GPU
First, let's say a few words about the subject of our discussion - the graphics processor. The GPU is a device that performs graphics calculation (rendering), that is, it takes an active part in creating an image. Due to the architecture features, the graphics processor copes with graphics processing tasks much more efficiently than central processors. The GPU can be implemented as part of a video card or in hybrid processors (integrated on the processor chip); less often, it can be part of the northbridge on the motherboard.
GPU clock speed
We talked a little about the graphics processor, now we can move on to the main topic - GPU clock speed.
The clock frequency of the graphics processor is measured in megahertz, just like for central processors. But the average GPU frequency today is much lower than that of the CPU and is about 900-1100 MHz for top models.
Again, as with central processing units, the higher the frequency, the more tasks the processor can perform per unit time. Therefore, the GPU clock speed directly affects the performance of the video card.
For technically identical graphics processors, an increase in frequency indicators leads to a proportional increase in the resulting performance.
If we look at two top competitive models from Nvidia and AMD, for example, take the average performance of devices such as the Asus Radeon HD7970 and Nvidia GTX 680 video cards, we will see the following picture:
- GPU HD 7970 frequency is 925 MHz (with a real video memory frequency of 1375 MHz and a bus width of 384 bits);
- The GPU frequency of the GTX 680 is 1006 MHz (with a real video memory frequency of 1502 MHz and a bus width of 256 bits).
These are averages without specific patterns, just to show the general trend. Since we are well aware of the implicit leadership position among these two video cards, we can use this to speculate a little about the impact of GPU frequency on performance.
Evaluating purely frequency indicators, we see 925 and 1006 MHz in the difference in frequency indicators, which is quite significant. Considering the approximately parity performance indicators of both the Radeon HD 7970 and the Nvidia GTX 680, we can state the same dependence on the complexity of the characteristics. That is, the lower frequency of the video chip in the HD 7970 is compensated by other characteristics that will reveal the video card better in certain types of loads. Therefore, when choosing a video card, you need to select a model based on a set of characteristics, and not just on the amount of video memory or GPU frequency.
So I would like to emphasize once again that the complexity of the parameters is above all, the main thing is not to concentrate on one thing.
Selection based on price
There are a lot of different video cards on the market at the moment. It would seem that choosing a video camera is not an easy task. But in reality, everything is much simpler.
First you need to decide on the so-called “family” of video cards. There are only two of them on the Russian market - nVidia and AMD (green and red, as they are popularly called). Both sides have their advantages: video cards from nVidia, for example, can boast greater support for various interesting technologies (PhysX, 3D Vision, etc.), and video cards from AMD have a better price-quality ratio (and prices in general) compared to nVidia significantly lower for red cards). However, in fact, the difference is not very big and it’s all like the eternal debate between Intel vs AMD, that is, globally, as they say, to each his own.
In each family, video cards are divided into price segments (niches) for a specific type of video card on the market. There are the following segments of video cards:
- Video cards in the infra-budget price segment. Mainly used as an alternative to the built-in video chip in motherboards. Currently the cheapest on the market. Most often they are also called office ones, although this name is not always true. For example: For nVidia, these are video cards like GF210-220, GF410-420-430, GF510-520, etc. (hereinafter, GF is the well-known NVIDIA GeForce) For AMD, these are video cards like HD4550, HD5450, HD6450, etc.
- Video cards in the budget price segment Such video cards are perfect for replacing an old card, as they say, “on the fly”. Roughly speaking, if you did not intend to change the video card, but you had to due to the fact that the one you already had, for example, burned out, video cards of this particular price segment are the most optimal choice for you. This is because the budget price segment is replenished over time from video cards of higher price segments, that is, there are often cases when a person comes to the store to buy a new video card because his old one has gone sour, and suddenly discovers that the video card that was twice more powerful and cost much more, now it’s on display for a more than reasonable amount. “Why buy a new model of video card if I can buy the previous model for much cheaper?” - he will think. And he will often be right. Examples of such video cards: For nVidia, these are video cards like GF240, GF440, GF540, etc. For AMD, these are video cards like HD4830, HD5670, HD6670, etc.
- Mid-price video cards These video cards are the most common on the market. They are the ones that are mainly chosen when selecting a computer. Their characteristics are much higher than those of video cards in previous price segments and, accordingly, they are much more powerful and more expensive. These video cards are designed for any needs and requirements and they will cope with both new toys and graphics work with equal success. These are great for upgrading your computer, but may require additional costs, for example, a more powerful power supply. It is from this segment of video cards that another selection criterion is introduced, namely the relevance of the video card.
What is relevance?
Let's give an example: You purchased a new computer game, installed it, but it ungodly slows down. What to do? Answer: Most likely, you need to go to the store for a new video card. When you come there, you can save money and take a card from the budget price segment (essentially the same as yours, but relatively more powerful), or you can throw in some money and take it from the middle price segment, which is more expensive and significantly more powerful than yours. In the first case, you will, of course, be able to play a new toy, but after a month, perhaps, an even newer toy will come out again and it will again “slow down”. It's a shame. But in the second case, your video card will cope perfectly with this game and any other for some time.
This time (that is, the time that the card runs new games and applications, as they say, without brakes and at maximum settings) is called the period of relevance of this video card, that is, for example, a video card from nVidia on the GF450 chip. It is still in the mid-price segment, but its relevance is less than that of the video card on the GF550 chip.
Examples of video cards in the mid-price segment: For nVidia, these are video cards like GF450, GF550, GF460, GF465 For AMD, these are video cards like HD5750, HD5770, HD6750, HD6770, HD5850, HD6850
- High-end video cards These video cards are the most expensive on the market and they are the benchmark for power and performance. With the help of these video cards, nVidia and AMD corporations show “who’s boss.”
Updating with them is often expensive because, most likely, you will need to replace almost all components (in any case, the processor and power supply, as a rule, have to be changed exactly), and you will have to fork out significantly for the card itself, since its price is usually close to the price Your computer in generalIn general, these video cards are, so to speak, the dream of any tech geek and the sweet dream of an advanced gamer. The advantage of these is that they remain relevant for a very long time, because even the GF285 series video card from nVidia, released almost 4 years ago, has no problems even now and will be relevant for a relatively long time.
The choice of these video cards directly depends on the capabilities of your wallet, since almost any of them is relatively expensive (and some models even cost almost like a tank).
Examples of such video cards: For nVidia, these are video cards like GF285, GF470, GF480, GF 570, GF580, GF590, etc. For AMD, these are video cards like HD6870, HD5870, HD6950, HD6970, HD5970, HD6990, etc.
Something like this. In general, the information on video cards in the sections listed above is by no means a dogma when choosing them; rather, it is simply a division into monetary segments, in order to create some kind of guideline for you.
Naturally, the article on choosing a video card would not be complete if I did not tell you about the characteristics of these, because when choosing a video card, you should always rely not so much on the price as on the characteristics, because cards of the same price segment (even of the same type and on the same chip) can often differ in their parameters and power.
Let's take a closer look at what characteristics there are, what they are responsible for and why they are needed.
Why do you need a GPU?
This chip in the video card is busy with the most important thing: it renders graphics, calculating 2D and 3D objects and their interaction with each other and thereby forming an image, which is then transmitted to the monitor display. Thanks to its architectural features, this chip processes graphics much more efficiently than a central processor, despite its lower power.
Such a chip can be either an integral part of a video card, or integrated into the northbridge of the motherboard, or as a logical block on the CPU. As a rule, the last two types are less powerful and are suitable for performing everyday tasks, but are weak at rendering complex objects.
What does its frequency affect?
Core clock speed is the number of operations the GPU performs per second. Today, in powerful video cards this figure has already exceeded gigahertz.
The higher the clock speed, the more data the graphics accelerator can process. This affects not only the number of FPS in games, but also the number of primitives in rendered objects, that is, the quality of graphics.
Such indicators were achieved by reducing the technical process of the graphics chip, increasing the number of logical blocks on the same chip area. You can read more about the technical process of the video card here.
The two main competitors that produce graphics chips, Nvidia and AMD, are constantly competing to improve the frequency characteristics. To release a new top-end model, which in terms of technical parameters will outshine its competitors for at least a couple of months, is more a matter of prestige than an urgent market need.
Even in developed countries, not every gamer can afford such a device.
How many cores does the video card processor have?
A video card has many computing cores, usually several thousand, but they are combined into blocks, usually 32 for NVIDIA video cards, and have common elements, including registers. The architecture of the GPU core and logic elements is much simpler than on the CPU, namely, there are no prefetchers, branch predictors, and much more.
Interesting materials:
How to properly apply hair removal wax? How to write the address correctly on a parcel to Germany? How to write a thesis correctly without plagiarism? How to write the days of the week correctly? How to write a petition to the Magistrates' Court correctly? How to write a wedding vow? How to write hears correctly? How to correctly write a letter of resignation without service to a pensioner? How to wear a beige coat? How to wear a classic vest correctly?
Is it possible to increase the frequency and why do it?
There are a number of programs that allow you to boost a graphics chip, increasing its frequency characteristics (of course, if the component supports such an option). This may include:
- ASUS GPU Tweak – works best with video cards of this particular brand, giving the user access to additional options;
- MSI Afterburner is an omnivorous utility that doesn't care about overclocking;
- RivaTuner is the “progenitor” of all modern overclocking programs, on the basis of which all subsequent products were created.
In addition to increasing the GPU frequency, these utilities can increase the memory frequency, adjust the rotation speed of coolers, and much more. “What does this do in practical terms?” – an attentive reader may ask.
Increasing the clock frequency, as you might guess, allows you to increase the quality of graphics and the amount of FPS in games using software, that is, without buying a new video card.
Such a “crutch” can be used as a temporary solution when the user is not yet mentally mature enough to buy a new device, but already wants to play a new game that the computer does not support according to the system requirements.
It should be borne in mind that overclocking a video card requires a careful and thoughtful approach - if you go too far with increasing the frequency and “give soot” more than the video card can physically handle, the graphics driver will restart, which usually leads to a crash of the running game or video editor.
It is very difficult to break a device in this way, due to the “foolproof” provided by the programmers. However, I would also like to note that particularly persistent overclocking fans still manage to burn out the video card by giving it an increased load and reducing the number of cooler revolutions to a minimum.
As a recommendation, I advise you to pay attention to the Asus PCI-Ex GeForce GTX 1060 Dual 3GB (DUAL-GTX1060-O3G) video card, which will run all modern games at acceptable graphics settings.
Unfortunately, such a product is less suitable for mining than a similarly priced video card from AMD. Well, this is already the case - either play games or mine cryptocurrencies, right?
See you again on the pages of my blog, dear friends! Don't forget to share this article on social media and subscribe to the newsletter.
CaRo Jul 19, 2015
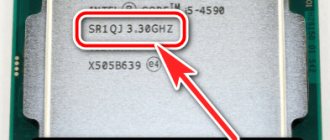
Hello. There's a problem. I borrowed a used AMD Radeon HD 6450 video card for a while. I installed the drivers, it seems to work. I launched a couple of games to check - the result did not live up to expectations. I wasn’t very disappointed and started installing other games (purely out of curiosity, to see what I could get from my favorite one). But here’s the strange thing: even those games that with fairly high graphics settings should run without a drop in FPS run with “brakes”. This surprised me. I started scouring the Internet to find the specifications for this card. Here's a quick summary:
(note the underlined item please)
Video processor name: Radeon HD 6450; Technological process: 40 nm; Base frequency of the video chip: 625 MHz; Number of universal processors: 160; Video memory capacity: 1 GB; Memory type: GDDR3; Effective memory frequency: 1334 MHz; Memory bus width: 64 bits; Maximum memory bandwidth: 10.6 GB/sec.
Now, the most interesting thing: stress tests and information about the video card of two different programs (screenshots)
What could be the problem and how to solve it? Help me please.
Gaming Graphics Card Buyer's Guide
There’s a lot to explain to you, it’s better to read it once.
Video memory frequency
Another parameter that affects memory bandwidth is its clock frequency. And increasing the bandwidth often directly affects the performance of the video card in 3D applications. The memory bus frequency on modern video cards ranges from 533 (1066, taking into account doubling) MHz to 1375 (5500, taking into account quadrupling) MHz, that is, it can differ by more than five times! And since bandwidth depends on both the memory frequency and the width of its bus, memory with a 256-bit bus operating at a frequency of 800 (3200) MHz will have greater bandwidth compared to memory operating at 1000 (4000) MHz with a 128-bit bus.
Particular attention to the parameters of the memory bus width, its type and operating frequency should be paid when purchasing relatively inexpensive video cards, many of which only have 128-bit or even 64-bit interfaces, which has an extremely negative impact on their performance. In general, we do not recommend purchasing a video card using a 64-bit video memory bus for a gaming PC. It is advisable to give preference to at least a medium level with at least a 128- or 192-bit bus.
Post edited by Vyacheslav2011: July 19, 2015 - 18:51
Effect of video memory frequency
The special RAM built into the video card is called video memory and in its abbreviation, in addition to DDR (double data transfer), it contains the letter G at the beginning. This makes it clear that we are talking about GDDR (graphics double data transfer), and not about some other type of RAM. This subtype of RAM has higher frequencies compared to conventional RAM installed in any modern computer, and ensures sufficient performance of the graphics chip as a whole, giving it the ability to work with large amounts of data that need to be processed and displayed on the user’s screen.
Memory Bandwidth
The clock speed of video memory directly affects its bandwidth (BW). In turn, high bandwidth values often help to achieve better results in the performance of most programs that require participation or work with 3D graphics - computer games and programs for modeling and creating three-dimensional objects are confirmation of this thesis.
Memory bus width
The clock frequency of video memory and its effect on the performance of the video card as a whole is directly dependent on another, no less important component of graphics adapters - the width of the memory bus and its frequency. It follows from this that when choosing a graphics chip for your computer, you need to pay attention to these indicators so as not to be disappointed in the overall performance level of your work or gaming computer station. If you do not approach it carefully, it is easy to fall into the trap of marketers who installed 4 GB of video memory and a 64-bit bus in their company’s new product, which will very slowly and inefficiently pass such a huge flow of video data through it.
It is necessary to maintain a balance between the frequency of video memory and the width of its bus. The modern GDDR5 standard allows you to make the effective frequency of video memory 4 times higher than its real frequency. You don’t have to worry that you will constantly have to calculate the effective performance of the video card in your head and keep this simple formula of multiplying by four in your mind - the manufacturer initially indicates the multiplied, that is, the real frequency of the video card memory.
Conventional graphics adapters, not intended for special computing and scientific activities, use memory buses from 64 to 256 bits wide. Also, in top gaming solutions there may be a bus with a width of 352 bits, but the price of such a video card alone can amount to the cost of a full-fledged PC of medium-high performance level.
If you need a “plug” for the video card slot on the motherboard for working in the office and solving exclusively office tasks such as writing a report in Word, creating a table in Excel (after all, even watching a video with such characteristics will be difficult), then you can confidently purchase a solution with a 64-bit bus.
In any other cases, you need to pay attention to a 128-bit bus or 192, and the best and most productive solution would be a 256-bit memory bus. Such video cards for the most part have a sufficient supply of video memory with a high frequency, but there are also inexpensive exceptions with 1 GB of memory, which is no longer enough for today’s gamer and you need to have at least a 2 GB card for comfortable gaming or working in a 3D application, but here You can safely follow the principle “the more, the better.”
PSP calculation
For example, if you have a video card equipped with GDDR5 memory with an effective memory clock frequency of 1333 MHz (to find out the real GDDR5 memory frequency, you need to divide the effective memory frequency by 4) and with a 256-bit memory bus, then it will be faster than a video card with an effective memory frequency of 1600 MHz, but with a 128-bit bus.
To calculate the memory bandwidth and then find out how productive your video chip is, you need to resort to this formula: multiply the memory bus width by the memory frequency and divide the resulting number by 8, because that’s how many bits are in a byte. The resulting number will be the value we need.
Let's return to our two video cards from the example above and calculate their bandwidth: the first, better video card, but with a lower video memory clock speed, will have the following - (256 * 1333)/8 = 42.7 GB per second, and the second video card only 25.6 GB per second.
You can also install the TechPowerUp GPU-Z program, which is capable of displaying detailed information about the graphics chip installed in your computer, including the amount of video memory, its frequency, bus bit size and bandwidth.
Conclusion
Based on the information above, you can understand that the frequency of video memory and its impact on operating efficiency is directly dependent on another factor - the width of the memory, together with which they create the value of memory bandwidth. It affects the speed and amount of data transferred in the video card. We hope that this article helped you learn something new about the structure and operation of a graphics chip and provided answers to your questions.
Video card characteristics
A video card is one of the main components of a computer. It is responsible for processing graphics and displaying images on the monitor screen. Therefore, when choosing a video card, it is very important to pay attention to its characteristics. Since it depends on the characteristics of the video card whether it can satisfy all the user’s requirements.
In this article we will look at the main characteristics of modern video cards. We will also tell you how to use this information in order not to make a mistake when choosing a video card.
GPU (chip)
The first thing you should pay attention to when choosing a video card is the graphics processor. All other characteristics of the video card depend on the GPU model.
NVIDIA names its GPUs as follows: GeForce GTX 123.
Where 123 is a numerical designation that indicates the position of this graphics chip in the line of video cards from NVIDIA. The first number (1) indicates the generation of the video card. At the moment, the latest generation of video cards is GeForce GTX 7xx. The second (2) and third (3) digits indicate the position of this graphics chip in the line of current generation video cards. The larger the numbers 2 and 3, the higher the level of this video card. Thus, the GeForce GTX 780 video card is more powerful than the GeForce GTX 770, and the GeForce GTX 770 is more powerful than the GeForce GTX 760.
AMD uses a very similar naming scheme for its graphics chips. Chips from AMD are designated as follows: Radeon HD1234. Where number 1 indicates the generation of the graphics chip, and numbers 2, 3 and 4 indicate the position of the chip within the current generation.
Now let's look at the real characteristics of video cards.
GPU clock speed
The clock speed of the graphics processor is one of the most important characteristics of a video card. Typically, the clock speed of a video card's GPU is indicated in megahertz (MHz); gigahertz (GHz) is less commonly used. The higher the clock frequency, the faster the processor processes information, and this directly affects the performance of the video card.
It should be noted that the same graphics processor in different video cards can operate at different frequencies. This happens because some video card models use factory overclocking.
The amount of video memory is a characteristic that many inexperienced users pay too much attention to. This is due to not very honest advertising, which focuses primarily on a simple and understandable idea that the more memory, the faster the device works.
In fact, everything is completely different and, in principle, you can not even pay attention to the amount of memory. The manufacturer will not install less than what is needed for a given video card model. But more - they install with pleasure. Again, this is done to attract the attention of non-experienced users.
On the other hand, if the budget allocated for the purchase of a video card allows, then you can safely buy a model with a large amount of memory. In any case, it definitely won't hurt.
The type of memory is already a more significant characteristic of a video card. Nowadays you can find video cards on sale with the following types of video memory: DDR3, GDDR3, GDDR4 and GDDR5. What you need to know about video memory types is that GDDR3 is better than DDR3, GDDR4 is better than GDDR3, and GDDR5 is correspondingly better than GDDR4.
At the moment, most modern video cards are equipped with GDDR3 or GDDR5 memory. GDDR3 memory is used in low-end video cards, while GDDR5 is used in mid-range and high-end video cards.
Video memory frequency
Video memory frequency is a characteristic that affects the speed of data exchange between the processor and memory. Naturally, the speed of data exchange between the processor and memory affects the overall performance of the device. Therefore, the higher the video memory frequency, the better.
Memory bus width
Memory bus width is another characteristic that affects the speed of data exchange between the processor and memory. Now on sale you can find video cards with memory bus widths: 32, 64, 128, 196, 256, 384, 512 and 768 bits.
Video cards with a memory bus width of less than 128 bits are cheap devices for office use. Mid-level and higher video cards are equipped with a bus with a bit width of 128 bits or more.
Connectors for connecting to a monitor
An important parameter is the connectors on the rear panel of the video card, designed for connecting to a monitor. In most cases, a DVI connector is used to connect to a monitor. This type of connection is supported by most video cards and monitors.
But, if you plan to connect a TV to your computer using an HDMI port or a projector using a VGA port, then you need to make sure that the selected video card is equipped with the port you need.
Memory bus width
Like the type of memory, they depend on the price segment of the video card:
- For video cards in the infra-budget price segment, these are 64 and 128 bits
- For video cards in the budget price segment, these are 128 and 256 (sometimes, most often for transitional video cards)
- For video cards of the middle and high price segments - these are 256, 384, 448, 512, 2*512 (if the video card is dual-chip), 768 and so on
Please note that the amount of video memory in all segments can be the same, say, 1024 megabytes, but some have DDR2 memory type and 64 bits, while others have GDDR5 memory type and 256 bits. I’ll give a comparative example to make it clear that in this case it’s faster.
Imagine the situation: You came to the store to buy a new video card. After reviewing the product, you see two video cards on the same chip and from the same manufacturer. Reading the specifications, you discover that they have the same memory types, but its volume and bus width are different. One has 512 MB and 256 bits, and the other has 1024 MB and 128 bits. What do you think is the best video card to choose? Based on what I said above, the right choice would be a video card with 512 MB and 256 bits, because its throughput will be significantly greater, which means the overall performance of the card will differ significantly.
Speaking from my own experience, the bit depth is almost the main characteristic and, say, once grabbing a card with a bit depth of 512-768 bit, you will be able to avoid replacing it at all for several years and about 5-7 generations of video cards, saving a significant amount of money and nerves on regular upgrades (updates of computer components).
So, for example, I once took a GTX 285 card with a capacity of 512 Bit and still don’t feel the need to replace it, even when playing Crysis 2 with improved textures and maximum settings. By the way, judging by GPU-Z, this is not very surprising because the throughput characteristics between, say, a 580 card with 364Bit and a 285 card with 512 are quite close, despite the difference of 9 generations (I haven’t counted 320 yet -th and all sorts of small varieties and form factors) between 580 and 285 cards.
Next we have...
How to choose a video card?
With this article, our website continues a whole series of useful materials, the purpose of which is to make it easier to choose any product from the thousands of options offered on the market. Agree, choosing a specific model of a device always takes a lot of time, which can be spent usefully. In today's material we will talk about choosing a video card for your home PC.
A video card is one of the main components of any personal computer. For office tasks, any modern model or even a not very powerful video chip built into the processor will be enough, and separate and more expensive options are almost always intended for gamers. In this article we will talk about the features of choosing gaming video cards and their characteristics - after reading, you will definitely be able to choose an excellent option for yourself within the budget and your own needs.
The performance of your computer in most games directly depends on the selected video card (some games, however, are more dependent on processor performance, but these are becoming less common). If you use a modern monitor with a resolution of at least 1920x1080 pixels (FullHD), then you will probably want to use this resolution in games, and also get a frequency of at least 30, and better yet, 60 frames per second.
It is worth noting that the technical characteristics of video cards, like, say, the technical characteristics of processors, do not tell the whole story. For example, a model with 4 GB of video memory will not always be more productive than a model with 2 GB of video memory. When choosing a video card, it is better to rely on test results - for example, those presented on this site. This is due to the fact that video cards use a wide variety of chip architectures, as a result of which direct comparison of their characteristics is often meaningless.
However, it is still useful to know about the important parameters of video cards - at least to broaden your own horizons. In the next section, we will talk about what GDDR5 is and how many PCI-E slots on the motherboard you will need to install a video card in your PC, and then we will present to your attention the twelve best video cards in four price categories.
How much video memory do you need for games: four, six or eight gigabytes?
Pages of material
Table of contents
- Introduction
- Test configuration, tools and testing methodology
- Benchmark Results: Assassin's Creed Odyssey Performance Comparison
- Battlefield V
- Call of Duty: Modern Warfare (2019)
- Far Cry New Dawn
- Hitman 2
- Need for Speed Heat
- Shadow of the Tomb Raider
- Star Wars Jedi: Fallen Order
Introduction
This review will attempt to identify the impact of four, six and eight gigabytes of video memory on the performance of video cards in games. The task is not trivial, since it is very problematic to find identical models with such volumes. Therefore, the study of this issue will not be carried out by comparing the performance of graphics accelerators, but in a different way.
Basic characteristics of the video card
Connection type
Once upon a time, video cards used AGP slots on motherboards, but today the vast majority of their models are inserted into PCI-Express slots. Such slots are found on any modern motherboard - you don’t need to worry about their presence.
Purpose
Most of the video cards on sale are designed to meet the needs of PC gamers. But there are also video cards in stores for professionals - they provide high speed operation of special software, which is intended, for example, for creating 3D models or video editing.
Video Processor Unit (GPU) Manufacturer
At the moment, the video card market is divided between two major players - AMD (bought ATI several years ago with its Radeon video cards) and Nvidia (owned by Intel, which produces processors and other electronics). The latter's products are more popular - the latest generation of Nvidia video cards require less power, do not heat up as much as their AMD counterparts, and often win in performance tests. In addition, most game developers optimize their titles primarily for Nvidia video cards, and the stability of Nvidia drivers (special software that “explains” to the operating system the principles of working with a video card) is considered higher than the stability of AMD drivers.
However, this does not mean that AMD video cards are significantly worse - they have their advantages (for example, often lower cost with the same performance). In the end, the choice between these two manufacturers depends on specific conditions - the budget and the tasks that you plan to set for the video card.
GPU frequency, MHz
Directly characterizes the speed of the main component of any video card - the processor. Comparing performance in this parameter, however, is only possible within one series of cards - for example, among several GTX 960 variants from different manufacturers. The reason is the use of different architectures, which is why performance comparisons are again best done in game and synthetic tests.
Number of occupied slots on the motherboard
Powerful and expensive video cards can occupy two or even three PCI-Express slots on the motherboard. This does not mean that the video card is inserted into these slots - it’s just that its cooling system takes up a lot of space and interferes with the installation of any other cards in the slots located nearby. If you plan to buy two or three video cards at once for use in SLI or CrossFire mode (more on this below), then you should consider the availability of free space for them.
Video memory type
The vast majority of modern video cards (and all gaming cards in general) use GDDR5 RAM - there’s no choice here. Such memory is characterized by high frequency, excellent bandwidth and low power consumption.
Video memory capacity, GB
To the naked eye, this is the main characteristic of any video card. It should be noted that this is far from true - the amount of video memory should always be adequate to the specific video card model. A cheap model equipped with 4 GB of memory will not be able to compete in performance with a higher-end model that is equipped with only 2 GB of memory. However, in recent years the trend of installing too much memory on cheap and weak cards has slowed down - in most cases this amount corresponds to the performance of the model. A modern gaming video card should have at least 2 GB of memory, and preferably 3 or 4 GB.
Video memory clock frequency, MHz
Directly characterizes the performance of memory chips installed on a specific video card. Unfortunately, the situation with the memory frequency is the same as with the GPU frequency - it is not recommended to use it for direct comparison of models due to differences in architecture and other parameters.
Data exchange bus with memory, bit
The higher this indicator, the faster the two main components of the video card - the GPU and memory - can exchange information. Naturally, performance depends on many other factors, but high-performance gaming video cards use a bus that is at least 256-bit wide. Budget solutions, however, can also receive 128-bit wide buses - often the bandwidth of such a bus is sufficient for them.
Low profile cards
Such cards can be installed in a small case and take up very little space inside the computer. Unfortunately, among these video cards there are no gaming models - they are all intended for office and media computers.
Cooling type
Most video cards use active cooling - the heat generated by the processor and memory is dissipated using a complex structure of metal tubes, a radiator and powerful fans. Sometimes you can find water cooling, but most video card manufacturers use air cooling, assuming that only the most avid enthusiasts will install the water cooling manually.
Less powerful cards can do without a fan - just a radiator. There are no gaming models among them.
SLI and CrossFire support
Modern video cards can be used in configurations of two or even more models at the same time. Models with Nvidia chips use SLI technology for this, models with AMD chips use CrossFire technology. In this case, it is worth remembering several principles: 1) only cards with the same chips and the same amount of memory can operate in SLI or CrossFire mode, preferably completely identical ones; 2) the amount of memory does not increase - its contents are duplicated in all simultaneously used video cards; 3) the productivity increase will never reach 100%, and rarely - 60%-70%; 4) working in these modes is often associated with bugs and other difficulties - optimization of games for SLI and CrossFire is highly dependent on the developers and engineers who write the drivers.
Support for different DirectX versions
All modern video cards support the latest version of DerictX and even the new version of DirectX 12, which will appear only in Windows 10 - the architecture of the latest AMD and Nvidia chips implies this.
Video outputs
Video cards can be equipped with a wide variety of video outputs—ports through which video signals are sent to a monitor or other display. In most cases, these are VGA ports (the oldest standard with poor image quality), HDMI / Mini HDMI, / DVI-I or DisplayPort. If you want to use a video card with several monitors at once (or, for example, with a monitor and a TV), be sure to make sure that it has the necessary ports to connect to them.
Need for additional nutrition
Powerful gaming video cards require the connection of one or even two additional power cables from the computer's power supply. When purchasing such a video card, be sure to make sure that there are free cables and, in general, that your power supply can handle a powerful video card (manufacturers always indicate the approximate power of the power supply that should be used with their video cards).