A weak WiFi signal is a pressing problem for residents of apartments, country houses and office workers. Dead zones in a WiFi network are typical for both large rooms and small apartments, the area of which even a budget access point can theoretically cover.
The range of a WiFi router is a characteristic that manufacturers cannot clearly indicate on the box: the WiFi range is influenced by many factors that depend not only on the technical specifications of the device.
This material presents 10 practical tips that will help eliminate the physical causes of poor coverage and optimize the range of your WiFi router; you can easily do it yourself.
Install the antennas in a vertical position
The radiation from the access point in space is not a sphere, but a toroidal field, shaped like a donut. In order for WiFi coverage within one floor to be optimal, radio waves must propagate in a horizontal plane - parallel to the floor. For this purpose, it is possible to tilt the antennas.
The antenna is a donut axis. The angle of signal propagation depends on its inclination.
When the antenna is tilted relative to the horizon, part of the radiation is directed outside the room: dead zones are formed under the “donut” plane.
A vertically mounted antenna radiates in a horizontal plane: maximum coverage is achieved indoors.
In practice : Mounting the antenna vertically is the easiest way to optimize indoor WiFi coverage.
Place the router closer to the center of the room
Another reason for the occurrence of dead zones is the poor location of the access point. The antenna emits radio waves in all directions. In this case, the radiation intensity is maximum near the router and decreases as it approaches the edge of the coverage area. If you install an access point in the center of the house, the signal will be distributed throughout the rooms more efficiently.
A router installed in a corner transmits some of the power outside the house, and distant rooms are at the edge of the coverage area.
Installation in the center of the house allows you to achieve even distribution of the signal in all rooms and minimize dead zones.
In practice: Installing an access point in the “center” of the house is not always feasible due to the complex layout, lack of sockets in the right place, or the need to lay a cable.
Reasons for a bad signal from a Wi-Fi router
First, it’s worth understanding what could cause a router’s Wi-Fi signal to be bad. This will help you decide on a method to solve the problem in the future. Let's highlight the most popular cases:
- It's not the router, but the quality of the connection itself. You can check this by connecting to the Network via a wire. If the speed is equally low, then this is exactly the case. In this case, you do not need to do anything with the router. It is recommended to contact the technical support service and request a free visit of a specialist to your home.
- The router operates at full power, but this is not enough for a good signal throughout the house. It is best to purchase or rent a stronger router or terminal, which will immediately solve the problem. However, there are other ways, which we will look at below.
- The device is not positioned or configured correctly.
Provide direct visibility between the router and clients
WiFi signal frequency is 2.4 GHz. These are decimeter radio waves that do not bend well around obstacles and have low penetrating ability. Therefore, the range and stability of the signal directly depend on the number and structure of obstacles between the access point and clients.
Passing through a wall or ceiling, an electromagnetic wave loses some of its energy.
The amount of signal attenuation depends on the material the radio waves travel through.
*Effective distance is a value that determines how the radius of a wireless network changes in comparison with open space when a wave passes an obstacle.
Calculation example: WiFi 802.11n signal propagates in line-of-sight conditions over 400 meters. After overcoming the non-permanent wall between the rooms, the signal strength decreases to 400 m * 15% = 60 m. The second wall of the same type will make the signal even weaker: 60 m * 15% = 9 m. The third wall makes signal reception almost impossible: 9 m * 15 % = 1.35 m.
Such calculations will help calculate dead zones that arise due to the absorption of radio waves by walls.
The next problem in the path of radio waves: mirrors and metal structures. Unlike walls, they do not weaken, but reflect the signal, scattering it in arbitrary directions.
Mirrors and metal structures reflect and scatter the signal, creating dead zones behind them.
If you move interior elements that reflect the signal, you can eliminate dead spots.
In practice: It is extremely rare to achieve ideal conditions when all gadgets are in direct line of sight to the router. Therefore, in a real home, you will have to work separately to eliminate each dead zone:
- find out what interferes with the signal (absorption or reflection);
- think about where to move the router (or piece of furniture).
Selecting the correct position for receiving devices
In addition to choosing the optimal router position , do not forget about the device that receives the signal. After all, even small changes in position can significantly affect the result. Let's take a laptop for example. Place the laptop so that the display cover, which houses the antenna, faces the direction of the wireless signal source. Then slowly move or rotate the device, thereby you will learn how to find the optimal signal reception area . You can also check the result using the inSSIDer program (link above).
Using a USB extension cable
A long antenna cable can negatively affect the quality of reception, while a USB cord up to 5m long will not cause such problems. Therefore, it makes sense to place the wireless USB adapter within the coverage area of the wireless network, using a long USB cable. Using the holder included with many USB adapters, the device can be mounted at a certain height to achieve more reliable reception from the router. Using a USB extension cable would be a good option for a room far away from the router. For example, I used it in the bedroom for a mini-ITX computer.
Internal cards for connecting a PC to a wireless network
It is no secret that expansion cards with a Wi-Fi module are available for desktop computers, but due to their internal location, the antennas, as a rule, are hidden under the table or behind the wall of the cabinet. In my HTPC, I used exactly this option, since the shelf under the equipment did not have a back wall. If the antennas cannot be removed, then a wireless adapter connected via USB will be a more effective and affordable solution. A good model is the TP-Link TL-WN822N, since its antennas can be rotated in the desired direction, and placed not only at the back of your system unit.
Place the router away from sources of interference
The 2.4 GHz band does not require licensing and is therefore used for the operation of household radio standards: WiFi and Bluetooth. Despite the low bandwidth, Bluetooth can still interfere with the router.
Green areas are the stream from the WiFi router. Red dots are Bluetooth data. The proximity of two radio standards in the same range causes interference, reducing the range of the wireless network.
The magnetron of a microwave oven emits in the same frequency range. The radiation intensity of this device is so high that even through the protective screen of the furnace, the magnetron radiation can “illuminate” the radio beam of the WiFi router.
Microwave oven magnetron radiation causes interference on almost all WiFi channels.
On practice:
- When using Bluetooth accessories near the router, enable the AFH parameter in the settings of the latter.
- The microwave is a powerful source of interference, but it is not used very often. Therefore, if it is not possible to move the router, then you simply won’t be able to make a Skype call while preparing breakfast.
Disable support for 802.11 B/G modes
WiFi devices of three specifications operate in the 2.4 GHz band: 802.11 b/g/n. N is the newest standard and provides greater speed and range compared to B and G.
The 802.11n (2.4 GHz) specification provides greater range than legacy B and G standards.
802.11n routers support previous WiFi standards, but the mechanics of backward compatibility are such that when a B/G device appears within the range of the N-router - for example, an old phone or a neighbor's router - the entire network is switched to B/G mode. Physically, the modulation algorithm changes, which leads to a drop in the speed and range of the router.
In practice: Switching the router to “pure 802.11n” mode will definitely have a positive effect on the quality of coverage and throughput of the wireless network.
However, B/G devices will not be able to connect via WiFi. If it is a laptop or TV, they can be easily connected to the router via Ethernet.
Boosting devices
But, if the settings are not enough to get the desired radius, or you don’t want to flash the firmware, then how can you strengthen the router’s signal?
Through replacement of antennas and additional modules!
The correct settings and auxiliary tools, although you have to spend money on them, together will give you excellent communication quality.
Antennas
The antenna is the source of the signal; it distributes it around itself in a certain area. Point the antennas vertically upward so that their propagation zones cover a larger area.
Replace weak ones with more powerful ones, usually the longer the more powerful, or use attachments if the signal is just a little lacking. There are also antennas on the wire that can be placed closer to the desired location without moving the router. See how they can be replaced on your router, and whether there are any unoccupied connectors: the more antennas, the denser and more stable the signal.
Repeater or additional router
A very effective way. The repeater will receive and duplicate the signal. Why is it needed: an additional router, if it cannot work in repeater mode, will have its own network, and you will have to constantly switch between the network of the first and second, moving between rooms.
The repeater takes up less space - all you need to do is connect it to an outlet, and it works on the same network as the router. Take a model that matches the range of your router, but it’s better to have a dual-band one - even if you don’t have a 5GHz router, one will definitely appear in the future.
There are two important details:
- the repeater does not amplify, but duplicates, that is, the signal strength from it will be the same as from a router;
- also, the repeater only accepts one network, for example, it is impossible to transmit both home and guest networks at the same time;
- The data transfer speed drops, but not much.
Routers can operate in repeater mode, but not all - it depends on the model. A second router will cost much more than a repeater and will also take up a lot of space, but the advantage is that, if necessary, it can be improved with new antennas or boosters for greater coverage. If you need to duplicate the signal over a very large area, then take a second router with a repeat function.
A repeater is a good option in a private house with several floors.
Wi-Fi booster
A booster is needed to specifically strengthen the WiFi signal, that is, to increase the coverage area of the router itself, this is different from a repeater. Plug it into the antenna jack and it will improve communications significantly.
Select the optimal WiFi channel in the settings
Almost every apartment today has a WiFi router, so the density of networks in the city is very high. Signals from neighboring access points overlap each other, draining energy from the radio path and greatly reducing its efficiency.
Neighboring networks operating at the same frequency create mutual interference, like ripples on the water.
Wireless networks operate within a range on different channels. There are 13 such channels (in Russia) and the router switches between them automatically.
To minimize interference, you need to understand which channels neighboring networks operate on and switch to a less loaded one. Detailed instructions for setting up the channel are presented here.
Congestion of WiFi channels in the entrance of a high-rise building.
In practice: Selecting the least loaded channel is an effective way to expand the coverage area, relevant for residents of an apartment building.
But in some cases there are so many networks on the air that not a single channel provides a noticeable increase in WiFi speed and range. Then it makes sense to turn to method No. 2 and place the router away from the walls bordering neighboring apartments. If this does not bring results, then you should think about switching to the 5 GHz band (method No. 10).
Flashing DD WRT
Exactly what was discussed before. DD WRT can turn even a cheap router into a good server. If you don’t know how to improve the signal, then use this method, the difference will be noticeable.
This is a multifunctional firmware written on the Linux OS kernel, providing a large number of settings with which you can strengthen WiFi and speed up communications, as well as many other useful additions. Read the instructions carefully, because... Incorrect installation can damage the router, and you can only throw it away.
The main thing is not to rush, then no problems will arise.
Working with the new firmware is difficult at first, but the interface, as well as the documentation, have been translated into Russian, and after a little practice you will be able to fully appreciate all the advantages.
Adjust the router transmitter power
The power of the transmitter determines the energy of the radio path and directly affects the range of the access point: the more powerful the beam, the further it hits. But this principle is useless in the case of omnidirectional antennas of household routers: in wireless transmission, two-way data exchange occurs and not only clients must “hear” the router, but also vice versa.
Asymmetry: the router “reaches” a mobile device in a distant room, but does not receive a response from it due to the low power of the smartphone’s WiFi module. The connection is not established.
In practice: The recommended transmitter power value is 75%. It should be increased only in extreme cases: turning the power up to 100% not only does not improve the quality of the signal in distant rooms, but even worsens the stability of reception near the router, since its powerful radio stream “clogs” the weak response signal from the smartphone.
Minimize router usage on 2.4 GHz frequency
The main reason for the weakening of the router signal is nearby household radio electronics and devices. This can be any equipment - subwoofers, radio telephones and intercoms, microwave ovens and any household appliances on the remote control, wireless security, surveillance and security systems, etc.
Try to calculate the direct (shortest) route for the Wi-Fi signal to propagate from the router to the PC or laptop, and remove all electronics from this area. Or at least replace it with equipment without radio emissions. Checking the emission of interference and signal suppression of the router is very simple: just turn off nearby devices one by one and monitor the level of the Wi-Fi signal. This method, although approximate, often works.
Wi-Fi interference emission test
Replace the standard antenna with a more powerful one
Most routers are equipped with standard antennas with a gain of 2 - 3 dBi. The antenna is a passive element of the radio system and is not capable of increasing the flow power. However, increasing the gain allows you to refocus the radio signal by changing the radiation pattern.
Antenna gain is similar to focusing a flashlight beam: a narrow beam shines further than a wide beam.
The higher the antenna gain, the further the radio signal travels. In this case, the narrower flow becomes similar not to a “donut”, but to a flat disk.
There is a large selection of antennas for routers with a universal SMA connector on the market.
Replaceable omnidirectional antenna.
Omnidirectional whip antenna.
Directional indoor antenna.
In practice: Using an antenna with high gain is an effective way to expand the coverage area, because simultaneously with the signal amplification, the sensitivity of the antenna increases, which means the router begins to “hear” remote devices. But due to the narrowing of the radio beam from the antenna, dead zones appear near the floor and ceiling.
Antenna change
In theory, installing a more powerful antenna should increase the network coverage radius, but in reality I have not tested this myself. Standard antennas are set at 2-3 dB. If you have a large apartment, then 7dB will be enough. For a large house, you can take a 14 dB antenna or make it yourself. In stores, such antennas cost from 1000 to 8000 rubles, depending on the signal amplification power. For a large village, you can fold and buy one 30dB antenna, the radius will be huge.
NOTE! Routers without an antenna or with an internal transmitter work much worse than antenna ones.
Use signal repeaters
In rooms with complex layouts and multi-story buildings, it is effective to use repeaters - devices that repeat the signal from the main router.
Repeaters expand the WiFi network, covering the surrounding area and the upper floors of a country house.
Repeaters help deploy a wireless network in rooms with complex layouts.
The simplest solution is to use an old router as a repeater. The disadvantage of this scheme is that the throughput of the child network is half as much, since along with client data, the WDS access point aggregates the upstream flow from the upstream router.
Detailed instructions for setting up a WDS bridge are provided here.
A router in WDS mode helps expand WiFi network coverage.
Specialized repeaters do not have the problem of reducing bandwidth and are equipped with additional functionality. For example, some Asus repeater models support the roaming function.
In roaming mode, devices automatically connect to a more powerful network, and the connection is not lost when moving between access points.
In practice: No matter how complex the layout, repeaters will help you deploy a WiFi network. But any repeater is a source of interference interference. When there is free air, repeaters do their job well, but with a high density of neighboring networks, the use of repeater equipment in the 2.4 GHz band is impractical.
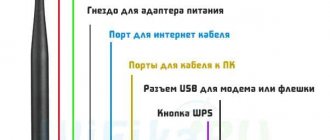
Selecting a location for installing the router
If the wifi signal reaches the end equipment is too weak, to improve it, it is enough to move the router closer to the destination: laptop, smart TV, workplace. Physically moving the router will reduce the attenuation of the transmitted wave - and therefore minimize possible interference during transmission.
When choosing a new location, we recommend to improve the wifi signal:
- Mount the device higher, preferably on a wall or a shelf located under the ceiling. From a height, the waves will spread evenly in all directions without colliding with obstacles.
- If possible, place the router in the central point of the apartment - radio waves travel in all directions at the same speed, which means that the home network will cover the maximum area of the house.
If you can’t change the position of the device, try moving your computer or laptop closer to it, or changing the location of your workplace: this way you will achieve a slight increase in the quality of Wi-Fi reception.