You have to use the search function in Windows 10 much more often than in previous versions of the OS: with the help of search, you can quickly find the desired application, file, setting item, system function, or even search the Internet. However, in some cases, Windows 10 search stops working. When you try to find any application or file, Windows Search returns an empty list (usually this happens after a system upgrade/update). In this article, we have collected basic tips that should help if search in the Start menu, taskbar and other elements of the Windows interface does not work in Windows 10.
On February 5, 2022, search stopped working en masse for Windows 10 users (it produces empty results). The issue is related to the temporary unavailability of Bing cloud search services and is resolved by disabling the Bing search integration (see solution below).
Restart Search Services in Windows 10
SearchUI .exe, is responsible for searching from the taskbar . If search in the Windows 10 taskbar is not working for you, try restarting this process:
- Launch Task Manager (Ctrl+Alt+Del);
- Go to the Details ;
- Find it in the list of processes SearchUI.exe, right-click on it and select Cancel task;
- End the SearchApp .exe ;
- The next time you try to search in Windows 10, the process will automatically restart.
Enable Windows Search
This service is responsible for the functioning of the search in the top ten. Naturally, when it is turned off, the search in the system will not work.
- Launch the “Run” window. We write the command “services.msc” and press OK (or Enter).
- In the list of services on the right side of the window, find the line “Windows Search”, then check:
- service status – should be “Running”.
- startup type – must be set to “Automatic” or “Automatic (delayed start)”.
- If any parameter does not correspond to those described above, double-click on the line with the name of the service to open a window with properties where we can make adjustments, and then save the changes by clicking OK.
Search does not work in the Windows 10 start menu
If search does not work in Windows 10 only in the Start menu, try the following solution:
- Terminate the Explorer process (Explorer.exe) by right-clicking on an empty space in the taskbar while holding down the Ctrl+Shift keys (select Exit Explorer), or using the task manager (Ctrl+Shift+Esc);
- Launch the registry editor from Task Manager (File -> Run new task -> regedit.exe);
- Delete the following registry key HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\FolderTypes\{ef87b4cb-f2ce-4785-8658-4ca6c63e38c6}\TopViews\{00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000}. In the 64-bit version of Windows 10, you need to delete the registry key HKLM\SOFTWARE\Wow6432Node\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\ Explorer\FolderTypes\ {ef87b4cb-f2ce-4785-8658-4ca6c63e38c6}\TopViews\ {00000000-0000-0000-000 0-000000000000 };
- Run Explorer.exe through the task manager (File -> Run new task -> explorer.exe).
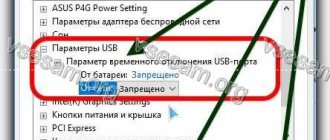
In Windows 10 Creator Update (1703) and newer versions, there is another common issue that may cause search to not work. In the Settings - > Privacy - > Background apps section , enable the Let apps run in the background option . If you disable this option, searching among newly installed applications may not work.
If you don't find this option, you can enable it through the registry:
- To do this, go to the registry key HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\ Windows\CurrentVersion\ BackgroundAccessApplications ;
- Create a new DWORD (32-bit) named GlobalUserDisabled with a value of 0 ;
- Then change the value of the BackgroundAppGlobalToggle to 1 in the registry key HKCU\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Search;
Or you can change these settings from the command line: REG ADD HKCU\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\BackgroundAccessApplications /v GlobalUserDisabled /t REG_DWORD /d 0 /f REG ADD HKCU\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Search /v BackgroundAppGlobalToggle /t REG_DWORD /d 1 /f - Restart your computer.
Editing the Registry
You can also try editing the keys that are responsible for the search function using the Registry Editor.
- In the “Run” window, type the command “regedit” and press Enter (or OK).
- In the editor window that opens, go to the path: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows Search.
- In the right part of the window (in the contents of the “Windows Search” folder) we find the “SetupCompletedSuccessfully” parameter and double-click on it to open the properties.
- In the field with the value, instead of zero, enter the number 1 and click OK.
- Now, on the left side of the window, open the “Windows Search” branch, find the “FileChangeClientConfigs” folder and, by pressing the F2 key, rename it to “FileChangeClientConfigsBak”.
- Afterwards, you can close the registry editor, restart the PC and check if the search is working.
Indexing service and indexing settings
Check if the Windows Indexing Service is running. For this:
- Open services.msc ;
- In the list of services, find Windows Search ;
- Check that the service is running and its startup type is automatic;
- Start/restart the WSearch service;
- Now open the classic Control Panel and open the Indexing Options (Control Panel\All Control Panel Items\Indexing Options);
- Make sure that indexing of all desired locations is selected (at a minimum, Start Menu, Users indexing should be enabled, you can add your local drives and Outlook);
- Click the button Additionally and in the section Troubleshooting click the button Rebuild;
- The reindexing process can take quite a long time. Wait for it to finish.
Note : Check that there is enough free space on the system disk. In some cases, the size of the Windows Search index file (Windows.edb) can be quite large.
Options for solving problems with the “Search” option
The question of how to set up a search in Windows OS is relevant for every active computer user who has encountered such a problem. Indeed, it is much easier to enter the name of the file required for work in the search bar, and immediately begin operation, rather than trying to manually search for the required element by opening many folders on the computer. Windows 10 has search parameters that are not fundamentally different from the service of the previous, most popular version of Windows 7, the only difference is that the modernized system uses element indexing to find the desired file, additionally using specific algorithms and databases. Accordingly, troubleshooting the Windows 10 search system costs the same as previously setting up the “Search” option in previous versions of the OS.
Setting up a search service is possible by eliminating system errors using the following methods:
- Via the command line.
- By activating the search service.
- By amending the register.
Let us consider each of the most popular and effective options for solving the problem in more detail.
Command line
If the problems are caused by incorrect software updates, virus attacks, or a conflict between installed utilities, the dilemma of how to restore the functionality of the search engine in Windows 10 can be resolved by scanning the software. This can be done by making changes via the Command Line. To complete the task, we call the system utility, which will allow you to make corrections and troubleshoot problems. You can check the integrity of the files responsible for the search using the SFC utility. To do this, you need to call the utility following the algorithm:
- Launch the “Run” program line. To do this, press the Win+R button combination.
- Next, you need to open the command line interpreter by entering cmd in the command field, confirm the request by pressing the OK or Enter button.
- If the actions are performed correctly, the program will call the console - a command line on a black field, where you will need to enter a further command to perform a scan with parallel correction of software errors.
- The sfc/scannow command is responsible for restoring system files, including the search system, after entering which incorrectly working files will be found and corrected.
This algorithm also answers the question of how to enable search in Windows 7, in contrast to subsequent methods for solving the problem, intended for the tenth variation of the OS.
Services
The next solution to the problem of how to open a search in Windows 10 is to activate the functioning of the service itself, which authorizes the operation of the search engine. The problem may be hidden in a simple, independent disabling of the search service subsequently caused by incorrect operation of the Windows 10 OS. You can activate the service in the following way:
- By simultaneously pressing Win and R you will need to open the search service window.
- In the open line, enter the wording services.msc and confirm the directive with the Enter key. In this way you can open a list of available services.
- In the list that appears, you need to find the Windows Search configuration. This will not be easy to do, since the service registry is not systematized; you will have to manually find the required element.
- After you find the required service, right-click on it. In the drop-down menu you need to open the “Properties” item.
- In the “General” tab, opposite o, you need to set the “Automatic” command, and then confirm the innovations by pressing the OK key.
After the manipulations have been performed and the computer is restarted to update the data, the search should begin to function in standard mode.
Editing the Registry
The third option for resolving the problem when “Search” has disappeared in Windows 10 involves interfering with the structure of the system registry, therefore, performing the troubleshooting procedure requires the performer to have basic skills in working with software and special care in order to avoid the occurrence of more serious malfunctions. You can achieve a positive result from the procedure by following the instructions, performing the following steps step by step:
- Go, as in the previous two cases, to the “Run” menu using the Win + R command.
- Enter the “Registry Editor” by entering the regedit command into the line.
- In the registry, find the folder named HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE, and in it open the SOFTWARE item.
- Next, you need to go to the Microsoft item, and then open the Windows Search folder, where you will need to select the SetupCompletedSuccesfuly parameter by double-clicking on it.
- After completing the procedures, the user will see a window for changing parameters, where in the “Value” item you will need to enter the number one and confirm the correction by pressing the OK key.
- Return to the Windows Search folder and open its contents by clicking on the “checkmark” on the left, select the FileChangeClientConfigs item in the drop-down list of folders that you need to rename.
- You can change the name of a sub-item by right-clicking on the folder name, selecting “Rename” from the list, and entering the name FileChangeClientConfigsBak instead of the old name.
After restarting the computer, the changes in the registry will take effect, and the functionality of the Windows search engine will be restored.
Troubleshooting the Indexing and Search Service
Try using the built-in Indexer Diagnostics (Troubleshooter) troubleshooting tool. For this:
- Go to Settings -> Search -> Searching Windows. Scroll down the list and click on the link “ Run the indexer troubleshooter to resolve common search issues”;
You can run the Search Error Fix Wizard from the command line: msdt.exe -ep WindowsHelp id SearchDiagnostic - The Search and Indexing Services Troubleshooting Wizard will launch;
- Select your problem (most likely it will be “ Files don't appear in search results ”) and click Next;
- Wait until the “Search and Indexing troubleshooter” scans your computer and tries to fix the error, then restart your computer and check the search.
Defragmentation of the hard drive for search to work in start
All files on the hard drive occupy separate memory cells - clusters. When documents are frequently recorded or deleted, so-called gaps appear between data streams. These gaps negatively affect the performance of the search engine. To fix this problem, you can defragment the disk. To defragment, you need to right-click on the disk, select the “properties” menu, go to the “Service and Maintenance” tab and select “defragment”. The defragmentation process will then begin, which will take a certain amount of time, depending on the amount of memory on the computer. If only an SSD is installed on the PC, defragmentation is not required. The file storage system here is different.
Re-registering Windows 10 Universal Apps
If you have the Cortana voice assistant installed on your computer (let me remind you that there is still no Russian version of Cortana), re-registering all universal applications in the system can fix the problem of Windows 10 search not working. To do this, in a PowerShell command prompt running with administrator rights, run the command:
Get-AppXPackage -AllUsers | Foreach {Add-AppxPackage -DisableDevelopmentMode -Register "$($_.InstallLocation)\AppXManifest.xml"}
After finishing the command, restart your computer.
What to do if the search bar is missing
Some users are encountering a problem - the search bar in new tabs has disappeared in Google Chrome. This occurs when the search engine changes.
It's easy to fix the error:
- Go to settings.
- Select "Search Engine" from the left menu.
- In the first column from the list, select Google.
- Restart your browser.
Select Google as your default search engine
Windows 10 search does not work when Bing integration is enabled
On February 5, 2022 , many users noticed that search from the taskbar does not work in Windows 10 1909 and 1903. The search window in the taskbar opens, but when you enter any query, the search returns empty results.
Most likely the cause of the problem is the unavailability of Bing cloud search services. The fact is that by default, Windows 10 sends everything you enter in the Start Menu search to its servers, which return search results from Bing to you.
The easiest way to fix this problem is to disable Windows 10 Search integration with Microsoft's Bing search engine.
- Launch the registry editor (Win+R -> regedit.exe);
- Go to the registry key HKEY_CURRENT_USER\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Search\;
- Change the settings BingSearchEnabled And CortanaConsent on 0;
If these registry values are missing, create them manually (type REG_DWORD 32 bit). You can create and change these settings with the following commands: REG ADD HKCU\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Search /v BingSearchEnabled /t REG_DWORD /d 0 /f REG ADD HKCU\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Search /v CortanaConsent / t REG_DWORD /d 0 /f
- Restart Explorer.exe or restart your computer.
This solution will help if you have a search window open, but when you enter text to search, nothing appears. At the time of writing, Microsoft engineers have already fixed the problem with Bing, and Windows search services are working normally. Although, in my opinion, Windows 10 search integration with Bing should be disabled forever.
Rebuilding the Index in Indexing Options
See also: “How to speed up your computer (laptop) in Windows 10”
This method can help not only restore the search function, but also speed up its operation.
- Launch the Control Panel. You can also do this through the “Run” window by typing the “control” command.
- Having configured viewing in the form of large or small icons, go to the “Indexing Options” section.
- In the parameters window, click on the “Change” button.
- Check the indexed locations and save the settings.
- Now let's go to additional settings.
- In the “Indexing Options” tab, click on the “Rebuild” button.
This process may take a long time, during which the search will not work. - When the operation is completed, launch the Task Manager. This can be done through the context menu, called up by right-clicking on the Start menu or pressing the Win+X keys.
- In the “Processes” tab we find the line “Explorer” (or “explorer.exe”). By right-clicking, we call up the context menu, in which we select the “Restart” command.
Search does not work in Windows 10 Settings
The Windows 10 Settings app has its own search box for quickly jumping to system settings items. If search in Settings stops working for you:
- Launch File Explorer and navigate to the %LocalAppData%\Packages\windows.immersivecontrolpanel_cw5n1h2txyewy\LocalState directory;
- Open the properties of the Indexed folder, click the “Other” button, and check that the option “Allow the contents of files in this folder to be indexed in addition to file properties” is enabled;
- If the option is already enabled, disable it, click OK, and then enable it again.
Incorrect operation of the standard search for Windows operating systems
Introduction
I was prompted to write this article by the desire to add my two cents to the discussion of one of the latest releases (at the moment) of the most popular Windows operating system among users. And also a state of confusion and bewilderment if it turns out that the bug in the search system I describe below is really an “architectural feature of the product,” as Microsoft support specialists answered me. The material presented below is presented on the basis of my experiments with search in the Windows-8-Pro-64bit operating system (installed independently on a “clean” laptop, licensed, activated). Similar experiments were previously carried out on a laptop with a pre-installed Windows-7-HomeBasic-64bit system. In both cases the result was the same. In my opinion, the search module of the above operating systems (I suspect not only them) has a serious bug in the search mechanism. Although, as I mentioned above, Microsoft experts believe that this is not a bug, but a feature. Here's a brief summary: 1. Searching only by file names does not work correctly, namely, the file will be found only if one of the conditions is met: a) the searched sequence of characters is the beginning of a word;
b) the searched sequence of characters is located after some characters such as a hyphen, period, underscore and possibly others. 2. Search by file names and file contents does not work correctly, namely, a file with the content we need will be found only if two conditions are met: a) the file type is included in the list of types for which the operating system performs a text search; b) the searched sequence of characters is either the beginning of a word, or is located after some characters such as a hyphen, period, underscore, and possibly others.
Those who are interested can familiarize themselves with the technical details of my experiments in the material below. A quick note: Since there is more than one way to open the items and settings windows I describe, I chose the Windows Control Panel as my starting point. It can be opened by pressing the Win+X key combination and selecting “control panel” from the list that appears.
Description of the search system
Let me start with the fact that the search system is a component of the operating system. Let's open the Windows component settings: Control Panel → Programs and Features → Turn Windows components on or off. Our component is called Windows Search. If you disable it (uncheck the corresponding box), then after a reboot the native Windows search stops working, and the field for entering search queries in the upper right corner of the window disappears from the Explorer window.
By default, the component is, of course, enabled. And when you enter the first character in the search field, the system begins the search without waiting for the full query to be entered. This is the so-called “live” search, it’s so fashionable now. Let us remember that in Windows XP, to start the search process, it was necessary to give a command - click the “Find” button.
An integral part of the search system, which serves to speed up the search process, is the content indexing service with the same name Windows Search, launch type - automatic, deferred. (In the figure below, this service is disabled).
To configure services, open: control panel → administration → services. The properties of the selected service can be viewed by opening the context menu - right-click. As I understand it, this service indexes certain content (names, properties, file contents) in the locations specified to it and enters this information into its database. And subsequently the search takes place in this database, which is stored in “C:\ProgramData\Microsoft\Search”, thereby reducing the search time.
Search system settings
Search settings are concentrated in three places, apparently for convenience. Moreover, some of them are found in more than one of these three places, some only in one. We write the minus to the Microsoft account. (Some settings remained a mystery to me). Here are the locations of these settings: 3.1.
Control Panel → Indexing Options; 3.2. Control Panel → Folder Options (Search tab); 3.3. Windows Explorer window → activate the search bar (put the cursor in it) → the “search” tab appears in the main menu of the window, click it if it is not expanded. Let's go through these places and briefly look at the search parameters.
3.1. Control Panel → Indexing Options.
In the indexing parameters, we are given the opportunity to specify what and where will be indexed. So far, a plus for Microsoft. Microsoft Help does not recommend selecting many indexed locations, such as the Windows or Program Files folders, since, in its opinion, there is nothing for users to look for there. In addition, indexing (index rebuilding) is a lengthy process.
As you can see from the figure, each file type is associated with the required filter, and you can index either only the file properties or both the properties and content. And this means (lo and behold!) that we, for example, can type the name of our musical deity in the search bar of the explorer, and he will be found using music tags. The truth is that the condition/presence of those same music tags in our favorite, often faceless mp3 files is not taken into account. After all, names like track_01.mp3 are not uncommon. By the way, the path (location) of a file is also a property of the file, so you need to be prepared to see in the search results all files whose path contains the word typed in the search query. For me, this is already unnecessary. As a result, we have a complicated search. And, as they say, the philosophy of the Python language is that simple is better than complex. Therefore, my indexing service is stopped.
3.2. Control Panel → Folder Options (Search tab).
The folder options contain the most important, in my opinion, search parameters.
The options in the How to Search section apply to both indexed and non-indexed locations. The “Search for partial matches” parameter, which is necessary and understandable to everyone, does not require comments. The meaning of the “Do not use index when searching for system files in folders” option remains a mystery to me. After all, the indexing parameters already indicate what and how to index.
As the name suggests, the options in the Search Unindexed Locations section apply only to unindexed locations. The parameter values are clear. Having the ability to search in archives is another plus. The next important option is “Search by file names and content.” What to say? They pleased us and gave us a fair warning – not all at once and now.
3.3. Windows Explorer window → when the search bar is activated, the “search” tab appears in the main menu of the window.
Well, the third place to configure search parameters is any Windows Explorer window; once you activate the search query field, the “search” tab appears in the main menu of the window:
There are many useful features here, including customizable ones only here. For example, search only in the current folder, or in all subfolders too. You can limit your search by file modification date, type, size, and other properties. I don’t use them, so as not to be tormented by doubts later. A feature for repeating Internet searches (however!), a log of search queries, as well as additional parameters (these are exactly the ones we have already discussed above).
Troubleshooting and the bug itself
Let me start with the fact that the operating system has built-in modules for finding and fixing various problems. I think the feature is necessary, but I’ll say right away that it didn’t save me. So, open: control panel → troubleshooting → view all categories → search and indexing. Why not show all categories at once? There are not that many of them, they fit on my 14 inch screen. We start troubleshooting the search, in the window that opens, click “Advanced”, click “Run with administrator rights”, click “Next”. Again a new window with a choice of problem, check the box “Files are not displayed in search results” - we have finally reached my grief! Click “Next” and we get this diagnostic result:
As we can see, this concerns the indexing service (which was enabled and working at that moment). I did not touch the permissions for the indexing service directories, and I did not know about the existence of these directories until I saw this window with diagnostic results. Let me remind you where these directories are: “C:\ProgramData\Microsoft\Search”. I haven’t found a way to fix this error, and I don’t think there’s any need anymore (my indexing service is now disabled). And it follows that this applies only to indexed locations. And my problem is relevant for all locations. It's time to explain my problem in detail. Let me clarify right away that the state of the indexing service (“running” or “disabled”) does not matter.
4.1. Search by file name.
So, in the first part of the experiment, in the global search parameters (related to any placements, indexed or not), we activate the “Search for partial matches” option. Next, for non-indexed locations (in my case, for all), uncheck the “Search by file names and contents” checkbox so that the search is performed only by file names. Let's start the experiments. The folder under investigation contains several files of various types:
Type fa
and we see:
It would seem that Windows Search coped with the task; even the results are highlighted in yellow. What else could you dream of? But where is the SearchFalse.vsd file? Isn't fa
not part of the name SearchFalse.vsd?
Maybe it's a registry issue? But in the example above, names are found where f
is in both upper and lower case.
To calm down, let's enter Fa
and see that the result has not changed. At least we have no problems with the register!
Let's try to enter cm
, we get:
It's as if everything is normal.
Enter ro
:
“There are no items matching the search criteria” - how can this be, brothers and sisters? Three files match the search criteria (Error.cmd, Error_critical.txt, Wrong.txt), but they were not found. Everything is lost? This is what we have so far: a sequence of characters that is obviously in the file names is entered into the search field. But the search results only contain files for which the specified sequence is the beginning of the name, or the beginning of the extension, or is located after a hyphen. But this contradicts, I’m sure not only my idea of how search works!
Let’s try a trick: enter “asterisk” as the first character of the query *ro
:
It's done, the files have been found! But without the wonderful yellow backlight. There is no mention of such tricks in the certificate. The development of events as a whole is alarming.
4.2. Search by file name and content.
The nut of knowledge is hard, but we are not used to retreating... We turn on the “Search by file names and contents” setting so that we can now search by file content.
In the folder already familiar to us, five files (Error.cmd, Fail.xlsx, Foul.jpg, Mistake.bat, Wrong.txt) contain the same content: Get off My Cloud As Tears Go By Paint_It_Black Mother's Little Helper Lady-Jane
The Foul.jpg file is a text file with a modified extension.
Type tea
, (to match the beginning of the word Tears):
It seems like luck, but the file Foul.jpg was not found. But this can be explained by the fact that Windows obviously does not consider it text and does not look for text there. Here the questions arise: where does Windows search get information about file types and secondly, most importantly, how to make us search for text where we want it. As for the first, it’s apparently in the registry. But with the second one, it’s not clear where to find this magical setting? Again I did not find the answer. As a note, I note that the text can be found in .pdf files.
bla in the search field
, (so that the characters come after the underscore):
The files have been found, but it’s too early to talk about luck. Enter jan
, we get the same result. What is expected.
Let's try to complicate the task even more by typing the request ear
:
The four files that should be found are missing. Again a failure, but one for which we must be prepared. We have a counter move! Enter *ear
:
This time the failure is unexpected, which already causes despondency. Is there really a need for another magic symbol to replace the beginning of the word? I have tried: ~, @, $, %, -, !, even a space. But everything is in vain - the files were not found. By the way, if you enter a hyphen in front, the search result is all files except pe.pdf, again a mystery.
4.3. Conclusions.
Based on everything stated above, we can conclude that the search mechanism is the same for searching by file names and searching by names and contents. The error, in my opinion, is one and very critical, as it leads to incomplete search results. In addition, it misleads a person who is logical in his thinking and forces him to make cunning guesses. The result is a big minus for Microsoft. The only good thing is that the bug is being fixed, at least for searching by file names.
Diagnosis
We can sum up some disappointing results:
1. Searching only by file names (with the “search by file names and contents” option disabled) does not work correctly. Namely, the file will be found only if one of the conditions is met: a) the searched sequence of characters is the beginning of a word; b) the required sequence of characters is located after some characters such as hyphens, dots, underscores and possibly others, which I consider a waste of time to determine a list of.
This bug can be cured by using the saving symbol
*
“asterisk” at the beginning of the desired sequence.
2. Search by file names and file contents (with the “Search by file names and contents” option enabled) does not work correctly. Namely, a file with the content we need (we are interested in the content of the file) will be found only if two conditions are met: a) the file type is included in the list of types for which the operating system performs a text search; b) the searched sequence of characters is either the beginning of a word, or is located after some characters such as a hyphen, dot, underscore, and possibly others, which I consider a waste of time to determine a list of.
I have not yet found a cure for this bug.
I almost forgot, a brief description of this problem was sent by me (after system authentication) to Microsoft support. The answer was received, I must say, promptly, but faith in humanity was lost. The response stated: “We inform you that we are talking about the normal operation of the product - this is its architectural feature. You can find additional information on the issue you are interested in by visiting our portals – support.microsoft.com and technet.microsoft.com.”
How to live further?
Is this really an architectural feature or was I sent politely? I am inclined to think that it is still the first. Although the second would be better, because architectural bugs, as I understand it, cannot be cured with patches! This means we don’t write negatives anymore – this is “Epic Fail”
!
As a conclusion, some thoughts, including about the causes of the phenomenon
In the Windows XP operating system, this behavior of the search system is not observed; the search works, as is customary in the field of information technology. The settings are concentrated in one place and are clear. Except that the search is not “live”, but this “live” search only bothers me: I haven’t entered a query yet, but some attempts are already beginning. In Google search this feature is at least disabled. It seems that Microsoft specialists were tasked with introducing some kind of innovation into the search system. So they would “revive” it, plus they would make a cool highlight of the results - and happiness to everyone! Why break the principle itself, why touch the basics? The innovative search, opened from the Windows 8 sidebar, only searches for files in indexed locations, and given the bug, its value is lost for me. One more small note and I’ll finish. While I was googling my problem, I read a number of articles by Vadim Sterkin (aka Vadikan on oszone.net). For example: https://www.outsidethebox.ms/9973/ and https://www.oszone.net/10893/Windows7_Search_Part2. On his blog and on the oszone.net forum there are songs of praise about Microsoft. To be fair, it must be said that the articles contain necessary and useful information. But with regard to Windows Search, it seems that search examples are deliberately left behind the scenes when the desired sequence of characters is located, say, at the end of a word. I can’t help but remember the fable about the cuckoo and the rooster...
Other options to fix search problems in Windows 10
If the methods discussed above did not help restore the search functionality, try the following options:
- Create a new user and check if the search works under it;
- Boot from the LiveCD and delete the Microsoft.Windows.Cortana_*** folder in AppData\Local\Packages (you can also end the process from Windows using unlocker ). After the reboot, the folder will appear again and after a few minutes the search should work (this method has helped several of our visitors);
- Check the integrity of system files: sfc /scannow or dism /Online /Cleanup-Image /RestoreHealth ;
- If problems with search are observed in the MS Outlook email client, see another instruction: Searching for letters in Outlook does not work.