If your device runs out of free space, it becomes necessary to clear the memory of unnecessary files and folders. Android includes a large number of directories, but the question arises - which folders can be deleted on the phone and which ones cannot be touched?
This article is suitable for all brands that produce phones on Android 11/10/9/8: Samsung, HTC, Lenovo, LG, Sony, ZTE, Huawei, Meizu, Fly, Alcatel, Xiaomi, Nokia and others. We are not responsible for your actions.
Attention! You can ask your question to a specialist at the end of the article.
We are not responsible for your actions
Before deleting folders, check out the article How to increase memory on Android.
Android folders - structure
h21,0,0,0,0—>
The list of folders may vary depending on the Android version. Some applications can create their own directories in memory - for example, instant messengers. However, in general, the list of folders will be the same on all versions of Android, so you just need to know what is stored in them.
p, blockquote6,0,0,0,0—>
- Cache – folder with temporary update files. If you are not going to update the system, you can delete it.
- data/app – installation files of all third-party applications. If you don't use them, you can delete them.
- data/data – settings, saves and other service information necessary for the operation of applications. If you do not use installed programs, delete the directory.
- data/clipboard – data clipboard with the latest screenshots. It is not recommended to delete.
- data/dalvik-cache – cache memory area for the Java virtual machine, which allows the phone to run APK files. Files must be cleaned regularly, but cannot be deleted. (read How to install cache for a game on Android)
The Documents folder stores a variety of documents. If they are not interested in the content, feel free to delete the directory. The same applies to the Bluetooth directory, which contains files received via this wireless technology.
p, blockquote7,0,0,0,0—>
Increase
The DCIM folder stores photos taken with the camera. If you don’t have the photos you need, you can safely delete the catalog. Deleting the Images, Pictures, Musi, Audio, etc. folders will not affect Android operation.
p, blockquote8,0,0,0,0—>
Read: How to recover deleted photos on Android
p, blockquote9,1,0,0,0—>
Is it possible to delete the thumbnails folder
If you need to free up space in your phone's memory, you can delete both the thumbnails folder and its contents.
This will not affect the operation of the phone, the Android operating system or installed applications. You can delete this folder either from the phone itself using an application with file manager functionality, or by connecting the phone to a computer. But simple removal will not give a long-term effect. As soon as you go to the Gallery application, the phone will again create a thumbnails folder and again start saving thumbnails for photos and videos into it. If you wish, you can try to prevent the phone from creating thumbnail images. To do this, you need to connect your phone to your computer and find the thumbnails folder. As already mentioned, this folder appears in the DCIM folder and other folders with photos and videos.
Next, delete this folder and create in its place an empty text file with the same name as the folder (.thumbnails). The file name should be exactly that, a period and then “thumbnails”. The presence of such a file will not allow the Android operating system to re-create the thumbnails folder since such a name will already be occupied by our files. And since the folder cannot be created, the thumbnails will not be saved.
Folders that cannot be deleted
h22,0,0,0,0—>
There are folders in Android that absolutely cannot be deleted, since without them the system will not work correctly. Remember these names:
p, blockquote10,0,0,0,0—>
- efs – information about IMEI, Mac, Bluetooth and Wi-Fi.
- etc – configuration files used when loading the system and processes of various built-in programs.
- lib – libraries necessary for the operation of programs and modules.
- mnt – images of mounted systems.
- proc – key information about the installed system.
- sbin – executable files of all programs involved in system management.
- sys – current system configuration.
Under no circumstances should you delete the system folder with all its subdirectories. System is the backbone of the system, so if you delete any data from here, you will have to flash the phone again.
p, blockquote11,0,0,0,0—>
What is this folder
The folder with the intriguing name “Thumbnails” is a system folder. It is used by the operating system to store a cache of thumbnail images and video files. This is done to speed up the process of displaying them in applications such as Gallery. This program is known to many. Some other applications can also use this folder. If there are an indecent number of images on the device, then the cache size is also quite large. And it eats up precious space.
What is useful to know for those who want to put an end to this disgrace, delete the entire cache and everything that can be deleted? The Thumbnails folder is a system folder. This means that it is hidden and cannot be easily reached. In addition, deleting the cache at first will help. But then the folder will be full of thumbnails again. You'll have to delete everything again. But we’ll talk about how to force the system not to fill this folder a little lower. In the meantime, let's figure out how to remove thumbnails.
(
114 ratings, average: 1.00 out of 5)
Removal methods
h23,0,0,0,0—>
To delete system folders, you need superuser rights - root. If you don't have them, then you definitely won't be able to break Android. If you have root rights, you need to be extremely careful - deleting important system files will result in you having to flash the device again.
p, blockquote12,0,0,0,0—>
Read: Android does not recognize the microSD memory card (flash drive)
p, blockquote13,0,0,0,0—>
If you figure out which folders can be safely deleted, then proceed to clearing memory using standard functions:
p, blockquote14,0,0,1,0—>
- Open the Android main menu and launch the file browser (file manager).
- Find the folder you can delete. Press it and hold your finger.
- When the menu appears, select Delete.
Enlarge
The screenshot shows a manager option with multiple selection support. The delete button is located in this case at the top right in the form of a trash can icon.
p, blockquote15,0,0,0,0—>
The standard file manager does not display all Android files and folders. To clean your device's memory well, use ES Explorer or another third-party file manager.
p, blockquote16,0,0,0,0—>
- Launch ES Explorer.
- Choose what you will clean - internal storage or memory card.
- Hold your finger on the folder you want to delete. Once it's checked, start highlighting other files and folders.
- After selecting all the items to delete, click on the “Delete” button in the bottom menu.
Enlarge
You can not use file managers on Android, but simply connect your phone to your computer by selecting the media device mode, in which you can view and change the contents of the memory.
p, blockquote17,0,0,0,0—>
Read: Android does not connect to computer via WiFi
p, blockquote18,0,0,0,0—>
Increase
p, blockquote19,0,0,0,1—>
After connecting to your computer, you can open the internal memory of your smartphone in Explorer and delete unnecessary folders to free up space.
after—>
January 24, 2017
Based on materials from androidauthority.com
File managers on Android can be a convenient tool for organizing data storage on your smartphone, but the Android structure itself (or its apparent lack thereof) can seem a little confusing if you're not used to it. App data, pictures, music - and accessing it all from one root folder - is a slightly different approach to hierarchical structure than what PC and Mac users are used to, and it gives users much more options than iOS.
On Android, you won't be able to access deeply hidden system files through a regular file manager or by connecting to a PC. But this does not mean that you can delete any file you want on a whim. Let's take a look at how typical folders are organized in the device's memory, what they are for, and what you can delete from them and what you can't.
Android device memory hierarchy
Since Android is a Linux-based operating system, your phone's file system is also organized like Linux. In this system, each device has six main partitions: boot, system, recovery, data, cache and misc. microSD memory cards also have their own memory hierarchy. Devices carrying Android 7.0 Nougat are able to continuously update due to the fact that a second one is created in conjunction with the system partition and one of them is updated in the background, and when rebooted, a switch occurs, allowing the updated system to work.
Here's a quick description of what's in each folder.
- boot – This folder contains the kernel, virtual disk, etc., that is, what is required to boot the phone when you turn it on.
- system – The system folder contains the operating system files (also known as the system image), which also includes the Android GUI and pre-installed applications.
- recovery – An alternative option to boot the OS, programs from the recovery folder allow the user to make backups of other folders and restore them.
- data – The data folder stores user information, from contacts and messages to applications and music, and this is the section you have access to through a file browser. After a factory reset, this partition is erased.
- cache – Android stores frequently used data and application components here. This partition can be erased to fix certain problems and will be automatically restored and updated over time.
- misc – This section contains other important system settings information such as USB configuration, your carrier's network settings, and other hardware settings that appear as on/off switches in the GUI.
Without root, Android users can only access the data partition that opens to you when you connect the device to your PC or use a file browser. If your phone's memory can be expanded using a card, the card's memory is also included in this section with data accessible through a PC or file viewer.
Typically, you only have access to application data that is stored in the user data section. To access the rest of the memory you will need root rights
Applications and folders in the data section
So, taking a quick look at the main folders, we noticed that we do not have access to boot files, recovery files, or Android system files when we simply view the files using the browser. Which leads to a comforting conclusion: you can’t just go ahead and cause the collapse of the system with your actions. A completely different situation arises when you have root rights. One way or another, you need to be more careful with what is stored in this section: certain applications can use the data stored here, and moving or deleting them can lead to unstable operation of the system.
Now let's see what's in the data section of your device. To make this possible, phones with Android versions Marshmallow or Nougat have their own file manager, which gives access to the entire partition. This option can be found in the Settings-Memory-Storage-Other menu. Some devices running older versions of Android may or may not have their own file manager, depending on the manufacturer.
Alternatively, there are many third-party apps available on the Play Store that serve the same role, such as FX File Explorer or Total Commander.
You can also manage your files from your PC using a USB connection. Just make sure your phone is in MTP (File Transfer) mode so you can see all your files.
You can access your device's memory using a PC or directly through a file browser
If you have a feeling that your device's memory looks full and there are too many folders, take a closer look at them. You'll see numerous folders associated with applications, perhaps even remnants of applications you've already deleted. As a general rule, it's best to leave any application folders alone, but if you remember that the application was uninstalled and the folder remains, deleting it won't cause any harm. Most likely, it is empty or there are some useless log files left in it.
Even if you haven't installed many applications, by default this user data section may contain a number of folders - they store your contacts, music, pictures and everything else. Here are the most basic non-third party app folders you can find.
- Android is where app cache and data are saved by default. It is not recommended to delete this folder if you do not want to lose application data. Deleting this folder may cause some of them to not work correctly.
- Alarms, Ringtones, Notifications – as the names suggest, these folders store audio files for alarms, ringtones and notifications, which can be used by both default and third-party applications.
- Cardboard – Data for a number of VR applications is stored here, and if there are none, it remains empty.
- DCIM - This is where you'll find photos you've taken using your main camera app. You may also see such a folder on the microSD card if you save photos to it as well.
- Downloads – This is where everything you downloaded from your web browser, such as Chrome or Firefox, is located.
- Pictures, Music, Movies, Video – These are the default folders used by your media applications. Some applications allow you to designate other folders, but most media players will default to these directories. Screenshots are most often saved in the pictures folder.
- Podcasts – This folder is used by a number of applications to separate podcasts from other music files. If you don't use podcast apps, it will be empty.
So, what folders can I (or should) delete?
If you're not sure, don't delete it. This is true for all application folders and should not be touched unless you know exactly what you want to do. It’s absolutely safe to add and remove files from any media folder, but try not to destroy the folder itself in a rush to restore order. If you see that the folder is empty, for example, there is nothing in the Alarms folder, you may think that it itself is not needed. But, on the other hand, the folder does not take up much space. And perhaps some application will need it later, so is it really necessary to remove it?
Over time, your device's internal memory will contain many more folders than those listed above. You will install and uninstall more and more applications. Therefore, it never hurts to tidy up your device, unless you rarely move files on your phone, download and delete them. And yet, deleting an empty folder will not free up additional memory space for you. So, if you want to win a place, it’s better to look at which apps/movies you can delete that you won’t watch, etc.
Now that you have a more complete picture of what these folders are stored in the memory of your device, it will be easier for you to manage your files without the fear of “doing something wrong.”
Questions and answers
I accidentally deleted photos from my Camera folder. In the internal storage, I was deleting unnecessary items to free up space and accidentally selected DCIM to erase. Can I recover a photo? This happened 5 days ago. I checked the Trash folder in the Gallery, but it shows files that won't open.
Answer
. Thumbnails from the DCIM folder can be restored even without root, but to obtain the original photos it is necessary. We have already talked about similar cases, study the cases of other users.
Help me recover files on my phone. When connected to a computer, the photos in the DCIM folder (internal memory) were not visible, although the photos were viewed on the phone. I wanted to download them to my computer. As a result, she created something incomprehensible. Now in this folder all the photos are in the form of gray squares with an exclamation mark. When I try to open it, the cursor freezes and spins, and then writes that this format is not supported. I somehow merged two DCIM folders and replaced them. As a result, space was freed up in the phone's internal memory. Is it possible in this case to revive photos and videos from this folder and if so, how?
I have lost photos and videos on my Samsung galaxy j5 smartphone. I'm looking in my files, there's nothing in the DCIM folder, but the memory is busy. Android receives a notification that you need to free up memory. What to do?
I transferred photos from my phone to a memory card, but they disappeared there, instead there was a triangle with an exclamation mark... I found them (on your advice) in DCIM camera, but the quality leaves much to be desired (no clarity at all!).
I moved photos from phone memory to SD card. The operation was performed through a desktop computer by connecting the device to it via a USB port. There is access to the Android Gallery, photos are in the DCIM/Camera folder. But there is no access to photos and videos from Viber and WhatsApp.
When using an Android smartphone, you will invariably come across new menu items or folders whose names interest you. In this article we will talk about one of these folders - it is called Thumbnails. What is this folder and what is it for?
The first is a hidden folder, so it is not displayed by default in the smartphone’s file manager. As for a computer or laptop, in some cases it is displayed, and in others you have to enable the display of hidden files and folders in the settings.
Second, in the folder you will find thumbnails of images located on your smartphone. As a rule, they take up a little free memory, so there is no need to worry about running out of space on your smartphone. However, there are exceptions when files can really take up a lot of space.
Is it possible to delete a folder? You shouldn’t touch the folder itself, but delete the contents if you want. Deleting, by the way, is as easy as shelling pears - select the file, then click “Delete”, for example:
Whether this is necessary is up to you to decide. Just remember that the thumbnails will still be created by the system. Thumbnails are generated automatically and are necessary in order not to use smartphone resources.
Preface about structure
Many people have a computer and Windows OS is installed on them. Everyone knows perfectly well that in this OS everything is distributed across disks:
C: - the system is located on this disk
D: - for personal files (the disk may not exist if it is not “partitioned”)
E: - Z: - flash drives, portable hard drives, CD or DVD drives.
In Windwows, everything is distributed across different drives. In UNIX/Linux, which includes Android (as well as BSD, which includes Mac OS X), everything looks a little different. The file structure is tree-like. It may not be clear now, but it will become more clear as you read the article.
It is also worth knowing that Android, like Linux, is very case sensitive, unlike Windows. For example, the folder Name, NaMe, name, NAME are 4 different folders, while Windows can only create one folder with that name.
To make it more clear what we are talking about, it is recommended to install the Root Browser file manager.
What applications can be deleted?
There is no single list of programs that can be safely removed without harming the system, so everyone must determine for themselves which of them are not needed. We offer a list of basic programs and those elements, the removal of which will not harm the operation of the Android device, for example, Google maps.
List of programs:
- Voice search or dialing;
- Help and support from the manufacturer;
- Standard email client or browser (Internet);
- Unused video, audio players;
- Unnecessary Google services (Maps, Gmail, Gtalk, etc.);
- All kinds of games, books, etc.
Under no circumstances should you randomly delete applications or files you don’t like, this can lead to a crash of the entire system! Any application is a file with the apk extension. It is this file that should be deleted. If available, you also need to delete files with the .odex extension. Then this procedure can be considered completed correctly.
This is what the program system file itself looks like:
Here is a list of possible system applications to remove:
- AccuweatherWidget.apk - weather informer;
- AnalogClock.apk - analog clock widget;
- BlueSea.apk, Aurora.apk, etc. – all types of live wallpapers;
- ChatON_MARKET.apk - chat from Samsung;
- Encrypt.apk - memory card encryption;
- Geniewidget.apk – news widget;
- GooglePartnerSetup.apk is another Google social program;
- Kobo.apk – magazines;
- Layar-samsung.apk - augmented reality browser;
- MobilePrint.apk - remote printing of documents;
- PlusOne.apk is another social service from Google;
- SamsungWidget* - different types of widgets from developers from Samsung;
- VideoEditor.apk - video editor;
- Voice*.apk – programs for working with voice;
- Zinio.apk – Internet magazines.
Structure and purpose of folders and files Android
As mentioned above, the structure has a tree-like appearance. Every tree has a root, and UNIX/Linux also has one. The root is the starting point in the file structure; from the root, the system acquires folders and files. The root in UNIX/Linux is marked as a sign:
/
details about the cache section
This section contains temporary files when Android boots, and system updates are also downloaded here “over the air” - update.zip .
[collapse]
details about the dev partition
/dev/ - this section contains information about system devices and files.
[collapse]
details about the data section
section /data/ - user section in which installed applications and personal settings are located
folder /data/app - installed applications and games are located here.
folder /data/app-lib - additional libraries necessary for the operation of certain applications (present in new versions of Android).
folder /data/dalvik-cache - cache memory for running the Dalvik Java machine, which is the “engine” in Android responsible for launching and running applications.
/data/data folder - this folder contains individual settings for each user application, libraries and other files necessary for their operation.
folder /data/system/ - this section contains global settings for the user environment, synchronization, accounts, blocking.
files gesture.key, locksettings.db, locksettings.db-shm, locksettings.db- wal - graphic key, pin code.
[collapse]
details about the efs section
section /efs/ - contains files and folders responsible for IMEI (this section is not available on all Android devices).
[collapse]
details about the preload section
/preload/ section - this section contains additional files and folders that are mirrored to the /system/ (this section is not available in all Androids, mainly in Samsung).
[collapse]
details about the system section
/system/ section - this section contains system folders and files necessary for the functioning of Android.
folder /system/app - system applications and services are located here (in the new Android OS, service applications were moved to another folder priv-app ).
folder /system/bin and /system/xbin - the folder contains files and links to executable binary files.
file /system/xbin/su - the file responsible for Root rights.
folder /system/camerdata - this folder contains files responsible for the operation of the camera.
/system/etc folder - this folder contains configuration files necessary when loading the OS and also necessary during the operation of various programs.
folder /system/init.d - this folder contains scripts that can affect the operation of the system.
file /system/etc/ hosts - the file responsible for blocking and redirecting web addresses.
file /system/etc/apns.conf - file with information about Internet access points (APN).
file /system/etc/ gps.conf - GPS settings.
folder /system/fonts - folder with system fonts.
folder /system/framework - folder with Android “processes”.
folder /system/lib/ - libraries of system applications and services.
folder /system/lib/modules - system drivers.
folder /system/media - folder with system sounds and startup animation.
file /system/media/bootanimation.zip - executable archive with boot animation.
folder /system/priv-app - folder with Android services/applications.
folder /system/tts - folder with the system voice engines.
file /system/build.prop - a configuration file with which you can change system settings.
[collapse]
details about the proc section
/proc section is a virtual partition containing information about the kernel and its configuration.
[collapse]
details about the mnt section
partition /mnt - memory cards and internal memory and other virtual partitions are mounted (added) to this partition (also in new versions you can find the storage ).
[collapse]
details about the storage section
partition /storage - only real (existing, that is, not virtual) memory cards and internal memory are mounted in this partition.
[collapse]
details about the mnt and storage section
All files that exist on your Android (pictures, melodies, videos, documents) are recorded either on the internal memory or a memory card. If Android has its own memory (internal memory), then it is mounted under the name.
/mnt/sdcard or /storage/sdcard
Yes, I understand perfectly well that many people think of giving the name to their own memory with such a name, but what can you do...
If there is no internal memory, then this name is occupied by the memory card. If there is both internal memory and a memory card, then the internal memory remains under the name sdcard, and the memory card takes one of the names:
sdcard2 external_sd sdcard1 extSdCard
[collapse]
The Android file system is much simpler than it might seem, and consists of only 6 sections. We will describe the purpose of each section and take a detailed look at the folder structure in the data section. To confidently sort and move files on your internal storage, you need to know the purpose of folders in the Android file system. In the article, we will learn in detail which folders user information is stored in, and where application data, deleting or moving which will disrupt the operation of installed programs.
Android: Free up disk space
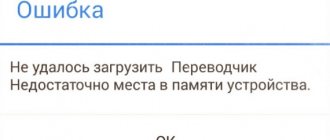
This entry will be an addition to the article “Android: Applications are not installed” and will help you figure out how and what exactly can be cleaned and deleted in the Android OS if applications are not installed due to lack of free space, that is, if there is an error:
Failed to load insufficient device memory space.
In Android OS, applications are installed in the /data/ folder (called internal memory), which is always allocated a limited amount of space: about 500 MB. I repeat: regardless of the amount of memory in your device (8 GB, 16 GB, 32 GB or 64 GB), 500 MB are allocated for the application folder, with the exception of tricky firmware, where this injustice was specifically eliminated.
Initial manual cleaning
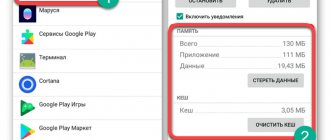
How much available disk space remains for applications can be seen in “Settings” - “memory”:
As you can see from the image, I have 27 MB of available internal memory left (do not confuse this with the built-in memory).
So we are interested in cleaning the internal memory, namely the “/data/” folder.
First of all, I would recommend moving all possible applications to the SD card.
Do not transfer to the SD card only:
- system applications and services
- applications you need without an installed SD card
- applications whose widgets you use, as widgets may stop working.
Which applications have not been transferred to the SD card can be seen in “Settings” - “Applications” - “SD card” tab:
Applications that are not ticked have not yet been transferred to the SD card. In order to transfer them to the SD card, click on the application and in the window that appears, click on the “move to SD card” button.
When you move an application to a card, not all application files are still moved. Some files remain in the internal memory in any case:
- Application - located in the /data/dalvik-cache/ folder - cache for quickly launching applications
- Data - located in the /data/data/application/databases/ folder - all your settings and saves in this application
- Cache - located in the /data/data/application/cache/ folder - such data as downloaded ad units, images and other temporary information that can be safely deleted
Android memory partitions
Since Android is a Linux-based OS, the Android file system includes six partitions. By default, the user has access only to the internal memory section – data. Accessing or changing files in other sections without ROOT rights is prohibited.
- Boot. Inside the folder, the system kernel, virtual disk and other files necessary to run the mobile device are stored.
- System. Used to store operating system files, user interface graphics, and pre-installed programs.
- Recovery. Folder with backup data for restoring and booting the system. Read more about Android recovery.
- Data. A section of internal memory where user information is stored: multimedia files, games, applications, etc.
- Cache. The folder is necessary for the system to temporarily store frequently used data and application components.
- Misc. Stores data about system settings, user-specified configurations, and cellular operator network parameters. There are also various parameters that are displayed in the system as switches.
What files are stored in LOST.DIR
Keep in mind that this contains renamed copies of unfinished data. Even if you find some strange names here, don't be surprised as these are just backup versions. Your data may end up in the LOST.DIR directory in the following situations:
- Forcibly removing the SD card from the Android phone, especially when transferring data;
- interrupting the process of copying photos, videos and other documents to the memory card or vice versa;
- sudden freezing or rebooting of the phone while shooting video or recording conversations;
- turning off or rebooting the device while reading or writing data.
The Android system uses these directories to temporarily store various documents and content. First of all, it stores temporary data for moving between PC and Android device. The directory serves as a backup if it is used when transferring between a computer and a smartphone when problems occur such as a disconnection when copying information, or if the SD card is unexpectedly removed. The documents themselves often contain only titles, which consist of numbers. The creation date is usually specified randomly, for example, 01/10/1980.
Folders in the data section
Uploading files, screenshots or installing applications is carried out in different folders of the DATA section.
- Android – the folder where applications are installed. Inside there are two folders – obb and data. The first stores the game cache, the second stores data from installed applications. Deleting or moving folders will result in loss of settings and incorrect operation of programs.
- Alarms, Ringtones, Notifications. Folders are designed to store sounds and music, for alarms, ringtones and notifications. Files placed in these folders will be displayed in the system when selecting melodies. Otherwise, you will have to select sounds using a player or file manager.
- Bluetooth. The folder contains files received via a Bluetooth wireless connection.
- DCIM . The folder stores photos and videos taken using a standard application. If “storing files on MicroSD” is selected in the program settings, then the footage will go to the DCIM folder on the external drive.
- Documents. A place to store text documents.
- Downloads. Download folder. Files downloaded via Chrome or other Google services automatically end up in this section. Third-party applications also save files in the Downloads folder, but more often they use their own folders.
- Pictures, Music, Movies, Video. Folders for storing multimedia files that are used by default players. Music or video placed there will automatically appear when you launch the corresponding application. Otherwise, you need to specify the path for the files manually. Screenshots are also stored in the Pictures folder.
- Podcasts. The folder is used by applications when listening to podcasts.
It is worth noting that unused folders remain empty. Third-party applications often create their own directories to store temporary and permanent files, such as Viber or Titanium Backup.
What background applications on Android can be disabled
The two main types of apps that you probably don't want running in the background are games when you're not playing them, and music players when you're not listening to music. Look at other background processes too. If you don’t need this application at the moment, then you can safely close the process.
The applications necessary for the operation of the device themselves will not allow you to close their background processes, this is how the Android system works. But do not close system background applications and those that you constantly use. If, for example, you close the processes of social networks and instant messengers, you will stop receiving notifications about new messages. Most applications and services whose names begin with “Google” should not be closed either. Here are the most important Google processes:
- Google Search
- Google Play services
- Google Contacts Sync
- Google Keyboard
- Google Play Store
Conclusion
Deleting any folder or file in the internal memory section will only result in the loss of some data. Therefore, it will not be possible to disrupt or damage the mobile device by such actions. The next time you launch the application, it will download and write the missing files.
But deleting/moving files outside the data section is guaranteed to violate the integrity of the system and make the device unstable. In this case, resetting to factory settings or re-writing the firmware will help. Therefore, if you have ROOT rights, it is not advisable to touch the files of the system partition.
Advertising One of the popular operating systems today is Android. It is installed on millions of mobile devices. The system is a set of folders and files that ensure its operation. But have you ever wondered what is contained in each folder? Some are quite heavy, so the hand is tempted to remove them. Before you do this, you should definitely familiarize yourself with what each folder is responsible for and how to make a backup copy, as well as how important it is for the operating system. We will also tell you what ways to delete an unnecessary folder. Advertising
What are background applications on Android
Background applications run background processes that are invisible to the device owner. The application seems to be closed, but it still consumes system resources, takes up space in RAM and reduces the device's battery life. Such processes start without your knowledge and run in the background - hence their name. There are generally good reasons for running these processes - it could be synchronization, retrieving location data, or other activity related to the purpose of the application.
But not all background processes are necessary. For example, we use some applications extremely rarely, and unnecessary background processes only unnecessarily load the device. The Android system has built-in tools with which you can always see what applications are running in the background, how much memory they consume and how they affect the battery charge.
To see which background processes are currently running, you need to:
- Enable in settings
- Select the menu item “Process statistics”
- Select application
In the window that opens, you will see all the information on the selected background application.
You can also see which applications and how much they affect the battery consumption of your device. To do this, go to the battery settings and select the “Battery Usage” menu item. You will receive a list in which, in descending order, there are applications that negatively affect the battery level.
Basic key directories in the android operating system
The first priority before deleting is to find out what the directory contains, because this determines whether it can be deleted or not. If you erase important files by mistake, you can not only disrupt the operation of some applications, but also cause the entire operating system to become completely inoperable.
Cache is a folder for storing temporary files. It may contain a system update. If you are not going to update to a more recent version of Android, then you do not need the update file. You can delete this folder, and in some cases it is even necessary.
Data is one of the largest catalogs, which, as you might guess from the name, contains a variety of data. This includes account data, information about saved passwords, Wi-Fi access points, etc. Since this folder contains a lot of information, let’s look at its subdirectories:
- App – a directory that contains installation files for various applications. You can delete it if you do not need all the applications downloaded to your phone;
- Data – includes settings, saves and other service information necessary for the operation of specific applications. If there is no data important to you in the applications, you can also delete it;
- Clipboard is a special data clipboard that also contains the latest screenshots. It is possible to delete this folder, but it is not recommended;
- Dalvik-cache is a cache area for a program called Davlink. This application is a Java virtual machine that allows the phone to run application apk files. To speed up this process as much as possible, files are created in cache memory. It is recommended to clean the contents regularly, but you should not delete dalvik-cache.
- App – system wallpaper, standard applications (calendar, notebook, SMS) are located in this folder.
- Bin includes executable files and links;
- Build.prop contains a huge number of settings for the phone, for example, how long the sensor is delayed after pressing, what is the screen density, and more;
- Fonts – information about all stock fonts supported on the phone.
- Framework – everything that is needed for the interface, in particular icons, curtains and other graphic elements;
- Lib – application library;
- Media – all standard melodies and sounds (alarm clock, SMS notifications, call tones);
- Tts includes language packs.
The efs folder contains information about the phone's serial number (IMEI), MAC address, Bluetooth and Wi-Fi. This directory cannot be deleted. Moreover, it is recommended to make a backup of this folder, since deleting it will lead to the loss of the unique number of your smartphone.
The etc directory contains configuration files, mainly used during OS loading, processes of various programs, for example, to determine GPS location. This is one of the system directories that cannot be deleted. Advertising
lib directory – it contains various libraries necessary for the correct operation of program functions and modules. This folder also contains files that ensure the drivers work. It cannot be deleted.
The mnt directory contains images of mounted systems. Partitions of an installed memory card, internal memory or other virtual devices may be located here. Naturally, you cannot delete this directory either.
The proc folder – it contains all the key information regarding the installed Android OS: information about the kernel, configuration parameters and hardware. All existing files and folders are virtual and weigh zero bytes. The system automatically creates them when the user accesses them. This folder cannot be deleted with normal user rights.
The sbin directory is one of the key folders required for the phone to operate. It contains executable files of all programs designed to manage the system. Accordingly, it cannot be deleted.
The sys directory contains the current system configuration. This is a dynamic directory. The information in it is constantly changing. This folder cannot be erased.
Advertising The system section is the “backbone” of the entire operating system, since it is where all the files are located, without which it is impossible for Android to work. The System directory (like any other internal directories) cannot be deleted. To get acquainted, let's take a closer look at the contents of this directory:
Documents – a folder that can contain various documents, in particular .doc and .pdf files. If the contents of the folder do not interest you, you can delete it.
Bluetooth – contains all files that were received by the device via Bluetooth. If there is no important data in it, it is deleted without problems. It can be located not only in internal memory, but also on an SD card.
DCIM is a special directory for saving photos taken using your smartphone's camera. As a rule, it includes a Camera section, in which all photos are located. If the photo you need is not on your phone, you can delete it. Sections such as Pictures, Images, Audio, Music (if there are no important files inside) can also be deleted.
Questions and answers
I accidentally deleted photos from my Camera folder. In the internal storage, I was deleting unnecessary items to free up space and accidentally selected DCIM to erase. Can I recover a photo? This happened 5 days ago. I checked the Trash folder in the Gallery, but it shows files that won't open.
Answer. Thumbnails from the DCIM folder can be restored even without root, but to obtain the original photos it is necessary. We have already talked about similar cases here, study the cases of other users.
Help me recover files on my phone. When connected to a computer, the photos in the DCIM folder (internal memory) were not visible, although the photos were viewed on the phone. I wanted to download them to my computer. As a result, she created something incomprehensible. Now in this folder all the photos are in the form of gray squares with an exclamation mark. When I try to open it, the cursor freezes and spins, and then writes that this format is not supported. I somehow merged two DCIM folders and replaced them. As a result, space was freed up in the phone's internal memory. Is it possible in this case to revive photos and videos from this folder and if so, how?
I have lost photos and videos on my Samsung galaxy j5 smartphone. I'm looking in my files, there's nothing in the DCIM folder, but the memory is busy. Android receives a notification that you need to free up memory. What to do?
I transferred photos from my phone to a memory card, but they disappeared there, instead there was a triangle with an exclamation mark... I found them (on your advice) in DCIM camera, but the quality leaves much to be desired (no clarity at all!).
I moved photos from phone memory to SD card. The operation was performed through a desktop computer by connecting the device to it via a USB port. There is access to the Android Gallery, photos are in the DCIM/Camera folder. But there is no access to photos and videos from Viber and WhatsApp.
“I can’t view photos from my phone. I have DCIM on my computer, but I don’t have CAMERA. How can I transfer photos? Look?"
Samsung deleted the DCIM and Android file on the phone's memory card! Is it possible to recover photos and videos in that case?
Hello! Tell me, is it possible to make it so that photos are displayed in the DCIM folder or so that they are visible, I need to transfer the necessary ones and delete unnecessary spam and texts, how to automate this easily. What do you recommend on how to save what you need in WhatsApp and delete what you don’t need in one fell swoop to clear your memory?
Removal methods
How can I delete a specific folder? The first way is to use standard functions. To do this you need:
- Launch the File Browser application or similar on your phone.
- Find the required folder and hold it with your finger.
- When the selection menu appears, click the “Delete” line.
Please note that standard tools do not display all existing folders and files, since system files are often hidden. Any third-party file manager, for example, the ES Explorer program, will help you see more. Advertising You can download it from the Google Play store. The application offers ample opportunities. With it, you can view existing folders, as well as delete some of them. To do this you need:
Sources used:
- https://androproblem.ru/nastroika/kakie-papki-nelzya-udalyat-na-android-a-kakie-mozhno.html
- https://android.mobile-review.com/articles/47343/
- https://androidp1.ru/struktura-i-naznachenie-papok-i-faylov-v-android/
- https://androfon.ru/article/naznachenie-papok-v-faylovoy-sisteme-android
- https://poandroidam.ru/setup/papki.html
SHARE Facebook
- tweet
Previous article
Next article6 best applications for preparing for the traffic police exam
How to disable background applications on Android
You can either disable the background process or force close the app completely.
- To disable a background process, you need to select the required one in the “Process Statistics” menu and click “Stop”
- To forcefully stop an application, you need to select the required one in the “Application Manager” menu and click “Stop”
Some applications themselves automatically launch in the background even after closing. To “put them to sleep” you can use Greenify. This utility prevents applications from starting automatically. If your device has ROOT rights, you can completely remove unnecessary applications from startup. You can read how to get ROOT rights in our other page.