When buying a processor, many people try to choose something cooler, with several cores and a high clock speed. But few people know what the number of processor cores actually affects. Why, for example, can a regular and simple dual-core processor be faster than a quad-core processor, or the same processor with 4 cores be faster than a processor with 8 cores? This is a rather interesting topic that is definitely worth understanding in more detail.
Intel and AMD processors
Today, Intel and AMD are direct competitors in the processor market. When looking at revenue and sales, the Blues have a clear advantage, although the Reds have been struggling to keep up lately. Both companies have a good range of ready-made solutions for all occasions - from a simple processor with 1-2 cores to real monsters with more than 8 cores. Typically, such “stones” are used on special work “computers” that have a narrow focus .
Hard disk capacity
Currently, there are two types of hard drives that differ from each other in internal storage technology - HDD and SDD. The hard disk drive (HDD) is the most common. Such disks are cheaper, but have a number of other disadvantages. Due to the fact that all information on them is stored in the form of magnetized cells and read by a special moving head, the devices are very easily damaged as a result of falls or exposure to magnetic fields.
Solid State Drives (SSDs) are based on flash memory technology. The same technology can be seen in USB flash drives. They are faster, shock-resistant, and also completely silent due to the absence of moving parts. Installing the operating system on a solid drive will allow you to turn on the device in a few seconds. The maximum capacity of SSD is currently inferior to HDD: 2 TB versus 512 GB.
Intel
So, today Intel has successful 5 types of processors: Celeron, Pentium, Core i3, i5, and i7. Each of these “stones” has a different number of cores and is designed for different tasks. For example, Celeron has only 2 cores and is used mainly on office and home computers. Pentium, or, as it is also called, “stump”, is also used in the home, but already has much better performance, primarily due to Hyper-Threading technology, which “adds” two more virtual cores to the physical two cores, which are called threads . Thus, a dual-core “percent” works like the most budget quad-core processor, although this is not entirely correct, but this is the main point.
As for the Core line, the situation is approximately the same. The younger model with the number 3 has 2 cores and 2 threads. The older line - Core i5 - already has full-fledged 4 or 6 cores, but lacks the Hyper-Threading function and does not have additional threads, except for 4-6 standard ones. Well, the last thing - core i7 - these are top-end processors, which, as a rule, have from 4 to 6 cores and twice as many threads, i.e., for example, 4 cores and 8 threads or 6 cores and 12 threads.
Bottlenecking bottleneck
This is a very important term to understand if you want to build a balanced PC for gaming. In short, if the components (in particular, the processor and video card) are selected incorrectly, one of them will work “in vain” when fully loaded - the others simply will not cope with the flow of ready data that it sends for further processing.
An example is the imaginary system already mentioned above with a Core i9-9900K CPU and a GeForce GTX 1660 GPU. The former will regularly be “idle” due to the fact that the GTX 1660 is a mid-budget model designed for low-cost computers. Thus, in this case, there was no need to spend extra money on a Core i9 (note, however, that in most cases this only applies to games).
It’s difficult to give exact advice here, but try to match budget processors with budget video cards, and expensive ones with expensive ones. Let's say, AMD Ryzen 3 and Intel Core i3 will perform well in GPUs like AMD Radeon RX 570 or Nvidia GeForce GTX 1650, Ryzen 5 and Core i5 - with Radeon RX 5700 and RTX 2060, Ryzen 7 and Core i7 - with RTX 2080, and Ryzen 9 and Core i9 - with RTX 2080 Ti, Titan or even two powerful GPUs at the same time.
AMD
Now it’s worth talking about AMD. The list of “pebbles” from this company is huge; there is no point in listing everything, since most of the models are simply outdated. It is perhaps worth noting the new generation, which in a sense “copies” Intel - Ryzen. This line also contains models with numbers 3, 5 and 7. The main difference from Ryzen’s “blue” ones is that the youngest model immediately provides full 4 cores, while the older one has not 6, but eight. In addition, the number of threads changes. Ryzen 3 - 4 threads, Ryzen 5 - 8-12 (depending on the number of cores - 4 or 6) and Ryzen 7 - 16 threads.
It is worth mentioning another “red” line - FX, which appeared in 2012, and, in fact, this platform is already considered obsolete, but thanks to the fact that now more and more programs and games are starting to support multi-threading, the Vishera line is again has gained popularity, which, along with low prices, is only growing.
Well, as for the disputes regarding the processor frequency and the number of cores, then, in fact, it is more correct to look towards the second, since everyone has already decided on clock frequencies a long time ago, and even the top models from Intel operate at nominal 2.7, 2.8 , 3 GHz. In addition, the frequency can always be increased using overclocking, but in the case of a dual-core processor this will not give much effect.
Removable drives
Despite the widespread use of the Internet and flash technologies, it is still more convenient to store some information on CDs and DVDs, which have the advantage of low cost and re-recordability.
At the same time, many manufacturers refuse to use optical drives, as this allows them to reduce the size and weight of the device. Therefore, ultraportable computers, as a rule, are not equipped with drives. However, if you plan to constantly install new games on your laptop and watch movies, you cannot do without using a DVD drive.
A good solution for those who want to keep the device compact and at the same time provide the ability to read and write CD and DVD discs is to use an external drive that connects to the laptop via USB.
How to find out how many cores
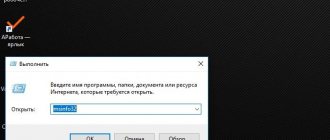
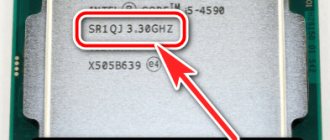
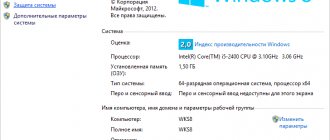
If someone does not know how to determine the number of processor cores, then this can be done easily and simply, even without downloading and installing separate special programs. Just go to the “Device Manager” and click on the small arrow next to the “Processors” item.
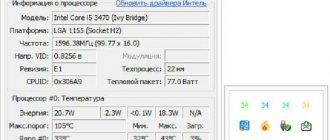
You can get more detailed information about what technologies your “stone” supports, what its clock frequency is, its revision number and much more using a special and small program called CPU-Z. You can download it for free on the official website. There is a version that does not require installation.
Energy consumption
The power consumption of a processor is closely related to its manufacturing technology. With decreasing nanometers of the technical process, increasing the number of transistors and increasing the clock frequency of processors, the power consumption of the CPU increases. For example, Intel Core i7 processors require up to 130 watts or more. The voltage supplied to the core clearly characterizes the power consumption of the processor. This parameter is especially important when choosing a CPU to use as a multimedia center. Modern processor models use various technologies that help combat excessive power consumption: built-in temperature sensors, automatic control systems for voltage and frequency of processor cores, energy-saving modes when the CPU load is light.
The better 4 cores
How can 4 cores be better than two? Better performance. Quad-core “stones” are designed for more serious work, where simple “stumps” or “celerons” simply cannot cope. An excellent example here would be any 3D graphics program, such as 3Ds Max or Cinema4D.
During the rendering process, these programs use maximum computer resources, including RAM and processor. Dual-core CPUs will be very slow in render processing time, and the more complex the scene, the longer they will take. But processors with four cores will cope with this task much faster, since additional threads will come to their aid.
Of course, you can take some budget “protsik” from the Core i3 family, for example, the 6100 model, but 2 cores and 2 additional threads will still be inferior to a full-fledged quad-core.
Differences between 2-core chips and 4-core ones
Let's look at the main points that distinguish the first category of chips from the second. At the hardware level, you can notice that only the number of computational units differs. In other cases, the cores are united by a high-speed data exchange bus and a common memory controller for efficient and efficient work with RAM.
p, blockquote 5,0,1,0,0 —>
Often, the L1 cache of each core is an individual value, but L2 can either be the same for all, or also individual for each block. However, in this case, the L3 cache is additionally used.
In theory, 4-core solutions should be 2 times faster and more powerful, since they perform 100% more operations per clock cycle (let’s take the identical frequency, cache, technical process and all other parameters as a basis). But in practice the situation changes in a completely non-linear way.
p, blockquote 7,0,0,0,0 —>
But here it is worth paying tribute: in multi-threading, the whole essence of 4 cores is fully revealed.
p, blockquote 8,0,0,0,0 —>
What is affected by the number of processor cores?
So, what else can the number of cores affect? First of all, to increase energy consumption. Yes, as surprising as this may sound, it is true. There is no need to worry too much, because in everyday life this problem, so to speak, will not be noticeable.
The second is heating. The more cores, the better the cooling system is needed. A program called AIDA64 will help you measure the processor temperature. When starting, you need to click on “Computer” and then select “Sensors”. You need to monitor the temperature of the processor, because if it constantly overheats or operates at too high temperatures, then after some time it will simply burn out.
Dual-core processors are unfamiliar with this problem, because they do not have very high performance and heat dissipation, respectively, but multi-core processors do. The hottest stones are those from AMD, especially the FX series. For example, take the FX-6300 model. The processor temperature in the AIDA64 program is around 40 degrees and this is in idle mode. Under load, the number will increase and if overheating occurs, the computer will turn off. So, when buying a multi-core processor, you should not forget about the cooler.
What else does the number of processor cores affect? For multitasking. Dual-core processors will not be able to provide stable performance when running two, three or more programs simultaneously. The simplest example is streamers on the Internet. In addition to the fact that they are playing some game at high settings, they simultaneously run a program that allows them to broadcast gameplay to the Internet online; they also have an Internet browser with several open pages, where the player, as a rule, reads comments people watching it and monitors other information. Not even every multi-core processor can provide proper stability, not to mention dual- and single-core processors.
It is also worth saying a few words that multi-core processors have a very useful thing called “L3 third-level cache”. This cache has a certain amount of memory into which various information about running programs, performed actions, etc. is constantly recorded. All this is needed in order to increase the speed of the computer and its performance. For example, if a person often uses Photoshop, then this information will be stored in memory, and the time to launch and open the program will be significantly reduced.
RAM
When choosing a laptop, it is very important not to make a very common mistake that many inexperienced users make. This misconception is due to the fact that many consider RAM to be the main characteristic that determines the speed of a computer.
In fact, RAM cannot in any way improve the speed of computer operations if other components do not allow it to do so. For example, a powerful multi-core processor will be practically useless if installed in a device with 512 MB of RAM, while resource-intensive applications that require 4 GB of RAM will not be able to run on a weak processor.
Also, keep in mind that RAM is a feature that can be upgraded, while the processor and motherboard cannot be replaced. Therefore, a good solution might be to purchase, for example, a laptop with 2 GB of RAM, but with a motherboard that allows you to increase it to 16 GB.
Please note that you should not purchase a laptop with more than 4 GB of RAM if you are going to install 32-bit Windows XP and Windows Vista on it, since these operating systems simply will not “see” a larger amount of memory.
Summarizing
Summarizing the conversation about what the number of processor cores affects, we can come to one simple conclusion: if you need good performance, speed, multitasking, work in heavy applications, the ability to comfortably play modern games, etc., then your choice is processor with four cores or more. If you need a simple “computer” for office or home use, which will be used to a minimum, then 2 cores are what you need. In any case, when choosing a processor, first of all you need to analyze all your needs and tasks, and only then consider any options.
Selecting a video card
Currently, the largest manufacturers of graphics controllers on the market are NVidia and AMD. These manufacturers constantly compete with each other for leadership, so the question of choosing an NVidia or AMD video card is incorrect. Each company periodically offers users new functional and productive products. Therefore, for comparison, it is necessary to analyze devices belonging to specific families of video cards.
If you are going to use a laptop to run modern 3D games on it, be sure to pay attention to the video card (type of graphics controller) of the device. Currently, you can find two types of graphics controllers in laptops: integrated, when the controller is built into the processor, discrete, when the controller is a separate device. Some devices have both built-in and discrete controllers at once.
Main characteristics of video cards
A video card integrated into the computer's motherboard uses the resources of the central processor and RAM to process graphics. Such a controller is much less powerful compared to an external one, but it also costs much less. If you are not going to use the laptop for 3D games, photo and video editing, and also want to save on its cost, the built-in graphics controller is your choice. The built-in video card is quite capable of playing non-resource-intensive games and even allows you to watch HD movies. It also allows you to run older games that did not use 3D graphics.
A discrete graphics system is characterized by the presence of its own processor, designed specifically for displaying graphic information. In addition, it has a separate RAM (video memory). Discrete memory is much more expensive and more powerful than built-in memory.
operating system
As a rule, laptops are sold with operating systems preinstalled on them. The most common operating systems currently are the Windows family: XP, Vista, 7, which are quite sufficient for the needs of most users. However, these systems require a license and therefore increase the cost of the laptop, so if you have the opportunity to purchase a laptop at a lower price with similar technical parameters, but an operating system that is not suitable for you, feel free to buy it, and you can install the desired OS yourself.
Apple laptops come with the proprietary Mac OS operating system and a set of all applications necessary for work. In this case, you won't have to reinstall anything. Most often, users abandon Linux/Unix-based systems, which require more qualifications and are not suitable for running games, as well as a number of other applications.
How to enable all cores on Windows 7 via BIOS?
Simply turn on the PC and in the first 5 seconds after pressing the “Power” key, click on the Escape, F5, F2, or F1 button. The lower left corner of the screen indicates which button to press. Next, the BIOS will launch. In some cases, turning on may take longer than one minute.
Interesting materials:
What can you do on a plane to Germany? What can you bring to Israel? What can be transported across the border from Ukraine to Russia? What can be transported across the border of Ukraine to Belarus? What can you bring across the Lithuanian border? What can be transported across the Russian border? What can you take in luggage to Dubai? What products can you bring to Germany? What can you take to Thailand in your luggage? What can you plant next to dill?