GLONASS is a domestic satellite navigation system. Using GLONASS in a phone allows the owner of the device to determine his location with a high degree of accuracy, as well as get directions to the desired point. The domestic navigation system is still the main competitor to the American GPS, with which users of mobile devices are much more familiar.
Despite the fact that work on creating the system was completed only in 2015, smartphones with GLONASS navigation began to be released back in 2011. Nowadays, you won’t surprise anyone with a gadget that supports GLONASS.
GLONASS in phones: the first damn thing is lumpy
It is believed that Apple was the first to provide GLONASS support for its smartphones. This opinion is wrong. The first smartphone with GLONASS navigation was manufactured by the Chinese manufacturer ZTE at the request of the cellular communications provider MTS. The budget model MTS 945 was presented in 2011 in a very pretentious manner. The leading shareholders of MTS personally showed the gadget to President V. Putin, saying that the device was in no way inferior to the iPhone 4, which was super popular at that time.
MTS 945 was a deafening failure in the market. According to MTS's plan, the volume of the first batch was supposed to be 500 thousand units - but in the end they managed to sell only 5 thousand units of goods, and it took six months. The failure occurred for a number of reasons: firstly , the functionality of the MTS 945 was simply ridiculous - especially judging by the standards of the modern market, secondly , the gadgets were mostly sold locked to MTS SIM cards, thirdly , consumers did not pay attention to support GLONASS as a serious advantage.
Due to low sales, ZTE stopped production of the MTS 945 at the beginning of 2012.
Around the same time, Apple quietly added GLONASS support to the list of features of the new iPhone 4S smartphone. The official version says that through this step, Apple wanted to improve the navigation capabilities of its flagship, but there is another opinion - the Russian government blackmailed the manufacturer, threatening to ban the import of iPhones if they were not equipped with support for the domestic navigation system. Whatever the reason, Apple gave birth to a new fashion - followed by smartphones with GLONASS from Nokia and Samsung.
Is GLONASS more accurate than GPS?
It is impossible to say unequivocally which navigation system is more accurate - GLONASS or GPS. To judge this, you need to understand how the satellites of the two navigation systems move.
GPS satellites do not fly north of the 55th parallel (in the northern hemisphere). Moscow is located on this parallel. In the capital, both navigation systems work equally effectively - but in cities that are located closer to Moscow to the pole (for example, in St. Petersburg), GLONASS provides more accurate information. Satellites of the Russian system reach the 65th parallel in both the north and south - this is why citizens of Scandinavian countries bordering the northern seas (Norway, Sweden) prefer to use GLONASS.
GLONASS is focused primarily on “its” user. The developers of the navigation system did not strive for international expansion.
The average error for the GLONASS system is 2.8 meters, for GPS – 1.8 meters. However, one should not draw hasty conclusions based on these statistics: the satellites are in constant motion, and if the GPS system at a particular moment in time they line up in an unsuccessful configuration (for example, in a line), then at that very moment the accuracy of GLONASS will be higher. The smallest average error will be when using GPS and GLONASS simultaneously – 1.25 meters. Now leading manufacturers of mobile electronics equip all their new gadgets with dual-system navigation chips.
Even the US Federal Communications Agency a couple of years ago thought about using GLONASS in combination with GPS to determine the location of 911 callers. Isn't this the best confirmation that a navigation system alone is not capable of providing a decent result?
The principle of operation of the GPS module in a smartphone
Inclusion
As a rule, the navigation control section in smartphones is a separate menu item. And in the same section you can make settings for using navigation.
The first download of the navigation program may take several minutes, subsequent ones will be faster.
If you are interested, you can evaluate the quality of the built-in GPS module using the GPS Test utility (downloaded for free from the Play Market). After launch, the utility shows how many GPS and/or GLONASS satellites the smartphone sees at the moment. The screen also displays positioning accuracy, current coordinates and signal strength from each satellite.
Speed of finding satellites
The speed of downloading satellite data depends on how long the GPS module in the smartphone was turned off. The fact is that each satellite transmits two types of coordinate data: almanacs and ephemeris. The almanac includes general parameters of all satellite orbits; this data is valid for more than a month, but is not accurate. Ephemeris implies the exact coordinates of the satellite and adjustment of its current position. It is updated every 30 seconds and is relevant for about half an hour.
After turning off for more than 30 minutes (the so-called “cold start”), the smartphone’s GPS module searches for satellites based on almanac data, which requires a certain time (up to 5 minutes). The smartphone itself must be motionless at this time so that the downloading of the almanac is not disrupted. “Warm start” (if the ephemeris becomes outdated, but the almanac remains relevant) takes about 1 minute. “Hot start” (after turning off for several minutes and keeping the ephemeris up to date) – a few seconds.
Features of work
The GPS module works best in open areas where there are no multi-story buildings or other high-rise objects. The module actually does not function indoors, since the interfloor concrete ceilings act as a kind of screen and block the signal. In addition, the weather also affects the performance of GPS in a smartphone. Cloud accumulations and heavy precipitation cause refraction and distortion of the satellite signal. As a result, the location is either not determined or is determined inaccurately.
Online and offline navigation
- Offline programs
(for example, TomTom or Navitel) store all maps on the internal memory of the smartphone. They only need an Internet connection to use online services like displaying traffic jams. In other words, such navigation applications will lay out a route through unfamiliar terrain, where there are practically no means of communication and the Internet. And this, among other things, allows you to save money on traffic. Such applications are paid, but they have a free trial period.
Thus, offline applications work everywhere, even in the wilderness, the main thing is that the map is loaded in the memory (therefore, they are great for traveling around the city or on public roads). However, they greatly consume the internal memory of the smartphone (due to the large volume of maps) and require regular updating of map data.
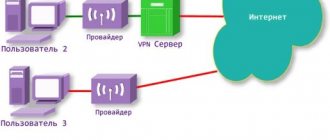
- Online navigators
work only when connected to the Internet. All their maps, databases, etc. are located on the developer’s servers; only an interface program for working with them is installed on the smartphone. Thus, maps are constantly downloaded to the smartphone, which requires a stable Internet connection. These applications have a fairly significant consumption of mobile traffic; this must be taken into account when choosing a tariff plan from your mobile operator. Especially when roaming.
The main advantage of such programs is the ability to load maps of different types (automotive, satellite, topographic, etc.). All data updates are downloaded automatically every time you start. The most popular are Yandex.Navigation, Goole Navigator. Their basic versions are free. It is best to use them off-road or for walking in large cities.
As a rule, users install several applications on their smartphone, for example, one for online navigation, the second for offline navigation. Thus, you can use the program that is most convenient at the moment, depending on your current goals.
So, today you can buy a cheap smartphone or an expensive fashion device - in any case, you will have the opportunity to use navigation.
Navigation in Highscreen smartphones
Among Highscreen smartphones, all models older than 2018-2019 have an excellent combination of GPS + GLONASS, which significantly increases the accuracy of the route.
Online store for mobile phones Highscreen Catalog of smartphones Highscreen
In the web interface of the service in the Settings section, you can configure the application to automatically turn off based on the battery charge, which will reduce battery consumption. Also, if employees spend most of their time inside buildings, we recommend turning off GPS on their phones and using only Wi-Fi.
Just like a regular SMS message from the service - through one of the “Send message” menus, but select the “GPRS” channel when sending a message and the employee will see the message in his application and will also be able to respond.
How to check GLONASS support?
You can find out whether your smartphone supports GLONASS by simply looking at the technical specifications of the device. If there is support, it will definitely be mentioned in a block called “Navigation” or something like that.
A user who believes that anything can be written and does not trust the specifications is recommended to conduct a test using the GPS Test program, which is distributed free of charge in the Google Play store. You just need to launch the application on your smartphone, go out into the open with your gadget and wait for the program to identify all the satellites. If the list of available satellites includes those marked with the Russian flag, it means that GLONASS is actually supported by the mobile device.
Image: apkthing.com
Unfortunately, you can’t pass the same test with an iPhone. The AppStore has an application similar to GPS Diagnostic, but it marks signals from GLONASS as if they were from GPS - and besides, this program costs as much as 229 rubles. However, iPhones are such popular gadgets that their characteristics are known to everyone, and there is no reason to doubt their reliability.
Setting up and adjusting GPS through the engineering menu
This method will help you check the quality of the established standards that indicate how well the GPS on your phone works.
- To do this, you need to go to the engineering menu. Enter the code (where we usually write the subscriber number) *#*#3646633#*#*;
- Next you need to find the YGPS item (or something similar);
- As a result, a map should appear with many yellow dots on it. They may not appear immediately.
It is these points that indicate the number of satellites that were found. If you record the time from the start of scanning until all found satellites are fully loaded, the quality of the installed GPS will become known. Later, this data can be compared with other devices, for example, by taking it from a friend.
How to use GLONASS?
manually activate GLONASS on your smartphone . It is enough to enable GPS and A-GPS through the settings, and GLONASS will also start working. There is no toggle switch that allows you to activate GLONASS without GPS.
It is curious that on chipsets from different manufacturers the procedure for enabling GLONASS is different. For example, the iPhone 4S runs on a Qualcomm chipset, and on this device the search for GLONASS satellites begins only if the main navigation system (which is recognized as GPS) cannot cope with determining the location. According to Qualcomm manager L. Splendorini, this is how all smartphones with Qualcomm processors operate. The manager claims that the simultaneous launch of GLONASS and GPS puts a large load on the battery - moving GLONASS “to the background” is due to the desire to save battery power.
How to make a mobile phone a tracking device
To track the location of an object, be it a car or your child's smartphone, you don't have to buy a tracker. By installing the “GPShome Tracker” mobile application, you can control the current position of the device.
So, GLONASS on the phone, how does the orientation program work? To transfer a data package, the Internet is required - Wi-Fi or a mobile network.
The connection algorithm is as follows:
1. Register on the developer's website. In the fields, write down your username and password, and enter your email address. Select the “Individual” checkbox and accept the user agreement. 2. A link will be sent to your email to activate your Personal Account. Go to the service and in the “Settings” window click “Add object”. Fill in the fields: • “Name”; • “Tracker IMEI” is the smartphone identifier; • click “Save”. 3. In the smartphone settings, enable the “Location: satellite” option. 4. Download the utility from Google Play. 5. Open “Settings” and check the boxes “Enable tracker”, “Use network” and “Use GPS”. 6. For convenient use, the program is divided into three blocks: “Information”, “Maps”, “Settings”.
The first section shows the coordinates, the second section shows the current location. The application quickly eats up battery power, so disable it if not needed.
Which smartphones support GLONASS?
There are a lot of smartphones with GLONASS and GPS, so listing them all is pointless. A user who wants to purchase a gadget with GLONASS will probably not go wrong if he chooses a device from one of the following manufacturers:
- Apple. All iPhones, starting with the 4S model, are capable of working with the Russian navigation system.
- Xiaomi. The Chinese company, which is becoming increasingly popular, has provided GLONASS support for its smartphones Redmi Pro, Mi Max, Mi 5S, Mi Note, Redmi Note 4 and others.
- Samsung. Not only devices from the A and S lines are capable of working with GLONASS, but also budget J-series gadgets - even the Galaxy J1.
- Asus. Any modern device in the Zenfone line can boast the ability to connect to the Russian navigation system.
- Yota. It would be strange if this domestic manufacturer did not equip its original gadgets with a GLONASS module.
Are there other navigation systems?
A new competitor to GLONASS and GPS is a Chinese navigation system called BeiDou .
This system began operating in 2012, and should reach full capacity only by 2022. Some manufacturers already began equipping their devices with BeiDou modules in 2016, but this trend has not yet gained mass popularity. In 2022, only two companies are actively working with Chinese satellites - Xiaomi and Samsung.
The European Union is also working on creating its own navigation system called Galileo, but this system will most likely have nothing to do with mobile technologies.
Does my Android smartphone have dual-frequency GPS?
Many smartphone manufacturers have started using the Broadcom BCM47755 chip that supports this feature, and Qualcomm lists it among the advantages of the Snapdragon 855 chipset. But even if a smartphone is equipped with the necessary hardware, this does not mean that the option is available. How can you check? Easy: just download the GPSTest app from Google Play, and if you see L5 or E5a in the CF (carrier frequency) column, you're lucky.
The application can track the main groups of satellite navigation systems included in the GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System): GPS (indicated by the American flag), Galileo (EU flag), GLONASS (Russian flag) and Beidou (Chinese flag). As well as SBAS satellite support systems, including QZSS (Japanese flag), GAGAN (Indian flag), ANIK F1 (Canadian flag), Galaxy 15 (American flag), Inmarsat 3-F2 and 4-F3 (UK flag), SES -5 (Luxembourg flag) and Astra 5B (Luxembourg flag).
As you can see above, the smartphones in the top row - OnePlus 7 Pro, P30 Pro, Oppo Reno 10x Zoom and Honor 20 Pro support dual-frequency GPS, while those below - Galaxy S10+, LG G8 and Pixel 3 , - do not have it. There is nothing to say about the situation with the iPhone yet, since there is no corresponding application for iOS.