The use of third-party utilities to configure Windows has long become a tradition among users, but it would be worth knowing that many parameters of the operating system can be configured using its own tools, without resorting to third-party and sometimes paid tools. What is the cost of PowerShell alone along with the command line. However, today we will talk not about them, but about MSConfig - a wonderful standard utility in many respects, designed to manage automatically launched processes and the Windows boot procedure.
Currently, the MSConfig utility is used mainly when carrying out various types of diagnostic work.
The tool itself is not a diagnostic tool; it allows you to sequentially disable services, minor drivers and startup items, eliminating their potentially negative impact on the operation of Windows and thus helping to identify the culprit of the problem. Another example of using MSConfig is enabling Windows safe mode, which is also used for diagnostic and repair work.
Less commonly, the utility is used to test the operation of the operating system and software when provided with a limited amount of processor and RAM resources. In addition, MSConfig can serve as a tool for managing boot priorities of multiple operating systems if they are installed on the same computer. Finally, MSConfig can be used as a sort of launcher to launch some administration tools.
But first things first.
A little history
MSConfig first appeared in Windows 98 as a tool for managing boot modes and services and applications that start when the operating system starts. For some reason, Microsoft developers decided to remove it in Windows 2000, but in XP they returned it to its place where it remains to this day. In Windows 98, MSConfig was significantly different from the configuration tool that is now available in Windows 10. Since earlier versions of the system did not yet have a registry, and settings were stored in configuration files, MSConfig included tabs of the same name that provided access to these files.
For example, by switching to the System.ini , the user could configure the loading of services and drivers specified in the system.ini file; similarly, access to system settings was provided from the Win.ini , Config.sys and Autoexec.bat . Access to startup objects was provided on the Startup , and access to Windows boot modes was provided on the “General” , and only with the transfer of system settings to the registry did the tabs receive names corresponding to the settings. After that, MSConfig remained almost unchanged, if you do not take into account the appearance of the window and the Startup , the tools of which were moved to the Task Manager in Windows 8.
MSConfig on Windows 10
In Windows 10, the MSConfig utility is an exact copy of itself in Windows 8.1. Its executable file msconfig.exe is located in the System32 ; you can launch it in different ways - with the same command from the “Run” .
- All about the System Configuration application in Windows
From the command line and PowerShell.
From the Explorer address bar.
Through the classic control panel "Administrative Tools" , as well as through system search.
The utility's small window contains five tabs: General , Download , Services , Startup and Service . The fourth Startup tab in Windows 10 does not contain any options except for a link to the Task Manager.
- What is the purpose of the msconfig command in Windows 10?
This is a kind of rudiment and, most likely, the tab will be removed in future versions.
MSConfig - General
“General” tab determine the operating system startup mode.
There are three modes in total:
• Normal startup - Standard startup of the operating system, loading with all services and startup items, including potentially unsafe ones. Active by default.
• Diagnostic startup - In this “clean” mode, Windows 10 starts without third-party services, programs, startup items and drivers. Used to remove dubious software that cannot be uninstalled during normal operation, as well as to gain access to key administration tools that for some reason were inaccessible.
• Selective launch - Essentially the same as diagnostic launch, only with the possibility of more flexible settings. So, you can choose which set of modules that start with Windows should be disabled and which not. Startup items, system services, and an alternative bootloader configuration are available for selective shutdown in this mode. The last item is enabled by default and cannot be controlled. It is activated only if you change the boot configuration on the second tab - very convenient when you need to quickly restore the default system boot parameters.
MSConfig - Loading
Perhaps the most interesting tab in the MSConfig snap-in. By switching to it, at the top of the window you will see at least one entry containing the name of the installed system. If you have multiple versions of Windows installed, the number of entries will be appropriate. You can manage bootloader entries by selecting one of the systems as the default boot. In addition to providing a list of Windows installed on one computer, its tools allow you to manage boot options - boot the system in safe mode.
There are four options to choose from.
- 7 ways to open Advanced startup options in Windows 10.
• “Minimal boot” option ensures safe mode with network drivers and startup items disabled, but with a full graphical interface.
• If you select the "Other shell" , then the only available management tool in Windows 10 will be the command line. The Internet will not work the same.
• Active Directory Restore option boots the system in normal safe mode with the GUI and Active Directory Services. Used mainly by system administrators when solving problems in a network environment.
• Finally, the Network boots Windows 10 in Safe Mode with a GUI and Internet connectivity.
Also pay attention to the block of parameters “No GUI” , “Boot Log” , “Basic Video” and “OS Information” . They are not directly related to safe mode and are used as additional settings.
• Without GUI - Used when debugging the system. The Welcome screen does not appear when Windows boots.
• Boot log - If you enable this option, information about drivers and services running along with the operating system will be recorded in the ntbtlog.txt log, usually saved in the Windows root folder. Used when you need to find out which startup driver or service failed.
• Basic Video - This option loads only the standard Microsoft video driver. It will come in handy if for some reason your native video card driver has crashed.
• OS information - Used in conjunction with “Without GUI” , displays a list of loaded drivers during the boot process.
• Timeout - A separate parameter that allows you to set the period of time during which the list of systems installed next to the main Windows system will be displayed on the boot screen.
On the same tab there is a button “Advanced boot options” , which opens settings for testing OS boot under non-standard conditions. For example, you can try to boot Windows 10 with a limited number of processor cores and RAM, ignore the BIOS “recommendations” that the OS follows when loading, and even test a newly developed driver for a new device.
And so, by and large, you don’t need these functions, since changing the amount of allocated resources will not affect the loading speed in any way, as for blocking PCI and other options, playing with them can lead to a system crash or freeze.
MSConfig - Services
Everything is much simpler here. On this tab, you can disable all or some third-party and system services. Sequential shutdown of services is used as part of diagnostics, allowing you to identify the culprit of problems in the operation of the operating system. “Services” partially duplicate the functionality of the “General” , which you can verify by disabling any service - the launch option on the “General” tab will automatically switch to “Selective startup” .
MSConfig - Service
An additional tab containing a list of commands for launching the most commonly used administration tools. Here you will find options to launch the command line, registry editor, system restore, different monitors and other goodies.
You don’t need to enter anything manually, just select the required element and press the “Launch” .
Bottom line
By and large, this is all you need to know about this useful tool. The MSConfig utility is very convenient when you need to boot Windows in safe mode, quickly disable components that load with the operating system, or launch some system snap-in. As for security, it is unlikely to harm the system with its “help”, therefore, after familiarizing yourself with the basic functions, the utility can be used even by novice users.
Windows comes with many built-in tools for managing your computer and operating system. One of them is the System Configuration module. This environment is designed to manage startup programs, computer startup options, services, and much more.
Msconfig won't start
Causes of failures and solutions to problems running Msconfig:
- First you need to check the system for malicious files. For a quick check, it is recommended to use the Dr.Web Cureit utility. Due to exposure to viruses, some components may be damaged;
- checking availability of access rights. In situations where the user is logged in as a Guest, msconfig may throw an error. It is better to try to log in under the “Administrator” account to remove restrictions on the use of certain OS elements;
- start the system in safe mode , and open the utility again, if the problem persists, this is due to damage to the executable file. You can fix the problem by restoring using a bootable LiveCD. You must insert the disk into the drive and follow the instructions of the recovery wizard;
- checking the integrity of the files . Launch a command prompt with administrator rights and enter the command “sfc /scannow”. This command will scan and restore damaged elements;
- let's check the registry. Launch “Run” with the key combination “Win+R” and enter the command “regedit” in the field:
open the tree and move along the following path [HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\App Paths\MSCONFIG.EXE] and check the default values, it should be like in the screenshot. - then go to the [HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\App Paths\HELPCTR.EXE] section and also check the default file path.
What is MSConfig and what is this module for?
MSConfig, or “System Configuration” (CS), is an environment for configuring the most important components of Windows. The CS is responsible for the operating system startup modes, startup applications at startup, and the operation of services. The configuration can also be used to launch some system applications, such as the command line, the Computer Management environment, the troubleshooting module, and others. MSConfig also allows you to manage different operating systems, the order in which they are launched, and even the removal of one version of Windows if there are several installed on your computer.
Third option
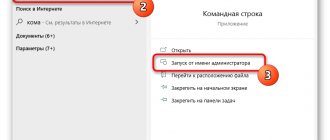
Each subsequent method contains more actions. You can run the Msconfig application on your computer from the command line. To do this, you need to go to the control panel through the “Start” button, select the “All Programs” line, click on “Accessories” - the “Command Prompt” will be there. Click on it and see a black window with a blinking horizontal line. We enter the “msconfig” command and the required utility starts.
In the command line window, it is appropriate to use only English letters - the Russian language is not used here.
The command line will not close - it can be used to activate other programs, configure the OS, etc. To do this, you need to know a large list of commands, and all of them must be written correctly, otherwise they will not be executed.
How to enter System Configuration in Windows 10
Like any important system control, MSConfig has several launch options.
Consider the following options for logging into MSConfig:
- using the Run utility or the command line console;
- through Windows 10 Explorer;
- via "Search";
- via the Start menu.
Sign in using Run or the Command Prompt console
The standard Run utility, like Command Prompt, are executable Windows programs and can launch internal system processes at the user's request.
To run MSConfig through the Run utility, do the following:
- In the Windows search bar, enter “Run” and select the most suitable option found. In the Windows search bar, enter “Run” and select the most appropriate option
- In the window that opens, enter the MSConfig line and click OK. In the “Run” window, enter MSConfig and click OK
In the same way, open “Configuration” through the command line console.
- Enter CMD in the search bar and select the most suitable option. Enter CMD in the search bar and select the appropriate option
- In the command line console window, type the msconfig command and run it with the Enter key. In the command line console window, type the msconfig command and run it with the Enter key
Login via Windows 10 Explorer
Like any program, KS has its own executable file, which means that it can be launched manually. For this:
- Using Explorer or any other file manager, open the C:WindowsSystem32 folder. In Explorer, open the C:WindowsSystem32 folder and run the msconfig.exe file
- Run the msconfig.exe file.
Login via "Search"
"System Configuration" can be accessed directly through the search function.
- In the search bar, enter “System Configuration” or msconfig and select the best match. In the search bar, enter “System Configuration” or msconfig and select the best match
- Launch the found application.
Login via the Start menu
As an administrative element, KS is in the list of special Windows programs. So you can run it like this:
- Open the Start menu.
- In the list of programs, click on the line “Windows Administration Tools” and in the submenu that opens, select the item “System Configuration”. In the list of programs, click on the line “Windows Administrative Tools” and select “System Configuration”
Video: how to open “System Configuration”
The first method is the easiest
In all Microsoft operating systems, it is easy to find and open this program through search. To do this, click on the “Start” button and see the search bar. We type “msconfig” in the line and the required program appears at the top of the window.
We left-click on it once and it starts. This is what the application shell looks like:
This is the easiest and fastest option to activate this OS configuration tool. Experienced users use it, but there are others.
How to use MSConfig
The msconfig utility window has five tabs corresponding to its functionality:
- The General tab allows you to select a system boot option, such as normal or diagnostic startup. If you suspect that your computer is infected with viruses or problems are noticed in the operation of WIndows, you must use the “Diagnostic run” to roll back to the previous configuration or to disinfect the system. In the “General” tab, you can change the computer startup option from normal to diagnostic
- The “Boot” tab is also responsible for starting the system, but it was created not to correct possible errors, but to use advanced settings. For example, if more than one operating system is installed on your computer, then in this tab you can select which OS will boot by default, set a timeout to be able to switch Windows versions at startup, and so on. In the “Boot” tab, you can select the operating system that boots by default, and also set a timeout for the user to select a system
- The “Services” tab allows you to activate or deactivate a particular Windows service without much hassle: you just need to uncheck or check the corresponding line and save the changes. This is much simpler than stopping each service separately through its properties in the interface of the same name. In the “Services” tab, you can bulk disable and enable Windows services
- The Startup tab redirects the user to the Task Manager program to manage applications that start when Windows starts. Through the "Startup" tab, you can launch the "Task Manager" and edit the list of automatically launched programs
- The “Service” tab contains information about all the main service utilities of the operating system. They can be launched directly from the Configuration interface by selecting the application and clicking the Launch button. In the “Service” tab, select the desired program and launch it by clicking the “Run” button