Author of the article
Kristina Gorbunova
Higher education in the specialty “Information Systems”. In the field for more than 7 years, he develops websites on WordPress and Tilda.
Ask a Question
When connecting to the Internet, beginners often have a question about what MTU is in the router settings and how to change this parameter. We will tell you how to determine the optimal value of this characteristic and when you should not change the maximum size of a useful data block in a packet.
What is MTU?
MTU is an abbreviated English concept for Maximum Transmission Unit, which translates as the maximum value of the size of a data packet that a device receives or receives within a local wifi network or via the Internet.
The MTU size is set by default in the router settings. It works as follows - the entire volume of information that, for example, a computer or laptop transmits to a smartphone or TV, is not sent in its entirety once, but is divided into equal packets, that is, fragmented. After which the receiving device combines them back. The size of these packets is precisely the MTU. It is measured in bytes.
Automatic configuration - PMTU discovery
There are operating modes of some devices when the MTU size is determined during connection to a remote server (PMTU discovery). The algorithm is the same as the one that was used when setting the MTU on the router. At the beginning of operation, the device sends data blocks of different sizes, trying to determine the maximum packet size that will arrive without fragmentation.
There is one problem in this algorithm called " MTU Discovery Black Hole ". It occurs when network administrators, in order to avoid possible attacks on their servers, prohibit routers from transmitting ICMP , in particular those used by the ping command.
This is of course not the correct way to act. The device cannot continue to operate without receiving a response to the request.
What makes up the MTU size?
The entire package as a whole is also divided into component parts. This:
- MSS (Maximum Segment Size) - value can be adjusted
- IP header - 20 bytes
- ICMP header - 8 bytes
As a result, the total MTU size in bytes is 20 + 8 + the size of the main packet, which can be changed in the router settings. For what, you ask? The fact is that by default, each router automatically sets a certain MTU block value. And it is not always optimal. And if the value is set incorrectly, significant problems with the Internet may occur. For example, certain sites will load poorly or there will be speed drops when playing videos. In this case, the lower the MTU value, the more packets there will be, and the longer they will be processed.
This means that it is best to set the MTU value to the maximum that is acceptable for your provider
Diagnostics
Well, I think: something is wrong here. I have a network Mikrotik , there are a lot of possibilities, I’ll go look for the reason on my side. I look into the logs and see how DoH (RKN, hello) started pouring in and I’m extremely surprised by this. I decided to temporarily cut off DoH and give it 1.1.1.1... The situation has not changed. I started resolving the addresses of at least something, all at once. I decided to send a trace to Habr and look at the “scraps”. I think I’ll call support, maybe they’ll say something smart. They scratched their heads, said that they couldn’t see my network behind the router (nat >> forward >> change ttl >>+1 :D) and said something like “We are XZ.”
I started digging further. I remembered all the bullshit I know about packages and then it dawned on me.
What MTU value should I set on my router?
Now we come close to the question of how to determine the optimal MTU value in your specific situation. To check, we will use the Windows command line on a computer or laptop.
Open the search menu and type “cmd”
The first thing I would recommend is checking your current settings. To do this, enter the command
netsh interface ipv4 show subinterfaces
Press the “Enter” key and see the current packet size in the “MTU” column. For me it is standard for WiFi and equal to “1500”. Of these, 20 are the IP header, 8 are ICMP, and 1472 are the block size of the data itself. You can have an arbitrary value from 1400 depending on the settings of a particular provider, if you are checking from a computer connected to the Internet via cable.
In order to determine which MTU is the maximum in your network, you need to “ping” various values until the system issues a message about the need for additional fragmentation (division) of the current packet.
For example, I know that my maximum MTU is 1472 bytes. But let’s check what response there will be from the remote wifika.ru server if we try to push 1700 bytes. To do this, enter the command
ping -f -l 1700 wifika.ru
We get the following answer:
- "Packet fragmentation is required, but the deny flag is set"
- "100% loss"
- "sent - 4, received - 0, lost - 4"
If you set 1471 bytes, then packets must be sent and received. We check:
ping -f -l 1471 wifika.ru
Result:
- Packet transmission time
- "0% loss"
- "sent - 4, received - 4, lost - 0"
That is, all information was successfully transmitted. The same thing will happen if you specify “1472”, but “1473” will no longer work. That is, for my network, the maximum and also the optimal MTU value is 1472 + 20 + 8 = 1500. This must be specified in the router settings if something else is automatically set in it.
It is also worth noting that the MTU size also depends on the type of Internet connection. By default they are as follows:
- Dynamic or Static IP – maximum allowed 1500 bytes
- PPPoE – 1420 bytes
- L2TP or PPTP – 1460 bytes
Setting up on a computer
You can change the MTU in Windows 7, 10 in a few minutes.
The step-by-step process looks like this:
- Determine the current MTU value. Launch Command Prompt. Enter the command “netsh interface ipv4 show subinterfaces”. A table will appear on the screen, in which you can see that the parameter value is 1500.
- Set a new value for the maximum size of transmitted packets. To do this, enter the command “netsh interface ipv4 set subinterface “Ethernet” mtu=1300 store=persistent”, where 1300 is the new value of the transmitted data block.
- Check the entry of new settings. You must enter the “netsh interface ipv4 show subinterfaces” command again. The check is considered successful if the value has changed to 1300. If the value remains the same, then enter the command from step 2 again.
After saving these settings, packets will be sent from the computer, the maximum size of which is limited at the IP level to 1300 bytes. But at the MAC level their value will be 1314 bytes. Larger data packets will not be sent.
In Linux operating systems, you can also change the MTU. To do this, launch the console using the combination Ctrl+Alt+F1.
Further procedure:
- Determine the MTU value using the ip link command.
- Set a new value for the maximum transmitted data block using the command “ip link set dev eth0 mtu 1200”, where 1200 is the desired MTU size.
Using the command, the value of the maximum size of transmitted packets is temporarily replaced by 1200. After a reboot, the default value will be restored. To make the new value permanent, edit the /etc/network/interfaces. Add mtu 1200 as a separate line to the description of the desired interface (eth0).
After saving the settings, run the command ifdown $eth0 && ifup $eth0, where eth0 is the name of the interface.
MTU value on the router
Once you have checked the maximum value for your connection, you need to set it on your router.
TP-Link
To manually install MTU on TP-Link models, you need to go through the browser to the control panel and open the menu “Advanced settings - Network - Internet”. And expand the “Additional” block
What is your opinion: is WiFi harmful?
Yes
22.91%
No
77.09%
Voted: 36517
In the old version of the administrator section, this parameter is located in the main “WAN” item
Asus
To indicate MTU on Asus, open the “Internet” section in the new firmware version
For older routers you need to open the “WAN” settings
Keenetic
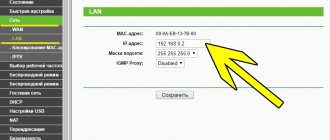
In Keenetic routers, you can set your own MTU value in the “Wired Internet” menu
The required parameter is located in the “Wired connections” block
D-Link
To select MTU parameters on D-Link routers, open “Network - WAN” and select your Internet connection
Tenda
For Tenda routers, this configuration is located in “System settings - WAN”
Mercusys
To find the MTU in the Mercusys panel, you need to open the “Advanced Settings” menu and go to the “WAN” item
It even draws special attention to the fact that there is no need to change the default value of 1500 unnecessarily
Netis
In Netis, click on the “Advanced” button
Next, open the “Network - WAN” menu and then click on the “Advanced” button
Upvel
Setting the MTU value on Upvel routers is done in the “WAN Interface” section
Linux
ip address
More modern systems use a utility for working with network interfaces - ip address. Enter the command:
In the resulting result we find the required network interface and a line similar to:
eth0: mtu 1500 qdisc pfifo_fast state UP qlen 1000
* what we are looking for is mtu 1500 .
ifconfig
On earlier systems or with ifconfig installed, enter:
* where eth0 is the network adapter for which we want to find out the MTU.
In the resulting result we find something like:
eth0: flags=4163 mtu 1500
* where mtu 1500 is our value.
Do not Fragment and Destination Unreachable, Fragmentation Needed
Packets can travel arbitrarily across networks, and it is impossible to calculate in advance all the routes and the maximum packet size for each connection. RFC 1191 specifies the methodology for determining the MTU size. The process by which a host for a particular connection can detect a smaller MTU size than its own network interface supports. Two components are key: the Do not Fragment (DF) bit of the IP header and the subcode of the ICMP Destination Unreachable, Fragmentation Needed message.
Setting the DF bit in an IP packet prevents the router from performing fragmentation when it detects an MTU smaller than the packet size. Instead, the packet is discarded and a message is sent to the sender via ICMP indicating that the packets need to be fragmented. Essentially, the router is indicating that it needs to break the packet into pieces in order to forward it further, but the Don't Fragment (DF) flag prevents this from happening. RFC 1191 extends the ICMP fragmentation request message to include the MTU size for the current connection.
Now that the maximum packet size for a connection has been detected, the host can cache this value and generate subsequent ones of the appropriate size. Note that discovering the maximum packet size for a particular connection is an ongoing process. When dynamic routing is used and the route between the sender and receiver is rebuilt, the host periodically continues to try to set the DF flag to detect further reduction in packet size. RFC 1191 also allows you to periodically test the ability to increase the maximum packet size for each route, sometimes attempting to transmit a larger packet than the cached one. If the packet is transmitted successfully, the packet size limit is increased.
Cancel Configuration
What to do when you enter the wrong value? If the settings are set incorrectly, using the Internet will be accompanied by even more glitches and slowdowns.
To reset the changes you made, go to your router settings and change mtu manually again. Consider the optimal value depending on the data transfer protocol used on your PC:
- For the PPPoE protocol, the normal value will be 1420;
- Dynamic/Static IP – 1500;
- L2TP -1460.
Remember! The mtu number should not be greater than the optimal value.
More than 90% of user computers use Dynamic/Static IP. We advise you to find out the exact type of protocol; in the router settings, follow these steps:
- Click on the “Quick Setup” tab;
- Then to “Automatic detection of connection type” and “Next”;
Rice. 7 – determining the type of connection used
- Wait until the system automatically selects the correct option;
- Look at what type of connection was detected and enter the optimal value in the settings based on the numbers indicated in the previous list.
After completing the setup, restart your computer and its connection to the global network. If Internet problems persist, contact your ISP for individual advice. The problem may also occur on the communication service provider's side.
How to change MTU through the registry
For those who don't like the command line, there's PowerShell and the registry. There is a branch in the Windows registry:
The class contains information about all your network cards, namely drivers, their versions and the GUID of the card itself. The GUID will be required to determine the network card in another registry branch, but don’t worry, I will show you a faster method for determining and matching the GUID and the network card via PowerShell. What you need to pay attention to in this section:
- Folders 0000, 0001 and so on are folders listing your network interfaces in Windows, here you will need to find the one you need using the parameters listed below
- DriverDesc - Description of the driver, essentially you will see the manufacturer of your network card here, it will help you determine the correct adapter
- NetCfgInstanceId is the card GUID
Now knowing the GUID, we follow the path:
Among the interfaces we find the one we need, we can make sure that it has the correct IP address. Find the MTU key, if it is not there, then you need to create a REG_DWORD with the desired value.
Now how not to bother with searching for the GUID of a network card. Open PowerShell ISE and run my script:
$aGUID_SET = @(Get-ItemProperty "HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\services\Tcpip\Parameters\Interfaces\*" | select -ExpandProperty pschildname)
Get-ItemProperty "HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Class\\*" -exclude "Properties" | Where-Object | ForEach-Object "" $_.DriverDesc $_.NetCfgInstanceId >
Or simply if you need to display all GUIDs from the desired branch:
I'm suffering from a really strange problem where I randomly get "Connection to server failed" errors when trying to access web pages (HTTP error 12031 according to Windows Network Diagnostic Tool) - this happens regardless of the web page. which I am trying to access is on the external internet or even if it is a local Apache instance running on localhost. It affects all the computers on our local network (Ethernet, not wireless), all of which are running Windows XP.
It has been suggested to me that this may be related to the MTU used for network traffic. If I do a Ping test to find out the largest packet that can get through unfragmented, I can ping localhost with a packet of 1492 bytes (+28 bytes for the header?), and I can ping our router with a packet of 1462 bytes ( which is 1490 bytes if the 28-byte header is included). If I try to ping something externally like Google, I can't get anything higher than 1430 (which is 1458 with the header).
I tried various command instructions to update the Windows XP registry with this MTU setting by updating HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\Tcpip\Parameters\Interfaces\\MTU . I haven't tried any alternative values: the most obvious correct value seems to be 1490, but I've also tried 1462, 1458, 1430, etc., etc. When I restart the computer for the changes to take effect, this seems to work for a few minutes (hard to say for sure since it's always random rather than sequential), but it never lasts long.
Changing the MTU in the router
Router users can independently change all settings for the connection and operation of wi-fi on the global network. To do this, go to the configuration menu. Open any browser installed on your PC and enter the local IP address 192.168.0.1 in its address bar and press Enter.
If the authorization window does not appear, enter the address 192.168.1.1 in the line
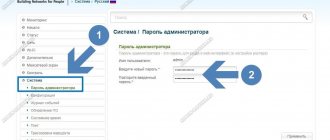
In the dialog box that opens, a form will appear for entering the PC administrator login and password. In both fields, write the word admin or other information to log into the network (you can read them in the instructions for the router or ask your provider). Wait for authorization.
The settings window for each router model may have external differences, however, the structure of the fields is basically the same. First you need to decide on the final value of mtu. Take the result obtained during the testing process. In our case it is 1458 bits and add another 28 bytes. The extra bytes are space for the packet and request headers. As a result, we get 1458+28 = 1486 bytes for mtu.
For TP-Link routers
To change mtu, click on the “Network” menu item. Then, on the right side of the window, find the mtu field and enter the required value, as shown in the figure:
Rice. 5 – change the value for TP-Link