Read what smartphone screen resolution is. And what do display resolution names like HD, Full HD, WQHD, UHD, 4K, 5K, 6K and 8K actually mean?
There are countless smartphones on the market with different display sizes, different screen resolutions and special names for these characteristics. It's not easy to understand the difference between them all. Full HD or WQHD – what do these abbreviations mean? And what does 1920×1080 have to do with numbers?
Screen resolution
One of the main parameters when choosing a smartphone is screen resolution. The higher it is, the better. The screen size is specified in inches, the number of vertical and horizontal pixels (how much information it can display), and the pixel density per inch.
If you know the screen size, you can calculate the number of pixels per inch. This parameter is called pixel density - PPI.
Let’s consider HD (1280 x 720 pixels) as the minimum resolution, since modern gadgets usually don’t have lower resolutions. Let's also pay attention to the screen brightness characteristics.
| Permission | Number of pixels (horizontal and vertical) | Name | Smartphone examples |
| Real 4K | 4096 x 2160 | 4K, Cinema 4K, True 4K | Not yet |
| 4K Ultra HD | 3840 x 2160 | 4K, Ultra HD, 4K Ultra HD | Sony Xperia XZ |
| 2K | 2560 x 1440 | 2K | HTC 10, Nexus 6P, Moto Z, Galaxy S7, LG V20 |
| 1080p | 1920 x 1080 | Full HD, FHD, HD High Definition | OnePlus 3, Sony Xperia X, Huawei P9, iPhone 7 Plus |
| 720p | 1280 x 720 | HD, High Definition | Moto G4, Galaxy J3, Xperia M4 |
HD
HD translates as High Definition, high resolution. This is 1280 x 720 pixels. It doesn't matter what screen size; If the resolution is this, it’s an HD screen.
The smaller the HD screen diagonal, the higher the pixel density. In theory, this means a better picture. Different HD screens may produce different images. On a 5-inch screen the quality will be one thing, on a 10-inch screen another. Screen sizes are measured diagonally and may have different aspect ratios.
On a 4.3-inch screen, the pixel density in HD format will be 342 ppi. On the 4.7-inch screen, the pixel density drops to 312 ppi, but in both cases it is HD. Apple called 300 ppi a sufficient value, above which the human eye ceases to distinguish individual pixels when viewed from a certain distance.
Is it possible to change the resolution
You can't change the resolution like you can on a computer, but you can change the pixel density per square inch (ppi).
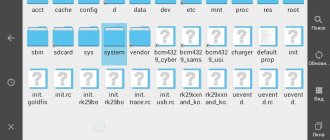
The procedure will require: root rights, the Root Explorer file manager and a text editor. The procedure is as follows:
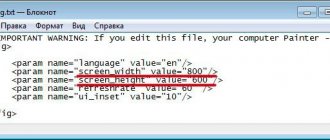
- Launch Root Explorer and in the System folder (root section) find the prop.
- Open the document in a text editor and find the line ro.sf.lcd_density.
- Increase the value by 10 and save changes.
- Reboot your smartphone.
- Repeat steps 3 and 4 until the image quality is acceptable.
To summarize, resolution is an important display characteristic. The comfort of using the device, the quality of the played video and graphics in games depend on it.
Full HD
Full HD resolution is most often found in smartphones released over the past year. Although some devices are increasingly equipped with 2K (QHD) screens. The first of these were Oppo Find 7 and LG G3.
Full HD resolution is 1920 x 1080 pixels. Again, pixel density depends on the screen diagonal. A 5-inch screen gives a density of 440 ppi, while 5.5 inches means 400 ppi.
Method 1: System Tools
Recently, devices with high (2K and higher) resolution matrices are increasingly appearing on the market. The developers of such gadgets understand that this does not have the best effect on performance, so they add tools to the firmware for appropriate settings.
- Launch the settings application, then go to the “Display” item in it (otherwise it may be called “Screen”, “Screen and brightness”, “Screen settings”, “Screen” and other similar meanings).
Next, select one of the options that is acceptable to you and click “Apply”.
The changes will be applied immediately.
This method is the simplest, but it can be used on a limited number of firmwares, which, unfortunately, do not yet include pure Android.
QHD, Quad HD, or 2K
QHD means Quad HD, that is, the resolution is 4 times higher than standard HD. The same size screen fits 4 times more pixels than HD resolution. Namely 2560 x 1440 pixels. The 5.5-inch display has a pixel density of 538 ppi. The same Full screen has a pixel density of 400 ppi.
Sometimes permissions are designated differently. HD is written as 720p, Full HD 1080p, etc. QHD is called 2K because the maximum value here is more than 2000 pixels. This may confuse users since it would be more logical to name it 2.5K.
Many smartphones from Samsung, Motorola, Huawei and other major manufacturers these days have 2K screens
4K, or Ultra HD
As with 2K, the name 4K comes from the higher resolution. But in fact there are not 4000, but 3840 pixels. So while the two terms are interchangeable, they actually mean slightly different things.
Ultra HD is a resolution of 3860 x 2160 pixels, and 4K is 4096 x 2160 pixels. Often both of these options are cut down to 2160p. The difference in the number of pixels is small, but it is there. One of the first smartphones with a 4K screen was Sony's Xperia Z5 Premium, which features Ultra HD resolution on a 5.5-inch screen.
Sony calls it 4K, but it's actually Ultra HD. The Sony Z5 Premium has a pixel density of 806 ppi, far more than any other smartphone and far more than most users need.
Method 2: Developer Settings
Screen resolution depends on the DPI (dots per inch) value, which can be changed in the developer options. This is done as follows:
- Open “Settings” and go to “System” – “Advanced” – “For Developers”.
If the last option is missing, use the instructions below.
Read more: How to activate developer mode in Android Scroll through the list, find the option called “Minimum width” (otherwise it may be called “Minimal width” or similar in meaning) and tap on it.
A pop-up window should appear with an input field for the DPI value, which we will change (it is recommended to remember the default one). The specific numbers vary by device, but most range from 120-640 dpi. Enter any of this sequence and tap “OK”.
At this point, work with the developer settings can be considered complete. The only negative is that the appropriate number will have to be chosen at random.
Future trend
Smartphone screens are getting larger, but manufacturers are in no hurry to use 4K resolution. Unless Sony chose this option in the Xperia Z5 Premium and XZ Premium.
Instead, 2K panels are increasingly being used. This allows you to use less power than at higher resolutions. Modern smartphones can’t boast of good battery life anyway; manufacturers don’t want to spoil it even more. Unless Sony has released another smartphone - the Xperia XZ3 Premium model.
Display Types
There are many types of displays for mobile devices: LCD, OLED, AMOLED, Super AMOLED, TFT, IPS and some rarer ones like TFT-LCD. IPS LCD panels are often found on mid-priced devices. What do all these abbreviations mean? Let's look further.
LCD, TFT, IPS
LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) – liquid crystal display. As the name implies, it is based on liquid crystals, behind which there is a backlight. Their low price makes such screens popular among manufacturers of smartphones and other devices.
LCD screens are usually easy to see in sunlight because they are backlit. True, they do not have as accurate color reproduction as non-backlit types of screens.
Smartphones use both TFT and IPS displays. TFT (Thin Film Transistor) – thin film transistor. This is an advanced version of active matrix LCD, like AM in AMOLED. Each pixel has a separate connection to a transistor and a capacitor.
TFTs are favored by their relatively low production costs and increased contrast compared to traditional LCDs. At the same time, TFT screens consume more energy compared to other types of LCD, they have worse viewing angles and color rendition. Because of this and the decreasing price of other technologies, TFT screens are rare in modern smartphones.
IPS (In-Plane Switching). This is a further development of TFT LCD technologies. There are better color rendition and viewing angles here. Two transistors are used per pixel, and the backlight is more powerful. Because of this, energy consumption increases, but it is still less than that of TFT panels.
There are other options, like IPS-NEO. This is the name of JDI's proprietary technology that supposedly eliminates backlight leakage, but the principle is essentially the same as other IPS LCD panels.
AMOLED
AMOLED (Active Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode) is an active matrix based on organic light-emitting diodes. It sounds complicated, but it really isn't. Active matrix is also used in TFT LCDs, while OLED is another term for thin film technology.
OLED is an organic material that emits light when current passes through it. Unlike LCD panels, which have a backlight, OLED panels are always turned off unless current is applied to individual pixels. This means OLED screens have purer blacks and use less power when the screen is dark. On the other hand, bright images on AMOLED screens use more power than LCD screens. OLED panels are more expensive to produce compared to LCD.
Because the black pixels on OLED screens are turned off, the contrast is higher than on LCD. They also have a higher refresh rate, but worse visibility in the sun. There are problems with screen burnout and diode degradation, since they are organic.
But AMOLED panels can be made thinner than LCDs, since they do not need a backlight layer. They can also be made flexible.
What is the difference between OLED, AMOLED and Super AMOLED?
OLED stands for Organic Light Emitting Diode. OLED screens are made of thin films of electroluminescent material. They emit light and do not require backlighting, reducing energy consumption. OLED displays are often called AMOLED when used on smartphones and TVs.
AM stands for “active matrix,” as opposed to passive matrix OLED (P-OLED), which is less commonly used in smartphones.
Super AMOLED is the name of Samsung's similar screens. At first they were on flagship smartphones, now they have reached cheap ones. Like IPS LCDs, Super AMOLED screens are an improved version of simple AMOLEDs. The touch layer is built into the screen itself, rather than sitting on top of it.
As a result, Super AMOLED panels are more visible in the sun than regular AMOLED panels and consume less power. Samsung panels are considered the best.
Innovation
Removing the OGS air gap
Every year engineers introduce image enhancement technologies. Some of them are forgotten and not used, and some make a splash. OGS technology is just that.
Typically, a phone screen consists of protective glass, the matrix itself, and an air gap between them. OGS allows you to get rid of the extra layer - the air gap - and make the matrix part of the protective glass. As a result, the image appears to be on the surface of the glass, rather than hidden underneath it. The effect of improving display quality is obvious. Over the past couple of years, OGS technology has been unofficially considered a standard for any more or less normal phones. Not only expensive flagships are equipped with OGS screens, but also budget phones and even some very cheap models.
Screen glass bending
The next interesting experiment, which later became an innovation, is 2.5D glass (that is, almost 3D). Thanks to the curves of the screen at the edges, the picture becomes more voluminous. If you remember, the first Samsung Galaxy Edge smartphone made a splash - it was the first (or not?) to have a display with 2.5D glass, and it looked amazing. There is even an additional touch panel on the side for quick access to some programs.
HTC was trying to do something different. The company created the Sensation smartphone with a curved display. In this way it was protected from scratches, although it was not possible to achieve any greater benefit. Nowadays, such screens cannot be found due to the already durable and scratch-resistant protective glass Gorilla Glass.
HTC didn't stop there. The LG G Flex smartphone was created, which not only had a curved screen, but also the body itself. This was the “trick” of the device, which also did not gain popularity.
Stretchable or flexible screen from Samsung
As of mid-2022, this technology is not yet used in any phone available on the market. However, Samsung in videos and at its presentations demonstrates AMOLED screens that can stretch and then return to their original position.
Photo of a flexible display from Samsung:
The company also presented a demo video where you can clearly see the screen curving by 12 mm (as the company itself states).
It is quite possible that Samsung will soon make a very unusual revolutionary screen that will amaze the whole world. This will be a revolution in terms of display design. It's hard to imagine how far the company will go with this technology. However, perhaps other manufacturers (Apple, for example) are also developing flexible displays, but so far there have been no such demonstrations from them.
Retina
Another marketing name, this time from Apple. Retina screens have no specific characteristics, except that they must have a resolution higher than the minimum. This resolution does not allow the human eye to see individual pixels, and the pixel density here is more than 300 ppi. However, Apple measures pixel density differently than other manufacturers.
Measurement depends on screen size and resolution. The Retina concept has been promoted since the iPhone 4 with a resolution of 960 x 640. It used a 3.5-inch IPS LCD screen with a pixel density of 330 ppi.
These days, on Android screens under 6 inches with QHD resolution, the pixel density reaches 400-500 ppi. Because of this, Apple had to reconsider the idea that 300 ppi was a sufficient value. iPhone 6 Plus with Full HD resolution has a pixel density of 401 ppi. On the iPhone 7 and iPhone 7 Plus, the pixel density is 326 and 401 ppi, respectively. On iPhone XS and XS Max this value is 458 ppi.
Marketing moves
Retina and Super Retina. Translated from English, this word means “retina,” and Steve Jobs chose it for a reason. During the presentation of the iPhone 4 in 2010, he said that the human eye is not able to distinguish pixels if the display PPI exceeds 300. Strictly speaking, any relevant display can be called Retina, but for obvious reasons no one except Apple uses this term. The display of the future iPhone X has been called Super Retina, although it will have an AMOLED display and not an IPS display, as in the company's other smartphones. In other words, the name also has nothing to do with the screen manufacturing technology.
0
Displays of the future
Smartphones are gradually getting closer to 4K screen resolution. Monitors and TVs can reach the 8K level (7680x4320). This year, the RED Hydrogen One smartphone with a holographic screen was introduced. The resolution here is 2K, but “4V” content could be revolutionary.
Micro LED. This is a new technology that is still in its infancy. But it has the potential to become ubiquitous in the future. Micro LED screens work like OLED, but are thinner. They are made of inorganic semiconductors such as gallium nitrite. There are also light-emitting diodes here, which are smaller compared to the diodes in OLED panels.
Micro LED backlight is not needed, nor is a polarizing filter. The glass layer above the panel can be made thinner. Brightness per unit power, which measures the efficiency of displays, is better compared to OLED and LCD panels. At the same brightness, a Micro LED screen consumes 2 times less energy compared to OLED and often even less. Very small diodes allow increased resolution on a uniform surface. With such screens you can create smart watches with 4K resolution. Micro LEDs are not subject to burn-in like OLED panels.
The main disadvantage of Micro LED at the moment is the price. Production is complex and the defect rate is high. There probably aren't even production lines for Micro LED yet. All this does not help reduce prices. Experts expect the first consumer products with such screens to appear in 2022 and 2022. Apple has been investing in the development of this technology since 2014. Perhaps the Apple Watch will be the first.
Which screen type is better?
As you can see, different types of screens can be used by different manufacturers. AMOLED doesn't always mean Samsung, and Retina doesn't always mean Apple, although other companies don't use that term. IPS LCD screens for iPhone are produced by LG, and Samsung produces screens for iPad. Not all Samsung devices have AMOLED panels. It's not about which screen is better in absolute terms. Each has pros and cons, and cost must be taken into account.
It is necessary to pay attention not only to the technical characteristics when comparing the screens of two smartphones, but to the image quality (color reproduction, brightness, view of the sun on the street). It's impossible to evaluate two screens on paper. You need to see colors, saturation, brightness and contrast, viewing angles, etc. with your own eyes.
You also need to take into account your own application scenario for the device. If you stare at a screen on the couch at night and sit in front of a computer monitor all day, good LCD panel visibility isn't that important to you. If you often spend time outdoors, LCD is better.
If you want the longest battery life, richest colors and best contrast, AMOLED screens are your choice.
Method 4: ADB
If none of the above methods are suitable for you, the most difficult option remains - using the Android Debug Bridge.
- Download the required software from the link above and install it according to the instructions.
- Activate the developer settings on your phone (see step 1 of the second method) and enable USB debugging on it.
On your computer, run Command Prompt as an administrator: open Search, enter command line in it, click on the result and use the options.
Read more: How to open Command Prompt as an administrator in Windows 7 and Windows 10
After launching the terminal, type in the drive letter where ADB is located and press Enter. If the default is C:, go directly to the next step.
Next, in Explorer, open the folder in which the adb.exe file is located, click on the address field and copy the path from there.
Return to the Command Prompt window, type cd followed by a space, paste the path you copied earlier, and press Enter again.
Go to the phone again - connect it to the PC and allow debugging access.
In the Command Prompt, enter adb devices and make sure the device is recognized.
If the list is empty, disconnect your phone and try connecting again. Use the following command:
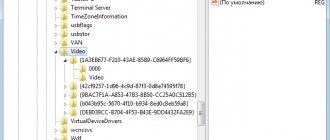
adb shell dumpsys display
Carefully scroll through the resulting list, find a block named “Display Devices”, in which look for the parameters “width”, “height” and “density” - they are responsible for the resolution in width and height, as well as for pixel density, respectively. Remember this information or write it down so you can reset it in case of problems.
Now you can move on to editing. Enter the following:
adb shell wm density *number*
Replace *number* with the pixel densities you want, then press Enter.
The following command looks like this:
adb shell wm size *number*x*number*
As in the previous step, replace both *numbers* with the data you need: the number of points in width and height, respectively.
Be sure to make sure there is an x between the values!
For the changes to take effect, the phone needs to be rebooted - this can also be done via ADB, the command is as follows:
- After restarting the device, you will see that the resolution has been changed. If after loading you encounter problems (the sensor does not respond well to touches, interface elements are too small or large, some software refuses to work), then connect the device to ADB again and use the commands from steps 9 and 10 to set the factory values obtained in step 8 .
Using Android Debug Bridge is a universal method that is suitable for almost all devices.
We are glad that we were able to help you solve the problem.
Add the Lumpics.ru website to your bookmarks and we will be useful to you. Thank the author and share the article on social networks.
Describe what didn't work for you. Our specialists will try to answer as quickly as possible.