Hello everyone, Let's talk about how to find out where the program is on the computer, where it was installed, and generally where it is located. This information is not very useful, you just need to know this information, you never know what can happen, you can always see what is going on inside the folder with the program. Well, this is true, for example, the situations may be different..
This means that in general all programs should create their folders in one system folder, Program Files, so that there is order on the computer. But there are programs that are installed where they see fit, for example, simply on the system drive or in general where programs usually store their settings or service information. Well, I won’t burden you with this information, I’ll just show you how you can find out where the program was installed, I think everything here will be clear to you
So look, here I have Windows 7, let’s imagine that I need to find out where the program was installed and for example I’ll take Mozilla. I have its shortcut on the desktop, I right-click on it and select File Location there:
Then this folder opened:
But how can you find out the folder itself, that is, where Mozilla is installed? Here you need to click once here:
Then you will see the path itself, that is, the folder where you have Mozilla installed:
That is, in my case it was installed in this folder:
C:Program Files (x86)Mozilla Firefox
But it’s clear that this is not the only way to find out where the program is installed. Here is another interesting case, this is Chrome. Here's how you can find out where it was installed: take its shortcut, right-click on it and select Properties:
Well, the Properties window has opened, look what it says:
Do you see there is such a thing as a Working Folder? This is the folder where the program is installed, well, in our case it’s Chrome. As you can see, everything is also simple! By the way, here you can also click on File Location and the folder where the program is installed will immediately open to you. This applies to all shortcuts, not just Chrome
So, what else should I show you? It may be that you have the program in the Start menu, then there you go, right-click and select Properties, and then look there.
In general, roughly speaking, the programs should be placed in this folder:
Well, or if you have 64-bit Windows, this can also be placed here:
C:Program Files (x86)
But some programs are still not installed here and I don’t quite understand why. There is Yandex Browser, it is generally placed in this folder:
Where VirtMachine is, this is the name of the computer, that is, the name of the account. Well, why Yandex Browser is installed there, it’s not entirely clear to me..
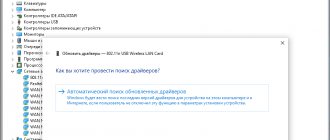
And sometimes there is a situation where you have some program running and you need to find out in which folder this program is installed. It was so? Well, if it wasn’t, then maybe it will be, so look at what you need to do here to find out this folder. Let's imagine that our program is uTorrent. First we need to open the Task Manager, to do this, right-click on the taskbar and select this item there:
Then we look, yeah, here you can see on the Applications tab that the uTorrent program is running, here you right-click on it and select Go to process:
The Processes tab will open, here you will now see the process under which the program is running. In my case, this is the uTorrent.exe process, and to find out where it started from, right-click on it and select Open file storage location:
And that’s it, after this the folder where the uTorrent program is installed will open:
That is, finding out where the program is installed, then as you can see, this is not a difficult task
As a last resort, well, as a last resort, you can still do this. For example, you need to find out where the uTorrent program is located, in general, find out all the places where it is located. To do this, you open the system drive and there in the upper right corner there is a field for entering a word, well, this is for searching, that’s where you write the word utorrent and wait. Then you will have search results, well, something like this will be:
To disk (C:)
By default, all programs are installed on the system drive. The drive on which the system is installed is usually (C:). You can make sure exactly which drive programs are installed on by following simple steps.
Open the Computer section from the desktop icon:
And look at your disks in the window that opens. The system disk usually has a special Windows icon and a corresponding name.
Open the system partition and see one or two folders Program Files. It is in them that almost all programs are installed by default.
Application systems
Routers
- CatOS from Cisco
- iOS from Cisco
- Cisco PIX from Cisco
- freesco is a free and open replacement for commercial routers (in particular from Cisco), supporting up to 10 Ethernet/ARCnet/Token Ring/Arlan network cards and up to 10 modems.
- Huawei VRP from Huawei
- IOS XR from Cisco based on QNX
- JUNOS from Juniper Networks
- LinkBuilder from 3Com
- MikroTik RouterOS from MikroTik
- RapidOS from Riverstone Networks
- ScreenOS from Juniper Networks
- SeOS from Ericsson
- SROS from Alcatel-Lucent
- ZyNOS from ZyXEL
For microcontrollers, embedded and real-time OS
- AMXOS KADAK
- Contiki (Atmel AVR supported)
- eCos
- FreeRTOS
- Integrity
- ITRON
- LynxOS
- Montavista Linux
- Nucleus
- QNX
- OS-9 - from Microware
- OS-9000 - from Microware
- OSA - for PIC (Microchip) and AVR (Atmel) microcontrollers
- OSE from ENEA
- OSEK
- RDOS
- RTEMS - the initial development was carried out by order of the US Department of Defense, now free (GPL-like license).
- RTOS
- ThreadX
- TRON OS developer - Ken Sakamura
- uC/OS-II for microcontrollers
- uOS developer - Sergey Vakulenko
- scmRTOS - for microcontrollers
- μClinux
- VxWorks
- Snake OS
- Salvo - for microcontrollers
Other cases!
In some cases, when installing a program, at first glance it is impossible to select the program folder manually. But most often there is a button or checkbox “Open advanced settings”! It is with the help of this function that you can change the folder or at least see and remember where the program was installed !
I hope you have figured out the folders where your programs are stored. Good luck!
Created: 02/07/2015 Added by: Sergey
If you want to know where a program was installed
, then this article will help you. Here I will describe in several paragraphs where programs are usually installed and how to find these folders.
Where was the program installed?
How to view installed programs on any Windows
Search tools through the Start menu are available in any modern version of Windows. The “Control Panel” with the components installed in the system is also available everywhere. Removing software using the tool described above allows you to quickly and easily get rid of unnecessary “garbage” and files.
Installing and removing programs in the Control Panel
Windows 10 Power Options - How to Find and Open the Menu
The best way to uninstall applications in all versions of Windows is the “Control Panel”, or rather its separate utility “Software and Components”. Instructions for working with it look like this:
- Go to the Start menu.
- Find “Control Panel” in the search bar and select the desired window.
- Change the display mode to “Small icons” and look for “Programs and Features”.
- View the list of all applications and double-click on the item that should be deleted. This can also be done by clicking the right mouse button.
Important! Sometimes when you launch the “Control Panel”, instead of the “Programs and Features” item, you can only see “Applications”. In this case, you should click on this item and select the link leading to the deletion window.
All applications in Windows 10 in one list
How to view programs through System Settings on Windows 10
You can also get to the desired utility using “Settings” - the second “Control Panel” that appeared in Windows 10. This utility helps systematize the search for important settings and has a more pleasant and updated interface. To search and delete applications in Windows 10 through “Options” you need to:
- Click on the Start menu and select the gear icon. You can also press Win + I.
- Wait for the utility window to load.
- Select “Applications” on the left side of the window.
- View all installed software components and information about them. They can be removed if desired.
This is a faster and more convenient method, as it allows you to see all installed applications, their size and installation date. To delete an item, just select it and click on the “Delete” pop-up button.
To disk (C:)
By default, all programs are installed on the system drive. The drive on which the system is installed is usually (C:). You can make sure exactly which drive programs are installed on by following simple steps.
Open the Computer section from the desktop icon:
And look at your disks in the window that opens. The system drive usually has a special Windows icon
and the corresponding name.
Open the system partition and see one or two folders Program Files. It is in them that almost all programs are installed by default.
How to find out the list of running processes from Power Shell
Information from a file obtained in a similar way will be a little more informative. This option is available to owners of copies of Windows 7/10, and the cmdlet for displaying the list on the same Desktop will be like this:
for a local copy of Windows:
- Handles – the number of threads that the process has opened for itself.
- NPM(K) is the size of the nonpaged memory pool used by the process, in kilobytes.
- PM(K) – size of the paged memory pool used by the process, in kilobytes.
- WS(K) – size of the process’s working set, in kilobytes. It consists of memory pages accessed by the process in the current session.
- VM(M) – the amount of RAM occupied by the process, in megabytes (including pafefile ).
- CPU(s) – time in seconds spent by all processor stones.
- ID – PID of the specified process.
- ProcessName – Process name.
Other cases!
In some cases, at first glance it is impossible to select the program folder manually. But most often there is a button or checkbox “ Open advanced settings”
"!
It is with the help of this function that you can change the folder or at least see and remember where the program was installed
!
I hope you have figured out the folders where your programs are stored. Good luck
!
Hello! For an inexperienced user, it is not so easy to find this or that program on your computer. A shortcut on the desktop will not show you the location of the program, but will only launch the program itself. And it happens that the program does not create a shortcut on the desktop at all and you may not even know about the existence of this or that program on your computer. Today I will show you how easy it is to search for programs on your computer and show you where all the programs are located on a Windows 10 computer, and indeed on any Windows computer.
Links
- Operating systems in the Open Directory Project (dmoz) link directory
- ALT Linux (Simply Linux)
- AlfaOS
- Astra Linux
- Calculate Linux
- LinuxWizard
- PuppyRus Linux
- RedOS
- Rosa Linux
- RunOS
- Russian Fedora
- MSVSphere
- NauLinux
- Raidix
- Kraftway Terminal Linux
- WTware
- Ulyanovsk.BSD
- Stopped projects: AgiliaLinux
- ASPLinux
- EduMandriva
- InfraLinux
- Linux XP
- MOPSLinux
- VS School Linux
- BKUNIX
- Express OS
- Kolibri
- MagOS Linux
- Matuntu
- Runtu
- Stopped projects: Miraculix
- Phantom
- Embox
- Jet OS
- Kaspersky OS
- RelMK-653
- Zarya-RV
- MOS-OP
- Neutrino
- KPDA.00002-01 (QNX)
- os2000 (Baguette 2.x)
- os3000 (Baguette 3.x)
- Baguette 4.x
- POK
- EOS
- PTS-DOS (DOS-Baguette)
- Atlix
- gosLinux (TD OS AIS FSSP of Russia)
- Zarya
- INTROS V/VM
- WSWS
- ZOS Olivia
- HOMONYM
- OS (OS-RT)
- Dawn
- RoMOS
- Synergy 1.0
- Synthesis-OS
- Foros
- Zircon
- Elbrus (OS_E90
- OSL)
- Janux
- CROS-SCADA
- Ivan OS
Mobile: Sailfish Mobile OS RUS on android: Yandex.Kit Taiga YOTA OS 3.0 on tizen: Z3, elvees-salut
| Distributions | Amateur | Historical | RTOS | Special | ||
| For servers or workstations | Unix-like | Not Unix-like | ||||
| Built-in | ||||||
| Other | ||||||
In the work of an administrator, there is often a need to check whether a certain program is installed on a certain computer on the network and what version it is. For example, you can check to see if an important Windows update is installed or if all workstations have the correct version of Office. How to do this using CMD command files (BAT) or scripts (using VBScript as an example) is described below. The idea is based on the fact that information about installed programs is located in the system registry at: HKLM\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Uninstall\
The specified registry hive lists only programs installed "for all users", and programs "for this user" are listed in the hive: HKCU\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Uninstall
In Windows x64, the list of programs is also saved in the registry folder: HKLM\SOFTWARE\Wow6432Node\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Uninstall
Accordingly, to obtain a complete list you will need to scan information from all three branches of the registry.
For example, in VBScript:
Const HKLM = &H80000002 'HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE strComputer = "computer" strKey = "SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Uninstall\" strEntry1a = "DisplayName" strEntry1b = "QuietDisplayName" strEntry2 = "InstallDate" strEntry3 = "VersionMajor" strEntry 4 = "VersionMinor" strEntry5 = "EstimatedSize" Set objReg = GetObject("winmgmts://" & strComputer & _ "/root/default:StdRegProv") objReg.EnumKey HKLM, strKey, arrSubkeys WScript.Echo "Installed Applications (" & strComputer & ") " & VbCrLf For Each strSubkey In arrSubkeys intRet1 = objReg.GetStringValue(HKLM, strKey & strSubkey, _ strEntry1a, strValue1) If intRet1 <> 0 Then objReg.GetStringValue HKLM, strKey & strSubkey, _ strEntry1b, strValue1 End If If strValue 1 <> "" Then WScript.Echo VbCrLf & "Display Name: " & strValue1 End If objReg.GetStringValue HKLM, strKey & strSubkey, _ strEntry2, strValue2 If strValue2 <> "" Then WScript.Echo "Install Date: " & strValue2 End If objReg .GetDWORDValue HKLM, strKey & strSubkey, _ strEntry3, intValue3 objReg.GetDWORDValue HKLM, strKey & strSubkey, _ strEntry4, intValue4 If intValue3 <> "" Then WScript.Echo "Version: " & intValue3 & "." & intValue4 End If objReg.GetDWORDValue HKLM, strKey & strSubkey, _ strEntry5, intValue5 If intValue5 <> "" Then WScript.Echo "Estimated Size: " & Round(intValue5/1024, 3) & " megabytes" End If Next
The script connects to a computer with the network name strComputer, looks at the registry key SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Uninstall\ and displays information about programs.
Similar actions can be performed in a CMD command file. This batch file produces a list of programs:
@echo off rem This batch file records a list of programs installed on a rem remote computer. rem %1 The network name of the computer in PCNAME format (an empty value means rem is a local computer). rem Determine the path to the registry folder set reg_key=hklm\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Uninstall if not “%1” == “” set reg_key=\\%~1\%reg_key% rem Enumerate installed programs for /F “ tokens=1,2,*" %%a in ('reg query "%reg_key%" /s') do ^ if "%%a" == "DisplayName" echo %%c
To check whether a specific program (by name) is installed on any one computer, you can use the following batch file check-app-pc.cmd
@echo off rem This batch file checks whether the specified program is installed on the remote computer. rem %1 The full name of the program or part of the name, for example, KB2570791. rem %2 The network name of the computer in PCNAME format (an empty value means rem is a local computer). rem Return codes: rem 0 The program is installed. rem 2 Program not found. rem 87 Error in parameters. set app_name=%1 set pc_name=%2 rem Check if call apps.cmd is in the list %2 | findstr /i "%~1" if errorlevel 1 echo '%~1' program not found && exit /b 2 echo '%~1' program installed. && exit /b 0
Accordingly, the check-app-pc.cmd KB2570791 ws_alex command will check whether the KB2570791 update is installed on the WS_ALEX computer. Now you can automate the work of this batch file by adding a scan of more computers to the list. To do this, create a command file check-app-pclist.cmd with a loop that iterates through the lines of a text file with network names of computers.
@echo off rem %1 Full program name or part of the program name. rem %2 Name of a file containing a list of computers. rem Note: This batch file uses check-app-pclist.cmd if "%~1" == "" exit /b 87 if not exist %2 exit /b 2 for /F %%a in (%2) do ( echo %%a… call check-app-pc.cmd %1 %%a )
Example pc.list file list
Fixing search parameters
Users usually need to use the same search parameters. In Windows 7, there is a convenient option for saving them in order to eliminate the time wasted on re-entering them in the future.
For this purpose, it is enough to specify the necessary parameters once and, having received the result, click “Save conditions”. Next, a menu will be displayed in which you should type the name of the request and click “Save”.
During the next search with similar parameters, the user will only need to enter the “Favorites” section and click on the previously specified name of the request.
Using a special search interface "Windows 7"
Of course, the relevance of this method has almost completely disappeared after specialists from Microsoft introduced a search field directly in the start menu, but knowing about its capabilities will be useful for any owner of a computer running a “Seven”.
The following sequential steps are required:
- While holding “WIN”, click on “F”;
- In addition to all the functions mentioned above in the previous method, the menu that appears allows you to additionally apply convenient filtering of the search query.
Safety when downloading some files
So, the system may issue a warning about the safety of opening files with the .exe
:
Since there are pests that distribute programs containing viruses, etc., the system warns us to download such files only from sites we trust.
About security on the Internet, this is a separate topic for conversation, but if you want, you can read about it by clicking on the link provided in the window: How to determine which program can be run?
Naturally, I personally have no reason to spread viruses. So, if you trust me and my site, you can agree and run the file without any problems. But, to be on the safe side, you can always additionally check any files or any website, for example, using the Dr.Web online scanner.
If you need to check the site, then choose: URoLog Dr.Web
.
If you need to check a file, then choose: Dr.Web File Pathologist.
Those. download the file, but without running it yet, upload it for checking into the Dr.Web scanner using the Browse
and click on
Check
. You wait a little and get the result of checking whether the file is safe or not:
How to configure search parameters
The following steps need to be taken:
- Click “Start”;
- In the search column, type “search parameters”;
- Click on the line “Change search parameters...”;
- Next, in the window that appears, go to the “search” tab and check the box required by the user;
- You can then mark the parameters of interest;
- After completing the settings, you must click “Apply” to save the adjustments made;
- Click “Ok”;
- Done, setup complete.