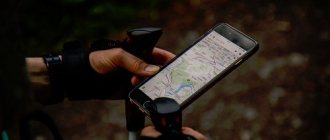
Increasingly, in the characteristics of the communication capabilities of smartphones, one can find mention of BeiDou or BDS in the “navigation” column. Therefore, uninitiated users have a question about what exactly this function is and what opportunities it provides to the owner of the device. Many people are also interested in which devices have Beidou, whether this function works in Europe and how to use it.
Beidou is a Chinese combined navigation system. Commissioning began in 2000. It is named after the Chinese name for the constellation Ursa Major. The system is designed to become a competitor to the American GPS and Russian GLONASS. Like its rivals, it is a dual-use system, intended primarily for the military, but also available to civilian users. At present (beginning of 2022), the system is not yet on a global scale, since it does not cover the entire earth’s surface. The Chinese plan to achieve this goal in 2022.
Getting to know Beidou
So, you bought a brand new gadget. Among other things, in its technical characteristics you will find: support for the Beidou satellite system. Sometimes in the section devoted to navigation parameters, it is also called the abbreviation BDS. But what is it?
"Beidou" is a navigation system of Chinese origin. Similar to American GPS and domestic GLONASS. Named after the constellation Ursa Major. It is not so new - it was launched in test mode back in 2000. However, it took the inventors more than a decade to develop it to its modern state. A circle of Chinese users learned what Beidou is in a smartphone only in 2012.
"Beidou" is a navigation system not only for civilian, but also for military purposes. According to tests conducted in 2014, its greatest error is only 1 meter!
Operating principle
To understand in more detail what it is in the Beidou smartphone, a brief introduction to the operating principles of the system will help us. They are, in general, the same as those of GLONASS and GPS.
The whole system consists of two structures:
- Space - several satellites rotating in near-planetary orbits.
- Ground - stations on Earth that increase the accuracy of navigation and the speed of the entire system.
How is location determined in Beidou? It’s very simple - by measuring the time it takes a radio wave to travel from the receiver (in your case, a smartphone, tablet, car or tourist navigator) to a satellite or ground tower. It should be noted that before indicating where you are, Beidou will check information from 3 sources.
Radio wave measurements are used because its speed is static - always equal to the speed of light.
How many episodes are there in Galileo?
Galileo (TV show)
| Galileo | |
| Language | Russian |
| Number of seasons | 14 (1) 2 (2) |
| Number of issues | 1084 (1) 29 (as of 04/15/2021) (2) |
| Production | |
Interesting materials:
Where is the SSD installed? Where is TLauncher installed? Where is Python installed? Where can I get a job with a diploma in international relations? Where to dispose of mercury from a broken thermometer? Where to dispose of a mercury thermometer in Odessa? Where does Viber save Android documents? Where to hang a rag in the kitchen? Where to insert JavaScript? Where is the catheter inserted in women?
"Beidou" today
Having learned what it is in a smartphone - Beidou, the reader will ask a logical question: “Will the Chinese navigation system replace the usual GPS and GLONASS in the near future?” As for this year, Beidou is not a full-fledged competitor of these systems. After all, most of its ground-based towers are concentrated only on Chinese lands.
But if we look at a number of Asian countries (China itself, Thailand, Laos, Brunei), then BeiDou and GPS navigation are popular there at the same level. In addition, Beidou intends to expand.
It is known that in 2013, a tower of this system was installed in Pakistan. The authorities of this country fear that in the event of a conflict with the United States, they may be left without navigation at all. Therefore, we gladly responded to the proposal of the Chinese developers. In 2015, the first station was installed in Europe - in Belgium.
As for our country, will BeiDou be useful in a smartphone? For the most part, no, because her work is unstable. Without ground towers, relying only on space satellites, it is difficult for a navigation system to show the exact location of the receiver. After all, the fact is that satellites do not stay above Russian territory all the time, but revolve around the Earth.
History [edit | edit code]
The Chinese National Space Administration plans to deploy the BeiDou navigation system in three stages [7].
- 2000–2003: Experimental Beidou system of three satellites.
- by 2012: Regional system to cover China and surrounding areas.
- by 2022: Global navigation system.
Beidou-1 [edit | edit code ]
The first satellite, Beidou-1A, was launched on October 30, 2000. The second, "Beidou-1B", - December 20, 2000. The third satellite, "Beidou-1C", was sent into orbit on May 25, 2003 [8] [9]. The system was considered put into operation with the successful launch of the third satellite.
On November 2, 2006, China announced that Beidou would offer open services with a location accuracy of 10 meters from 2008 [10]. Beidou system frequency: 2491.75 MHz.
On February 27, 2007, the fourth satellite of Beidou-1, sometimes called Beidou-1D and sometimes called Beidou-2A, was also launched. It served as a safety net in case one of the previously launched satellites failed [11]. It was reported that the satellite had problems with its control system, but these were subsequently corrected [12] [13].
Beidou-2 [edit | edit code ]
In April 2007, the first satellite of the Beidou-2 constellation, named Compass-M1, was successfully launched into orbit. This satellite is a tuning satellite for Beidou-2 frequencies. The second satellite, Compass-G2, was launched on April 15, 2009 [14]. The third (“Compass-G1”) was launched into orbit by the Changzheng-3C carrier on January 17, 2010 [15]. The fourth satellite was launched on June 2, 2010 [16]. The Changzheng-3A launch vehicle launched the fourth satellite from the Xichang satellite site on August 1, 2010 [17].
On February 24, 2011, 6 operational satellites were deployed, 4 of them are visible in Moscow: COMPASS-G3, COMPASS-IGSO1, COMPASS-IGSO2 and COMPASS-M1.
According to some sources, at the beginning of 2011, the State Council of the People's Republic of China reviewed the system architecture and made adjustments to the spacecraft launch plan. It was decided to complete the formation of an orbital constellation to serve the regional consumer by the beginning of 2013. According to the adjusted schedule, the Compass/Beidou system constellation by the beginning of 2013 will include 14 spacecraft, including: 5 satellites in geostationary orbit (58.5°E, 80°E, 110.5° E, 140°E, 160°E); 5 satellites in inclined geosynchronous orbit (altitude 36,000 km, inclination 55°, 118° E); 4 satellites in medium-Earth orbit (altitude 21,500 km, inclination 55°).
On December 27, 2011, Beidou was launched in test mode, covering the territory of China and adjacent areas.
On December 27, 2012, the system was launched into commercial operation as a regional positioning system, with a satellite constellation of 16 satellites.
On May 8, 2014, the system underwent expert testing, during which it was found that in the Tianjin city area, the accuracy was less than 1 meter thanks to the newly built ground correction station. [18] .
Beidou-3 [edit | edit code ]
It is planned to deploy a global navigation system consisting of 35 spacecraft by 2022 (according to other sources - 36 spacecraft, according to third sources - 37 spacecraft), including: 5 satellites in geostationary orbit; 3 satellites in inclined geosynchronous orbit; 27 satellites in medium Earth orbit; several additional satellites may form an orbital reserve [2] [19].
5 geostationary satellites ( Be >[2] .
27 satellites ( Be >YZ-1 [en]; 2 satellites each using the Changzheng-3B launch vehicle and YZ-1 upper stage; and 4 satellites at a time using the future Changzheng-5 launch vehicle and YZ upper stage -2 [2] .
In 2015, the first satellites of the new generation were launched: 2 into medium Earth orbit (BDS M1-S and BDS M2-S) and 2 into inclined geosynchronous orbit (BDS I1-S and BDS I2-S).
The future of Beidou
If we look at measurements taken last year, 2022, we will see that the signal from six Beidou satellites in Eastern Europe is already quite stable. Research also confirms that in the Baltic states, European Russia, Ukraine and Belarus, Beidou is currently working quite well.
The developers themselves assure users that by 2022 their brainchild will become a worthy replacement for the usual GPS. This will happen due to an increase in coverage area - the number of space satellites is planned to increase to 35 units. In addition, since November 2022, the Chinese began to launch into orbit devices with improved characteristics in many respects - Beidou-3.
As for you and me, it is very likely that Beidou will replace the good old GPS in our smartphones in a couple of years. After all, it is already known that since 2015, the possibility of a mutually beneficial exchange has been negotiated between Russia and China: the neighbors will install 3 Beidou ground stations on the territory of our country, and 3 towers of the domestic GLONASS will operate on their lands.
General principles
BEIDOU consists of several interconnected objects:
- groups of spacecraft catching special signals;
- ground control base;
- user navigation devices;
- ground radio beacons;
- radio systems for making corrections and increasing the accuracy of coordinates.
The Chinese State Tax Service BeiDou is managed by the Center in the Chinese city of Xi'an. The time scale is provided by the Universal Global Time control center in Beijing. The ground complex consists of a centralized network of unsolicited measurement stations scattered throughout China.
Regional services are provided to countries in Southeast Asia and offshore facilities in the Pacific Ocean. Provides operation of 24 navigation satellites. The frequency range of operation is regulated taking into account interaction with Russian, European and American GNSs.
Which smartphones support BeiDou?
Today, owners of those gadgets that were released primarily for the Chinese market can appreciate what it is in the Beidou smartphone. Among the world's major flagships, Samsung can be distinguished.
We also list the world-famous smartphone models that support the BeiDou module:
- Meizu M6 Note is a Chinese novelty that is gaining popularity around the world and is collecting a lot of positive reviews from experts.
- Samsung Galaxy Note 8 is the most modern and functional model from the South Korean manufacturer, supporting the S Pen stylus.
- Nokia 8 is a symbol of the revival of the legendary corporation, a metal camera phone with Carl Zeiss optics.
- Xiaomi Redmi 4A is the most affordable of all the devices listed in the list, which also supports BeiDou (its cost today does not go above the 5 thousand rubles level).
- Huawei P10 is an excellent model that, in addition to supporting the new navigation module, is known as an excellent camera phone with Leica technologies.
Does my smartphone support Beidou?
If you want to check whether your gadget supports BeiDou, then it’s easy to do - download the AndroiTS GPS Test application. Go to the list with satellites. If there are points with red flags (as China’s satellites note), then we can talk about support for the Beidou smartphone.
Beidou (we've covered what it is in a smartphone) is an actively expanding navigation system that is already supported by a number of popular Chinese smartphones. Perhaps in a few years it will become a full-fledged replacement for GPS both in Russia and in the world.
How does the GLONASS system work in a car?
Essentially, this is a mobile phone with a navigation system that determines the current coordinates of the car according to the GLONASS
. ... In the event of an accident, the system itself sends a message about the accident to the control center. And from there, emergency vehicles are called to the scene.
Interesting materials:
How to set a song to a contact on a Samsung? How to install a Russian keyboard on Samsung? How to set a ringtone on a smartphone? How to install new applications on an old iPad? How to install applications on an old iPad? How to install a fork player on an LG TV? How to install invisible on WhatsApp? How to find recently installed programs? How to find an installed game on Steam? How to find an installed program on your computer?