The web browser is the gateway to access the global Internet. The web is growing exponentially and users are seeing huge changes in software, yet Firefox continues to eat up memory over time. This is especially noticeable when several additional tabs are opened, the browser begins to slow down the entire operating system.
Fortunately, this can be fixed, but first you need to check memory usage in Firefox. To do this, enter “cache/Device = memory” in the address bar and press Enter. The browser will display the current number of records, maximum storage size, in use and inactive.
Causes of poor memory
Mozilla increases the number of features over time and, therefore, when Firefox eats up memory, the amount of system resources increases dramatically. Even if you add just a few extensions out of the 1000 available, the browser will begin to consume hundreds of megabytes of memory and take up large amounts of disk space. The latter circumstance will immediately affect the loading of pages, which will take a lot of time, since the opening speed will drop.
This fairly common failure is caused by fragmentation in databases. This phenomenon is especially noticeable when the browser remains open for several hours, the memory consumed reaches several gigabytes or more, which happens even with only a few tabs open. This phenomenon demonstrates the problem of long-term memory leaks, and the real way to limit Firefox's memory is to ensure that the SQLite databases used are compact. It becomes fragmented, and its optimization reduces read and write times.
The main reasons affecting overload:
- Crowded session history.
- Extensions and applications.
- Firefox Add-ons.
- Plugins.
- Settings, tabs and local storage size.
To deal with the problem quickly, there is a fairly simple solution; everything can be done using add-ons called Memory Fox. This software is written in the excellent lho language, so it will automatically manage memory usage from Firefox so that it is not wasteful on the computer. It constantly monitors memory when the user leaves the tab inactive and it is in standby mode. Suppose, for example, that 5 tabs are open, and only 1-2 are viewed, then the memory on the other tab, which is “idle,” will be cleared by the program, which means that the browser will feel easy.
Reducing session history
The browser.sessionhistory.max_entries parameter sets the browser history limit, that is, the maximum number of URLs that can be navigated using the Back/Forward buttons. The default value is 50. Typically, users do not view more than 5 websites, and there is no need to save more than that, since Firefox then takes up a lot of RAM. Installation procedure:
- Open browser.
- Enter about: config into your browser.
- Press CTRL+F and find browser.sessionhistory.max_entries.
- Double click on 50 or whatever value you set and change it to 5 or something like that.
- Restart the browser.
- To reduce Firefox's memory consumption for a more recent version, another configuration can be used - sessionhistory.max_total_viewers, which also sets a limit for "bfcache" caching (fast rewind/forward). The default number is 1 and is calculated based on available memory. By setting it to 0, no pages will be saved, and by setting it to 5, 5 pages will be saved.
Version
If you are using an outdated version, you should update it. It is worth understanding that developers strive to improve their creations. In particular, Firefox's memory consumption is a priority for them.
If an update is required, the following window will appear:
Advice! You should not use third-party sites to update, as in this case there is a high risk of encountering malicious toolbars. The browser itself should notify you that you need to install the latest version. All you need to do is follow the instructions.
Disabling extensions
By using fewer extensions, the user can experience real productivity gains. Leaving all unnecessary topics in the browser creates conditions under which Firefox eats up memory. When an extension may only be needed in the future and is not currently used at all, it is possible to disable it, which also reduces the memory load. In addition, it is necessary to constantly update them to the latest version.
Sequence for disabling extensions:
- Press the “Menu” and “Settings” button.
- Go to "Extensions". A list will open.
- Click “Disable” next to the one you want and restart the browser.
According to user reviews, many had memory problems after working with Firefox add-ons: Ghostery, Skype Click to Call, Greasemonkey and dictionaries. If these extensions are used, it is recommended that you disable them.
How else can I reduce Firefox's memory consumption? Plugins!
Now, as for the “Plugins” (plugins, not add-ons), because they also need to be put in order, which, by the way, not everyone does simply without knowing about their existence. In order to manage them, go to the “Tools - Add-ons - Plugins” tab.
Here, perhaps, it is worth disabling everything except Shockwave Flash and Java TM Platform (although this plugin is not always needed and not for everyone). The rest, as a rule, are add-ons wrapped around various applications, which have absolutely no meaning. As an option, you can still use Adobe Acrobat (responsible for opening PDF files directly in Firefox), but personally I prefer to use the application of the same name rather than a plugin.
When you are finished working with plugins and extensions, restart your browser.
Setting default themes
Many users like to customize Firefox with new themes. While some of them look visually impressive, they can consume too much memory. To resolve this issue, it is recommended to revert to the default themes and check to see if memory growth is prevented. To do this you need to do the following:
- Click on “Menu”.
- Go to the “Appearance” tab and make sure the theme is set to “Default”.
- Restart the browser and check if everything works correctly.
In addition to extensions, some plugins also cause memory issues in Firefox. To fix the problem, you need to disable them. To do this, carry out the following actions:
- Click "Menu" and "Add-ons".
- Open the “Plugins” and “Properties” tab, set: “Never activate” for a specific plugin, reload.
- After rebooting, check if the problem persists or if Firefox is still eating up memory. If it is not resolved, then you need to turn off the second and then the following plugins in a similar manner.
- After discovering an application causing memory problems, be sure to connect all the plugins back, except for the problematic one.
- If you need to use this particular plugin, you can try updating it to the latest version and see if the problem is resolved.
Working with add-ons
Next, I would like to note that a huge chunk of resource consumption is allocated not so much to FireFox itself, but to the plugins and extensions attached to it, and therefore let’s do a little optimization in this area. To do this, open “Tools - Add-ons” and look at what we have installed there:
- First of all, you should remove everything that you definitely don’t use or the purpose of which you don’t know. To do this, simply select “Delete” next to a particular extension.
- Next, I recommend using the “Disable” button opposite those plugins that you currently do not use at the moment, but which you periodically need. As an example, this could be, say, a plugin that you sometimes use to download music and videos, but you don’t do it regularly (for example, I use this plugin at most once a week or two, and the rest of the time I have it turned off). Do this with all extensions that are not currently used and simply enable them as needed.
Checking Flash hardware acceleration
High memory usage can also occur due to Flash hardware acceleration, and this glitch is also easy to fix. To do this you need to do the following:
- Open a page with Flash video.
- Click on the video player and “Settings” in the menu.
- Click the icon in the lower left corner and open the screen panel.
- Check the "Enable hardware acceleration" checkbox.
- After doing this, be sure to check if the problem is resolved.
When Mozilla Firefox is eating up memory, you can temporarily fix the problem by restarting the browser. Some users report that memory usage may increase if the application runs for long periods of time, so this solution will benefit you either way. Don't forget to close unused tabs. Each tab you open increases the amount of memory Firefox uses. If more than ten tabs are open, the user will surely encounter problems.
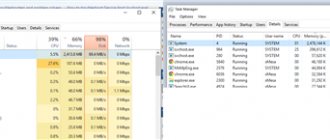
Memory consumption before Firemin
To measure the consumed RAM, I didn’t download any special programs or go into the jungle of system diagnostic utilities, but simply launched the task manager.
This is what it showed with several simultaneously open tabs in the browser...
Nothing strange or surprising - regular users of this browser have long been accustomed to such numbers (1755 MB), right? Now let's just run the program...
Application selection and memory functions
Firefox consumes a lot of memory due to applications that can be quite demanding on PC resources, so it is recommended to close any intensive programs, especially those running in the background. By doing this, the user will not only free up memory, but also improve performance. Firefox makes it easy to analyze your memory usage.
The process is quite simple, you can do it by following these steps:
- In Firefox's address bar, type about: memory and go to this page.
- Here you can view detailed memory usage reports and get free backup. To do this, click the “Minimize memory usage” button in the “Free memory” section.
- You can solve this problem by using the RAMBack extension.
Getting rid of intrusive content
Many Internet resources are crammed with unnecessary content: banners, drop-down animations, audio and video content that turns on spontaneously. This is largely why Mozilla consumes a lot of memory. However, there is a way to get rid of such content by installing the appropriate extension (more details):
- NoScript – allows you to disable any server scripts;
- Flashblock – blocks all content that uses Flash technology. As a rule, it is such content that requires more resources;
- Ad Block is the most advanced and multifunctional tool. We'll talk about it a little later.
Changing Browser Settings
Incorrect configuration is another reason why Mozilla Firefox eats up a lot of memory. According to the advice of users, it is easy to reduce memory consumption in the browser simply by changing its settings. To do this, perform the following steps:
- Enter in the about: config line.
- After the warning, select the option to continue.
- A list of parameters will appear, you need to change them as follows: browser.cache.memory.capacity to 0, browser.tabs.animate - disable, browser.sessionstore.max_concurrent_tabs - 0.
- After making the changes, restart Firefox and check if the problem is resolved.
Certain web content can also be quite resource-intensive and needs to be hidden to prevent memory leaks. According to users, Flash content and some scripts can be quite resource intensive, so it's best to disable them. If Firefox consumes a lot of memory, you need to use third-party extensions. To block Flash content, you can use the Flashblock extension.
Regarding scripts, the NoScript extension will allow you to select scripts to disable on certain sites. After disabling their use, Firefox's memory should improve. Please be aware that disabling some scripts may affect the operation of some websites, so choose which scripts to disable carefully.
Removing content-prefs.sqlite
Firefox stores user data (their settings, preferred screen magnification, etc.) in a folder on the computer, and this can also cause the browser to slow down.
Tweaking Firefox
Removing it may help, but it is important to understand that this will reset all settings. To find this file you need:
- Open settings.
- Select the Help section and click Troubleshooting Information.
- In the tab that opens, next to “Profile Folder,” click on “Open Folder.” It is in this folder that you need to delete the content-prefs.sqlite file.
This file will be created again the next time you start the browser, but now it will take up much less space, which will reduce the load on the processor.
Minimizing Firefox
When a new page loads, Firefox caches the data so it doesn't have to be reloaded to display it. By default this option is set to -1 for browser.cache.memory.capacity and a number that can be easily determined by going to Tools -> Options -> Advanced -> Network/Cache for browser.cache.disk.proacity. And check that browser.cache.memory.enable and browser.cache.disk.enable are set to True. Set browser.cache.disk.enable and browser.cache.memory.enable to False.
Memory reduction can be accomplished by changing just one parameter. Sequencing:
- Launch the browser.
- Enter: config and then Enter.
- In the drop-down window, type config.trim_on_minimize and click Next.
- Select True and press Enter.
- Restart Firefox.
Changing the sessionhistory function
According to experts, if Firefox eats up all the memory and freezes, you can fix the problem simply by changing sessionhistory. To do this you need to do the following:
- In an open browser, enter about: config.
- When the page opens, enter browser.sessionhistory.max_entries in the search at the top.
- Double-click browser.sessionhistory.max_entries in the list of results and enter the number 5. Click OK to save the changes.
- Restart your browser and check if the problem is resolved.
- Change browser.cache.disk.proacity memory limit value.
- After performing these steps, performance will become slower and if it is too much, then you need to use a higher value or return it to its original state.
Another useful configuration preference is browser.sessionhistory.max_total_viewers. Which sets the limit on the number of pages in RAM. By default, the number is 1. You can set this value to zero to not store any pages in memory, or 1 for 32 MB, 2 for 64 MB, 3 for 128 MB, etc.
Why does Firefox consume a lot of RAM?
Some people use Opera, others like Chrome, but I'm used to Mozilla. And it’s not a matter of quality or popularity, I’m just used to this browser, that’s all (you can also read about the history of browsers). From personal experience I can say that firefox consumes a lot of RAM for three reasons:
- Watching videos on YouTube - I don’t know why, but as soon as I start watching videos on YouTube, memory consumption immediately begins to increase. It is YouTube, or any other site (unless it also shows videos from YouTube) that allows you to calmly watch movies and not worry about the load on the system.
- Vkontakte applications - yes, any lame Vkontakte application (for example, the treasures of the pirate bay), like a hungry aborigine, eats up memory and system resources. This also applies to online games.
- Advertising on websites - there are various advertising blocks. Some are simple banners, others load a whole herd of various JAVA scripts. If a site, like a Christmas tree, is hung with advertising, then it instantly loads the system and memory.
While you can install a blocker for advertising, you can’t do much with videos and online games. Among other things, before the Internet was weak, and it was simply not possible to open many tabs with videos or even online games. Now the situation is completely different.
How to reduce memory consumption in Mozilla Firefox
Unfortunately, it often happens that Firefox consumes too much memory - usually almost 800 MB, and often even more than 1 GB of RAM.
Luckily, Firefox is a highly customizable browser. Behind the huge number of plugins, Firefox offers a simple panel for advanced customization. To make this panel appear, just enter about:config . This table-style panel shows many Firefox options.
There are many articles on this topic, and I will only describe the most common method of reducing RAM in Firefox.
Wanting to optimize the consumption of RAM occupied by Firefox, we look for the browser.cache.memory.capacity .
If there is no such key, then you need to add it by right-clicking on the panel and selecting: New / Whole. If we provide, for example, the number 512 as a value, then this will mean that Firefox can use up to 512 MB of memory.
Other useful parameters can be set:
- browser.sessionhistory.max_entries – indicates how many memorable entries there are in the history. The default value is 50, you can change it to 10 - this also seems to improve Firefox performance
- browser.urlbar.autofill – fills in the entered address just like Chrome does. Default value is false, can be changed to true
I’ll say right away that I tried to edit such settings, and instead of improving performance, I only got additional crashes. I mentioned this method only as an option, so that you know what it is and where you need to dig with your nose for a more detailed acquaintance. Personally, I'm not a fan of this type of thing as it can cause more harm than good.
Adjusting cache storage size
Firefox stores a version of a website in a cache, thereby reducing any future re-enables required to load the code. By default, you can get a maximum of 1 GB of saved cache from the Internet. This is quite a large amount of total disk space. Firefox 8.0 had only 256MB of local cache storage by default.
This is also quite a lot, especially when the user clears personal data at the end of the session. However, if it runs for a very long time, each time you visit the site again will clog the cache. Setting sequence:
- In the top menu open Tools -> Options.
- Click the “Advanced” tab.
- Somewhere in the middle of this menu, find “Limit Cache” along with the input number, for example 1024 MB.
- Click “OK” and restart the browser for this to take effect.
Suspend tab extensions
If you want to reduce memory usage in Firefox on any platform, you can use the Suspend Tab extension. It can reduce memory consumption by suspending background tabs, and also allows you to automatically stop them after a certain period of time and then manually resume them.
After installing the Suspend extension, you can right-click and select Suspend Tab from the context menu. This will immediately clear all memory used by that tab and put it in the background. At any time, if you want to return to this paused tab, you can right-click it and select Resume from the menu. This will load the web page.
In the Suspend extension options, you can automatically suspend background tabs after a specified period of time, the default is 30 minutes. Suspend allows you to reduce the memory consumption of the Firefox browser. Unlike the Memory Fox extension, which only works on Windows, it can be used on all platforms.
Optimizing RAM with Rizone Memory Booster
There are a huge number of programs for optimizing RAM on the software market. Most of them have similar features to each other and hence, choosing the best apps is not that easy. The program we're reviewing, Rizone Memory Booster, does basic optimization of your computer's RAM, but still stands out from the crowd.
Memory Booster does not require installation and is properly supported by Windows, 2000, XP, 2003, Vista, Windows 2008 and Windows 7 operating systems. The main window provides statistics on virtual memory usage, physical memory and CPU load. Thanks to time graphs, you can accurately track resource consumption. The memory optimization option allows you to immediately release it.
Rizone Memory Booster by default starts the RAM optimization process every 15-20 seconds. The elapsed time between attempts can be seen at the bottom of the window, just above the status bar. Frequency optimization can be changed by selection in the parameters.
We begin testing Rizone Memory Booster
After waiting for a while, I decided to check the Task Manager and Process Explorer metrics again.
In addition, I launched another video on YouTube. From the screenshots you can see that the RAM consumption in Firefox is above 800 MB, and more virtual memory is allocated.
Now let’s launch the Rizone Memory Booster program and take a look at the situation.
Let's look at the screenshots:
It can be seen that RAM consumption has decreased (the value jumps between 100 - 400 MB), and there is still a lot of virtual memory allocated.
At some point the firefox browser crashed. I started it again and restored the previous session.
In this case, the picture has changed a little:
As you can see, virtual memory consumption has decreased by almost one and a half times. Firefox also uses less RAM – within 100 MB. Rizone Memory Booster program is launched.
In fact, we can say that Rizone Memory Booster really works.
Debugging memory with Firemin
If crashes occur due to the browser slowing down your computer, you can solve the problem using Firemin. This tool allows the browser to periodically dump unused memory and dramatically reduce its usage. Firemin is only available for Windows and supports all versions from XP to 8.1.
This is a portable application so there is no need to install anything on the system. You just need to extract the firemin.exe file from the downloaded archive to any folder and run it. Once the file is launched, it places an icon in the Windows notification area and begins monitoring the process in the background. This tool will help you fix common computer errors, protect your computer from file loss, malware, hardware failure, and optimize your PC for maximum performance.
Firemin is free and open source software. Works with Windows XP/Vista/2008/7 and Windows 8 with 32 and 64 bit versions of operating systems. Firefox can eat up to 150 MB at startup, after letting the browser run for a couple more days, this will result in approximately 800 MB of RAM being lost. Memory leaks are to blame for this, and Firemin can easily fix them.
Firemin quick launch:
- run in safe mode;
- apply the SQLite Vacuum function to optimize databases;
- use the slider to configure memory.
If you need to configure the Firefox browser, then Firemin also has this function. You can access the optimization section from the Firemin taskbar context menu by selecting Optimize Firefox. This allows you to enhance SQLite databases by freeing up unused space within them.
Optimizing Firefox loading speed, as well as stability and speed
As a rule, long startup times and excessive slowness/freezing are associated with a weak disk subsystem and an overly bloated (or crookedly configured) cache. You and I have already partially configured the cache (and will partially configure it again), but everything else needs to be tinkered with. In particular, we will make several useful browser settings that will somewhat speed up its loading and overall operating speed.
To begin with, I recommend speeding up the operation of the disks a little, for which you need to make several settings to optimize them, which I wrote about in the article “A few settings to optimize the operation of the hard drive,” and also do defgramentation.
Next, I personally recommend moving firefox to the C:/ drive, namely to its root (that is, not to any of the subfolders, ala Program Files, but just C:/firefox). If my memory serves me correctly, then reinstalling the browser is not necessary for this - just use the right mouse button and the “Cut - Paste” command. If necessary, create a new shortcut (the old one may not work due to a change in the path), which is done by the same right-click on firefox.exe and the “Create shortcut” item. If C:/ is not the fastest drive in the system and there are physically faster ones, then move firefox there.
Let's move on to the settings. The fact is that when starting, the browser checks too many things, which slows down the loading. So let's remove this. To do this, launch Firefox, open “Tools - Settings”. In the settings window that appears, go to the “Advanced” tab and the “General” subtab.
Here I recommend unchecking the last 3 boxes, namely “Always check at startup if Firefox is the default browser”, “Send crash reports” and “Send performance data”.
Next, go to the “Network” subtab. Here we check the “Disable automatic cache management” checkbox and set some of our own values.
On the “Updates” subtab, disable checking for Firefox updates (this can always be done manually using “Help - About firefox - Check for updates”) and search engine plugins, that is, uncheck the corresponding items. In general, you can also disable checking for add-on updates, since they are checked every time the browser is updated. Here, think for yourself what is more convenient for you (mine is disabled).
Using the SpeedyFox tool
Optimizing memory for the browser reduces time consumption and leaves more memory for other programs. SpeedyFox is a tool designed specifically to compress SQLite database files, which in turn will reduce the time spent reading and writing. In addition to Firefox, for which it was originally developed, SpeedyFox can now also integrate databases for Chrome, Epic Browser, SRWare Iron and Pale Moon.
It also supports Mozilla Thunderbird and Skype tools. When you launch the portable executable, SpeedyFox automatically detects and loads a default profile for each of the supported applications. Since it is very popular these days, it is also possible to download user profiles for portable versions of Firefox or Chrome. Procedure:
- Click on the SpeedyFox menu bar and select “Add a custom profile” or drag the folder into the Firefox program window, memory optimization will begin after checking the application profiles and clicking the “Optimize” button.
- SpeedyFox will begin compacting SQLite databases. The progress window will show which databases have been optimized and how much space is being saved. You need to make sure that the programs being optimized are not currently running or they will not be processed. The author of SpeedyFox recommends running the tool every 1-2 weeks depending on the usage of enabled browsers.
- SpeedyFox also works from the command line, and can easily be placed in the form of a shortcut or script. To do this, you'll need to click "Command Prompt" then "Copy" to copy the current command and options to the clipboard and place them in a batch file or desktop shortcut to be launched by double-clicking.
If none of the previous solutions work, you can try using a different browser, as some PCs conflict with Firefox. If the same problem occurs with other browsers, you might want to consider upgrading your RAM.
Memory consumption after starting Firemin
Yes, I understand that you don’t believe me and your eyes