It happens that the router fails to cope with its main task - to provide the opportunity for different devices to connect to the Internet. These are computers, smartphones, laptops, tablets, any devices connected to it via a network cable or via Wi-Fi.
The fact that the router does not distribute Wi-Fi can manifest itself in different ways. Sometimes the network disappears. Or all devices see it, but the pages do not load. You either see a completely white screen in front of you, or a message that the network is unavailable.
To resolve these issues, pay attention to the router as well as the network settings. Let's consider the sequence that should be followed and what to do when the router does not distribute the Internet, step by step.
There is no Internet connection on the router
It happens that you turned on the router, but it is not connected to the Internet. It's very easy to find out about this. Your device will not see the network, it will disappear. First you should turn off the router. Wait 2-3 minutes and turn on the power again.
Remember that a number of models from TP-Link, Keenetic, Zyxel are equipped with a separate button that turns Wi-Fi on and off. Perhaps it was simply pressed, which caused the problem.
You can make sure everything is working by looking at the status of the Internet LED indicator on the back of the router. When everything is normal it should flash. If the device does not have access to the Internet, it simply lights up steadily or does not light up at all.
Sometimes the problem is in the PC, laptop or smartphone itself. For example, if you have an iPhone, find the selected channel in the Wi-Fi settings of the “Home Network” segment. It may turn out that it was chosen incorrectly. You should find a free channel and activate it.
Need help with a similar problem?
Leave a request and our specialists will promptly resolve your issue
The network may disappear if the WAN settings, that is, the connection to your provider, are incorrect. You need to reset the router settings and configure it again, enter the data provided by the provider. If the connection type (static, dynamic IP, PPPoE, etc.) is correct, the router should establish a connection.
It is very rare, but there is a situation that the router does not distribute Wi-Fi when the wireless module is turned off in the settings. When setting up your device, go to “Wireless Settings” and make sure that “Wi-Fi Communication Status” is in the “On” position.
If you are sure that you did everything correctly, but there is still no connection, the reason may lie in a hardware error.
Method 1: Download a backup
The functionality of the web interface of almost any router from TP-Link allows you to save the current settings into a separate file so that it can be used for recovery in the future. If you have not yet reset the configuration and want to create a backup copy of it for later loading, this is done like this:
- After authorization, go to the “System Tools” section through the left panel.
- Here, open the “Backup and Restore” category.
- Click on the designated button called “Backup”.
After opening the Explorer window, all that remains is to select the location on local or removable storage where you want to save the item in which all the current router settings are recorded.
Then you can proceed with a hard reset or any other action without worrying about losing any important settings. If you need to restore the same configuration, follow these steps:
- In the Internet center, again go to “Backup and Restore”, where click on the “Select file” button.
- When you open Explorer, find and load the same object that was saved earlier.
- Through the web interface, click on “Restore”.
- The setup process and further reboot will take several minutes. Do not close the current tab to avoid interrupting the operation.
Now all the parameters that were placed in the backup file have been successfully restored, and you can proceed to interact with the router. However, this method is not suitable when, for example, the problem with the device is an incorrect configuration. Then after the reset, the configuration is performed using one of the following two options.
How to check the router and cable?
See if the power LED is lit. If not, then the problem is more likely with a faulty power supply or wire.
Once again, we draw your attention to the fact that some models have a button that turns off Wi-Fi. Check its position, maybe that's why you can't connect.
The network cable that is routed into a house or apartment may have poor contact. In this case, more often it disappears precisely in the connecting connector. Try connecting it directly to your computer. If everything works, then the problem is not in the cable. Then the router does not see the Internet cable due to damage to its WAN port. There is no way to do this without repairing or replacing the device. With some exceptions, your router may also have a LAN port. If so, then you should try connecting a cable to it.
Don't rush to buy a new router! If you do not have access to the network, be sure to call the specialists of your provider company. It happens that problems are found in their equipment. Unfortunately, it cannot be ruled out that the distribution cable laid through the entrance and corridor to the apartment was accidentally or intentionally cut by someone.
And the whole world is not enough, or Who gives us the Internet
Without a doubt, and hardly anyone will argue with this, the Internet is a significant achievement of which a person is capable. We can say that this is a whole world where there is almost everything you might need. These are electronic magazines, books, useful articles on various sites and much more. With the help of the Internet, you can learn something new, improve yourself, and even find a suitable job.
But here’s an interesting question: “Who gives us the Internet?” In our daily life there are a large number of terms that come from different languages. The word provider is no exception - something “foreign” is immediately visible in it. Meanwhile, this definition hides nothing more than a company that provides access to the World Wide Web to residents of many countries.
There are primary and secondary providers. The first of them distribute traffic in large volumes, while the second rent channels from them. Residents of almost all countries of the world use the services of secondary providers.
Network without Internet access
Often things are like this: the router works, Wi-Fi is visible on all devices, but sites do not open. At the same time, in the lower right corner of the screen, an exclamation mark appears on the panel on a yellow background. If you move your cursor over the network status icon, it will say “Restricted” or “No Internet access.” A similar warning will appear on your smartphone or tablet.
As before, you first need to check the condition of the network cable. Perhaps it is not inserted tightly or is damaged? Try unplugging it, then plug it in again. If it is faulty, the router will not receive a signal from the provider. In this case, Wi-Fi will work, but you will still not be able to access Internet resources.
If the cable is working properly, you need to use software methods. You need to find out from your provider the type of connection and its correct parameters. The exact names of the sections for making changes to the settings vary among different router manufacturers. For example, if you have TP-Link, then this data is entered on the “Internet” tab, which is located in the “Advanced settings” section. If you have an ASUS model, these values can be set in the “Internet Settings” section in the Russian version or “WAN” in the English version.
What to do if everything is filled out correctly, but there is no Internet connection? Contact your provider. Ask him if he uses MAC address binding. If there is one, this address should be entered.
What are the provider settings?!
In order to successfully set up an Internet connection and Wi-Fi distribution on your wireless router, you must first find out what type of connection your provider uses. You can find out either on its official website in the “Support” section, or by calling the technical support hotline at the number listed on the provider’s website. Here is information on the largest providers in Russia:
- Rostelecom - mainly PPPoE, but there are branches where Dynamic IP (DHCP) is used
- Dom.ru - PPPoE
- Beeline - Dynamic IP(DHCP)
- MTS - PPPoE
- TTK - mainly PPPoE, but there are branches where Dynamic IP (DHCP) is used
How can you easily understand what type of connection you have? When connecting, the agents or installer should have left you a contract and authorization data. If the login and password are specified there, then the PPPoE protocol is used. Otherwise - Dynamic IP. Just don’t confuse the connection password with the Wi-Fi network password.
Internet is not available via cable
It happens that a router connected by wire to a PC does not distribute the Internet. Look at the LAN indicator. It can glow steadily or blink - then the distribution is normal. Or it doesn’t light up at all – then the problem is in the router.
Try connecting the provider's network cable directly to your computer, bypassing the router. Or connect through your router to another computer and see if the Internet loads. It is possible that there is some kind of problem with your PC.
The problem may be caused by a faulty PC network adapter or uninstalled drivers. Visit Network and Sharing Center. We'll tell you how to do this. It may turn out that your network adapter is not on its list. But there is an “unidentified device” with a yellow exclamation mark. Then you need to install the driver. Find it on the PC motherboard manufacturer's website. If you have a laptop, then on the manufacturer's page. Download and install. If the problem persists, unfortunately, you will need a new network card.
The procedure is as follows:
- call the “Run” line by pressing Win and R on the keyboard at the same time;
- write the command: devmgmt.msc;
- The manager and a list of all devices installed on the PC will pop up;
- go to the “Network adapters” section, where the network card should be located.
Configuring WAN settings
We have found out why the Internet may not be available after setting up the router. As a rule, it is the router that is to blame, not the provider. But to rephrase a little, you simply wrote the wrong configuration for the access point, which is why the global network connection does not work. Each operator uses a different connection: “Dynamic IP”, “Static IP”, “L2TP”, “PPTP”, “PPPoE”.
If the first option is used, then the connection to the global network is made immediately, since the router automatically receives the required configuration. If the provider uses “Static IP” and there is no Internet, then here you will need to check whether you have specified the WAN type correctly. The same applies to "L2TP", "PPTP", "PPPoE". But in addition, you need to double-check the correctness of the specified username, password, server and mask.
Next, we will show how to set access point parameters for different routers. Please note, since we all use the services of different providers, you will have to write data such as “Name”, “Password”, “Server” and “Mask” yourself. You can find the necessary information in the contract, on the operator’s website, or by calling the technical support service.
TP-Link
Popular and universal routers from this manufacturer boast an intuitive interface, so you shouldn’t have any problems:
- We log in to the system. To do this, you need to know the router's IP. You can view the information in the user manual or on the sticker located on the back cover of the device.
- In the login and password entry form, enter your credentials and click “Login.”
- Find the “Network” item in the navigation menu.
- Select the subcategory named “WAN”.
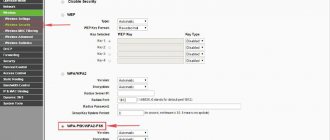
- If your provider uses a DHCP server, then you must select the “Dynamic IP” connection type. In this case, you do not need to fill out any settings yourself; the router itself will receive the configuration from the supplier src=»https://ustanovkaos.ru/wp-content/uploads/2021/04/09-dinamicheskij-IP.jpg» class=»aligncenter» width=”580″ height=”449″[/img]
- If “Static IP” is used, then you need to set the IP address, subnet mask, default gateway, MTU size, and preferred DNS. The mask will look like this: 255.255.255.0. MTU size (data transfer volume): 1500 MB.
- If your ISP uses a PPPoE connection, you must provide a username and password. The access key will have to be duplicated. In the “Secondary connection” section, you must check the “Disabled” checkbox. In the “Connect on demand” item, you need to select the maximum idle time after a connection attempt. You can write any parameter in seconds. In additional settings you need to specify the MTU size - 1460 MB.
- In a situation where the operator uses “L2TP/L2TP Russia”, you need to set a username and password, and also click on the “Connect” button. Don't forget to specify the type of IP address: “Dynamic IP” or “Static IP”. If you intend to use a VPN, then you need to specify the appropriate configuration here. In the “Connect on demand” item o.
Now try connecting again. If the Internet still does not work, then you need to check the network configuration of the operating system; we will touch on this topic a little later.
Keenetic
As in the previous case, we need to configure the access point configuration. See step-by-step guide below:
- You must be authorized in the web configurator. To do this, you need to know the router's IP and password. All information can be found in the user manual or on the sticker on the back of the device.
- You need to select the “Internet” item.
- In the “Access Protocol” tab, specify the connection type: “Dynamic IP”, “Static IP”, “PPPoE”.
- Write your username and password. If the user wrote the configuration incorrectly, he will have to reset the parameters to reconfigure.
- Select an authentication algorithm. It is better to clarify this information with the operator’s technical support.
Now you can check whether the Internet works or not. Next, let's look at the procedure for setting parameters for a connection via the L2TP protocol:
- In the navigation menu, select the “Internet” button.
- O and “Use to access the network.”
- In the “Description” section, indicate the name of the access point.
- In the “Protocol” section, select the type of connection used in the drop-down list.
- In the “Connect via” tab, set the “Use any connection” option.
- Specify your username and access key.
- In the “Authentication Method” section, select “Auto”.
- In the “Service Address” section, enter the IP specified in the contract for the provision of telecommunications services.
- In the “IP Settings” tab, select “Use any”.
- Write the primary and secondary DNS address.
- Activate the “TCP-MSS Auto-tuning” option.
- Click on the “Apply” button.
After applying the parameters, check the functionality of the connection; if there are any disconnections, reset the configuration using the “Reset” button, which is located on the back cover of the device:
- Hold the key for 10 or 15 seconds and release.
- The indication will go out and then re-activate.
Configure the device again according to our instructions and carefully check whether you have checked the “TCP-MSS” checkbox.
Tenda
Let's figure out the correct PPPoE settings for the Tenda router:
- In the navigation menu you need to find a section called “WAN”.
- Then go to the subcategory “Virtual Dial-up (PPPoE)”.
- In the “Account” item we indicate the user name, which is specified in the agreement with the provider.
- In the “Password” section we write the password for the access point.
- In the “MTU” item, enter the size of the data transfer packet. 1492 MB recommended. The settings named “Service Name” and “AC Name” are left unchanged.
- In the “Internet Connection Option” tab, set “Connect Automatically”.
- Click “Apply”.
Now let's change the parameters for the static IP:
- In the “WAN” section we find the “Static IP” tab.
- In the “IP Address” item we indicate the value that your provider gave you.
- In the “Subnet Mask” item we write 255.255.255.0.
- In the “Gateway” section we indicate the WAN gateway.
- Enter the addresses of the primary and secondary DNS server.
- For the changes to take effect, click “Apply”.
We do not touch the configuration for cloning the MAC address. You can try connecting to high-speed Internet.
D-Link
Now let's talk about correctly setting up an access point on D-Link routers. The instructions are universal for all devices, since the same firmware is used.
Dynamic IP:
- Open the “Advanced Settings” item.
- Select the “Network” or “WAN” tab.
- Click on the “Add” button.
- In the “Connection Type” section, select “Dynamic IP”.
- In the “Interface” item, indicate “WAN”.
- Write only the username.
- ABOUT.
- Next, you need to activate the “Obtain DNS automatically” option.
- Set a name for the access point.
- In the “Miscellaneous” item, check the following checkboxes: “Enable IGMP”, “NAT”, “Firewall” and “PING”.
- Click on the “Apply” button.
Parameters for PPPoE:
- Open "Advanced Settings" and select the "Network" category.
- In the drop-down list, specify the connection type “PPPoE”.
- You must use exclusively “WAN” as the interface. Pay close attention to this, if you set “PPPoE”, the Internet will not work. By the way, owners of a D-Link modem often complain why the router does not connect to the Internet after setup. It is precisely because of this parameter.
- In the “Name” item, set a custom value for the access point.
- In the "PPPoE" section, enter your username and password.
- In the “Authentication Algorithm” tab, set the value to “AUTO”.
- In the “MTU” item, set the packet size to “1492”. This is the recommended setting.
- The remaining settings do not need to be changed.
- All you have to do is click on the “Save” button.
If the Internet also does not work, then read our article further and we will give some more tips on how to fix the error.
ASUS
Let's try to set the parameters for ASUS:
- In the web configurator panel we find the “Internet” item.
- In the drop-down list, select the WAN connection type.
- Check the “Enable WAN” and “Enable NAT” checkboxes.
- In addition, be sure to activate the “Enable UPnP” option.
- ABOUT.
- In the “Account Settings” section, we do not change any parameters, including “Authentication”.
- Fill in the parameters in the “Special Vendor Requirements and MAC Address” tab. In the “DHCP Request Mode” item, set the value to “Aggressive”.
- In addition, do not forget to deactivate the “Expand TTL value” option.
- Click “Apply”.
UPVEL
This is a fairly common device, but some owners experience errors when connecting to the network. Let's try to configure the network in accordance with the manufacturer's recommendations:
- In the address bar of the browser we enter the IP of the device: 192.168.10.1.
- Log in to the control panel using your login and password: admin and admin.
- In the navigation menu, open the “Basic settings” item.
- Select the subcategory “WAN Interface”.
- In the “Internet connection type” item, select the desired protocol. It all depends on your provider.
- Set the MTU size. The manufacturer's recommended range is indicated on the side.
- In most cases, cloning a MAC address is not required, but your operator may require it, check with support.
- We register the primary and secondary DNS.
- Click “Apply changes”.
Problems in obtaining an IP address
The whole problem may be this: the PC is having difficulty obtaining an IP address. Often, a certain address is already set on it, or automatic detection of network settings is simply disabled. Identification will show whether this is so. What is it?
Your router, when operating normally, should be the main router on your local network. This assumes its built-in DHCP server is active and assigning IP addresses to all devices. So, it may turn out that this server is inactive.
To find out all this, you need to go to the settings. By right-clicking on the network status icon, you will be taken to the “Network and Sharing Center”. Next we do this:
- select “Change adapter settings”;
- pay attention to the “Ethernet” or “Local Area Connection” icon - if the cable is disconnected or there are problems with it, a red cross will appear under the icon depicting computers;
- we make the cross disappear, which means that the cable is connected;
- right-click on the field and find “Properties” in the drop-down menu;
- select the “IP version 4 (TCP/IPv4)” field, click on “Properties”;
- in a new window about.
All that remains is to click “OK” in this window and restart the PC. Problems with Internet distribution have been resolved.
Emergency situations
But in some cases, the Internet may actually be interrupted due to the provider. The reason may be a hardware malfunction. Or it could be an emergency situation - maybe the cable was broken somewhere, or something else. In this case, the Internet may be absent for from several minutes to hours.
In this case, all that remains is to contact the hotline and report the problem. Then calmly wait until she is eliminated. Such cases are rare, but apt. Therefore, it is worth considering other reasons why the Internet on a laptop periodically disappears.
The port or router is burned out
It may happen that the WAN port on the router burns out. The fact is that on all such devices the ports are programmed by firmware, but in essence they are the same. That is, the VAN input in the router looks like this only because of the firmware. Only with Mikrotik the ports can be programmed for any use.
For other routers, there are two outputs. Fix it yourself or take it for repair if the router is expensive. There the port is simply soldered onto the board. The second option is to reflash the router in such a way as to reprogram the “healthy” LAN port so that it becomes the WAN input.
Why does the Internet keep dropping out?
1.The most relevant periodic “disappearance” of the Internet is when the router distributes a connection to the World Wide Web to several devices simultaneously.
In most cases, this is due to the technical capabilities of the router: the router simply cannot cope with the network load placed on it.
Let's look at why the Internet constantly disappears through a router using a specific example. Let’s say the Internet is distributed by a router to 3 computers at once:
- — on the first one, the user watches the movie online;
- - on the second - they play an online game;
- — the third computer at the same time downloads a “heavy” file from a torrent.
Of course, an average router cannot withstand such a network load (especially if it is from “old times”) and cuts off the Internet connection. After rebooting the router, the Internet appears, the user again launches all suspended programs - and the situation repeats.
In this case, the optimal solution would be to buy a new, more powerful router. If for some reason it is not possible to replace the router, then on the “old” router you should set a limit on the simultaneous use of large Internet traffic.
2. Another common reason why the Internet regularly disappears through a router is outdated firmware of the device. Let's look at how to update the router firmware using the example of the D-link 2640U router:
- — first, look at what letter certificate is assigned to your router: it is usually indicated on the device’s case and has the value A, B, C, etc. You need to know this parameter, since the firmware will be selected specifically “for the certificate”;
- — now you need to determine the version of the current firmware: it is indicated in the router interface (for example 1.0.24);
- — then download the latest firmware version from the manufacturer’s official website (for example, this is 1.0.32);
- — save a backup configuration (in case of an emergency);
- — in the router interface, go to the “Software Update” section, specify the path to the downloaded file and wait until the router updates and reboots.
Why is there no access to the global network when WiFi is connected?
To understand why in some cases there is no Internet connection, but there is access to a WiFi network, you need to understand how a Wi-Fi router works. Many people, when talking about this wireless connection, assume the Internet. But it's not right. The technology itself does not provide access to global networks. This is a connection for organizing local groups within the same apartment or private house.
The range of the access point, with direct visibility, does not exceed 200 meters. And this is only a theoretical indicator. Typically, in practice the coverage area is much smaller. Thus, just connecting to an access point is not enough to access the Internet. To do this, the base station (WiFi router) must be connected to the Internet using a cable or other connection.
Therefore, the Internet does not work when Wi-Fi is connected, first of all you should check the settings of the router (the so-called access point).
Unsatisfactory signal
Each router is equipped with a Wi-Fi transmitter and has an antenna or even several. And if there is no Internet, then the first thing you should do is check the antenna contacts. They can be removable or non-removable. In the first case, problems should usually not arise. Otherwise, you will first have to make sure that the wireless router is out of warranty. Only then can you disassemble the device and inspect it from the inside - perhaps the antenna contact is broken.
If the Internet on your laptop via WiFi periodically disappears, this may be due to a weak signal. If, for example, everything is in order on the computer, but there is no connection on the laptop, you should place the wireless router in a place from where the signal spreads evenly throughout the apartment.
It is worth paying attention to what frequency the equipment operates at. If it is 2.4 GHz, then a working microwave oven or landline radiotelephone may interfere with the transmission of the Wi-Fi signal.
How to update software
If you still need to perform the update operation, you must visit the manufacturer’s official website. There you need to download the required file depending on the router model. After this, you need to go to the equipment’s web interface by entering the IP address (described above).
On the right side you need to find the “System Tools” item, but if the menu is in English, then System Tools should be written. Then you need to look for "Firmware Update" or something like that. Here you need to click on the “Browse” button (or something else) and specify the path to the downloaded file. Then all you have to do is click on the “Update” button. After this, the equipment should restart itself.
Upon completion of the procedure, you need to reconfigure the router and check whether the Internet is lost or not. In most cases, this helps solve the problem.
It's all about the firmware
It’s not uncommon for there to be no Internet precisely because of bad firmware. In this case, if there is a connection, it does not work properly, periodically breaking off, or other troubles occur.
In this case, you can try updating the firmware. This is special software that is present on every router or modem. It is this that controls the operation of the processor, memory, traffic and other necessary tasks.
But when equipment, for example, TP-Link, loses the Internet periodically, updating the software does not always help. Therefore, it is better to first visit various forums and study reviews.
The router is slow and glitchy
The simplest situation is that the router malfunctioned and therefore the Internet via Wi-Fi disappeared. I most often encounter precisely such cases. Moreover, models from completely different manufacturers are susceptible to this “disease” - from cheap to premium. The factors influencing this are very diverse: it could be a defect, it could also be an unsuccessful firmware version. There have been cases when the router becomes dull and generally glitches due to a large number of operating hours - apparently the capacitors have dried out from old age and the device becomes terribly dull. What to do?
Reboot your router.
For this purpose, many Wi-Fi routers have a special On/Off button. If your device does not have one, simply unplug the power supply from the outlet and after 30 seconds plug it back in. You won’t believe it, but this solves a good half of the cases when there is Wi-Fi, but does not connect to the Internet.
Looking at the router indicators
Now pay attention to the indicator lights that are found on any regular router. There should always be three indicators - Power, connection to the Internet or WAN provider network, and a Wi-Fi wireless network. We are interested in the Internet connection indicator. This is what it looks like on different models. If it does not light up at all or lights up in red, scroll through the instructions below.
If the indicator glows a pleasant green light, it means the connection to the provider’s network was successful and the router has connected to the Internet, but for some reason it cannot distribute it to the connected devices. Again, from my experience, I will say that most often it’s just a buggy router. Then it needs to be reset to factory settings and then reconfigured. For these purposes, absolutely all such gadgets have a special Reset button, which allows you to reset all the settings made to those that were hardwired into it from the factory.
A factory reset is very easy to do. With the router turned on, simply hold this button with a paperclip or match and wait 5-8 seconds, then release. The router should reboot with factory settings.
Comment! If absolutely all the indicators on the router are lit, even those that should not be lit, then most likely its firmware has failed. Usually, you will not be able to access its settings through 192.168.1.1 or 192.168.0.1. Try to reset the settings first, and if that doesn’t help, then look on the Internet for how to restore the firmware for your specific model of access device. The same situation can occur when not a single indicator on it is lit at all except the power supply - Power.