Hard drives, just like any other part of a personal computer or laptop, can break, become damaged or fail. Sometimes in such cases, restoring the hard drive using special programs can help. They allow you to thoroughly test the disk and eliminate any minor failures that are detected.
One of these programs is Victoria HDD, which is completely free and is freely available on the World Wide Web. Thanks to its simple interface and wide capabilities, any user, even an untrained one, can easily understand how to use the Victoria hdd program.
Victoria's hard drive testing program works on all Windows, including all the latest versions, regardless of platform.
From MS-DOS to Windows 10
Victoria was conceived as a means of advanced diagnostics of drives (then hard drives, and today also SSDs) and managing their operation settings through low-level commands. Belarusian programmer Sergei Kazansky developed it for ten years and released his own set of utilities for data recovery. During this time, many commercial releases of Victoria were released, several free versions and one unofficial one, which we will pay special attention to.
Victoria was originally a disk utility for MS-DOS, written in assembly language. The ancient operating system was better suited than Windows due to the fact that in a single-tasking environment it is easier to provide exclusive access to the disk. With the advent of support for the porttalk.sys driver version 4.xx, Victoria has learned to work in the WinPE multitasking environment, as well as in Windows from XP to 10 of any bit size. It has become easier to launch it, the actions in the graphical interface have become clearer, and the operating mode itself has changed. But here's the problem: without understanding the new features of the program, some users began to lose data and entire disks instead of restoring them. Therefore, the latest official version 4.46b has developed “fool protection”.
By default, only non-destructive operations with drives are available. This is not just a read-only mode, as in other utilities that access the HDD/SSD using the Windows driver. Victoria also blocks the ability to change the HPA (and screw up the disk geometry) at the first start, accidentally launch low-level formatting, and “shoot yourself in the foot” in more sophisticated ways.
Universal Soldier
Victoria is the most universal utility. It addresses any type of drive (HDD, SSD, USB Flash) and any ATA-compatible interface. Its job is to transmit ATA commands to any device that supports them. Therefore, everything that has been said about Victoria’s work with disk drives is also true for solid-state drives, with the exception of what relates to their design features. It is clear that for an SSD it is pointless to watch the spindle spin-up time and try to control the head positioning speed - it has neither one nor the other. Nevertheless, it is quite possible to test and even restore an SSD using Victoria.
Conclusion
Victoria HDD is a universal program for checking the storage device, which helps to find and restore damaged blocks of the storage device and improve system performance. Numerous user reviews indicate that this is the best solution for initial device diagnostics.
One of the main advantages of the program is the ability to use all the functions of the utility for free. Therefore, Victoria HDD software does not require additional “treatment”: downloading a crack or an activation key. The software does not require a localizer; the language can be selected in the program menu.
INFO
At the time of writing, the abandoned website of the Victoria program developer was infected.
Therefore, instead of the URL www.hdd-911.ru specified in the documentation for the program, a link is provided to an alternative source for downloading the Victoria utility. Although Victoria is far from a new program, it also contained critical errors that required correction. One of them led to the fact that it was impossible to run Victoria on 64-bit versions of Windows. Another could cause problems when working with large disks. If the volume was higher than a terabyte, then Victoria 4.46b simply spent all the virtual memory on drawing and color marking the LBA blocks being checked. In version 4.47 Shcherbakov fixed all this.
Running Victoria 4.47 on Windows 7 SP1 x64, API mode
Other articles in the issue:
Xakep #210. A short excursion into Ethereum
- Contents of the issue
- Subscription to "Hacker" -70%
Settings
Victoria HDDs are ready for use right away; no basic settings need to be made. But you can do a number of additional things in the “Settings” section.
- Select the location of the text file with logs on your computer. Also here you can enable or disable saving basic information about disk testing to a separate log.
- Check whether the functions are enabled: “Get a passport by double-clicking on the list of PCI devices” - used to obtain a passport of an information storage device by simply clicking on the line of the PCI controller; “Auto-detect USB drives” - when connecting USB devices to the computer, the Victoria HDD application will report a new device found.
An optional settings item is to enable or disable program sounds in the “General” section. The “Night mode” (formerly “NIGHT-mode”) parameter enables night mode in Victoria HDD, during which most sounds are turned off.
It is recommended to leave the remaining parameters in the “Settings” section unchanged, as they affect the efficiency of the Victoria HDD program.
PIO vs API
Victoria has two operating modes: PIO (port input/output) and API (application programming interface). In PIO mode, the drive controller is polled by the program through the porttalk.sys driver. If you select API, operating system tools will be used. Disk performance in PIO mode is reduced because DMA and high-level read and write optimizations are not supported. However, PIO mode allows you to use all the features of Victoria and send any ATA commands directly to the disk controller, bypassing the OS and standard drivers. It is through PIO that they most often work with disks in data recovery laboratories. Victoria supports both drives with the modern SATA interface and the old ones - PATA (aka IDE). Victoria can also work with external drives (features will be described below).
Having selected the PIO mode, at the beginning of work you need to scan the bus and identify the disk controllers using the PCI-Scan button. To the right of it, a window for selecting a disk port is displayed. Internal ones are usually detected without problems, but for external drives you will have to first find out their port. This can be done in the hardware properties or in any diagnostic program (for example, AIDA64). After this, you need to manually set the port in Victoria. While scanning, you can check the All dev (all devices) checkbox and use the exclusion method to find the desired disk in the list of found ones.
Victoria 4.47 in PIO mode
It is advisable to use the PIO mode specifically for low-level commands. A simple search for bad sectors and their reassignment to the spare area of the disk is much faster (but less reliable) in API mode.
The API mode restrictions are as follows: you cannot set or remove ATA passwords; work with the Host Protected Area and viewing registers are also disabled. If any of these functions are needed, you can switch to PIO mode. It happens that PIO mode is not available. This happens when using older versions of Victoria on 64-bit OSes. Another reason could be errors in working with the porttalk.sys driver or the choice of SATA AHCI mode. There is a guaranteed way out of the situation as follows.
- We write a bootable USB flash drive with WinPE x86 and place the Victoria program on it by simply copying it.
- Connect the desired drive to the SATA/PATA port, if you have not already done so.
- Disable all other HDDs or SSDs (optional).
- Go to CMOS setup, switch the SATA controller mode from AHCI to compatible (compatible, native or IDE).
- Download WinPE. If necessary, we install drivers, including porttalk.
- We launch Victoria in PIO mode, initialize the desired HDD or SSD and execute the necessary command.
Settings can be set via the GUI or in the vcr40.ini file. The same file will help to remove the blocking of work with the primary port. By default, it is enabled in order to protect the system disk from accidental modification. To be able to select Primary in the list of ports, you need to do two things:
- Disable the “only non-destructive functions” option and close the program.
- In the section of the vcr40.ini file, add the line Enable PM=1, save the changes and restart the program.
Stage II: download Victoria program and prepare for scanning
When downloading, you will need to select one of the Victoria options. For a desktop computer it will be Victoria for Desktop, for a laptop for Notebook, the remaining items load the DOS shell and the Volkov Commander file manager, i.e. in normal cases they are not needed.
Program selection options:
It is possible that when you first start you will need to select exactly the hard drive that you want to test (and not the one that is registered in the vcr.ini file - the Secondary Master is indicated there in the distribution). To do this, press the P key.
A menu with channel names will appear. The selection is made using the up and down cursor keys. When you move the cursor, an indication (light bulbs) is displayed in real time, which allows you to judge the readiness of the HDD.
A working hard drive will always have 2 lights on: DRSC and DRDY (some may also have INX). In the error registers, the red AMNF lamp may be lit, and the others should be extinguished. For more information on the purpose of indicators, see the end of the article. After placing the cursor on the desired item, press ENTER.
The last item of this menu is responsible for selecting a hard drive on an external (additional) PCI/ATA/SATA/RAID controller. After pressing ENTER, the search for external controllers and hard drives on them will begin. Only really present and serviceable hard drives in the MASTER position will be detected; the system will not “notice” the rest. When each additional port is found, the table will display:
- Name of the ATA controller manufacturer (or its Vendor Code)
- Controller name (or its ID Code)
- Class: EXT / INT / RAID (external, internal, RAID)
- Port address (or a dash if it could not be determined)
- Name of the connected hard drive, if it is on the channel and is working
All found ports will be numbered. All you have to do is select the one you need by pressing the appropriate key and confirm with Enter.
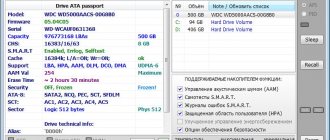
Note: The program may not find hard drives on some Promise controller models. Next, press F2 to “give” the passport. An HDD passport is information hardwired at the manufacturer’s factory that characterizes the hard drive family and its individual features.
Scanning works closely with the passport, receiving all the necessary parameters from it.
External drives
External drives are regular laptop (2.5″) or desktop (3.5″) models in containers with USB and FireWire interfaces. They are equipped with various controllers with the general name “SATA bridge”. Many of these bridges do not broadcast low-level commands. Therefore, Victoria can immediately work with some external drives in PIO mode in the same way as with internal drives, while with others you will have to suffer at first. In the simplest case, it will be enough to remove the disk itself from the case (do not open the HDA!) and connect it to the port directly.
Rare beast: SATA hard drive without SATA port
Western Digital and, possibly, other manufacturers produced some external hard drives with a soldered SATA-USB bridge. Therefore, they do not have a regular SATA connector. However, they can still be connected directly to the port by soldering a SATA cable to the pins on the drive board. To understand whether your disk belongs to such a series, you will have to google the model number and look for datasheets.
Operating modes
The Victoria program can work in four different modes:
- Ignore simple hard drive diagnostics without carrying out “repair” work;
- Remap faulty areas are replaced by backup ones;
- Restore recovery of sectors with problems using the software method;
- Erase rewrites bad sectors using low-level formatting. However, after using this function, all data will be deleted.
Use the last Erase item only when the “Remap” and “Restore” modes did not give the expected effect. Before starting it, it is recommended to save all necessary information to other media.
Passwords
One of the most popular low-level commands in PIO mode is working with passwords. According to the specifications, access to the disk can be limited using a password. It is set by the user from the BIOS or using external utilities. There is also a master password preset by the manufacturer. The drive can only be locked using a user password. If you have forgotten it, you can remove the lock using the master password.
Depending on the specified security level, the result of entering the master password will be different. At a high level, the master password acts the same as the user password. It just unlocks the drive and that's it. If the maximum security level is set (max), then entering a master password instead of a user password will unlock the disk only after all data on it is completely erased (secure erase).
Working with ATA passwords is also complicated by the fact that according to the standard they always consist of 32 bytes (no matter how long you specify it). Extra characters are ignored, and missing ones are added automatically. The problem is that different programs add them in different ways. Standard security utilities on some laptops are especially guilty of this. Instead of traditional zeros (or at least spaces), they use non-printable characters. The code 00h cannot be entered from the keyboard at all (even through {ALT}+code). There is only one way out: do not enter the password in the program window, but read it from the file. Any characters can be written to a file using a hex editor.
Often the user cannot unlock the drive even when he enters the correct password. If you change a laptop or lose the standard utility, any other one (for example, HDDL) will add up to 32 bytes to the password with its own characters.
There is also a preliminary modification of the password. On many laptops it is actually encrypted before it is sent to the controller. Usually these are the simplest logical operations, but this doesn’t make it any easier. The user thinks that this is a password he knows, while in reality the controller accepts a completely different one. If you have tried all the options for the proposed user and standard master passwords, but have not achieved any results, then there is only one way out - take the drive to the laboratory, where they will work with it in technological mode.
How to get back a lost terabyte
Sometimes it is very helpful to be able to work Victoria in PIO mode with HPA (Host Protected Area) - a service memory area in which the disk geometry is recorded.
It determines the storage capacity by specifying it as the number of LBA blocks. There was an interesting case in my practice. I received a standard complaint: “the computer does not turn on” (read, the OS does not load). The owner complained that he had been suffering for about a month. First, he visited all the service centers, then invited various Enikey people - to no avail. I came, looked and also thought deeply. All components are in good condition. The disk is detected in the BIOS, but booting from it does not work. I launched Linux from a flash drive. The hard drive is visible, but logical partitioning utilities show a strange picture: 64 MB of total volume and one partition with an unknown file system.
And then I realized that the HPA had simply failed on the hard drive. As a result, a terabyte disk began to be defined as a 64-megabyte stub. I switched the SATA port mode from AHCI to compatible in CMOS setup, took a USB flash drive with WinPE and launched Victoria in PIO mode. Next, I sent the NHPA command (restore factory volume).
Usually in such cases it is possible to instantly restore the passport value of LBA blocks, but this time the miracle did not happen. Therefore, I found a service utility for hard drives of this series and sent a similar HPA recovery command from it. A terabyte of data returned from oblivion on the next reboot.
Why did Victoria fail? I assume because this disk had some specific features unknown to me or the universal program.
Bad sectors
Most often, Victoria is used to find and fix bad sectors. If everything is fine with the HPA of the disk and there is no password protection, but no utilities can read files from it in a reasonable time, then it’s time to check the surfaces. Victoria can do this in any mode (PIO/API) using sector-by-sector reading (read), writing (write) and writing with verification (verify).
Bad sector detection
When restoring data, you can use read-only, but its options also vary. The simplest of them is sequential: from the first block to the last. The starting and ending LBA values can be specified manually, which is convenient for many reasons. Firstly, this makes it possible to check disks of any size, simply by performing the test in fragments of up to one terabyte. Secondly, you can re-check the suspicious area and exclude external factors. Victoria analyzes the time it takes to access the sector. Typically, for new disks it does not exceed 5 ms for 80% of sectors. Sectors with a polling time of less than 50 ms are also considered normal. Those for which it is measured in hundreds of milliseconds are candidates for bad sectors.
Candidates for bads
If the sector was counted after a few seconds, then this is a clear bad block. The disk controller must independently identify such disks during idle time and replace them in the address table with good sectors from the reserve area. However, in practice this does not always happen. Victoria can ask the hard drive to perform such an operation (Remap) for those sectors that have not responded to requests for too long. Formally, part of the information is lost during this procedure, but in reality it was already lost at the moment when the sector became faulty.
In the paid version of Victoria, the Restore function was available - an attempt to read data from a bad sector at any cost and then rewrite it to a good sector. However, the program has not been officially supported since 2008, so it is unlikely that you will be able to purchase its full version. Free Victoria has helped out more than once by restoring HPA, resetting passwords, and eliminating bad sectors that caused other data recovery programs to freeze.
Reading graph during HDD surface test
How free Victoria saved a secret job
I'll share one more story with you. Laboratory at a research institute, our time. The analytical instrument is controlled from the computer that came with it. The computer comes pre-installed with very specific software that the developers no longer support. There is no distribution kit either on the disk or on the website. There is only an installed program, and it has stopped working. The laboratory carried out research under a multi-year government contract. Without the miracle device, the employees found themselves tied hand and foot. We struggled and found out that the problem was with the disk. From ancient times it became covered with bad things, and normal work became impossible. An attempt to make a disk clone by skipping bad sectors was unsuccessful - the cloning program froze. We ran the disk through the Victoria test with the Remap function. We have pre-selected the necessary settings. By the evening of the same day, we successfully removed the disk image, and then restored everything from it to a new hard drive. The device came to life, the contract was completed on time.
Test tab
Next you need to go to the “Test” tab. The hard drive test is carried out by measuring response time, that is, how long it takes from sending a request to each sector to receiving a response.
By scanning the device, the program evaluates the tested sectors and displays on a graph areas where any problems are found, marking them with rectangles of different colors. What do the colors mean, you ask?
The color of the cluster designation depends on its state:
- gray - sectors are clearly readable;
- the green response is a little longer, but they are still considered normal;
- orange sector reading is very long. They are the ones that slow down the operation of the entire disk and, although they still work, they will soon fail. There should be no more than 50.
- red sectors - damaged. They are not readable and cannot be restored. If such sectors are detected, you should already plan to replace the hard drive;
- blue with a cross - attempts to read sectors cause failures. The data contained in them cannot be restored. These sectors need to be repartitioned so that the hard drive stops “communicating” with them in the future. The remap function is used for this.
Mode actions will be applied to sectors marked with check marks.
Additional features of Victoria
Victoria analyzes the condition of the drive in detail and can eliminate almost any failure in its operation. Actually, this is what distinguishes Victoria from the mass of other utilities. While most programs simply show SMART attributes, they can forcefully run entire sets of self-diagnosis tests.
Victoria detects hidden defects using SMART analysis
Victoria has four methods and three types of surface testing (twelve modes in total). In each, it automatically counts the total number of defective blocks and writes their addresses to the log. Like a disk editor, Victoria can show the contents of sectors and allows you to change them. In PIO mode, Victoria displays information about logical partitions on the media even if it is not detected at all in the BIOS. No utility with API access is capable of this. Additionally, Victoria can control the level of acoustic noise of the disk (AAM), adjusting the speed of movement of its heads during search, launch low-level formatting, change the HDD capacity and run benchmarks. It can even be used to check the physical interface (the status of cables and ports). At home, it will save an HDD or SSD in many difficult situations, except for severe mechanical damage that requires opening the HDA. The laboratory will cope with them too, using Victoria as one of the proven utilities.
Disk passport, forced launch of the SMART test and AAM management in the Victoria 4.46b program
Program functionality
According to the information presented on the official website, the Victoria program is capable of:
- speed up your computer;
- restore the stability of both the operating system as a whole and its individual components.
In order to obtain the expected results, the utility:
- replaces defective sectors with spare ones;
- eliminates bad sectors;
- repairs damaged areas.
By using the program in question, you can not only improve the performance of the drive, but also increase its service life.