This article will focus on the Windows registry; the article is relevant for Windows 10, Windows 7 and all other versions of operating systems.
In this material we will examine the following questions:
What is the Windows Registry?
What is Registry Editor and where is it located?
How to open Registry Editor in Windows?
Windows Registry Device
Examples of using the registry to restore Windows operation
What is the Windows Registry?
Many have heard, but not everyone knows, “what is the registry on a computer,” now we will correct this shortcoming.
System registry , or Windows registry , is a database for storing operating system settings, installed programs, user and hardware settings, in addition, the registry stores information about computer devices (configurations).
That is, this is the place where most of the settings of your PC are stored.
Example: you changed your desktop wallpaper, information about this is entered into the Windows registry.
The next time you boot the operating system, the data will be read from the registry, and the desired image will be displayed on the desktop. The system registry is available in all modern (and not so modern) operating systems of the Windows family: 10, 8, 7, XP.
Is it safe to run reg files?
Because when you run a reg file, it can modify the registry of your OS, then when you run a malicious reg file, there can be very sad consequences, ranging from the installation of unwanted software and viruses, to the failure of the operating system and the theft of your personal data. Therefore, the answer to the question about launch security depends on how much you trust the source from which you received this reg file. If this is some reputable site, then the likelihood that it will turn out to be malicious is much lower than some kind of file dump. It is also worth at least opening such text with a text editor and seeing what it does.
What is Registry Editor and where is it located?
To view the settings in the registry and change them, you can use a special program called “ Registry Editor ”.
This program is located in the Windows folder, the file is called regedit. exe
But there is no shortcut to launch Registry Editor in the Start menu! This was done for a reason. The fact is that erroneous changes in the system registry can lead to computer malfunctions, so the manufacturer has hidden the ability to quickly launch the registry editor.
Cleaning the system registry
During the process of installing and uninstalling applications, sections dedicated to software accumulate keys that the installer built into an unnecessary product could not remove, as well as records about the association of various file types. You can get rid of unnecessary entries manually only in one case - when you delete a program or game.
- Open regedit using the command of the same name or through Start.
- Expand the HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE , and in it - the SOFTWARE .
- Find the subkey that belongs to the removed product and get rid of it.
Sometimes it is located in a directory with the name of the developer company, for example Finereader, you should look for the path HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\ABBYY.
Never change data in the registry unless you are completely sure of the correctness of the actions. If you have a backup copy, the information can be easily restored, but it is better to prevent such a situation.
Check out our other posts about the meaning of cleaning the Windows registry:
- How often should you clean the Windows 10 registry?
- Can cleaning the registry improve performance?
How to open Registry Editor in Windows?
I described in detail how to open the Registry Editor in each version of Windows (10, 8, 7, XP) in this article:
How to Open Registry Editor in Windows
The fastest way to launch Registry Editor
I will reveal the fastest way to launch the Registry Editor, which is relevant for all versions of Windows:
- Press the Win+ R (hold down the Windows key and, without releasing it, press the R key);
- In the “Run” window, type the command “ regedit ” (without quotes) and click the “ OK ” button;
- If prompted, confirm launching Registry Editor with the “Yes” button.
For example, two more ways to launch the Registry Editor can be seen in this video (using Windows 10 as an example):
Windows Registry Device
When you open Registry Editor, you'll see a window that looks a lot like Explorer:
On the left side of the window there are registry keys, also called “keys” (they look like folders), on the right side of the window the parameters (like files) and their values are displayed.
Windows Registry Keys
The Windows 10, 8, 7, XP registry consists of five standard sections - root keys:
- HKEY_ CLASSES_ ROOT – information about file types registered in Windows
- HKEY_CURRENT_USER for the user logged into Windows
- HKEY_ LOCAL_ MACHINE – settings related to the computer
- HKEY_ USERS – settings for all users
- HKEY_CURRENT_CONFIG – about hardware settings
For simplicity, they are often indicated in an abbreviated designation (abbreviation of the first letters): HKCR, HKCU, HKLM, HKU, HKCC .
Purpose of registry keys
Let's look at the Windows 10 registry keys in a little more detail (if it seems complicated, go straight to the registry settings):
| Registry key | Description |
| HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT (HKCR) | The section stores information about all file types that Windows needs to know about (avi, doc, jpg and all the others). For each type, the program associated with it is indicated, an icon is assigned that is displayed in Explorer, commands that can be used for these files (open, print, etc.) are given. After installing various programs, new file types are registered here (for example, after installing the 7-Zip archiver, the file type appears .7z) The partition is a copy of the HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Classes subkey |
| HKEY_CURRENT_USER (HKCU) | This section contains the settings of the currently logged in user. Screen settings, keyboard layout, network connections, program settings and much more are stored here. Most recommendations for registry settings apply to this section. |
| HKEY_USERS (HKU) | Here are the settings for all users of the operating system, as well as the default settings. In fact, the HKEY_CURRENT_USER section is one of the subsections of the HKEY_USERS section and all settings changes made by the user are saved in the subsection allocated for it. |
| HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE (HKLM) | This section stores information about the computer settings (software and hardware configuration). Anything you change in this section will affect all PC users. This section is the second most popular of the changes made. |
| HKEY_CURRENT_CONFIG (HKCC) | The section contains information about setting up equipment for the current session (hardware profile). This section is a copy of the subkey “HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Hardware Profiles” and is practically not used for manual changes. |
Congratulations, we're halfway through the lesson and you know about the five root registry keys!
To study the registry structure, it remains to become familiar with the parameters and their values.
Backup of the entire registry or a specific section
We have already talked about the dangers of working with the registry. There is always a possibility of causing harm to the system and you need to take care of creating a copy in advance. You should enter the Windows Registry Editor and open the “File” section. In the list that appears, select the “Export” item. Now you can create a copy of the entire registry or a specific subsection. For convenience, the process is demonstrated in the screenshot below.
In order to increase reliability, it is possible to save a copy not only on the device’s hard drive, but on external media.
So, the worst happened and the system crashed. What needs to be done in such a situation? It is worth considering three recovery methods, each of which has its own characteristics. In any situation, you must first shut down all programs and applications. It will not be superfluous to disable antivirus tools.
Recovering from a file
Let's move on to the document that was previously saved. There should be a copy of the entire Windows registry. You need to double click and then confirm the received message. It is shown in the screenshot below.
Some time will be required for recovery, and the process itself will be completed after the device is rebooted.
Merger
You need to open the folder with the copy and right-click on it. A menu will appear in which you need to specify “Merge”. For your convenience, this action is presented in the screenshot.
As in the previous case, the recovery will be completed after a reboot.
Import
You need to open the Windows registry . How to do this has already been discussed previously and several approaches have been presented. In the editor itself, we are interested in the “File” menu. There you should select “Import”. You will be prompted to specify the path to the saved copy.
Separately, it is necessary to consider an option that involves restoring the entire system. This involves the use of built-in tools. It is important to make backups yourself or not disable backups.
Recovery using live CD
In some situations, loading the operating system may not be possible. This is the most difficult option and it is recommended to use a special method to solve this problem. It consists of loading via a live CD. When this is done, you need to proceed further - visit the root of the disk where Windows is installed. The following instructions are provided:
- Create a temporary folder on the system disk. It needs to be named tmp. This is where the defective registry files will be located.
- Now we log into the folder C:\WINDOWS\system32\config
- All files found here should be moved to the previously created temporary folder C:\tmp\
- We go to the recovery folder, which is located in the C:\System Volume Information\ directory. It should contain a number of folders of the following type - _restore{long character code with hyphens}. We check the creation date of such folders and find the latest one in the list.
- Inside there will be folders named RP1, RP2 and so on. We are again interested in the very last one. It is important to familiarize yourself with the date and clarify whether the OS was working stably at the specified time. If not, select the last working save.
- Go to the Snapshot\ folder. This is where backup copies of the registry files are located.
- Required to use _REGISTRY_USER_DEFAULT, _REGISTRY_MACHINE_SECURITY, _REGISTRY_MACHINE_SOFTWARE, _REGISTRY_MACHINE_SYSTEM and _REGISTRY_MACHINE_SAM
- The files specified in the previous paragraph are copied and they replace similar registry files in the C:\WINDOWS\system32\config directory. It is required to change the name to DEFAULT, SECURITY, SOFTWARE, SYSTEM and SAM
- In order for the changes to take effect, you must reboot.
You may often encounter a request about how to clean the registry on Windows ( Windows ). Here you can use specialized software or a manual method. In the first case, a fairly large number of applications can be recommended. The most popular ones include Reg Organizer, CCleaner and Windows Cleaner. These programs have proven themselves to be excellent - their capabilities for optimizing system operation are at a very high level.
Manually cleaning the Windows registry is more suitable for experienced users who know what they are doing. It is recommended to first copy the files in order to restore in case of failure.
The cleaning process itself requires removing any information about an already deleted program. Similar data is contained in “HKEY_CURRENT_USER” and this is where our path lies. In the Software subsection you need to find the required folder. The screenshot below shows an example for the Skype program.
Types of Windows Registry Settings
As we already know, sections and subsections contain parameters (in English - value entries). Parameters can have different meanings, for example: file path, program name, various numbers, etc.
Registry settings come in three main types (and several flavors):
- String parameters – REG_SZ
- Binary parameters – REG_BINARY
- DWORD parameters – REG_DWORD
Learn more about registry settings
I'll try to briefly describe the differences between the registry settings:
| Parameter | Description |
| String parameter REG_ SZ | Contains a string of text, such as the path to a file or folder (“C:\Windows”). |
| Extended string parameter REG_ EXPAND_ SZ | May contain special variables, for example, instead of “C:\Windows” you can specify %systemroot% (in fact, this will be the same path, but we can use it if we do not know in advance where the OS is installed). |
| Multiline parameter REG_ MULTI_ SZ | Can contain more than one line, convenient if you need to enter a whole list. |
| Binary parameter REG_ BINARY | A set of binary data that is displayed in hexadecimal format (for example, 10 82 A0 8F). Used to store information about equipment. |
| REG_ DWORD parameter | This is an integer that can be in binary, decimal, or hexadecimal (for example, 0x00000020 (32) - the decimal key value is in parentheses). The length of the number is 4 bytes (32 bits). Often this parameter works like a switch: 1 – on, 0 – off. |
In fact, there are twice as many types of parameters, but to understand the principles of the registry structure, it is not necessary to understand them (but if you want to, be sure to write in the comments!)
Registry Value Types
When you create a new registry value, you will be presented with the following options:
- REG_BINARY: This key type stores raw binary data.
- REG_DWORD: A 32-bit variable-length integer.
- DWORDS: Typically used to define device driver settings and software customization options.
- REG_SZ: Fixed length string value.
- REG_EXPAND_SZ: The expandable length of the string value, also used for environment variables.
- REG_MULTI_SZ: A multi-string that can contain a list of values, usually separated by commas or spaces.
- REG_RESOURCE_LIST: list of resources, nested arrays, used device drivers.
- REG_RESOURCE_REQUIRMENTS_LIST: List of hardware resources used by device drivers.
- REG_FULL_RESOURCE_DESCRIPTOR: Nested arrays used to store lists of physical device resources.
- REG_LINK: A symbolic link (UNICODE) to the following registry key that specifies the root key and the path to the target key.
- REG_NONE: Data that does not have a specific type.
- REG_QWORD: 64-bit length variables.
Note : There are some differences between the registries of 32-bit (x86) and 64-bit (x64) Windows operating systems. The 64-bit qword option is not supported on 32-bit versions of the Windows operating system. Additionally, the registry handles 32-bit and 64-bit keys in such a smart way that the file system handles multiple versions of the same dll files but maintains compatibility, which you can find in the registry section HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\WOW6432Node.
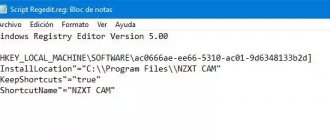
.REG files
.REG files differ from registry files in several important ways. First, although they store registry keys and values, they are intended to be backed up and transferred between PCs, and install Windows from those values and keys. Additionally, .REG files, unlike registry database files that contain a binary system, are stored in ASCII text format.
.REG files open automatically (or at least should if everything is installed and organized correctly) when double-clicked in the Windows Registry Editor.
You can use .REG files in the registry editor itself to export the entire registry or its individual keys.
You can also manually edit the contents of the .REG file in Windows Notepad or any other text file editor. Right-click on the .REG file in Explorer, and in the context menu that appears, open the “edit” option.
In the example in the figure, the key is HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Control Panel\Desktop\WindowMetrics, and it is highlighted here because it includes an addition to the default configuration.
At the end of the key is a section called "MinWidth", which has a numerical value of 54. This key changes the behavior of Windows taskbar icons (not grouped) so that program icons, when running multiple instances, appear separately, but without their labels.
Overall, although the Windows Registry is a huge, bloated behemoth with thousands of complex binary, hexadecimal and ASCII values and codes, it is quite easy to work with.