Despite the fact that today almost everywhere there is already free Wi-Fi, everyone still prefers to use mobile Internet. Firstly, because it often turns out to be faster. Secondly, because it does not require additional authorization, like public networks. And thirdly, cellular traffic is usually either not limited at all or is available in large quantities. However, there are also tariffs where the amount of cellular data that can be used is far from unlimited. Therefore, users have to ensure that they do not exceed the established limit, or entrust this to their smartphone.
Are you tired of notifications about exceeding your traffic limit? We'll fix it now
How to disable MIUI optimization and why you need it
If your smartphone independently monitors your mobile data usage, it may occasionally send you a notification that you've exceeded your limit. It is possible that you did not manually activate the corresponding mechanism - it could very well turn on itself. This happens quite often. The device simply requests information from your mobile operator about the amount of traffic available to you, and then automatically calculates it based on the number of days in a month, allowing you to use it within established limits.
Network restrictions
This option allows you to prevent apps running in the background from using selected Wi-Fi networks. Apps will also display warnings before using these networks to download large amounts of data (torrents, for example).
It's better not to bother with this option at all.
Home » FAQ » How to set Internet traffic limit on Android FAQ
To do this you need to take a few simple steps:
This method allows you to set an Internet traffic limit for an entire month. If you need a daily limit, then you will need to change the start date of the statistics period every day, and set the limit value itself to what you need for one day. Yes, don’t forget to set your Internet traffic limit according to the tariffs of your operator.
Example 1. Your Internet provider provides you with 5 GB of Internet traffic for a month. Everything is simple here, go to the settings, check the “Set limit” checkbox and set the desired Internet traffic limit on the graph.
Example 2. Let's say your mobile operator gives you 50 MB per day. We check the box next to “Set limit”, set the desired limit for the day (first set a warning, and then the limit value), and then set the date of the statistics period for the day you need. Don’t forget to change the start date of the statistics period every day.
But that's not all the possibilities. In this menu, you will have access to detailed statistics on Internet traffic consumption; to do this, you need to scroll down. Using these statistics, you can find out which application uses the most traffic. Oh yes, I almost forgot, there is also such an item in the limit settings - “Show when blocked”. This item is activated automatically when the limit is enabled. With this option, an air circle appears on the lock screen displaying information about traffic consumption. For myself, I always leave this option enabled.
This is the functionality Android has. I hope the article was useful for you. If you have any questions, don’t hesitate to ask them in the comments.
Stay tuned, there is still a lot of interesting things ahead.
In your mobile phone settings you can find a section called “Data Transfer” or “Data Usage”. This section calculates the traffic that the user spends on his phone.
Denying applications access to the Internet
Many instant messengers lead to large data leaks. These include, in particular, Instagram, Telegram, WhatsApp. This is not a complete list of such programs. To save megabytes, you should disable the ability to upload pictures, videos or audio files in the WhatsApp application.
To do this, it is recommended to go to the “Data and Storage” section and select “Media Autoload”. It is recommended to download videos using WLAN.
Background updates on Facebook consume a lot of information. To refuse them, it is recommended to go to “Settings”. However, you should use a wireless network for updates. Copying files to cloud storage is necessary when using WLAN.
For more effective savings, it is worth installing programs that can function offline. Instead of using special services, you can simply save music to your smartphone. It is also permissible to use maps, translators and other programs offline.
Which application is eating traffic?
Check which apps are using the most data
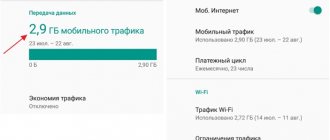
By the way, here you can see which applications consume the most cellular data. For example, in my case it is Instagram. Since the beginning of the month, I have already spent more than half a gigabyte on it. Actually it's not much. In fact, it could have cost even more if I had not used Wi-Fi to save money. This approach does not irritate me at all, and is even a kind of quest for me, forcing me to look for any available wireless networks - whether at a party or in public places.
However, if an application uses an excessive amount of data, I recommend turning off access to the cellular network for it. In this case, it will only be able to access the Internet when connected to Wi-Fi. This may be relevant for social networks like Instagram or TikTok, which tend to waste a lot of traffic. And since Wi-Fi is free and unlimited in most cases, it can be a good lifesaver, saving your traffic.
Source
Removing pest apps
Sometimes the high consumption of downloaded information is not related to user activity. Some applications that constantly transfer data waste a lot of megabytes. Using a standard tool built into any smartphone with Android OS, the user can calculate how mobile Internet traffic is spent.
- Visit Android Settings.
- Select "Data transfer".
- Go to "Mobile data transfer".
After the transition, a general graph of Internet consumption will appear. Below you will see how mobile Internet traffic is spent. You can reduce consumption by clicking on each program and turning off the background mode.
Note! Before identifying costly programs, you need to understand what Internet consumption is normal for an application. Those working with a small amount of data should remain untouched.
Bottom line
The superiority of third-party software over the standard method of limiting traffic is more than obvious. Flexible parameters will allow you to adapt to any tariff plans and stretch the provided megabytes for as long as necessary. You can easily automate the entire process and not interfere with the operation of the application, or make adjustments if necessary when necessary.
In addition to setting a limit on megabytes, you can optimize consumption by compressing network traffic.
Where to look for traffic settings
To get to the appropriate settings, we will take turns opening the nesting dolls, one after another. The largest of them is “Applications” (screenshots are provided for Android 5.0.2):
Rice. 1. Open Applications in Android
Having opened Applications in Android, we find Settings there:
Rice. 2. Android Settings
In the settings we need “Data Usage”:
Rice. 3. Open “Data Usage”
Updating or downloading programs from the App Store
Current applications and games can reach 2-3 gigabytes in volume, and Apple has taken care of preserving traffic - you cannot officially download a program with a volume of more than 100 megabytes from the App store (though we know). But at the same time, there are a large number of programs that are less than this threshold of 100 MB. And it is they who can devour your Internet package.
Here we are talking not so much about downloading (you see what you are downloading), but about independently updating these programs via the cellular network. Therefore, such an update needs to be disabled:
That's it, now programs will stop using the cellular network for their updates, and will do this only via Wi-Fi.
Wi-Fi Data Usage
Here, the menu displays statistics on data transfer over a wireless Wi-Fi network for the last 28 days. At the same time, it records which applications used how much traffic. For most it will be youtube, like for me.
Next, each program can be configured to use traffic. Just tap on the application, a new window will open.
We can prevent the application from using mobile traffic in the background. And additionally allow the receipt/transmission of mobile data, even if traffic saving is enabled. I do not recommend enabling this option.
Enable data saving in Android
An effective way to save Internet traffic on an Android phone is a special mode. It can be enabled manually. Step-by-step instruction:
- Visit "Settings".
- Select the “Mobile network” section, and then “Data transfer”.
- Launch the “Data Usage Cycle” tab.
- Set the time during which the restriction will apply.
- Set a maximum Internet volume that cannot be exceeded.
- Check the box next to the line “Limit mob. traffic."
Versions of Android 7.0 are equipped with a special mode that saves Internet. Starts in 2 clicks. You need to go to the quick settings panel and turn it on.
Disable app updates via mobile network
Automatic application updates can be disabled in the Play Market. For this you will need:
- Go to Play Market.
- Go to the "Settings" section.
- Open the "Auto-update applications" tab.
- Select “Never” from the options offered.
To disable automatic updating of one application, you need to enter its name into the search bar or find it in the “My applications and games” tab. Then uncheck the box next to “Auto-update”.
What is traffic
Traffic is the amount of information that a mobile phone sends and receives from the Internet. Traffic can be measured in packets, bits, or bytes. But in phones, bytes and their derivatives (kilobytes, megabytes and gigabytes) are usually used as a unit of measurement. Traffic counting is necessary so that the user can control his Internet expenses.
When traffic is counted, it is usually divided into several types. This can be incoming, outgoing, internal or external traffic. But the phone usually doesn’t have such detailed statistics about traffic usage. Instead, the phone simply shows the total amount of data that has been used over a period of time. In some cases, separate counts may be kept for mobile Internet (traffic transmitted via cellular communications) and Wi-Fi.