You can increase the Internet speed on a 3G or 4G modem using software and hardware methods. The first include: changing the DNS server, reconnecting to the base station, removing the limitation on the channel width set by the operating system. Hardware includes: correct placement of the modem, connecting an antenna to it to amplify the signal and minimize losses, and its correct direction.
The need to speed up wireless Internet appears when the modem works without an antenna, during bad weather, or due to the characteristics of your location. The problem is also relevant during rush hour, but here the user is powerless.
Which operator do you use?
Russia
Ukraine
Wireless internet speed problem
- A wireless Internet connection provides users with a number of benefits. No cables are needed; in most cases, the modem case contains a router; the user is not tied to the length of the twisted pair cable installed in the apartment or house - he can work on the Internet almost anywhere.
- Wireless Internet also has disadvantages – speed. It is unstable, changing sharply throughout the day and even an hour. The highest speeds are obtained by users located closer to the base station or tower and having devices with more powerful antennas. At night, the load on the cellular station is the least, at this time the highest throughput of the Internet channel is observed.
- During the day, even during coronavirus (remote work and study), the Internet speed is usually decent. In the evening, from 18–19 hours to midnight, the quality of communication is not always satisfactory. The main reason is the high load on the network. Also, the modem's throughput drops due to its location, weather conditions, the quality of the cables used and system settings.
Note that you can also distribute Wi-Fi from your laptop to your phone, which will allow you to load mobile versions of sites that are less demanding on connection speed. This can be an alternative option when it comes to watching the news or social networks.
Overclocking 4G: high-speed modems, aggregation and balancing
This spring, the website iXBT.com published a review of two models of Keenetic routers equipped with built-in 4G modems for working in cellular operator networks. In the discussion of the article, many readers noted that the use of an LTE Cat modem today. 4, especially taking into account its “built-in” nature, cannot be called interesting. Indeed, the Qualcomm Snapdragon X5 model is already about five years old and taking into account the constant growth in requirements from applications, as well as the development of cellular networks, its formal 150 Mbit/s for reception and 50 Mbit/s for transmission (real figures are usually one and a half to two times lower ) look uninteresting compared to the capabilities of current smartphones.
For example, Apple iPhone 12, Huawei P40 Pro and Samsung Galaxy S21 have data receiving speeds via LTE cellular networks of more than 1 Gbit/s. Note that here and below, unless otherwise indicated, we are talking about the maximum speeds stated in the technical specifications. Moreover, you shouldn’t think that this is a feature of only expensive top models - Xiaomi Redmi Note 7, which costs about 10,000 rubles, can also boast of this.
The secret of success is that smartphone chipsets use more advanced modems that support speed-increasing technologies. Among the latter, frequency channel aggregation is the most commonly used. In addition, MIMO 4x4 and 256QAM modulation may be encountered.
The key point in the whole story is the need to have similar capabilities at base stations. Operators are not ready to publicly share information about the characteristics of their equipment, with the exception of marketing campaigns to demonstrate the “fastest Internet.” And without appropriate support from a specific tower, there is simply no point in a more modern and expensive modem. In addition, we traditionally do not forget that the actual speed when operating in this scenario also significantly depends on the quality of communication, on the current load on the station and on the method of its connection to the operator’s core network. Let’s say, even if you see a newly installed tower through the window of your country house, you often shouldn’t count on high speeds, since it can be connected to the core network not via fast and predictable optics, but via a radio channel.
In addition, tariff plans and “features” of the implementation of services for access from modems and routers also play a role in this whole story. But in this material we will not touch on these topics, but will focus on technical issues.
And the last note - everything described below can only be relevant if connecting to a cellular network is the only available option and at the same time, the speed of tens of megabits per second provided by “regular” equipment is not enough for you.
Theory
The main resource for cellular operators is frequencies. Without sufficient bandwidth, it will not be possible to provide the client with high speed, nor will it be possible to serve a large number of subscribers, since physical laws cannot be fooled. Typically these resources are allocated based on region. On the Internet you can find lists of Bands taking into account the channel width. So, for example, in one area the operator may be allocated one set of frequencies and channels, and in a neighboring area – a completely different one. So this should also be taken into account when planning the implementation of high-speed Internet access via cellular networks.
The category 4 modem (LTE Cat. 4) supports MIMO 2×2 and on a 20 MHz channel has maximum download and upload speeds of 150 and 50 Mbit/s, respectively. Note that it happens that the operator is allocated a band of both less and more than 20 MHz in the region. The speed “capacity” changes accordingly. The category 6 modem already belongs to the LTE-Advanced class (LTE-A, LTE+, 4G+). It is capable of aggregating two frequencies (two channels) of the base station for downloading, which ultimately gives 300 Mbit/s. Note here that the modem category is its fixed hardware characteristic and cannot be changed by any firmware. Although you can turn on/off the supported MIMO and encoding modes.
The table below shows some of the category options that may be used in modern client equipment.
| LTE category | Reception speed | Transmission speed | MIMO | Encodings |
| 1 | 10 Mbit/s | 5 Mbit/s | — | QPSK |
| 2 | 50 Mbit/s | 25 Mbit/s | 2×2 | QPSK |
| 3 | 100 Mbit/s | 50 Mbit/s | 2×2 | QPSK |
| 4 | 150 Mbit/s | 50 Mbit/s | 2×2 | QPSK |
| 6 | 300 Mbit/s | 50 Mbit/s | 2×2, 4×4 | 64QAM |
| 12 | 600 Mbit/s | 100 Mbit/s | 2×2, 4×4 | 64QAM, 256QAM |
| 18 | 1200 Mbit/s | 210 Mbit/s | 2×2, 4×4, 8×8 | 64QAM, 256QAM |
| 20 | 2000 Mbit/s | 315 Mbit/s | 2×2, 4×4, 8×8 | 64QAM, 256QAM |
At the same time, the speeds given are the maximum ones and in fact, formally the numbers are not so round, but in this case this is not very significant.
When it comes to base stations, operators are constantly updating equipment, so determining the current capabilities of your closest stations is a difficult task. Formally, there is specialized software for this, but it will be difficult for an untrained user to use. So you can try to check the actual speed on a modern smartphone or refer to the databases of cell towers and their parameters, which can be found on the Internet.
In general, aggregation of frequency channels allows a client device to connect to one base station simultaneously via two or more channels (we remind you once again that only if these modes are implemented at this base station) and thus sum up the speeds. In this case, channels can belong to the same or different bands (Band), and also have the same or different widths. Depending on the equipment and its settings, the increase in speed may affect not only downloading, but transmission. Note that this technology works and has an effect even on a single-threaded load (say, watching a video or downloading a file via a direct link). Moreover, if there is no load or it is insignificant, the modem may not use aggregation to save resources, so its actual use should be checked during active data transfer tasks.
Equipment
USB modems that can be purchased at operator offices are mostly of category no higher than category four, that is, they do not support channel aggregation and provide download speeds of no more than 150 Mbit/s. So enthusiasts have to look for other sources, which are foreign online stores. Note that they usually sell devices that are not locked to an operator and support all bands, so there is no need to worry about this.
As for the format, modems are most often found in the form of M.2 3042 boards, originally designed for installation in laptops, specialized routers and other M2M equipment. M.2 is a universal format and has several variants. For modems, M.2 with key B is used, which means transmission through the connector of a pair of PCIe lines, SATA, USB 2.0 and 3.0 interfaces, audio, as well as several specialized buses. Actually, the modems from all of this use USB, contacts for the SIM card and, of course, power.
So if you want to use a modem with a regular router or computer, you will need a special adapter board with a standard USB output port. Plus, you will need to resolve the issue of connecting antennas, miniature connectors for which are located on the board of the modem itself.
The simplest option is a small board with an M.2 slot and a USB port. Additional details include the presence of a power converter. It doesn’t have a housing, so you’ll have to come up with something yourself. As you can see from the photo, the board can have two SIM card slots installed at once, which, in combination with the appropriate modem, allows you to change the operator on the fly by sending commands to the modem. Technically, it is possible to implement automatic switching options, but this is a question for the software that works with the modem.
There is nothing interesting on the back of this board.
To connect the antennas you will need special adapter wires - pigtail. They can be included with the board or sold separately. In the photographs, I have already secured them to the board so as not to damage the connectors on the modem due to the relatively large and heavy antennas. In this case, the antennas from the Keenetic Runner 4G router with a built-in LTE modem were used as the latter. If necessary, external directional antennas are also connected via pigtail (here a cable from the pigtail to the antenna may also be required).
As an alternative to the pigtail and antenna combination, if you are confident of a strong signal and/or need to ensure a compact design, you can try using antennas similar to those found in laptops. They usually come with connectors for connecting to a modem. True, here you still need to choose carefully - those shown in the photo, judging by the article number, are intended for Wi-Fi, so their effectiveness for LTE may not be as good as we would like.
If you wish, instead of a simple adapter, you can choose a more serious (and expensive) option with a ready-made case, which already has everything you need.
For example, this option has a metal case with the ability to fix it in the right place.
At one end we see two LED indicators and a USB Type A port. The latter is somewhat strange, since formally this port is usually used on the host side. So to connect the device you will need the included cable with a pair of identical connectors.
At the other end there are two standard connectors for antennas and between them a spring-loaded slot for mini SIM cards. At the same time, the card does not fit completely into it, so you can change it without using additional tools.
The body itself is a piece of metal profile.
Let's now see what we managed to get from the modems for testing. Let us remember that there are not so many manufacturers of modem chips; in fact, most models can be presented in online stores under different names, but have the same characteristics, and the most famous chip manufacturer in this area is Qualcomm.
In particular, one of the popular models based on Qualcomm Snapgragon X7 is the Dell Wireless 5811e (DW5811e), which can also be found using the keywords “Sierra Wireless EM7455”. This modem belongs to category 6 - when aggregating two channels, it is capable of providing a reception speed of 300 Mbit/s, and it still has the same 50 Mbit/s transmission speed as in category 4.
The device supports all common LTE bands and can also operate in 3G mode. It is possible to connect two SIM cards and a built-in GNSS receiver for determining coordinates. Connection interface - USB 3.0. The cost of the modem at the time of preparation of the article was approximately 2000 rubles.
The second option is based on the Qualcomm Snapdragon X20 - DW5821e (other search keywords are “Foxconn T77W968”). This Category 18 modem is capable of aggregating up to five 20 MHz channels per download, and has a maximum advertised speed of 1.2 Gbps. Using category 13 transmission allows you to reach 150 Mbit/s in this mode.
Plus there is MIMO 4x4 and 256QAM encoding. Connection is via USB 3.0. This modem is used in the Qualcomm Snapdragon 855 platform, so it is actually found in many smartphones. The cost of the modem is significantly higher and is about 6,000 rubles.
There will be no problems installing modems. Install the modem into the slot and secure it with a screw. Next we connect the cables from pigtail. Here, of course, you need accuracy and attentiveness. The connectors are very small.
Given current realities, in most cases, there is no point in focusing specifically on USB 3.0. In practice, this may only be interesting if there is confirmation that you can get more than 300 Mbit/s on your tower or as an investment for the future.
The second point that I would like to mention here is nutrition. It is no secret that for traditional “USB whistles” the situation when the modem is unstable or freezes precisely because of the power supply is common. For the described scheme with an M.2 modem and a USB adapter, this issue is usually solved by high-quality circuits on the adapter board (they are there in any case, since M.2 devices are powered by 3.3 V) and, of course, good sources in the router. As for consumption, for the devices described above, the actual values during tests did not exceed 3 and 5 W, respectively.
Qualcomm chips have built-in temperature sensors, so you can provide remote control of this parameter. From a practical point of view, for “normal” speeds and modes there will most likely not be a need for additional cooling. However, if we are talking about maximum performance and stable operation in difficult conditions, then it is recommended to pay attention to this and add a radiator and/or even a fan. At the same time, the behavior during overheating, judging by the messages in the forums, can be different - from a decrease in speed to a reboot.
In the photographs above you can see that there are no elements on the back side of the modem boards and it just begs to be installed on this side with a thermal interface and a heatsink. However, the adapters used are very suitable for this scenario. The first one has slots for SIM cards under the modem and there is little you can do here. The second one is more interesting, because you can try to transfer heat to its printed circuit board and then to the case. But in the general case, both options can hardly be called optimal from this point of view.
A separate issue is the firmware. Traditionally, this topic in numerous discussions on the Internet arouses considerable interest, dictated by the chance to improve something for free (except for the time spent). Of course, in this article there is neither the opportunity nor the point of retelling everything that has been written in recent years about the devices under discussion. Let us only note that if we are talking, in fact, about the main firmware of the modem, then the question is relatively simple - situations where changing the firmware somehow radically changed its behavior are very rare and usually this is immediately indicated in the headers of specialized forum topics. The process of replacing the firmware itself is usually relatively simple if everything goes according to plan. But, of course, you should treat it as carefully as possible, otherwise there is a chance of getting a “brick”. A more interesting point from a practical point of view is the ability to change the parameters and operating modes of the modem by editing special areas/firmware files in order to optimize and improve speed characteristics. In particular, we can talk about all the options described above - a set of channels for aggregation, encoding, MIMO. This is a more complex intervention, but in general, with some experience, you can figure it out.
Connection
Considering that these modems were originally created for laptops, their use with computers usually does not cause problems if the latest versions of the OS and drivers are available. But our goal is to work together with a wireless router to distribute Internet access to several clients.
Before we talk about the routers themselves and their firmware, let’s remember what protocol options are used today, also called “modes” in this case, for communicating with modems. In addition to directly connecting to the Internet, they are responsible for managing the modem settings, as well as monitoring its status. Considering that we are usually talking about solutions on Qualcomm chips, it is not surprising that the most common is QMI - Qualcomm MSM Interface. The relatively recently appeared MIBM (Mobile Broadband Interface Model), which is no longer tied to one manufacturer, is also similar. From a technical point of view, they usually look like several subdevices on a USB bus.
For the topic of high speeds under discussion, the remaining protocols are less relevant, so we’ll just mention them - NCM, ECM and RNDIS are implementations of “Ethernet over USB” of different generations.
In most cases, modems support several protocols, switching between which is carried out by special programs or commands. Additionally, they can also be used to turn on/off individual ports (for example, a diagnostic port) or select interface parameters (for example, limiting USB version 2.0). In general, all these interfaces have been introduced for quite some time and are successfully supported to varying degrees by modern software.
So the choice of router/firmware for our task is very wide and depends both on the budget and the level of technical training of the user. On one edge is the famous OpenWrt firmware, which is available for many hardware platforms. A little less time-consuming to set up is the ROOter project, based on the same OpenWrt. Next, we can recall the well-known brand MikroTik, which in many of its products supports working with cellular modems using modern interfaces. By the way, the company’s arsenal also includes fully ready-to-use solutions of categories 6 and 12. Another option for those who have more money than time are products from the domestic developer Kroks.
This time we are using a solution from a well-known brand - Keenetic. Let it be the Keenetic Viva KN-1910 - a dual-band gigabit router with a pair of USB 2.0 ports. Before the announcement of new high-end models, this was the third oldest device - with a powerful (for solutions of this brand) processor, but unlike Giga without SFP, only with USB 2.0 and with less RAM. It can also be called “the most affordable model from Keenetic with gigabit ports and USB.”
Setup and use
Usually I am against testing on unreleased firmware versions, but in this case the Alfa branch is indispensable - QMI support for new modems appeared in it. So we go to the router settings, select the “Test build” channel, update to version 3.7 Alfa 11, after the reboot we go to the same page again and in the selection of firmware components we add support for the QMI interface for modems (some screenshots were taken after the entire process itself testing, so new builds were released during this time).
We connect modems, and to complicate the task we use two at once - one in each of the two USB ports of the router (SIM cards from Megafon and Beeline operators are used), and reboot. Just a few minutes later we see a green Internet connection indicator on the router.
No special settings were required. All connection options were determined automatically. If necessary, the user can later change some parameters in the connection settings. Among them are network type, frequency ranges, APN, network (operator), ping check function, data roaming, work schedule and others.
Keenetic firmware also implements very useful capabilities for sending and reading SMS, as well as working with USSD codes.
In combination with KeenDNS, these operations will also be available remotely via the Internet.
Taking into account the type of connection in difficult situations, it is advisable to have in the router tools for monitoring and diagnosing connections with a cellular operator. This is implemented quite conveniently in the Keenetic firmware. You can start from the System Monitor page.
After clicking on "Connection Details", the user will be shown key information about the connection. In particular, there is the modem model and firmware version, operator, connection duration, signal level, network type, base station identifier, IMEI, IP addresses, current reception and transmission speeds, total volume of transmitted traffic, KeenDNS router name. Let's also pay attention to the button to force the modem to reboot.
More useful information for choosing the optimal configuration is presented on the connection settings page.
It is in this place that you can see the aggregation described above - in the “Band” field a list of bands and channel widths in each will be indicated. In addition to the station code, other data about the tower will be shown here, which will allow you to find it in online databases and determine how effective it will be to work with it. Plus there are drop-down fields with antenna and carrier data. Please note that, unfortunately, not all information corresponds to reality - in particular, the “Maximum speed” field clearly does not show what we would like to see. Given the active work on firmware, there is a chance that this will be fixed. Of course, provided that the problem is not in the modem itself, which provides such data. It is clear that the manufacturer himself is not inventing anything here, but taking data from him. In addition to the indicated options for working with modems through the GUI, there are also console commands. For example, via
show interface UsbQmi1
you can view the status of the modem (the number specifies the desired interface number). Similar data in json format is available via a browser request using a URL link
rci/show/interface/UsbQmi1
As for direct use, in fact, we can limit ourselves to a simple statement of the fact that “everything works.” Connections with providers are rising quickly; over several weeks of testing, no outages were noticed, except those associated with equipment reboots. For the reasons described above, it is difficult to take real speed measurements seriously. More precisely, one can only talk about them with the note “this also happens,” understanding that we are talking exclusively about this place and time. No one will ever give any guarantees for minimum speed. And in most cases, this is not required for home users.
While using the described configuration, I assessed the speed several times by launching a p2p client with several popular tasks on a computer connected to the router. The average figures can be roughly estimated as 120 Mbit/s for Megafon with a DW5821e modem and 50 Mbit/s for Beeline with a DW5811e modem. Let us recall that aggregation begins to work only when there is a need for it, that is, load from clients.
Practical conclusions that can be drawn from the testing are that in order to achieve good results, the user must at least have a good modem of category 6 and higher and high-quality antennas for it. Regarding dependence on the operator, before purchasing equipment it is worth checking the towers and their capabilities near the intended location. You can start by studying the maps and end with a speed test from a suitable smartphone. By the way, as for determining the aggregation mode, you can use the NetMonster utility from Google Play, which can show channel parameters, including width and aggregation, and does not require root access. As we can see, there is no way to rigidly link the connection to a specific tower in the described scheme. The only thing that can be done here is to use an external directional antenna, so that the modem would consider the desired tower to be the most successful for connection. The same method is used to improve results in cases where the exits are located far away.
Merge connections
As I wrote above, the test used two modems and two SIM cards from different operators. For this option, you can use another method that has long been implemented in Keenetic firmware - the standard function of connecting connections.
The setup is simple - in the “Internet Access Profiles” tab of the “Connection Priorities” page, we create a new entry and include our connections via modems in it. Next, on the “Linking devices to profiles” tab, select those registered local network devices that require such acceleration.
Unfortunately, that's not all - you need to go to the router console and enter several commands to activate the function. First, we look at the correspondence between internal profile numbers and their user names in the general list:
show ip policy
Then for the corresponding profile (in the example – Policy5) we enable the merging mode:
ip policy Policy5multipathexit
Save the configuration and exit:
system configuration saveexit
This operation is described in detail in the knowledge base article. If the channels (modems, operators) have different actual speeds, you can change the channel priority ratio for the internal algorithm (this is also described in the material at the link).
The result will be that the client uses the local network for outgoing connections from several providers simultaneously. In this case, the effect of increasing the overall speed is observed only in the case of several multiple connections. That is, this will not affect the speed of downloading a file from an FTP server, but downloading on p2p networks will be noticeably faster. A negative aspect of the implemented scheme may be difficulties (in particular, denial of access) when running special applications, in which, to increase the level of security, additional verification of client IP addresses is implemented during the session. However, over several years of using this scheme, I personally have not encountered this.
On the equipment used in this article, when combining channels for the task of downloading files, results were obtained at the level of 200 Mbit/s. At the same time, in the router’s Web interface one could notice that exactly two channels were used. It’s a pity that you can’t simultaneously display two connection traffic graphs on the “System Monitor” page.
Conclusion
If we describe the results in one sentence, then we can say, for example, “using high-category modems that support channel aggregation can have a significant effect in terms of speed.” But then there will be amendments “in some cases”, “depends on many conditions”, “no one gives guarantees”, “if it works well today, tomorrow it may not work at all” and so on. The most inconvenient thing in this story, perhaps, is that not so much depends on the user and one must be aware of this.
In my opinion, if the task is to ensure a comfortable connection to the Internet through cellular operators for a home (office, country house, etc.) network, then you need to start by checking the current state of affairs at a given point using several operators on a good smartphone. If we find a suitable option, we buy a modem/tariff/router and just use it. If the signal is weak, then we study the map of the location of the towers, evaluate the chances of improving the signal with an external directional antenna, and look for an opportunity to test this configuration. If the result is successful, we add an antenna to the specified set and close the question.
As for the choice of the modem model itself, at this stage of development of cellular networks and in the absence of guarantees of high speed, in my opinion, it is difficult to justify the purchase of devices of a category higher than the sixth. Yes, happy coincidences happen and you can find spectacular pictures on the Internet with several hundred megabits per second, but paying three times more... This may not apply to demanding mobile users who need the fastest possible speed in different conditions and who choose the best without limiting their budget. Well, as usual, let’s mention enthusiasts, for whom the process itself is often more interesting than the result. And here, of course, they have a rich field for experimentation - adapters, connecting to a router, changing modem settings and firmware, choosing antennas, and so on.
As for the Keenetic Viva router used for testing, as we saw, the manufacturer has done serious work to integrate new protocols and devices into the firmware (by the way, there is information that 5G modems are already being tested), so the end user does not have to deal with the connection. which significantly simplifies and speeds up the process. There are no questions about the reliability and stability of the router. The advantage is a unique set of supported services out of the box. I can’t help but remember such a useful technology as KeenDNS. Considering that today cellular operators only allow you to work with “gray” addresses, the ability in these conditions to provide remote access to the router and even the devices behind it without significant effort will be very useful. If the only question is remote performance monitoring and access to settings, then a proprietary mobile application that works through a cloud service will come in handy.
Is it possible to speed up slow Internet via a USB modem?
Most modems are connected to computers and laptops via USB for setup, or less often via Ethernet. In many cases, it is possible to speed up 3G/4G Internet, but not always. The problem will remain or the effect of our advice will be minimal for two reasons:
- The base station is overloaded - the problem cannot be solved without upgrading it.
- Locations.
If your home is in a low-lying area where there is virtually no signal from a cell tower, there is little you can do. Is it possible to raise the antenna to a height of ten or more meters? When there are obstacles between the modem (antenna) and the tower - buildings, walls, many trees, then you will have to work hard to increase the Internet speed.
However, it’s worth a try; an integrated approach will always give results.
Boosting a 3g modem signal with a USB extender
This is not the best, but it works, how to easily boost the signal of a 3g modem with your own hands. It is well suited for people who do not want to disassemble or re-solder their device. The design works on the principle of a satellite dish. To make it, you need to buy a “reflector” (jar, bowl, CD), a 3-meter female-to-male USB cable. The creation process is as follows:
- In the middle of the disk, make a mount for a flash drive, or tape it with tape.
- Connect the cable at one end to the computer and the other to the modem.
- You can use a stick instead of a holder or simply attach the disk from the street side to the facade of the house.
- Point the flash drive in the direction where the signal is strongest.
The increase in connection quality is not very large, because the USB cable loses some of it due to its length, but still improves the connection. The mirror surface of the CD acts as an amplifier. It is recommended to use a bowl instead of a disc because its reflective surface is larger and the reception will be even better. Enameled options are not suitable; use stainless steel products.
Quick options
Let's start with the simplest solutions.
Reconnection
Usually there are several transceiver devices at the base station, and the modem will automatically connect to the fastest one - the least loaded one - to speed up the Internet, but not always. Try interrupting the network connection, then re-establishing it.
The AxesstelPst EvDO program will show which pilot the modem is connected to. If its number does not change, repeat the operation.
Changing DNS server
DNS server is a host or group of computers that convert domain names (links to websites) into IP addresses, which allows you to find sites on the Internet. It works similar to the address book on your phone. If an overloaded server is used, it will cause delays in processing and sending requests. To change DNS:
- Open “Network and Internet Settings” via the tray icon or Control Panel.
- On the left, click “Change settings...”.
- Select the properties of the current connection via the context menu (right click).
- Double-click on the line “IP version 4...”.
- Move the second checkbox to the “Use the following DNS...” position.
- Enter its address, for example, 8.8.8.8 - server from Google and save the settings.
You can also specify an alternative DNS.
If there are many tabs in the properties, to increase the speed of the USB modem, go to the “Network” tab.
Restart your computer to apply the settings.
Reviews
Every summer I go to the village with my children, but I have to go online every day. The operator's tower is far away from us, so the connection speed is simply terrible. I made myself an additional antenna from a USB cable, a mast and a huge bowl. The connection quality has increased by 30-40%, it could have been better if the USB cable was a little shorter. I'm often on the go, so I use mobile Internet. I noticed that sometimes the speed dropped significantly, it turned out that my modem automatically switched to a 2g connection. After setting the settings to use only 3g frequencies, the situation changed for the better, although in “deaf” places the connection still drops to zero. I live in a hostel, everyone here uses the Internet, so good communication is impossible without additional devices. I used simple copper wire, which I wrapped around the SIM card in the device, and a large shiny dish (I got it from my mom). I simply brought this “miracle” out the window and directed it towards the tower, the signal immediately became stronger. Found an error in the text? Select it, press Ctrl + Enter and we will fix everything! Did you like the article? Tell friends:
Using special software
A number of specialized applications and “tweakers” (adjusters) allow you to speed up the Internet, but sometimes cause harm to the system, especially network connection boosters. Before using them, create a rollback point or backup copy of the system disk.
AxesstelPst EvDO
The program will help you optimally configure (position) the antenna. If it is aimed precisely at the base station, the signal strength will increase and interference will decrease. True, this does not mean that the network speed will increase, for example, when a weak antenna is used or the operator’s (provider’s) equipment is overloaded.
- In the AxesstelPst EvDO program, click on the “Tool” main menu item.
- ABOUT.
- Click "Searching port".
- After identification, an information window will appear with the port or range used by the modem.
- In the “COM port” list, select the one specified and click “Confirm”.
If there are several of them, select each one and click “Confirm” until the numbers and inscriptions start running in the “1xEV” window.
The second way to find out the ports occupied by the modem: open Device Manager and expand the “Ports (COM and LPT)” list.
Rotate the antenna slowly and observe the values:
- RX1 or RX2 (the number is the number of the port to which the antenna is connected). Strive for a lower value, but no more than 70-75.
- PER – percentage of errors, maximum 1-2%.
- Ec/Io – shows the ratio of the useful signal level to noise, less is better.
DRC Requested depends on them - the maximum possible speed under ideal conditions.
HCPA Locker
The program will prevent switching data exchange modes, which lead to connection breaks and loss of speed. Use the slider to select the maximum value, click “Start” and test the result for several hours.
Traffic savings
The Opera browser has a traffic saving mode - it passes through the developer's servers, where it is compressed, reducing the size of loaded pages. There are similar add-ons for other browsers.
Programs and online services
To speed up the loading of pages on “heavy” sites, special Internet services are used. While the user is working on the computer, slowdown may occur for the following reasons:
- page overload when promoting scripts;
- simultaneous mass discovery of videos and photos ;
- the presence of numerous pop-ups and advertising banners .
Modern large search sites are initially equipped with a variety of services to optimize and ensure normal operation of the network.
Hardware methods to improve wireless internet: antenna
To increase the speed and quality of the signal when surfing the Internet far from a tower (more than a couple of kilometers), when there are obstacles between the modem and the transceiver, it is worth using an antenna.
Portable
It is not recommended to use a portable one for two reasons:
- Low gain.
- Reception of electromagnetic radiation in adjacent frequencies, which may adversely affect signal quality,
External (remote)
It is installed at the ridge level or higher and is directed towards the cellular operator tower or provider base station. The farther you are from it, the longer the antenna should be and more accurately aimed (using the AxesstelPst program). It will receive the signal as it propagates at the height of the antenna (5-8 m), where it is almost or not distorted by trees, buildings, walls and other obstacles.
A properly directed external antenna is the most effective way to speed up wireless Internet. Connects to the modem via a coaxial (TV cable) through an adapter that matches the connector on the device.
Directed
A compromise between an external and a conventional portable antenna, although it is itself portable. It can be installed in a house or apartment opposite a window and directed towards the signal source. Can slightly speed up 3G/4G.
Antennas
A nick generator
Antennas are the most important element that ensures stable operation of the 3G modem and the speed of the mobile Internet. Therefore, by enhancing their characteristics, you can achieve a significant improvement in reception from the mobile network operator.
Antennas for USB modems are:
- built-in;
- desktop, placed at a short distance from the modem;
- directional, receiving/transmitting a signal in one direction.
External antennas are taken outside the room, which causes some associations with twisted pair extension cords. Craftsmen also make an antenna for a modem using a homemade method.
Industrial
Naturally, an antenna made industrially inspires more confidence among users who are not very experienced in network technologies. Stores specializing in the sale of network equipment offer a wide selection of antennas of various types. When purchasing, it is recommended to pay attention to the following characteristics: radiation pattern and gain.
To increase Internet speed using an industrial antenna, you just need to purchase it, connect it to a modem, and point it towards the nearest tower of your mobile operator.
Homemade
Anyone who is not lazy will make an antenna for a 3G modem with their own hands. This is not as difficult as it seems at first glance, and it will cost much less.
We offer a simple method for making an antenna:
- You need to take a piece of thick copper wire and bend it in the shape of a number 8.
- Solder a cable with a resistance of 70-75 ohms to the wire.
- Remove the other end of the cable from insulation and wrap the central core of the cable around the modem.
After this, all that remains is to bring the antenna out and orient it in the desired direction.
Software solutions
You can further increase the quality of 3G/4G reception through proper software settings.
Change mode
If the modem software allows it, change the device operating mode to 3G or 4G instead of automatically selecting and switching between networks.
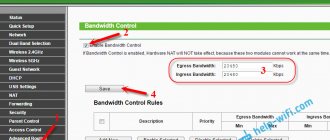
Remove bandwidth limit
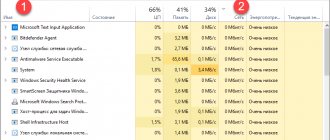
The operating system reserves 20% of the bandwidth for service and high-priority purposes. If the channel is loaded at 80% or more, for example, something is downloaded via torrent or from file hosting services, the reserved 20% remains for high-priority tasks. This indicator should not be touched if you do not understand what it means and how the option works. If the reserved 20% of bandwidth is not used by high-priority tasks, all bandwidth is available to applications.
How to strengthen a 3g modem signal using network settings
Before making antennas with your own hands, you should try another method on how to strengthen the signal reception of a 3g modem. Some mobile Internet users do not know that by default, when the connection quality is poor, the device automatically switches to 2g communication mode, which is not possible to work normally with. In this case, the transition occurs even if there are 2-3 “sticks”. To avoid such situations, you should clearly indicate through the device settings that you only need to use a 3g connection. How to change an option:
- run the network setup program;
- select the “Connection” tab (or with a similar name);
- Next, the network search mode needs to be changed from automatic to 3g.
This will force the device to work only on these frequencies, without dropping the connection to a lower speed one. Some modems do not have such an item in the application interface for the device. In this case, you should look for a combination to activate the built-in command in the device instructions or on specialized forums. Each modem model has its own programmed order for enabling the option.
Other solutions
You can only hope for a noticeable increase if you install an external antenna. If this is not possible, try the following solutions.
Changing provider
Buy a SIM card from another operator, having previously studied the conditions and tariff plans of other providers and the experience of cooperation with them of neighbors or acquaintances nearby. Ask the latter how they are doing with the Internet. Maybe the problem is in an outdated modem, which, for example, is not compatible with 4G networks and works according to the outdated 3G standard.
Make sure that the traffic available to you within the tariff plan has not expired. Typically, providers allocate a certain number of gigabytes of traffic (incoming and outgoing) per month. After it is exhausted, the speed decreases significantly.
Information available:
- In your personal account.
- The “Network and Internet” section called “Data Usage”.
- USB modem settings (not always).
An alternative is to distribute WiFi from your phone to a regular router (if you have one at hand), and connect other equipment to this router. This is possible if the smartphone uses a different service provider or the same one, but the Internet connection is better.
Peak loads
In the evening - approximately 18-19 and until 23 hours - the problem of low speed is not solved in any way. The network can be overloaded, because many people are surfing the Internet. The only way out is to prepare: download a movie, a game, or update something in advance.
Adviсe
Also try:
- Remove the SIM card from the modem for a couple of seconds, reboot it.
- Ask your operator and neighbors about the current network situation.
- Close applications that use the network.
- Disable automatic updates of Windows, anti-virus databases, and programs.
- Change the tariff, for example, to unlimited.
- Update the modem firmware.
- In the properties of the port through which the modem is connected, select the maximum value “Bits per second”.
More likely to harm than help
The Internet is full of advice that often brings the opposite result from the expected one.
Using a USB extension cable
USB extenders, especially inexpensive ones, are more likely to add problems, as are splitters. The modem must be connected directly to the connector of the computer or laptop. The only case when an extension cord can be useful is to connect a modem to it and hang it as high as possible near a window that faces the provider’s tower (base station). Provided that this is a high-quality adapter, and not a “dollar toy” from a Chinese trading platform or the nearest store.
Amplification through a repeater or router, like a repeater
Many people advise using a router as a repeater. If the modem receives the signal poorly, because the distance between it and the transmitter is large or there are many obstacles on the way, these tips are empty words. They make sense if you are ready to purchase a repeater with a USB connector for a modem and antenna, but the result obtained may not cover the financial costs. If you have the opportunity to test the device for several days or a week, take advantage of it.
Hardware methods for accelerating 3G
What are the differences between 3G and 4G networks: features, advantages and disadvantages
Hardware methods for speeding up the Internet mean options that involve the use of any technical means to achieve the goal. Unlike programs and Internet services, such methods are more effective. Although in this case we are talking, first of all, about ensuring its stability and improving the quality of reception.
Using a USB Extender
Using a USB extender is an affordable way to boost the signal passing through the modem. It’s easy to use an extension cord in practice; to do this, we perform several steps:
- We purchase a USB extension cable 2-3 m long and connect the modem to the computer through it.
- We raise the level of placement of the modem above the floor, placing it closer to the window.
- This way we improve the performance of 3G modems from Beeline, Megafon and other operators.
An extension length of 2 to 3 m is optimal. If it is exceeded, communication loss is inevitable. A short extension cord will also not achieve the desired effect.
How to increase the Internet speed of a 3G modem using a USB extension cable over twisted pair
This method is both simple and very effective in order to increase the speed of a 4G modem or 3G modem. In order to make such an accelerator, you will need:
- two USB-RJ45 adapters;
- a regular twisted pair cable used in a local network.
One adapter is connected to the modem, the other to the USB port of the computer, and they are connected to each other using a pre-crimped twisted pair cable.
The advantage of the method describing how to increase the Internet speed of a USB modem is that, compared to a conventional twisted-pair extension cord, the signal attenuation occurs more slowly.
This allows you to use a cable up to 30 m long. Thus, the modem can be easily raised to a considerable height and taken outside.
Those who are planning to make a 3G modem accelerator using this method must remember that the device was initially intended for indoor use and is sensitive to temperature changes in the external environment. In addition, you need to take care to protect the case from precipitation by placing it in some kind of case, for example, made from a plastic bottle.