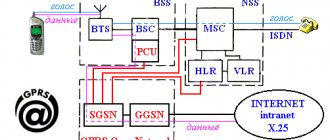
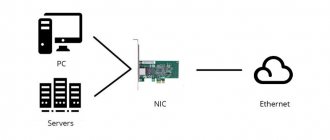
A huge number of dummies ask the same popular question, which is as follows - what is a modem, what is the difference between a modem and a router, and which one is better? It would seem that the purpose of both of these devices is to receive the Internet on the user device. However, this is absolutely not the same thing, and these two devices can complement each other, work in the same case, but not interchangeably. What does a modem do and how is it different from a router? Let's figure it out together!
Modem and its functions
The main function of the modem is to ensure communication between devices during data exchange. In simple terms, this device is designed to encode, transmit, receive and convert signals. The areas of application of such devices are very wide: they are used in civil and military communications. Among ordinary consumers, the most popular are modems, which are used to provide an Internet connection. Let's take a look at how they work.
The most popular among users are modems that provide Internet access.
Which is better, a modem or a router?
Despite the fact that these are completely two different devices, it is still a stretch to ask which is better - a modem or a router? It all depends on your specific tasks. If you want to connect only one device to the Internet, such as a laptop, then one modem will be enough.
If there are several, then it is better to choose a 4G mobile router or purchase separately a modem and a router that supports Internet connection via a modem. Moreover, the first option is also suitable if you plan to use the Internet somewhere outside the home - on a trip or at the dacha. And the second option is intended for stationary use.
How the modem works
Initially, such devices were used to create computer networks using telephone lines. All information processed in computers is in digital form, and is transmitted via telephone cable in the form of an analog signal. Therefore, devices were needed that could connect PCs at different ends of the line.
The word "modem" is a derived form of "modulator-demodulator". Before transmitting data, it transforms the signal into a form that meets the requirements of the communication channel used (it modulates the signal), and changes the received signal into a form suitable for processing by the user’s computer (it demodulates the signal).
The modem is used to transform the signal into a form suitable for processing by a computer
Concept and definition
First, let's answer the question - what is it? In general, “Modem” is an abbreviation for “MOdulator” or “DEMOdulator”. In simple terms, such devices convert one type of signal to another. Now I’ll give an example and it will become a little clearer.
Unfortunately, our computer understands only one type of information, which is encoded using zeros and ones. That is:
- 1 – there is a signal;
- 0 – no signal.
Morse code, invented by the great Alfred Weil, immediately comes to mind. Previously, there was a task to transmit information via wire. But how to do this if the receiver can only accept two states: either there is voltage or there is no voltage. As in our case, 0 and 1.
And that’s all, I said this to the fact that the computer only understands this peculiar language. Even now, you look at a computer or at the screen of a phone, tablet or even TV, and the device endlessly adds, subtracts and transmits a huge number of these same zeros and ones.
The problem is that our entire world operates with analog data. This is how the modem converts the analog signal transmitted over the wire into digital form. We can say that a modem is a kind of translator.
History of the device
Digital modems arose from the need to transmit data between air defense units in North America. Mass production of modems in the United States began in 1958, primarily for the Sage air defense system (the first time the term "modem" was used). The devices were used in networks connecting terminals at various air bases, radar sites and command and control centers scattered throughout the United States and Canada.
The first representative of Bell Dataphone 103 devices was released in 1958, its data transfer speed was 300 bps. The AT&T telephone company introduced dataphone service (the company provided information transmission via telephone channels). The Bell 212a modem, released later, allowed data transmission at a speed of 1200 bps, but it was characterized by increased sensitivity to telephone line noise. The modem developed by Racal-Vadic turned out to be more resistant to noise. From that moment on, competition began for standards and rights in this industry.
The modem is used to transform an analog signal into a digital one
Modems have become widespread since 1977, when Dennis Hayes and Dale Hethertington released the 80-103A model. By the mid-2000s, modems became part of the computer, helping it turn into a multifunctional device that provides the user with the opportunity to receive information from around the world. Modems made individual computers parts of a global network.
FAQ
For simplicity, I also selected a list of the most frequently asked questions on a similar topic, in case I was not able to indicate everything in the article earlier.
- Why and what is a modem needed for? Without this device, the computer will not be able to understand the analog signal.
- So what is the difference between a modem and a router? To put it simply:
- The modem is a “translator”.
- A router is a “post office” that intelligently sends letters with information to the desired device or user.
- the Internet and Wi- Fi the same thing? No, these are completely different things. The Internet is a global network of all computers. And Wi-Fi is a wireless local network (for example, in your home).
- What is the interface of a modem and router? Roughly speaking, this is the input port. For a modem this is most often a DSL input, while for a router it is a regular WAN network. Look at the pictures above.
- Can a modem affect Internet speed? If the device is made according to all technologies and correctly, then no. But there are cases when cheap receivers slightly reduced the speed on the network.
- How soon will modems disappear? aDSL - perhaps in 15-20 years. But devices that work with mobile Internet - probably never.
- What is better: mobile communication or cable connection? It depends on what cable you mean. If we talk about optical fiber, then this connection is the most reliable.
- What types of modems are there? aDSL, 3G, 4G, LTE, PCE, ZigBee, TNC, DOCSIS, EuroDOCSIS, ISDN. I discussed the most popular ones in the article.
- What does the modem look like? There is no specific design or appearance, but you can see the main prototypes in the article in all the pictures. And so, it can look like anything: in the form of a box or a flash drive. The most important thing is to look at the input interface. It may also have at least one LAN or USB port.
- What is “modem mode” in a phone? This is the most important mistake of the phone creators. The fact is that this mode in no way applies to modems. This mode enables an access point on the phone and it would be more correct to call this mode “router mode” or “router mode”. When you enable this function, the phone starts distributing a Wi-Fi network with the Internet, which other devices can connect to. Read more about the access point here.
If you still have questions, feel free to ask them in the comments, and I will try to answer them. You can also write your additions there.
Selecting, connecting and setting up an ADSL modem
ADSL modems are most often used when connecting to telephone networks.
The cheapest connection option is a modem equipped with a USB interface. Such devices are small in size and easy to set up. Unfortunately, not all computers are compatible with such modems.
Modem with USB interface is easy to use
Modems equipped with an Ethernet port are universal and connect to all computers and laptops. If you intend to use a desktop computer, and there is no need to create an internal Wi-Fi network, it makes sense to choose such a device.
Modems with Wi-Fi are the most popular. They provide for connecting devices both wired and wireless. Such a modem can work as a bridge or router. It provides Internet distribution via Wi-Fi network. These are the kind of multifunctional devices that you should choose for use. The main evaluation criterion when choosing them is the power you need. The price of the modem and the range of the Wi-Fi signal depend on it. Accordingly, for small rooms a cheaper option will suffice; in case of requirements for covering a large area, it is necessary to choose a higher power.
A Wi-Fi modem will help you create a home network
To configure such devices, information from the provider is required - DNS and IP address, PVC, login and password assigned to the subscriber. These parameters are entered manually. Many operators provide a disk with the necessary settings. In such cases, special knowledge and skills are not required to configure the modem.
If the modem has been used before, the best solution would be to reset it to factory settings. This function is mainly used when changing providers or in case of losing the access password.
To return the settings to the default ones:
- Connect the ADSL modem to a power source.
- Find a button or hole (depending on the model) labeled Reset on the modem body.
- Press the button for about 30 seconds.
- If a hole is provided in the device for these purposes, you need to insert a thin metal object such as a paper clip into it and hold it there for some time.
If the manipulations are performed correctly, the device will reboot and return to factory settings.
Directly connecting the modem is done in the following way:
- Connect the modem to the power supply.
- Connect the telephone cable to the modem.
- Connect the Internet cable leading to the computer to the LAN connector.
- If the modem can distribute Wi-Fi, and your device is equipped with a Wi-Fi receiver, you do not need to connect the cable. Find the network on your device and enter the password specified in the instructions for the modem.
- When connected correctly, the network indicator on the modems should blink.
Setting up a modem usually does not raise any questions even for the most inexperienced users if you have an installation disk. Everything happens automatically.
Video: how to set up an ADSL modem
What to look for when choosing a 4G modem for the Internet on a laptop?
Since there are many models, and we only need one modem, and one that can be inserted into a laptop if necessary, and connected to the Internet on a 4G router, before going to the store, you need to think a little about what characteristics need to be taken into account to select the correct LTE modem. We list the main ones:
- The main thing to consider is that the modem supports the 4G standard. Externally, they are no different from the already obsolete 3G, so look carefully at the description of the specification. Even if you don’t have LTE reception yet, the 4G modem will also work with a 3G signal, but you will get a device that will not lose its relevance for several years.
- If you have a router with a USB port, then think about the future that you may have to connect the modem to it, so choose a model that works with your router. To do this, simply go to the router description page on the manufacturer's official website and look at the list of supported devices.
- Finally, it is always useful to have a connector for connecting a 4G antenna for the modem. As we found out, this device is mobile, intended for those who move from place to place, and reception, as you know, is not the same everywhere. If you find yourself in an area where the connection is “not very good,” an external antenna will come in very handy so as not to lose contact with the outside world.
I hope it is now clearer what the purpose of a modem is on a network. And it’s impossible to say which is better - a modem or a router, since these are two completely different devices. I have already talked in detail about connecting and setting up a 4G modem in articles separately about each operator:
- Beeline
- MTS
- >>Megaphone
- >>Tele 2
I am sure you will find useful information for yourself!
Does Internet speed depend on the modem?
In reality, the speed of the device depends on the capabilities of the provider. However, each modem model has its own throughput, which also has a strong impact on this indicator. Estimated throughput capacities are usually indicated in the accompanying documents for the equipment.
But we should not forget about such factors as the number of end consumers using the Internet, or the load on the system with various programs running in the background. In addition, providers do not always provide the declared indicators. Don’t forget to timely optimize your system, update your antivirus software, and periodically clean your computer with utilities such as Glary Utilities.
Of all the variety of existing types and types, the most interesting for ordinary users are modems that provide wireless access to the Internet from anywhere in the signal coverage area. As the capabilities of cellular operators grow, this method of connecting to the network is gaining popularity. Soon, the speed of wireless Internet will be equal to the capabilities provided by high-speed cable connections.
By type of supported networks
This feature only applies to wireless devices. The following types of networks exist: GSM or 2G, 3G, LTE or 4G. All of these networks are backward compatible. In simple terms, 3G will work on the GSM network without any problems. If you wondered what a USB modem is, now you will get the answer. This device is most often created in this form. A flash drive is what this equipment looks like. Its main function is to provide wireless data transmission. It must have a slot for a SIM card. It connects to the computer in a USB slot.
Which modems are the best to buy online and have many advantages?
Being able to have an internet connection is extremely important today because it is a tool that will help you get almost everything you need. To do this, you need to have a high-quality modem that allows you to have a fast and stable connection at any time . Nowadays there are devices that are both a modem and a router , meaning they will also allow you to establish a wireless connection .
Knowing the importance of this type of device, here we will show you which are the best modems today that you can Acheter En Ligne and get to excellent advantages .
Choose the model that convinces you most:
TP Link TD-W2N Wireless Router with ADSL 8960+ Modem
“UPDATE ✅ Do you want to know what is a modem in computer science and how is it different from a wireless router? ⭐ LOG IN HERE ⭐ and find out all about it »
This is a modem router
which will allow users to have
a wireless hotspot with a 4-port router , it offers wireless connection speeds of up to 300Mbps, ideal for developing online games or heavy applications , a way to be able to perform various activities without any interruption.
It also gives you a high-speed connection option called Ethernet Wide Area Network , which allows you to connect via cable, fiber optic modem, or VDSL.
There is also
network access for guests in case of wireless connections .
Cisco DPC3010 modem
The DPC3010 is cable modem currently owned by Cisco, it has one port, 10/100/100 Ethernet speed and 8 x 4 channels. It stands out for its quality as a service provider. of broadband is able to provide a very fast connection through the 8-channel bond offer .
Likewise, it offers speeds above 320 Mbps and data download speeds of up to 120 Mbps, much faster than other devices of the same brand.
SBG6580 - Motorola
Another model that you will find today in most websites, it offers you the possibility of a wireless connection at home, thus offering data and multimedia services high speed in a very innovative way . This device was designed for fluid mobility which can be easily placed anywhere in the house .
This equipment offers 4 ports of 10/100/100 Ethernet speed with advanced firewall switch et 802.11n . That's why this device has become an excellent solution for connecting to a home network , allowing users to create personalized networks with excellent connection speeds , able to share information and files in seconds .
Modem-router AC1600 Archer VR600
AC1600 is a device that stands out mainly because it offers broadband Wi-Fi signal , exceeding 300 Mbps (2.4 GHz) speed and reaching 1300 Mbps (5 GHz) speed , so it becomes an ideal device for such users. those who constantly play online watch streaming programs, for which they download Torrent , among many other actions that require high speed.
In addition, it offers three antennas that undoubtedly improve coverage , each of them is removable and ensures that the signal coverage is always optimal.
How to choose the right 3G or 4G LTE modem for a laptop
When choosing equipment, you need to pay attention to the speed indicators it supports. This approach narrows the search range and allows you not to be distracted by unnecessary models. The equipment is conditionally divided into two categories, with a maximum speed limit:
- up to 3.6 Mbit/s;
- up to 7.2 Mbit/sec.
In addition to the router speed indicators, the user should focus on the following parameters:
- on the price - there are both budget and expensive models;
- package - for advanced users;
- appearance of equipment and software for fine debugging.
For beginners, it is easier to use the simplest equipment that does not require third-party intervention or knowledge to debug it.
Important! Telecom operators ZTE, Megafon, Motiv, Rostelecom, MTS, Beeline most often sell equipment from other companies with their own flash drive firmware.
Types of devices from service providers
The term 'modem' is short for the well-known computer term modulator-demodulator. A modem is a device that converts digital data coming from a computer into analog signals that can be sent over a telephone line. This whole thing is called modulation. The analog signals are then converted back into digital data. This thing is called demodulation.
The scheme is very simple. The modem receives digital information in the form of zeros and ones from the computer's central processor. The modem analyzes this information and converts it into analog signals, which are transmitted through the telephone line. Another modem receives these signals, converts them back into digital data, and sends this data back to the remote computer's central processing unit.
For example, in Windows 98, in the modem settings, there is an option Modulation type,
which allows you to select frequency or pulse modulation. Pulse modulation is used throughout Russia.
Analog and digital signals
Telephone communication is carried out through so-called analog (sound) signals. An analog signal identifies information that is transmitted continuously, while a digital signal identifies only that data that is defined at a specific stage of transmission. The advantage of analog information over digital is the ability to fully represent a continuous flow of information.
On the other hand, digital data is less affected by various types of noise and grinding noises. In computers, data is stored in individual bits, the essence of which is 1 (start) or O (end).
If we represent this whole thing graphically, then analog signals are sine waves, while digital signals are represented as square waves. For example, sound is an analog signal because sound is always changing. Thus, in the process of sending information over the telephone line, the modem receives digital data from the computer and converts it into an analog signal. A second modem at the other end of the line converts these analog signals into raw digital data.
Interfaces
You can use a modem in your computer using one of two interfaces. They are:
MNP-5 Serial interface RS-232.
MNP-5
Four-pin RJ-11 telephone cable.
For example, an external modem is connected to a computer using an RS-232 cable, and to a telephone line using an RJ11 cable.
Data compression
In the process of data transmission, a speed greater than 600 bits per second (bps or bits per second) is required. This is due to the fact that modems must collect bits of information and transmit them further through a more complex analog signal (a very sophisticated circuit). The process of such transmission itself allows for the transmission of many bits of data at the same time. It is clear that computers are more sensitive to transmitted information and therefore perceive it much faster than a modem. This circumstance generates additional modem time, corresponding to those data bits that need to be grouped somehow and certain compression algorithms applied to them. This is how two so-called compression protocols emerged:
MNP-5 (transmission protocol with a compression ratio of 2:1).
V.42bis (transmission protocol with a compression ratio of 4:1).
The MNP-5 protocol is usually used when transferring certain already compressed files, while the V.42bis protocol is applied even to uncompressed files, since it can speed up the transfer of just such data.
It must be said that when transferring files, if the V.42bis protocol is not available at all, then it is best to disable the MNP-5 protocol.
Error Correction
Error correction is a method by which modems test the transmitted information to determine whether it contains any damage that occurred during transmission. The modem breaks this information into small packets called frames. The sending modem attaches a so-called checksum to each of these frames. The receiving modem checks whether the checksum matches the information sent. If not, then the frame is sent again.
Frame is one of the key terms for data transmission. A frame is a basic block of data with a header, information and data attached to this header that complete the frame itself. The added information includes the frame number, transmission block size data, synchronizing symbols, station address, error correction code, variable size data, and so-called Start of Transmission (start bit)/End of Transmission (stop bit) indicators.
This means that a frame is a packet of information that is transmitted as one unit.
For example, in Windows 98, in the modem settings there is an option Stop bits,
which allows you to set the number of stop bits. Stop data bits are one of the varieties of the so-called boundary service bits. The table bit determines the end of the cycle during asynchronous transmission (the time interval between transmitted characters varies) of data in a short-term cycle.
MNP2-4 and V.42 protocols
Although error correction may slow down data transmission on noisy lines, this method provides reliable communication. The MNP2-4 and V.42 protocols are error correction protocols. These protocols determine how modems verify data.
Like data compression protocols, error correction protocols must be supported by both the sending and receiving modems.
Flow Control
During transmission, one modem can send data much faster than another modem can receive the data. The so-called flow control method allows you to inform the receiving modem that the modem will stop receiving data at some point in time. Flow control can be implemented both in software (XON/XOFF - Start signal/Stop signal) and in hardware (RTS/CTS) levels. Flow control at the software level is carried out through the transfer of a specific sign. After the signal is received, another character is transmitted.
For example, in Windows 98, in the modem settings there is an option Data bits,
which allows you to set the information data bits used by the system for the selected serial port. The standard computer character set consists of 256 elements (8 bits). Therefore, the default option is 8. If your modem does not support pseudographics (works only with 128 characters), please indicate this by selecting option 7.
In Windows 98, in the modem settings, there is also an option Use flow control,
which allows you to determine how to implement data exchange. Here you can correct possible errors that occur when transferring data from the computer to the modem. Default setting: XON/XOFF
means that the data flow is controlled by software using standard ASCII control characters, which send the command
to pause/resume
transmission to the modem.
Software flow control is only possible if a serial cable is used. Since flow control at the software level regulates the transmission process by sending certain characters, a failure or even termination of the communication session may occur. This is explained by the fact that this or that noise in the line can generate a completely similar signal.
For example, with software flow control, binary files cannot be transferred because such files may contain control characters.
Through hardware flow control, RTS/CTS transfers information much faster and more securely than through software flow control.
FIFO buffer and UART universal asynchronous interface chips
The FIFO buffer is somewhat similar to a transshipment base: while data arrives at the modem, part of it is sent to the buffer capacity, which gives some gain when switching from one task to another.
For example, the Windows 98 operating system only supports the 16550 series Universal Asynchronous Receiver Transmitter (UART) chips and allows you to manage the FIFO buffer itself. Using the Use FIFO buffers requres 16550 compatible UART
you can lock (prevent the system from accumulating data into the buffer capacity) or unlock (allow the system to accumulate data into the buffer capacity) the FIFO buffer.
Clicking the Advanced
will take you to the
Advanced Connection Settings dialog,
whose options allow you to configure your modem's connection.
S-registers
S-registers are located somewhere inside the modem itself. It is in these very registers that settings are stored that in one way or another can affect the behavior of the modem. There are a lot of registers in the modem, but only the first 12 of them are considered standard registers. The S-registers are set in such a way that they send the ATSN=xx command to the modem,
where N corresponds to the number of the register being set, and xx defines the register itself. For example, through the SO register you can set the number of rings to answer.
Interrupts IRQ
Peripheral devices communicate with the computer processor through so-called IRQ interrupts. Interrupts are signals that force the processor to suspend a particular operation and transfer its execution to the so-called interrupt handler. When the CPU receives an interrupt, it simply suspends the process and delegates the interrupted task to an intermediary program called Interrupt Handler. This whole thing works regardless of whether an error was detected in the operation of a particular process or not.
Information communication port or simply COM port
The serial port is very easy to find out. You can do this by simply looking at the connector. The COM port uses a 25-pin connector with two rows of pins, one of which is longer than the others. At the same time, almost all serial cables have 25-pin connectors on both sides (in other cases, a special adapter is required).
A COM port (serial port) is a port through which computers communicate with devices such as a modem and mouse. Standard personal computers have four serial ports.
COM 1 and COM 2 ports are usually used by a computer as external ports. By default, all four serial ports have two IRQs:
COM 1 is bound to IRQ
4 (3F8-3FF).
COM 2 is tied to IRQ
3 (2F8-2FF).
COM 3 is tied to IRQ 4 (3E8-3FF).
COM 4 is tied to IRQ 3 (2E8-2EF).
This is where conflicts can arise, since external ports of other I/O devices 1/0 or controllers can use the same IRQs.
Therefore, having assigned a COM port or IRQ to the modem, you must check other devices to see if they have
the same serial ports and interrupts.
It must be said that devices connected to the telephone line in parallel to the modem (especially Caller ID) can very significantly degrade* the quality of your modem’s operation. Therefore, it is recommended to connect phones through the dedicated socket in the modem. Only in this case will he disconnect them from the line during operation.
Your modem's flash memory
Flash memory is a read-only memory or PROM (read-only reprogrammable memory) that can be erased and reprogrammed.
All modems that have the string “V.” in their name are subject to reprogramming. Everything." In addition, “Courier V.34 dual standard” modems are subject to software upgrade if in the Options
the response to the ATI7 command contains the V.FC protocol. If the modem does not have this protocol, then the upgrade in “Courier V. Everything” is carried out by replacing the daughter board.
There are two modifications of Courier V. Everything modems - with the so-called supervisor frequency of 20.16 MHz and 25 MHz. Each of them has its own firmware versions, and they are not interchangeable, i.e. The firmware from the 20.16 MHz model will not work for the 25 MHz model, and vice versa.
Field programmable NVRAM
All modem settings come down to correctly setting the values of the NVRAM registers. NVRAM is a user-programmable memory that retains data when the power is turned off. NVRAM is used in modems to store the default configuration that is loaded into RAM when turned on. NVRAM programming is done in any terminal program using AT commands. A complete list of commands can be obtained from the modem documentation, or obtained in a terminal program using the commands AT$ AT&$ ATS$
AT%$.
Write factory settings with hardware data control to NVRAM - AT&F1 command, then make adjustments to configure the modem in conjunction with a specific telephone line and write them to NVRAM using the AT&W command.
Further initialization of the modem must be done through the
ATZ.4 command.
Application software for data transfer
Data transfer programs allow you to connect to other computers, BBS, Internet, Intranet and other information services. You may have a very extensive range of such programs at your disposal. For example, in Windows 98 you have at your disposal a very good terminal client, Hyper Terminal.
If you have problems establishing communication with other modems
First you need to assess the nature of the communication line. To do this, after a successful session, before re-initializing the modem, enter the ATI6
— communication diagnostics,
ATI11
— connection statistics,
ATY16
— amplitude-frequency response.
The received data must be written to a file. After analyzing the received data, it is necessary to make changes to the current configuration and then write them to NVRAM using the AT&W5 command.
Russian telephone lines and imported modems
The choice of modems today is quite large, and the difference in their cost is quite significant. Transmission speeds of more than 28,800 bps are usually unattainable on Russian telephone lines. Above 16,900 bps can only be obtained if the Internet service provider has lines on the PBX to which your phone is connected. In other cases, working on the Internet is too tedious, because at a typical (and not always achievable) speed of 9,600 bps, it becomes a complete wait. Therefore, for stable data transmission in the event of interference in the telephone line, you need a high-quality modem that costs at least $400.
Which modem is better - internal or external?
The internal modem is installed in a free expansion slot on the computer's motherboard and connected to the built-in power supply, while the external modem is a stand-alone device connected to the computer via a standard serial port.
Each of the designs has its own advantages and disadvantages. The internal modem occupies a system bus slot (and, as a rule, there are not enough of them), it is difficult to monitor its operation due to the lack of indicators, and besides, the described models are fundamentally not suitable for notebook-type portable computers that have a narrow-profile case and, in most cases, are not with expansion connectors. At the same time, the internal modem is several tens of dollars cheaper than external analogues, does not take up space on the table and does not create a tangle of wires. Using an external modem means that the computer to which it is connected has the most modern serial port control chips (UART). UART chips appeared in the first PCs, because even then it became clear that data exchange via a serial port was too slow and complicated and it was better to entrust it to a special controller. Since then, several UART models have been released. Computers such as IBM PC and XT, as well as those fully compatible with them, used the 8250 chip; in AT it was replaced by UART 16450. Until recently, most computers based on i386 and i486 processors were equipped with a 16550 controller, which included internal hardware buffers of the “ queue”, and today the UART 16550A is becoming the standard - a chip similar to the previous one, but with the defects eliminated. The lack of buffers in all chips except the last one causes data transfer through the serial port at speeds above 9600 bps to become unstable (using MS Windows reduces this threshold to 2400 bps).
If you need to connect a high-speed external modem to a computer that uses an older UART chip, you must either change the multicard or add a special expansion card (which will take up one bus slot and deprive the external modem of a critical advantage). Internal modems do not have this problem - they do not use a COM port (more precisely, they contain one). Now internal modems have another advantage, also related to speed. According to the V.42bis specification, data can be compressed by approximately four times during transmission, therefore a modem operating at 28800 bps must receive data from or send data to the computer at a speed of 115600 bps, which is the limit for serial PC port. However, 28,800 bps is not the limit for a telephone line, where the maximum lies somewhere in the region of 35,000 bps, and on digital lines (ISDN) the throughput exceeds 60,000 bps. Consequently, in this situation, the serial port will become the “bottleneck” of the entire system, and the potential capabilities of the external modem will not be realized. Modem manufacturers are currently developing models that can connect to a faster parallel port, but it is obvious that devices sold now will not be able to accommodate this.
At the same time, many modems can be upgraded to operate at high speeds, even being able to operate on ISDN. But everything depends on the restrictive barrier on the computer side, which for the internal modem is significantly higher than 4 MB/s (ISA bus bandwidth). By the way, all ISDN modems are internal. True, all this will happen tomorrow (or maybe the day after tomorrow), but today we can say one thing: choose a device of the type that you like - there are no functional differences between internal modems and their external analogues.
Which modem to choose and how to choose it
As you know, the quality of Russian telephone lines leaves much to be desired. The main thing that should worry you when choosing a modem is that the modem not only should, but must improve communication. For we live in Russia. And in this country, as you know, it is cold. Especially in winter. And the water, the infection, gets into the communication wells. The connection deteriorates, the noise level increases, parasitic jitter appears, the phase jumps, finally, the connection is broken, in general, it becomes unpleasant to work. The modem must adapt to such lines, i
The modem cannot be unique. Your modem must be understood by other modems. This means that the modem must support the maximum number of standards, that is, error correction, data exchange methods and data compression. The most common standard is V.32bis for modems with an exchange rate of 14000 bps. For modems with a speed of 28800 bps, the standardized protocol is V.34.
In addition, it must be emphasized that modems with a data exchange rate of 16800, 19200, 21600 or 33600 are not standard.
No error correction should be done in software. Everything must be built into the modem by its manufacturer.
About the outside and the inside. An external modem is connected to your serial port via a special cord. Such a modem, as a rule, has a volume control, information indicators, a power supply and other, sometimes useful accessories. If you are a professional, then you should not care which modem you choose - internal or external. Usually, a good internal modem, through special software, does a good job of emulating all the clarity of an external modem.
Do not buy purely imported modems. These pieces of iron do not get along on our ancient lines. Buy only certified modems, that is, hardware specially tailored for our dirty telephone exchanges.
In Russia, such a choice is very small. This market is dominated by two companies: ZyXEL from sunny Taiwan and US Robotics from the USA. Modems from the latter company are chosen by professionals (Courier), while the former is chosen by everyone else, that is, all those users who choose the so-called ultra-reliable ZyCell protocol.
So, choose Courier. And, believe me, this is not advertising.
If problems arise when connecting the modem to the laptop
Problems with the Internet can be resolved with the help of an employee from the technical support service or by independently searching for the source of the problem. In the latter option, the user must:
- enter the “network connections” block;
- create a new one indicating the “Internet connection” item;
- select manual installation mode;
- identify your modem in the proposed list;
- indicate authorization data for login - they are specified in the agreement with the provider;
- check the boxes next to the items that mention “collection of registration data” - to reduce the frequency of failures;
- create shortcuts on the desktop for the convenience of turning on and off the network.
Important! Correct execution will result in the Internet icon appearing in the tray.
Selecting equipment from the list