Make sure all your pieces fit together well.
So you've decided to build your own computer, but you don't know where to start. Building your own computer system can be fun, rewarding, and economical.
At the same time, it can be confusing and overwhelming for some. After all, no one wants to ruin their new setup considering how much it costs!
Many parts make up a computer system, and they all need to be compatible with each other in order to work. Otherwise, your system may not work correctly or at all.
In this article, we are going to discuss how to check all the parts of your PC and make sure that they are all compatible with each other.
Motherboards and Processors (CPUs)
Your first decision is to decide which processor and motherboard you will be working with. These two components go hand in hand and are the deciding factor in the compatibility of the rest of your build.
Aside from size, many other parts have wider compatibility than the processor unless you're dealing with very old models, so this factor is often the driving force behind your entire build.
General processors
Typically, for a gaming PC, you'll be choosing between two main processor lines: AMD's Ryzen line and Intel's Core line.
The Ryzen line has been made fully forward and backward compatible for the foreseeable future (and it just started in 2022, so you shouldn't worry about this unexpected change anytime soon). This also includes the latest Ryzen 5000 series processors, with extensive support from the X570 and B550 chipsets and further support from the 400 series on the horizon. However, each new generation of Intel Core processors requires a new motherboard.
Although 8th and 9th generation Intel processors use the same LGA1151 socket, they require motherboards based on the Intel 300 series chipset. Processors on this chipset are not backwards compatible with motherboards based on Intel 300 series chipsets 200 or 100. This also applies to the latest 10th generation Intel processors, which were designed for the new LGA1200 socket.
Chipsets
Next, you should make sure that the chipset supports the features you need. Chipsets are part of the motherboard and determine its capabilities.
Simply put; Chipsets are simply sets of chips. As technology advanced, certain operations on motherboards that required their own chip were reduced in size and integrated with other chips, giving us the word "chipset."
Processors support multiple tiers of chipsets, typically ranging from basic features on the motherboard, such as the AMD Ryzen A320 chipset, which does not allow overclocking, to more advanced chipsets, such as the AMD Ryzen X570, which allows full overclocking, and more.
Socket
To make sure your motherboard is compatible, you will need to look at which socket and chipset your processor is compatible with.
A socket refers to the physical slot on the motherboard that holds your processor in place. This should be easy to determine by simply looking at the socket size for the processor and motherboard you intend to use.
If you try to connect the processor to the wrong type of socket, you may ruin the processor and/or motherboard. Below are some examples to help you understand what to look for.
Motherboard form factor (size and shape)
To make sure your motherboard is compatible, you will need to look at which socket and chipset your processor is compatible with.
A socket refers to the physical slot on the motherboard that holds your processor in place. This should be easy to determine by simply looking at the socket size for the processor and motherboard you intend to use.
If you try to connect the processor to the wrong type of socket, you may ruin the processor and/or motherboard. Below are some examples to help you understand what to look for.
When choosing a motherboard, you should also consider the form factor, as their size may vary slightly. Smaller boards often have less RAM and GPU slots, and fewer SATA connections.
The most commonly used form factors for a standard desktop computer, in order from smallest to largest:
- Mini ITX
- Micro ATX
- ATX
- E-ATX
These are just standard desktop sizes. There are larger motherboards available for other applications, such as server boards.
An ATX motherboard is the most commonly used size for standard computers, and you'll probably want to use one unless you're looking for something significantly smaller or are building a server.
Let's sum it up
Considering all of the above, an inexpensive board made on socket 1151 and equipped with an Intel B250/H270 or B350/H370 chipset is suitable for multimedia or gaming computers.
Powerful gaming computers can also be assembled on a board with socket 1151, but you need to make sure that it has a powerful processor power supply, as well as an Intel B250/H270 or Z270 chipset if overclocking is planned. When purchasing eighth generation processors, the card is purchased with an Intel B350/H370 or Z370 chipset. Models of the game series will have higher quality sound and network cards.
If you plan to purchase a computer to solve professional problems such as video rendering or some other voluminous applications, the optimal solution would be to purchase a board on the AM4 socket, designed for a multi-threaded AMD Ryzen processor running on the B350/X370 chipset.
The size format, number and types of connectors must be selected as needed. Among manufacturers, it is best to give preference to well-known companies such as ASUS, MSI, ASRock and Gigabyte. This way you can get a motherboard that has the best balance of price, quality and functionality, and also fully satisfies the user's requirements at the lowest possible cost.
RAM
RAM, or Random Access Memory, is often misunderstood and can be confusing when it comes to speed and what it is compatible with.
Capacity
Many casual users won't need to worry about upgrading their RAM, but you might want to build a beast of a machine and make the most of all the features. In this case, pay special attention to the maximum memory capacity of your motherboard.
Typically modern motherboards support up to 64GB of RAM, but some support more or less than that.
Speed
When you look at what RAM can do, your biggest concern is speed. For DDR4 (current generation RAM), the standard speed is 2133 MHz. Anything after this is technically considered overclocking.
When RAM is rated at more than 2133 MHz, this is an abnormal speed. In this case, it tells you that it is designed to accelerate to the specified speed. When purchasing RAM speeds above 2133 MHz, make sure your motherboard supports it.
Processor Compatibility
When searching for RAM, you may see mention of its compatibility with AMD or Intel processors. Don't worry, they are still compatible with any of them and it's usually just marketing for overclocking.
Often RAM comes with two manufacturer-set "XMP" profiles that are optimized for a specific processor. Most processors from any manufacturer typically run with these profiles, although sometimes a little tweaking may be required for higher rated speeds.
Channels
RAM also usually comes in dual- or quad-channel kits, which provides more bandwidth. While dual and quad channel RAM is mostly standard, double check what your motherboard supports.
Dimensions of video cards
Small graphics adapters are suitable for compact or inexpensive motherboards. Too bulky ones can bend the board or won’t even fit on top. Typically, the smaller the size, the less powerful the video card is, which often does not have cooling provided.
A manufacturer's representative or sales consultant will tell you the exact dimensions. The more connectors it has, the wider the card will be. On budget varieties, only one row is usually installed.
Video cards: AMD Radeon and Nvidia
Graphics cards give you the biggest performance boost for graphics and gaming, but are often the most forgiving part of your build. Sorry about compatibility, not your wallet; Video cards are expensive.
PCIe
Motherboard compatibility is not usually an issue for graphics cards because they do not require a special graphics card socket or chipset.
PCIe is backwards compatible, so even a PCIe 3.0 graphics card will work on an older motherboard that only has PCIe 2.0. Although PCIe 3.0 has more bandwidth, so it is optimal. the same can be said for the latest PCIe 4.0 cards.
Running multiple video cards
While using multiple graphics cards on a single computer is not unusual for a high-end gaming rig, it is still one of the most common compatibility issues.
To use multiple graphics cards, you will need to look for models labeled "AMD Crossfire or Nvidia SLI/NVlink." This is how AMD and Intel connect two video cards together.
However, graphics cards labeled "SLI or Crossfire Ready" can still be used on their own.
It's worth noting that support for SLI from game makers has dwindled in recent years, and frankly, it's becoming less and less necessary from a gaming perspective year after year. Now with Nvidia's newest 30-series RTX graphics cards, we see it removed entirely, with the exception of the enthusiast-grade RTX 3090 GPU.
CPU compatibility
It is worth considering the power of your processor when selecting a video adapter. If your processor is not highly efficient, then you should not buy a very powerful card, as this will not lead to the desired result. But leaving everything to chance, choosing the simplest one, is also not an option. Since we started to figure it out, we will bring this matter to the end.
There are several methods for determining compatibility:
- calculated: you need to do the following: *=;
- frequency: calculation based on processor frequency;
- Recommended: All companies that manufacture new equipment conduct compatibility tests, so when you buy a new model, you may find a list of compatible devices.
| Frequency (MHz) | Adapter |
| 2500-3000 | R 7 370, GTX 750 Ti (light class) |
| 3200-3600 | R 7 RX 460, GTX 960 (middle class) |
| 3700-4000 | R 9 480,GTX 980 (heavy class) |
| 4000-5000 | Work in a pair of medium and heavy classes |
Tables (CPU+video card)
In the table you can check the compatibility provided for 2016-2018 (the data in the table gives the most compatible options; if you install from an adjacent cell, nothing bad will happen, but the difference will be felt).
Video card/processor compatibility data
More advanced users can use the following table:
Device comparison data for advanced PC users
Frame
When checking compatibility, yes! There are three main things to consider when checking compatibility: form factor (size), graphics card clearance, and airflow.
Form factor and video card size
Motherboards come in different sizes and you will need to find the right case.
Some smaller cases may have limited space for the graphics card. Each case should list the maximum height and length of the graphics card, and each graphics card manufacturer should provide you with their measurements.
Other size-related issues include the space of your cooling device, whether it's fans or something more advanced, and the expanded memory you might want to take advantage of.
Technology support
This information is primarily intended for gamers who are choosing an adapter that supports SLI or CrossFire.
For those who are not in the know: these technologies allow you to combine two or more video cards in order to be able to play games with super realistic graphics, processing them using the power of several video cards simultaneously. Well, or also be able to connect two monitors without problems.
So, these technologies are produced by different manufacturers: CrossFire - AMD (Radeon), and SLI - nVidia (GeForce). So before you buy a product from a particular brand, you should find out whether your motherboard has the ability to work in multi-channel mode.
In general, this is the case: if the motherboard supports SLI, then it is better to buy a video card from nVidia, if it supports CrossFire, then it is better to buy a card from AMD.
You can, of course, not follow this rule. But. If you put a video card from AMD on a motherboard with a chipset from Envidia, then everything will work, but you won’t be able to put a second one. That is, the bundle will not work because the chipset is “foreign”. Do you understand? And yes, if the video card stands alone, there will be no loss in performance.
Cooling
When upgrading from a stock cooler, you will need to make sure it matches the socket on your motherboard.
The CPU heatsinks are located right on top, which means it uses the same socket as the CPU itself. Whatever cooler you choose, it must also be compatible with the CPU socket.
When choosing a liquid cooling option, make sure you have enough space in your case. A liquid cooler uses a heatsink that typically has one to three fans and will require a chassis with a compatible fan layout.
What processors are for socket 775?
The best processors for socket 775
- Intel Core 2 Extreme QX9770. This is one of the top Intel processors of that time. ...
- Intel Core 2 Extreme X6800. ...
- Intel Core 2 Quad Q9650. ...
- Intel Core 2 Quad Q9550. ...
- Intel Core 2 Duo Extreme QX9775. ...
- Intel Core 2 Duo E8600. ...
- Intel Core 2 Duo E8500. ...
- Intel Core 2 Duo E8400.
23 Mar
2022 Interesting materials:
What is the best way to decorate walls? What is the best way to lay a heated floor? What's the best way to have breakfast in the morning? How can you get proteins? How can you wash white leather shoes? What can you use to rub glass? How can you degrease before painting a car? How can you treat drywall? How can you cover the hallway? How can you cover an old wooden door?
Does your power supply have enough power?
Your components have specific power requirements, and it's important to make sure your power supply meets them.
Motherboard and CPU power
There will be two areas on your motherboard that require power: the motherboard itself and the processor. Your motherboard will use a 24-pin power connector, and your processor will range from 2-pin to 8-pin.
GPU power
The graphics card can use anywhere from a 4-pin to a 12-pin connector, depending on how much power it needs.
Hard drive power
HDDs and SSDs that use a SATA connection will also require power for each. If you plan to use multiple drives, make sure your power supply has enough connectors.
Fans, LEDs, etc.
If you plan to add anything extra, such as LEDs and fans that are not powered by the motherboard, make sure your power supply has the correct connections.
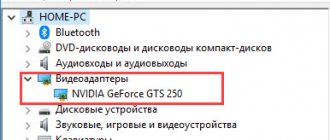
CPU Manufacturers
In order to understand how to select a processor for the motherboard, you need to determine the manufacturer of your processor that is to be replaced. Today there are only two of them – Intel and AMD. This can be done in at least two simple ways:
- Right-click on the My Computer shortcut. A context menu will open, at the very bottom of which select “Properties”.
- Press the Windows key and Pause/Break key combination on your keyboard at the same time.
In both cases you will get the same result. A window will open containing brief information about your system. It will display the version of Windows, information about its activation and below the model of your CPU and its manufacturer.
Finding the right monitor for you
There are many styles of monitors on the market, and they come with many features and upgrades over their ancestors.
Connector types
The three most commonly used connector types for displays today are DVI, HDMI, and Displayport. Most graphics cards now have at least one or two of these connectors, usually at least HDMI.
Permission
High-resolution monitors are growing and becoming cheaper, making them more affordable than ever. Before you go out and buy one, you should make sure that your graphics card is rated for higher resolutions, since most graphics cards are still unable to truly handle 4K graphics.
Bonus options
Depending on your graphics card, you may be able to get a monitor with some advanced features, such as a higher refresh rate or Freesync/G-Sync enabled. Maybe even both if you have the budget.
AMD FreeSync and Nvidia G-Sync are great features for a monitor if your graphics card supports them. On some compatible graphics cards, this allows you to synchronize the game's frame rate with your monitor's refresh rate to avoid screen tearing.
About connectors
The interface of devices is the most important link in the matter of their compatibility.
In older motherboard models, an AGP slot was allocated for the video card. Nowadays he practically never appears. But if you have very ancient hardware, perhaps this is what you are dealing with. In this case, I recommend spending money on a new motherboard, because you are unlikely to find a video card with AGP now. And in general: if you have such an outdated board, then it’s high time to think about replacing it, since it does not meet modern software and hardware requirements.
What replaced AGP?
In the mid-2000s, the mentioned interface was replaced by PCI-Express. Since its introduction, several generations of this connector have been implemented:
- 1.0. Its throughput is only 2.5 Gbps.
- 2.0. The data transfer speed has doubled compared to its predecessor.
- 3.0. According to tradition, the parameter has doubled. Another difference in version 3 is the presence of double bandwidths.
- 4.0. As you may have guessed, its throughput capabilities are already 20 Gbit/s. By the way, externally this and the previous two connectors are identical. They are also called PCI-E 16x, and they are installed in all modern devices.
Compatibility of PCI-E modifications
I would like to note that this indicator does not greatly affect the overall performance of the video adapter. Of course, it is desirable that the versions of the interfaces on it and the motherboard match. After all, in this case it will be possible to squeeze the maximum out of the video card.
But if that doesn’t work out, it doesn’t matter. When both devices are equipped with PCI-E, even if they are of different generations, they are essentially compatible. However, not all so simple.
Compatibility Checklist
Now we've talked about what parts are needed to build your computer and how to ensure they're compatible. This can be a lot of information to remember, especially if you're new to this.
To help with this, I'm going to provide a handy checklist you can use to make sure you don't forget anything.
CPU and motherboard
- Socket type
- Chipset
- Form factor
RAM
- Speeds
- XMP Profile
- Dual/quad channel?
Video cards
- Crossfire/SLI support (when using more than one video card)
Storage
- Connecting a storage device (SATA, M.2, HDD)
Cooling
- Aftermarket Cooler Hose Type
- Liquid Cooler Radiator Size
power unit
- Pin connectors - do you have the right ones?
- Sufficient output power
Recommendations for selection
Initially, you need to understand which brands are leading in this market and whether you can trust them. Here is a list of recommended motherboard manufacturers:
- Gigabyte is a company from Taiwan that produces video cards, motherboards and other computer equipment. Recently, the company has increasingly focused on the gaming machine market, which requires productive and expensive equipment. However, motherboards for “regular” PCs are still produced.
MSI is also a Taiwanese manufacturer of computer components, which is also focused on high-performance gaming computers. It is recommended to pay attention to this manufacturer if you plan to build a gaming PC.
ASUS is the most famous manufacturer of computers and their components. It presents a very large assortment of motherboards - from the most budget to the most expensive models. Also, most users consider this manufacturer to be one of the most reliable on the market.
Intel - in addition to producing central processors, the company produces its own motherboards, which are characterized by high stability, the best compatibility with Intel products and a very high price (however, their capabilities may be lower than those of cheaper analogues). Popular in the corporate segment.
If you have already bought powerful and expensive PC components, then under no circumstances buy a cheap motherboard. At best, the components will not work at full capacity, lowering all performance to the level of budget PCs. At worst, they won’t work at all and you’ll have to buy another motherboard.
Before assembling a computer, you need to decide what you want to get in the end, because... It will be easier to choose a board without purchasing in advance all the main components for the computer. It’s better to buy a high-quality central board (you shouldn’t skimp on this purchase if your capabilities allow it) and then, based on its capabilities, select the remaining components.
Chipsets on motherboards
The chipset directly determines how many components you can connect to the motherboard, whether they can work with 100% efficiency, and which processor is better to choose. Essentially, a chipset is something similar to a processor already built into the board, but which is responsible only for the most basic functions, for example, working in the BIOS.
Almost all motherboards are equipped with chipsets from two manufacturers – Intel and AMD. Depending on which processor you chose, you need to choose a board with a chipset from the manufacturer of the selected CPU. Otherwise, there is a possibility that the devices will be incompatible and will not work properly.
About Intel chipsets
Compared to the “red” competitor, the “blue” ones do not have many models and varieties of chipsets. Here is a list of the most popular ones:
- H110 is suitable for those who are not chasing performance and only require the computer to work correctly in office programs and browsers.
- B150 and H170 - there are no serious differences between them. Both are great for mid-range computers.
- Z170 – a motherboard based on this chipset supports overclocking of many components, making it an excellent solution for gaming computers.
- X99 is in demand in a professional environment that requires a lot of resources from the system (3D modeling, video processing, game creation). Also good for gaming machines.
- Q170 is a chipset from the corporate sector and is not particularly popular among ordinary users. The main emphasis is on security and stability.
- C232 and C236 - used in data centers, allows you to process a huge amount of information. Work best with Xenon processors.
About AMD chipsets
They are divided into two series – A and FX. The first is suitable for A-series processors with already integrated video adapters. The second is for the FX series of CPUs, which do not have a built-in graphics adapter, but compensate for this with high performance and overclocking potential.
Here is a list of major AMD chipsets:
- A58 and A68H are very similar chipsets that are suitable for a regular office PC. Work best with AMD A4 and A6 processors.
- A78 – for multimedia computers (working in office applications, simple manipulations with graphics and video, running “light” games, surfing the Internet). Most compatible with A6 and A8 CPU.
- 760G – suitable for those who need a computer as a “typewriter with Internet access.” Compatible with FX-4.
- 970 – its capabilities are enough to run modern games at minimum and medium settings, professional work with graphics and simple manipulations with video and 3D objects. Compatible with FX-4, Fx-6, FX-8 and FX-9 processors. The most popular chipset for AMD processors.
- 990X and 990FX are an excellent solution for powerful gaming and semi-professional machines. Best compatibility with FX-8 and FX-9 CPUs.
About guarantees
When purchasing a motherboard, be sure to pay attention to the warranties provided by the seller. On average, the warranty period can vary from 12 to 36 months. If it is less than the specified range, then it is better to refuse to purchase from this store.
The thing is that the motherboard is one of the most fragile components of a computer. And any breakdown of it will certainly lead, at a minimum, to the replacement of this component, at most - you will have to think about completely replacing the part or all the components that were installed on it. This is equivalent to replacing almost the entire computer. Therefore, under no circumstances should you skimp on warranties.
About dimensions
This is also a very important parameter, especially if you are buying a motherboard for a small case. Here is a list and characteristics of the main form factors:
- ATX is a full-size motherboard that is installed in system units of standard dimensions. It has the largest number of connectors of all types. The dimensions of the board itself are 305×244 mm.
MicroATX is an already stripped down ATX format. This has virtually no effect on the performance of already installed components, but it has fewer slots for additional components. Dimensions – 244×244 mm. Such boards are installed on regular and compact system units, but due to their size they are cheaper than full-size motherboards.
Mini-ITX is more suitable for laptops than desktop PCs. The smallest boards that the computer components market can provide. The dimensions are as follows – 170×170 mm.
In addition to these form factors, there are others, but they are practically not found on the market of components for home computers.
CPU socket
This is the most important parameter when choosing both a motherboard and a processor. If the processor and motherboard sockets are incompatible with each other, then you will not be able to install the CPU. Sockets are constantly undergoing various modifications and changes, so it is recommended to buy models only with the most current modifications, so that you can easily replace them in the future.
Intel sockets:
- 1151 and 2011-3 are the most modern types. If you prefer Intel, then try to buy a processor and motherboard with these sockets.
- 1150 and 2011 - they are still widely used on the market, but have already begun to become obsolete.
- 1155 , 1156 , 775 and 478 are outdated socket models that are still in use. We recommend purchasing only if there are no other alternatives.
AMD sockets:
- AM3+ and FM2+ are the most modern sockets from the “reds”.
- AM1, AM2, AM3, FM1 and EM2 are considered either completely obsolete or are already beginning to become obsolete.
About RAM
Motherboards from the budget segment and/or small form factors have only two slots for installing RAM modules. On boards of standard sizes for desktop computers there are 4-6 connectors. Motherboards for small cases or laptops have less than 4 slots. For the latter, this solution is more common - a certain amount of RAM is already soldered into the board, and there is one slot nearby in case the user wants to expand the amount of RAM.
RAM is divided into several types, which are designated as “DDR”. The most popular and recommended today are DDR3 and DDR4. The latter ensures the fastest possible operation of the computer. Before choosing a motherboard, make sure that it supports these types of RAM.
It is also recommended to consider the possibility of increasing the amount of RAM by adding new modules. In this case, pay attention not only to the number of slots, but also to the maximum capacity in GB. That is, you can buy a board with 6 connectors, but it will not support many GB of RAM.
It is recommended to pay attention to the range of supported operating frequencies. DDR3 RAM operates at frequencies from 1333 MHz, and DDR4 2133-2400 MHz. Motherboards almost always support these frequencies. It is also important to pay attention to whether the central processor supports them.
If the CPU does not support these frequencies, then buy a card with XMP memory profiles. Otherwise, you can seriously lose in RAM performance.
Place for installing video cards
Mid- and high-end motherboards may have up to 4 connectors for graphics adapters. Budget models usually have 1-2 slots. In most cases, PCI-E x16 type connectors are used. They allow you to ensure maximum compatibility and performance between installed video adapters. The connector has several versions - 2.0, 2.1 and 3.0. The higher the version, the better the characteristics, but the price is correspondingly higher.
PCI-E x16 connectors can also support other expansion cards (for example, a Wi-Fi adapter).
About additional fees
Expansion cards are additional devices that can be connected to the motherboard, but are not critical to the operation of the system. For example, Wi-Fi receiver, TV tuner. PCI and PCI-Express slots are used for these devices; more details about each:
- The first type is rapidly becoming obsolete, but is still used in budget and middle class models. It costs significantly less than its newer counterpart, but device compatibility may suffer. For example, the newest and most powerful Wi-Fi adapter will work worse or not work at all on this connector. However, this connector has excellent compatibility with many sound cards.
- The second type is newer and has excellent compatibility with other components. They have two variations of connector X1 and X4. The latter is newer. Connector types have virtually no effect on anything.
Information about internal connectors
They serve to connect important components to the motherboard inside the case. For example, to power the processor and the board itself, install hard drives, SSDs, and drives.
As for the motherboard power supply, older models work from a 20-pin power connector, and newer ones from a 24-pin power connector. Based on this, it is advisable to choose a power supply or select a motherboard for the desired contact. However, it will not be critical if the 24-pin connector is powered from a 20-pin power supply.
The processor is powered according to a similar scheme, only 4- and 8-pin connectors are used instead of 20-24-pin connectors. If you have a powerful processor that requires a lot of energy, it is recommended to buy a board and power supply with 8-pin connectors. If the processor is not too powerful, then you can get by with 4-pin connectors.
As for connecting SSD and HDD drives, almost all boards use SATA connectors for this. It is divided into two versions - SATA2 and SATA3. If an SSD drive is connected to the main board, then it is better to buy a model with a SATA3 connector. Otherwise, you will not see good performance from the SSD drive. Provided that you do not plan to connect an SSD, you can purchase a model with a SATA2 connector, thereby saving a little on the purchase.
Integrated Devices
Mother cards can come with already integrated components. For example, some laptop boards come with soldered video cards and RAM modules. All motherboards have network and sound cards integrated by default.
If you decide to purchase a processor along with an integrated graphics adapter, then make sure that the board supports their connection (this is usually written in the specifications). It is also important that external VGA or DVI connectors, which are needed to connect a monitor, are integrated into the design.
Pay attention to the built-in sound card. For most users, standard codecs such as ALC8xxx will be sufficient. If you plan to do video editing and/or sound processing, then it is better to pay attention to boards that have a built-in adapter with the ALC1150 codec, because It provides excellent sound, but also costs much more than the standard solution.
A sound card usually has from 3 to 6 3.5 mm jacks for connecting audio devices. Sometimes you come across models with an optical or coaxial digital audio output, but they also cost more. This output is used for professional audio equipment. For normal computer use (connecting speakers and headphones), only 3 sockets are enough.
Another component that is integrated into the motherboard by default is the network card, which is responsible for connecting the computer to the Internet. The standard parameters of the network card on many motherboards are a data transfer speed of about 1000 Mb/s and an RJ-45 network output.
The main manufacturers of network cards are Realtek, Intel and Killer. I use the first products in the budget and mid-price categories. The latter are more often used in expensive gaming machines, because provide excellent performance in online games even with a poor network connection.
External connectors
The number and types of external sockets depend on the internal configuration of the board itself and its price, because More expensive models have additional outputs. List of connectors that are most often found:
- USB 3.0 – it is desirable to have at least two such outputs. A flash drive, mouse and keyboard (more or less modern models) can be connected through it.
- DVI or VGA - available on all boards, because... You can use it to connect your computer to a monitor.
- RJ-45 is a mandatory design element. It helps you connect to the Internet. If your computer does not have a Wi-Fi adapter, this is the only way to connect the machine to the network.
- HDMI – needed to connect a computer to a TV or modern monitor. Alternative to DVI.
- Audio jacks – required for connecting speakers and headphones.
- Output for microphone or additional headset. Always included in the design.
- Wi-Fi antennas – available only in models with an integrated Wi-Fi module.
- BIOS reset button – allows you to quickly reset the BIOS settings to the factory state without disassembling the computer case. Available only on expensive boards.
Power circuits and electronic components
When choosing a motherboard, be sure to pay attention to the electronic components, because... The lifespan of the computer depends on them. Cheap models use conventional electronic capacitors and transistors, without any additional protection. After 2-3 years of service, they may well oxidize and render the entire system unusable. It is better to choose more expensive models, for example, those that use solid-state capacitors made in Japan or Korea. Even if they fail, the consequences will not be so catastrophic.
It is very important to pay attention to the processor power supply. Power supply distribution:
- Low power – used in budget motherboards, they have a power of no more than 90 W and no more than 4 power phases. Only low-power processors with low overclocking potential are suitable for them.
- Medium power - have no more than 6 phases and a power not exceeding 120 W. This is enough for all processors from the mid-price segment and some from the high-end.
- High power - have more than 8 phases, work perfectly with all processors.
When selecting a motherboard for a processor, it is important to pay attention not only to whether the processor fits the sockets, but also to the voltage. On the website of the motherboard manufacturer you can immediately see a list of all processors that are compatible with a particular board.
Cooling system
Budget models do not have this system at all, or have one small radiator that only copes with cooling low-power processors and video cards. Oddly enough, these cards are the least likely to overheat (unless, of course, you overclock the processor too much).
If you are planning to build a good gaming computer, then pay attention to motherboards with massive copper radiator tubes. However, there is a problem - the size of the cooling system. Sometimes, due to too thick and tall pipes, it can be difficult to connect a long video card and/or processor with a cooler. Therefore, everything needs to be checked first.
When choosing a motherboard, you need to take into account all the information that was indicated in the article. Otherwise, you may encounter various inconveniences and unnecessary expenses (for example, the board does not support a certain component).
Thank the author and share the article on social networks.
Assembling a computer yourself is an easy and very interesting activity. A huge proportion of users do not buy ready-made solutions, but assemble PCs themselves. Now this topic is very relevant due to the financial problems of most people in our country. Assembling a computer yourself helps not only to save quite a significant amount, but also to select the components that are ideal for your purposes.
Someone wants to buy a computer for modern and demanding games. First of all, he will need a powerful video card. Those who want to get solid computing power from their new computer need to make sure they have a good processor installed. Also, with self-assembly, you have the opportunity to choose less important computer components, such as a case or hard drive. You may have parts from your old computer that you need in your new work machine. In this case, start assembling your computer yourself.
The process of searching and assembling the necessary components raises a number of questions among users. First of all, they concern the compatibility of certain parts of the system unit. Nobody wants to build a computer that simply won't work. One of the most important components of a personal computer is the processor. Many people start selecting components from it. And for good reason. When choosing and purchasing a processor, you need to make sure that it is fully compatible with the motherboard that will be installed in your computer. It is this question that we will consider.
PC Part Picker Service
If searching for compatibility information is not interesting to you, you can use a special tool. PC Part Picker is a staple service of the PC building community and the primary source of information for new builders, and does all the hard work for you.
All you have to do is enter the make and model number of each component in your build, and then the website will do its best to make sure the hardware is compatible. If there aren't any, PC Part Picker can help solve some problems, allowing you to make corrections until you create a build that works.
You can save builds and come back to them later, or share them with more experienced developers for feedback and advice.
Graphics adapters - energy efficiency
Not all power supplies and motherboards support the required power for video cards. Also, they may not have connectors for connecting any type of card. This is something to keep in mind before purchasing. Also, the graphics adapter may not match due to high energy consumption, which will immediately affect the performance of the video card as a whole.
Based on consumption indicators, they are classified as follows:
- up to 70 W is usually called the initial class. They fit well with any power supplies and motherboards;
- no more than 150 W is classified as middle class. They are not compatible with all components;
- 150 to 300 watts are considered high performance. They will require special components adapted to such energy consumption.
How to choose a video card for the processor
The task is somewhat more difficult, but not much
In this case, it is important to remember that in terms of hardware compatibility there are no restrictions, since any processor will be able to work with any video card
The optimal ratio is when during the game the processor is loaded at 80% percent and the graphics accelerator at 100%. Then we can say that the “stone” fully reveals the potential of the video card.
For orientation, here are examples of compatibility between processors and video cards:
- For Intel Core i3 2100 and the entire generation up to I3 8100 or FX-8150, FX-8120 and Phenom II X6 1100T from AMD – GeForce GTX 670, GTX 660 ti, GTX 950, Radeon R9 370, R9 380;
- For i5 8400 or 9400 processor from Intel and FX-9590, FX-9370, FX-8350 and FX-8320 from AMD – GeForce GTX 780 Ti, GTX 970, Radeon R9 380X, R9 390;
- For Intel Core i7 or flagship AMD Zen – GeForce GTX 980 Ti, GTX 1080, Radeon R9 Nano, R9 Fury, R9 390 X.
If there is a significant discrepancy between the characteristics, as a rule, the performance of the video card decreases. This is reflected, first of all, in a decrease in FPS and periodic “freezes” when a large number of game objects accumulate in one place.
However, there is no need to rack your brains and test suitable devices for compatibility - this was done for us a long time ago. There are a lot of enthusiasts testing hardware and publishing the results for everyone to see. This data can be Googled in a few minutes.
Video memory and bus width
Today, video cards on the market have only 4 types of memory: GDDR3, GDDR5, GDDR5X and HBM. The last type is a new development by AMD and Hynix. In terms of performance, HBM significantly exceeds previous generations of GDDR5 and GDDR5X, and also consumes less power.
Almost all budget video cards are equipped with GDDR3 memory. This type has the lowest performance, the frequency of which does not exceed 2000 MHz. It is not recommended to choose a video card with a frequency of less than 1600 MHz, as it will not handle even weak games, and you can completely forget about watching online movies in good quality.
GDDR5 is the most popular option. Most video cards, including budget ones, are equipped with it. Its frequency ranges from 2000 to 7000 MHz. While more expensive adapters use GDDR5X with a frequency of 7000 to 10000 MHz.
You should also pay attention to the amount of memory. Budget boards are equipped with 1-2GB of video memory, while mid-segment boards already use 4-6GB of video memory
In the more expensive segment you can find 8GB and higher.
In most cases, it is recommended to give preference to cards with memory types GDDR5, GDDR5X and a capacity of 2-4GB. This way you will get a computer on which you can not only watch online movies in FullHD quality, but also play productive games for another 2-3 years.
Special attention should be paid to the bus width; it is measured in bits. The optimal value should be (128-384 bits) or higher
Otherwise, even weak applications will have difficulty launching.
Brief compatibility table for computer components
| Initial components | Characteristic | Compatible Accessory | Example |
| CPU | Processor socket (socket) | Motherboard | Processor Intel Core i5-3450 Socket LGA1155 |
| CPU | Memory type, Memory operating frequency | RAM | Processor Intel Core i5-3450 Memory type: DDR3 Memory frequency 1333-1600 MHz |
| CPU | CPU socket (socket), Heat dissipation | Cooler | Processor Intel Core i5-3450 Socket LGA1155 Heat dissipation 77 W |
| Motherboard | Processor socket (socket), Supports processor types | CPU | Socket LGA1155 Processor support: Intel Core i5-3xxx |
| Motherboard | Memory type, Memory operating frequency | Memory module | Memory type: DDR3 Memory frequency: Depends on processor |
| Motherboard | Video card connector type | Video card | PCI-Express x16 3.0 connector |
| Motherboard | Hard drive connection interface | HDD | SATA 6 Gb/s (SATA III) |
| Motherboard | Motherboard power type | power unit | Power supply 24+4 pin |
| Motherboard | Motherboard format | System unit case | Format: MicroATX |
| Motherboard | Interface for connecting peripheral devices | Keyboard and mouse | USB |
| Cooler | CPU socket (socket), Power dissipation | CPU | Socket LGA1155 Power dissipation 100 W. |
| RAM module | Memory type, Memory operating frequency | CPU | Memory type: DDR3 Operating frequency: 1333 MHz |
| RAM module | Memory type, Memory operating frequency | Motherboard | Memory type: DDR3 Operating frequency: 1333 MHz |
| Video card | Video card connector type | Motherboard | PCI-Express x16 3.0 |
| Video card | Additional power type | power unit | Power 6 pin |
| HDD | Hard drive interface | Motherboard | SATA 6 Gb/s (SATA III) |
| HDD | Power type | power unit | Power SATA |
| Optical drive | Optical drive interface | Motherboard | SATA 6 Gb/s (SATA III) |
| Optical drive | Power type | power unit | Power SATA |
| power unit | Motherboard power connector | Motherboard | Power supply 24+4 pin |
| power unit | Video card power connector | Video card | Power 6 pin |
| power unit | Power connector | HDD | Power SATA |
| power unit | Power connector | Optical drive | Power SATA |
| power unit | Power | All components | Video card consumption + 200 W Total: 350 W |
| Frame | Motherboard format | Motherboard | Format: MicroATX |
The table shows what characteristics you need to pay attention to when selecting compatible components. But let’s immediately make a reservation about several of them: But let’s immediately make a reservation about several of them:
But let’s immediately make a reservation about several of them:
Compatibility of components: features of choice
1. SATA III interface is backward compatible with SATA II and SATA. This means that if you have a SATA III connector on the motherboard, you can connect SATA II and SATA hard drives to it. They will simply be slower according to their interface standard;
2. PCI-Express interface, also backwards compatible with its predecessors;
3. A smaller motherboard, such as MicroATX, can be inserted into an ATX case;
4. It is better to take a cooler with a reserve of power dissipation. This way you will avoid overheating the processor;
5. To calculate the power of the power supply, it is necessary to add up the powers of all components connected to it. Conventionally, we can assume that the power:
– processor – from 50 to 120 W;
– motherboard – from 20 to 35 W;
– memory modules – from 20 to 50 W;
– hard drive – from 20 to 55 W;
– video cards – from 20 to 300 W;
– optical disc drive – from 15 to 25 W.
It is better to take a power supply with a power reserve of about 100-150 W.
6. It is better to take the same RAM modules for working in dual-channel mode: from the same manufacturer, volume and frequency.
How to choose the right video card for the processor
How to find out the motherboard socket
Weak processor and powerful video card. This happens during the process of updating an old computer or incompetent PC assembly. Many users hope to get a performance boost by installing a powerful video card. What a surprise they were when, after installing a new gaming graphics card, the number of frames did not change.
The processor operates at maximum, its operating temperatures are always high. The video card feels more than comfortable, as it never works at full capacity. We tried to achieve this by limiting the FPS in Windows 10 games.
Powerful processor and weak video card. A more than excellent combination of components that is used in all gaming computers. Nowadays, the power of modern processors is sometimes enough for several video cards. It all depends on the budget and work assignments. The CPU is taken with a large margin so that the video card can be updated.
The processor easily reveals the potential of the video card, working at half its capabilities. In the future, it allows you to install several or a newer video card. Of course, without replacing the central processor. Its power is more than enough.
By choosing the top-end processor AMD Ryzen 9 3900X and a video card below the segment GeForce RTX 2060 Super or AMD Ryzen 5 3600X and GeForce RTX 2080 Super. For editing, the first combination of video card and processor is better, but for gaming itself, of course, the second.