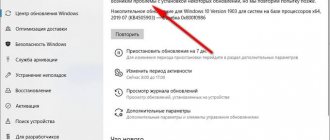
Naturally, before this, you need to try to close it in the usual ways - by clicking on the cross, through the menu - close, etc. If this does not help, then you should use the easiest way to stop a frozen program - using the Task Manager. To do this, right-click on any free space on the taskbar and select Task Manager from the drop-down list.
It is possible that the ill-fated program has frozen over the entire area of the monitor and is covering the taskbar. Then the described method of solving the problem will not help. Using the keyboard shortcut Ctrl+Alt+Delete to open the task manager will help (a blue screen will appear with several items, among which select the one you need).
The task manager window will display all applications currently running on your PC. Next to the name of the frozen program there will be a note “Not responding”. Select this application and click on End task.
Perhaps after this the frozen program will not stop working immediately, but a window will appear asking you to perform one of the actions. Select Close program. The procedure may be slightly different for different versions of Windows OS. But the essence remains the same.
After completing these steps, the glitched program should close and disappear from the list of applications in the task manager. If a program, or several programs at once, freezes on a regular basis, and at this moment the hard drive begins to make a lot of noise, most likely the hard drive will soon fail, and you should take care of replacing it.
I hope this article helped you solve your problem with freezing programs.
Sometimes some programs freeze and you need to end the process to force them to close. In today's article, we'll look at various ways to do this in Windows 10.
Key combination
One of the easiest ways to close a frozen game or application on Windows is by using special key combinations. As a rule, this trick works with most programs that are frozen.
Keys that close frozen applications:
- Ctrl+W;
- Alt+F4;
- Alt+Q;
- Esc.
You can also minimize the window of a frozen program using the keys:
- Alt+Enter;
- Alt+Tab;
- Win+Tab;
- Win.
Optimization of 1C work. Part 1. APPLICATION SERVER 1C 8.3
Several worker processes on one server make it possible to effectively use the amount of RAM and processor resources to execute requests, as well as connect a client session to another worker process if the current one “crash”. The Server Agent (ragent) program is responsible for understanding what is running on a specific server. Stopping the server agent will make the server unavailable for use by the cluster. The agent stores its information in the file srvribrg.lst.
Information about work databases and involved work processes is owned by the “Server Manager” (rmngr). It stores this information in the file 1CV8Reg.lst. Stopping the server manager can lead to a restart of client applications if the manager restarts successfully or to a complete stop of the working servers of the entire cluster.
1C: The enterprise allows the possibility of creating several independent clusters on one server. Each of them is identified on the network by a unique “IP port” and a unique number in service files. The first cluster receives port 1541 by default.
The Enterprise Servers snap-in is designed to manage a cluster. You can connect to servers by server name or IP address.
Stop typing immediately
You can quickly cancel the printing mission assigned to the equipment manually - to do this, just turn off the power to the equipment. For different devices, this button may be located in different places (for example, for a Samsung printer it can be found on the back panel).
But it is not recommended to use this opportunity: interference still occurs in the operation of a complex apparatus. Such incorrect “behavior” can lead to corresponding consequences, and the least of them is that the paper will become wrinkled and the device will have to be disassembled.
Server agent
The server agent “knows” about all the clusters that are running on the server. This information is stored in the file srvribrg.lst with a list of clusters and list administrators. The main port of the agent is 1540. On each Working server, only one agent can be launched, servicing all possible clusters on this server.
Let's take a closer look at the cluster properties
Restart interval
This parameter restarts 1C server work processes according to the specified value in seconds. Typically, the parameter is used on application servers that have a 32-bit system, since the memory capacity there is limited to ~ 3.7 GB if the operating system is 64-bit and the application server is 32-bit. If the OS uses a 32-bit architecture, then the total memory consumption of the working process is ~ 1.7 GB. And users can often receive an error message like “Insufficient memory on the 1C Enterprise server.” The easiest way to avoid this error is to restart the work processes, for example 86400 seconds (1 day). When changing the parameter, the time count starts from the start of the 1C application server service.
Allowed memory size
Restarting worker processes when a certain threshold of memory occupied by the worker process in kilobytes is reached.
Interval for exceeding the permissible amount of memory
This means that if within a specified number of seconds the memory specified in the “allowable memory amount” parameter is exceeded, then the 1C server will decide to restart the workflow.
Permissible deviation of the number of server errors
It is calculated as follows. We have server calls that can be seen in the technology log by the “CALL” event, and there are also various exception situations that can be seen in the technology log by the “EXCP” event. The platform calculates the ratio of these events. It is assumed that these events should be approximately the same. If in any work process this ratio exceeds the ratio of these events in other work processes by some significant amount, then such a work process is considered problematic. Just this value is set in this parameter. The recommended value is 50.
Force termination of problematic processes
If we enable this parameter, then according to the “permissible deviation in the number of server errors” parameter, problematic processes will be terminated. If the parameter is disabled, the platform displays the process log event “ATTN”, which indicates the problematic process.
Stop disabled processes after
If one of the “restart interval” or “allowable memory size” parameters is triggered, then when the working process is restarted, it may “fall off”. If the client does not access the server during the restart (is inactive), then the next time it accesses it, it will smoothly switch to the new worker process. If the client contacts the server at the time of restarting the workflow, then in this case it will receive an error message and terminate its work. To prevent this from happening, you must set the value of this parameter in seconds. Usually 120 seconds is enough. During this time, the workflow will have time to process current customer requests and transfer them to a new workflow. Those active clients that the process did not have time to process are terminated and the clients may receive an error.
Fault tolerance level
This setting lives on its own, regardless of the number of central servers. The fault tolerance level can take any value. For example, resiliency level = 1, then each user session is doubled. If the fault tolerance level = 2, then each session is multiplied by 3. The load on the server also increases. When changing the fault tolerance level, if we have a central server, it replicates to each central server: “cluster registry”, “cluster locking service”. There is also replication of services such as “session data service”, “online time stamp service”, “object blocking service”, “licensing service”, “numbering service” to other servers. Among them, the heaviest one is the “session data service”.
Load sharing mode
In terms of performance. When a client connection connects, it will connect to whichever server has a worker process with more available performance. The available performance is set in the workflow properties:
The available performance at the 1C level is calculated as follows: a reference server call is made to all work processes once every 10 minutes and the time of this call is measured. The resulting number is divided by 10,000 (ten thousand) and the application server mechanisms calculate the reference time. In the event that the productivity of a work process has become 25% less than that of the others, connections from this work process begin to go to other work processes until all connections are gone.
Memory priority. User connections will be made to a production server that has more available memory.
Possible problems
Having completed all these steps, the user must understand that the printing process will not stop immediately. This circumstance is due to the fact that the printing device has RAM - built-in random access memory. It is a kind of buffer in order to store documents arriving at the device (print queue). Therefore, for some time after issuing the cancel command, the equipment is still able to continue working.
Another reason for delayed command execution is that some versions of operating systems run late. However, it is not so significant: it is better to follow all the specified instructions and complete the job correctly than to then eliminate unpleasant consequences with the printer.
The working process
The Work Process is responsible for “working with clients.” There can be several worker processes in the 1C: Enterprise 8 cluster. The number of work processes is not created manually, but is calculated based on descriptions of task requirements for fault tolerance and reliability. The server manager decides which worker process will serve the client connection. For client connections, Worker Processes are by default allocated a range of IP ports 1560 – 1591. In addition, each Worker Process is assigned a Service port for communication with the cluster manager.
The working server settings, according to 1C documentation, can only be changed in the CORP version of the 1C application server. In fact, the settings work in both the CORP and PROF versions. If these settings are used in the PROF version, this will be a violation of the license agreement.
Maximum Workflow Memory
This parameter in itself does not limit anything. It works in conjunction with the “safe memory consumption per call” parameter. Let’s imagine that all our work processes in total have reached approximately the memory consumption of the specified value of this parameter. And now a certain user wants to make a certain server call that wants to consume a large amount of memory. As soon as the server call exceeds the amount of memory specified in this parameter by the amount of memory in the “safe memory consumption for one call” parameter, this particular user will receive an error of the form: “safe memory consumption for one client-server call has been exceeded.” This is necessary so that one user cannot overwhelm the working server. The value of parameter 0 is equal to 80% of the memory installed on the 1C server.
Safe memory consumption per call
A value of 0 (default) is 5% of the Maximum Workflow Memory value. The value may be -1. This means that any client-server call that exceeds the specified value of the “maximum worker memory size” parameter.
The amount of work process memory up to which the server is considered productive
Means, if set to a value and worker processes have taken up the amount of memory specified in this parameter, the server will continue to run, but will not accept new connections until the memory is freed.
Number of information security per process
There may be a decrease in performance when there are many infobases and one workflow. Therefore, with this parameter it is possible to reduce the number of databases per process. If you set the value to 1 (in most cases this works quite optimally), then a new worker process (rphost) will be created for each infobase.
Number of connections per process
Same as the parameter above, but depends on the number of connections per process. A value of 0 will mean that there will be only one worker process on each worker server.
Manager for each service
Each central worker server has a main cluster manager with certain services:
They are executed by one service “rmngr”. Let's imagine that this service begins to consume a lot of memory or waste CPU resources. There are usually a few typical suspects. But suddenly you are at a “dead end” and cannot understand what exactly is loading the service, you can check the “manager for each service” checkbox, the service will be divided into 21 processes (this is the number of services in the main cluster manager). And accordingly, using the PID of the process, it will be possible to calculate which service is loading the system.
Central server
This is the server that stores the cluster registry in the 1CV8Clst.lst file. The file stores a list of databases, a list of cluster administrators, a list of functionality assignment requirements, a list of security profiles, and in general all cluster settings. This file is present only where the “central server” checkbox is checked. There can be several central servers. Also on the central servers there are such services as “cluster blocking service”, “cluster configuration service”. As long as at least one central server is operational, the cluster is functioning. Once the most recent central server fails, the cluster becomes unusable regardless of fault tolerance settings.
Functionality assignment requirement
The 1C Enterprise 8.3 server cluster provides a certain set of functionality (called requirement objects), the distribution of which between working servers within the cluster can be controlled. For example, you can specify that all background jobs in the cluster will run on a selected worker server. In order to place a connection or cluster service on any production server, you need to create a functionality assignment requirement for the selected production server. This requirement determines the ability or impossibility of a particular server to perform a particular job. Let's take a closer look at what a functionality assignment requirement is.
Migrating User Connections
Let's say we want user connections to work on worker server #1, but if that server goes down, we want them to fail over to another worker server #2
To do this, we need to create a functionality assignment requirement on server No. 1:
On server No. 2, set the same settings, but change the priority:
The importance of priority is implemented in reverse. That is, priority 1 is higher than priority 2.
Remove the production server from the cluster
We can simply remove the working server from the cluster by deleting it from the list, but in this case all users will be “kicked out” from the system. To make the withdrawal more painless, you can do the following:
Create a functionality assignment requirement with the following settings:
This setting means that there will be no new connections to this production server. Those users who were working will continue to work, but will gradually move to other working servers.
Licensing service
Move the licensing service to a separate server. This is good because software licenses can be tied to a specific computer. Let's create a functionality assignment requirement with the following settings:
Background jobs
With the release of platform 8.3.7, background jobs were divided into 2 groups:
1. Background jobs called from configuration code
2. Routine tasks
Therefore, several settings for assigning functionality are required:
1. Disable all background jobs
1. Prohibit all scheduled tasks
1. To make background jobs run quickly, you need to add session data for background and scheduled jobs
1. Deny other services
After creating the necessary requirements for assigning functionality, you need to apply them:
Partial – application that will not disrupt the user experience
Full – an application that may disrupt the user experience.
In practice, I have never encountered a situation where, when fully applied, it disrupted the user experience or anything like that. But anything is possible, keep in mind. After application, restarting the 1C application server service is not necessary.
You can always contact 1C optimization specialists; our practical experience will save your time.
| You can send a request for a consultation by e-mail: [email protected] |
Stop typing immediately
You can quickly cancel the printing mission assigned to the equipment manually - to do this, just turn off the power to the equipment. For different devices, this button may be located in different places (for example, for a Samsung printer it can be found on the back panel).
But it is not recommended to use this opportunity: interference still occurs in the operation of a complex apparatus. Such incorrect “behavior” can lead to corresponding consequences, and the least of them is that the paper will become wrinkled and the device will have to be disassembled.
Terminating processes
If, while working on your computer, you begin to notice that it noticeably freezes, it means that it is difficult for it to perform all the tasks assigned to it. This happens when you start a lot of processes and then simply forget to stop them.
Of course, if you don’t get carried away with opening new applications, you’ll be able to encounter the problem of your computer freezing less often. Well, if you were working very enthusiastically, so you didn’t notice how you opened many windows, launched several software applications and utilities, then closing them by simply clicking on the “Exit” button may not work.
Algorithm of actions
To terminate unwanted processes that refuse to obey the user, you need to use the help of the Task Manager. If you have Windows 7 installed, just right-click on the bottom taskbar and select the “Launch Task Manager” option.
Step 1
In the window that opens, on the first tab, click on the utility that you no longer need, and then at the bottom of the window select the “End task” option. If the process is not completely hopeless, it will stop.
Step 2
You can go to the second tab “Processes”, in the same way click on the line that is causing problems at a particular moment, and then click on the “Finish” button.
Check the option to show all user processes
Unfortunately, even such advice sometimes turns out to be completely useless for some users, since the process in the Task Manager still does not close.
If such a problem happened to you, you despaired and already believed that the only way out of such a problematic situation would be to force a reboot of the operating system, we suggest that you do not panic, but read our following recommendations.
Step 3
So, do not say phrases like: “I can’t kill the process in the Task Manager,” but rather take advantage of the unique capabilities of the taskkill utility command. Many are ready to consider this team as a powerful tool.
To run such a command, first, of course, you need to open the command line by holding down two keys at the same time: “Win” and “R”. In the small window that opens, enter “cmd”.
Step 4
Now you will need to type “taskkill” and press “Enter”. However, to deal with an uncontrolled process, an additional option should be attached to this word.
Specifically, you can terminate a process using the taskkill command using the name of the application that refuses to terminate. To do this, type a small command phrase: taskkill / IM “application name”. Of course, instead of the phrase “application name” you should type the process that you cannot stop. For example, taskkill /IM excel.exe. If you use our example, then in this case the Excel spreadsheet editor will stop working. Choose your process that is causing you terrible trouble and add its name to the command.
In the window, processes are displayed not only with their name, but also with their identifier. If you wish, you can type the following command phrase: taskkill / PID 574, where the number 574 will be the ID of the problematic process.
Step 5
If there are several accounts on the computer, and it is absolutely clear that the freeze occurred precisely because of the unfinished processes of one of the users, you can use the following command phrase: “taskkill / F / FI “USERNAME eq username”. It is clear that in it you will have to independently change the username directly due to whose fault the problem arose.
Use the new command phrase
We recommend that you practice using these commands. If you succeed, you will be able to avoid forced reboots that mercilessly damage the operating system.
The “taskkill” command is indeed a powerful tool that even viruses and Trojans cannot resist. Such a team successfully completes even their negative and persistent “activities”.
Action List
The first item on the list is an item with which you can easily create a simple task.
By clicking on this item, you will be taken to the window of the wizard for creating them, which is used mainly for quickly planning everyday simple tasks.
Task creation wizard window
Next on the list is the task creation option, which allows you to select more complex tasks using various triggers and multi-level actions.
Task creation menu window
This window contains several working tabs necessary for work.
Among them are the following:
- General - a tab containing the name, location and description of the task, as well as the security settings used when executing it;
- The triggers tab allows you to apply certain conditions related to its launch to the created task;
- Actions - on this work tab, the user can assign certain actions to a task, the execution of which will occur in conjunction with its launch;
- Conditions - in this section you need to specify the conditions that, together with the installed triggers, will launch the task for execution. If the specified condition cannot be valid, the task will not begin;
- Options is the last tab and allows you to set some additional settings involved in completing the task.
LiveInternetLiveInternet
- Registration
- Entrance
-Music
- All (55)
—Photo album
- All (5)
—Categories
- Cartoon personality (13)
- Internet (11)
- Tomatoes (8)
- Culinary sites (2)
- Scrambled eggs (2)
- UFO (2)
- Alphabetical rubricator (1)
- Crackers (1)
- SHASHLIK. (71)
- “Stalik Khankishiev is preparing” (111)
- .Words of wisdom. (17)
- animations (34)
- Antiques. (37)
- Cars (144)
- Cars (112)
- PANCAKES, PANCAKES, PIES (844)
- Picnic dishes (23)
- Dishes from zucchini, eggplant (74)
- Cabbage dishes (202)
- Potato dishes (331)
- Meat dishes (872)
- Tomato dishes (8)
- Videos (166)
- Military news (188)
- Everything for home and garden (287)
- All about fishing (0)
- Everyone read (408)
- main courses (529)
- Stuffed cabbage rolls (137)
- Cities, castles and countries. (130)
- Mushrooms (298)
- Houses (61)
- pets (173)
- Homemade sausage (349)
- Feminine beauty. (43)
- life quotes (114)
- Preparations for the winter. (378)
- Snacks (252)
- Health (548)
- From lavash (121)
- Inventions (155)
- Icons (18)
- Interesting (776)
- interesting animals, birds, etc. (251)
- to the Easter table (14)
- Paintings (22)
- Clipard (21)
- NEXT buttons (2)
- Comments (33)
- Space (26)
- Beauty (66)
- Cooking (1608)
- 100 recipes for dishes with sausages (1)
- 100 bacon recipes (1)
- 100 corn recipes (1)
- 100 liver recipes (1)
- 100 ham recipes (1)
- Cuisines of the world (16)
- Medicinal herbs (32)
- Top sites (5)
- Manti (27)
- master classes (261)
- Medicine. (5)
- My cheat sheets (193)
- To my friends (56)
- My diary (4)
- my computer (247)
- Music (Audio) (105)
- music for the Soul (Video) (1194)
- Cartoons (2)
- "Happy Birthday" Captions (1)
- Back to the USSR (121)
- Drinks (113)
- Traditional medicine (14)
- Nakhodki (3)
- News (10)
- Wallpaper (1)
- advertisements (2)
- dangerous food (25)
- Postcards (31)
- hunting rifles, etc. (116)
- first courses (199)
- Songs of our yard (3)
- playcasts (49)
- Underwater world (1)
- Useful information (55)
- Useful sites (3)
- Holidays (266)
- Signs (17)
- nature (237)
- Herbs and spices (1)
- Artists' works (8)
- radio (15)
- Radio .1 (42)
- Frames (64)
- rare photo (36)
- Vegetable recipes (5)
- Romances (8)
- fishing (20)
- Fish recipes (803)
- Garden and vegetable garden (719)
- Website "Cellar". (1)
- Salads (438)
- Salo (131)
- do it yourself (242)
- Hidden Secrets (2)
- Emoticons (6)
- funny video (6)
- Tips (420)
- Sauces (126)
- Thank you (5)
- links (21)
- Poems (265)
- Soups (5)
- design schemes (47)
- TV (2)
- Cakes (189)
- Liru's Textbook (43)
- Porcelain (23)
- Movies (84)
- Backgrounds (5)
- Photos (44)
- Funny photo (9)
- Photoshop (17)
- khachapuri (63)
- Khinkali (7)
- history/archeology (1)
- Bread (50)
- Bread maker (3)
- aspic (92)
- Flowers (108)
- Roses (1)
- Quotes (34)
- Watch (1)
- pasties (224)
- encyclopedias (9)
- Humor (426)
—Links
- All (1)
—Tags
—Search by diary
—Interests
- All (1)
-Friends
- All (577)
— Regular readers
- All (905)
Possible problems
Having completed all these steps, the user must understand that the printing process will not stop immediately. This circumstance is due to the fact that the printing device has RAM - built-in random access memory. It is a kind of buffer in order to store documents arriving at the device (print queue). Therefore, for some time after issuing the cancel command, the equipment is still able to continue working.
Another reason for delayed command execution is that some versions of operating systems run late. However, it is not so significant: it is better to follow all the specified instructions and complete the job correctly than to then eliminate unpleasant consequences with the printer.
Options for accessing the Task Manager
Now there’s another important question about how to remove a task on a computer. Many users, when a program freezes, try to immediately use the standard three-finger combination. But this only causes a third-party screen to appear with you logging out and logging in again upon confirmation.
To solve the question of how to cancel a task on your computer when you call the “Task Manager” using a simpler method, you should use the combination Ctrl + Shift + Esc. But the best option, and a completely fail-safe one, is to call the console through the “Run” menu, where the taskmgr line is written. In this case, the user has access to terminate processes on a running system.