1) The usb 2.0 specification was introduced in 2000, and usb 3.0 in 2008, therefore version 3 is more modern than version 2.
2) The theoretical maximum speed of usb 2.0 is 60 megabytes per second. Theoretical maximum speed of usb 3.0 is 625 megabytes per second
3) The approximate, maximum, real usb speed, taking into account losses as a result, various factors and features, is:
up to 25 – 40 megabytes for usb 2.0 up to 400 – 450 megabytes for usb 3.0
4) Current strength usb 2.0 - 500ma (milliampere) Current strength usb 3.0 - 900ma (milliampere) Higher current strength allows you to use more energy-dependent devices, charge mobile devices faster, and also connect more devices, for example, through a usb splitter.
5) USB 3.0 uses asynchronous data transfer, that is, data is transmitted simultaneously in 2 directions, to put it very simply, data is read and written simultaneously...
It is recommended not to exceed a cable length of 5 meters for USB 2.0 and 3 meters for USB 3.0 to maintain stability and avoid performance loss.
History of the creation of Universal Serial Bus (USB)
The ancient parallel LPT ports and serial COM ports have already sunk into oblivion. Finally, computer users have begun to get rid of thick communication cables, keyboards and mice with COM tips and PS/2 connectors. They were replaced by the universal USB interface, in the English interpretation - Universal Serial Bus. And a universal port is universal so that, without hesitation, you can connect various external devices to it: large and small, low-speed and high-speed, powerful and low-power.
Developers of desktop computers and laptops have long been thinking about replacing various communication connectors with one universal one, capable of solving all possible problems. The first examples of the Universal Serial Bus interface began to appear in 1994-1996 and were designated USB 1.0. The novelty spurred the market for external devices, and by 2000, most printers, scanners and other devices began to be equipped with a newfangled interface. A big plus in the development of USB was the appearance in 1999 of the first 8 MB flash drive, which appealed to all users.
USB 2.0 and USB 3.0 read and write speed
In 2000, the world saw a new version - USB 2.0. She became forty times more productive than her predecessor. If USB 1.0, according to the specification, had a maximum data transfer speed of 12 Mb/s (megabits per second), now the speed has increased to 480 Mb/s. The successes did not arise out of nowhere - it is known that about 400 interested companies took part in the development of the innovation, including such well-known brands as Intel, IBM, Hewlett-Packard, Compaq, Microsoft, NEC, Philips and many others.
Enraged by the unprecedented results, the developers did not stop there and in 2008 proposed USB 3.0. The new specification made it possible to increase the data exchange speed by another 10 times and reached a value of 4800 Mb/s, which is equivalent to 4.8 Gb/s. At this speed, information from a 1-terabyte medium can theoretically be downloaded in less than 30 minutes (at a maximum possible speed of 600 MB/s), if there are no other restrictions. It should be noted that the near future lies with this type, so when buying a new motherboard, make sure that it supports this connection standard.
USB and its versions
USB stands for universal serial bus, and is translated into Russian as a universal serial bus. Universal – that means you can connect anything, any device, to it. USB comes in different versions, the main difference being speed.
Manufacturers took a long time to achieve universality. As many remember, at first the computer had many different ports, some of which remain to this day, for example, bulky COM with thick cables, PS/2 with fragile contacts, and others. Now printers, keyboards, mice and other equipment can be connected via USB.
The first USBs began to appear in 1994. In 1996, version 1.0 was released, which operated at a meager speed of 1.5 Mbit/s. Then in 2000, version 2.0 was released with an operating speed of 480 Mbit/s. This is a completely acceptable speed, which made it possible to connect different equipment to the port. In 2008, USB 3.0 was released, theoretically operating at a speed of 5 Gbps.
The development of USB 3.0 was funded by many global brands in the computer industry, which were interested in introducing standardization for connectors and improving equipment performance.
How is USB 2.0 structurally different from USB 3.0 and are they compatible with each other?
In terms of design, there are few differences between USB 2.0 and USB 3.0. They are partially compatible, but the latter contains an additional 4 pins for connecting two signal twisted pairs. The previous version has only 4 contacts: two signal, power and ground, the housing is used as a screen.
Partial compatibility implies the fact that you can easily connect a USB 2.0 plug to the USB 3.0 version socket, that is, the connectors are suitable for connecting any devices with a cable, as well as flash drives, hard drives or card readers. In this case, there is no need to use any additional adapters - everything will work, only at a reduced speed, according to specification 2.0. The same thing will happen when you connect a USB 3.0 plug to a USB 2.0 socket. Those connector options that are not included in the connection, naturally, will not work.
USB 3.1, 3.0, usb type-c - what's the difference?
Anything with a version number (such as 2.0 or 3.0) is a standard—a technology that allows data to be transferred over a cable from one device to another.
Anything that has a type (eg Type-A, Type-C) refers to the connector and its shape.
What's different about USB Type-C, however, is that it was specifically designed to take advantage of the new USB 3.1 standard. So, instead of specifying a version that determines the power and speed at which data can be transferred, in the case of USB-C it is the connector itself.
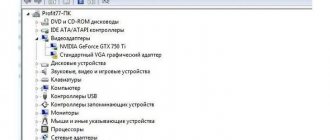
How to find out which port is on a computer or laptop?
You can visually distinguish USB 3.0 ports from USB 2.0 ports by color. The USB 3.0 version is blue, while the USB 2.0 is black. The same colors are used to mark the plugs on the cable.
In addition, there are several design options for USB connectors. Here are the main types of USB 2.0 connectors: type A regular (4x12 mm), Mini (3x7 mm) and Micro (2x7 mm); type B regular (7x8 mm), Mini (3x7 mm) and Micro (2x7 mm). The overall dimensions of the connecting part of the connector given in parentheses are rounded.
The designs of USB 3.0 connectors currently in use are as follows. For type A, only the regular version is used, for type B there is a regular, Mini and Micro version. For both specifications 2.0 and 3.0, universal connector options have also been developed: Mini-AB and Micro-AB. Type A and type B mating parts can be connected to them without problems. The USB 3.0 version additionally has a Powered-B type with reinforced power contacts. Manufacturers have also agreed that all USB 3.0 connectors will be blue to visually identify the port specification and its potential.
What is your opinion: is WiFi harmful?
Yes
22.91%
No
77.09%
Voted: 36485
What is USB?
USB (Universal Serial Bus) is an abbreviation of the term “universal serial bus”. Pronounced Y-ES-BEE. Allows a smartphone, computer, TV and other devices to “communicate” with connected flash drives and devices. In simple words, USB is a set of standards for information exchange and connection methods (ports, connectors, wires). There are several different functions that USB supports. Read more about them here.
First, let's learn about the most important differences between USB 1.0, USB 2.0 and USB 3.0. The very first USB standard is considered obsolete and is not used anywhere in new devices. But we will tell you about him anyway.
Different USB appearance
Blue color means USB 3.0 or 3.1.
The types of USB connectors and connectors are not associated with the USB generation. The developers tried to make the more modern standard compatible with the older one. The only thing is that the difference between USB 1.0, 2.0 and 3.0 can be determined by color
If you look at the color of the plastic inside the socket or connector, you will see that USB 1.0 is white, USB 2.0 is black, and USB 3.0 is blue. Sometimes you can see red plastic in a USB drive. This means that it will always be active, regardless of whether it is in standby mode or sleep mode.
The main conclusion: connectors and connectors for USB of different generations are the same in 99% of cases! Only with the USB 3.1 generation did some additional sockets and connectors appear. But they are rare and more about them below.
Data transfer speeds and directions
USB 1.0 supported a maximum data transfer rate of only 12 MB/second. But a little later, the USB 2.0 standard was introduced, which could already transfer data at a speed of 480 MB per second. The newest generations of USB 3.0 and 3.1 support maximum speeds of up to 5 Gbps and 10 Gbps, respectively.
But that's not all. USB 2.0 and USB 1.0 can only process data in one direction at a time. For example, if you copy a movie from a flash drive, you won’t be able to download anything to it at the same time. But the USB 3.0 and 3.1 standards allow data transfer in both directions.
The reason for this innovation is that version 2.0 uses a half-duplex data transfer method, and version 3.0 and higher uses a full-duplex data transfer method. Well, that’s it, information for general development.
What is USB 3.1 and how is it different from USB 3.0?
Let's take a closer look at the difference between USB 3.1 and 3.0. These are the latest versions of the USB standard. And they are increasingly found in modern devices. From smartphones, TVs and set-top boxes to computers.
USB 3.1. was so named because it did not bring significant changes to the standard itself, but is a development of 3.0. Supports data transfer speeds up to 10 Gbps. Often found together with the USB-C connector. But this does not mean that if the connector is different, then the USB standard in the device is necessarily older. USB 3.1 easily supports other types of connectors.
To achieve maximum USB 3.1 data transfer speeds, both cables and devices must support USB 3.1. USB 3.1 is also known as USB 3.1 Gen 2 (10 Gbps).
But the USB 3.0 generation supports data transfer speeds only up to 5 Gbps. USB 3.0 is also known as USB 3.1 Gen 1 (5 Gbps).
Once again, USB 3.1 is backward compatible with USB 3.0 and USB 2.0 in most cases. This means that if you have a flash drive that supports USB 3.0 or 3.1, then you can connect it to a computer with USB 2.0. It's just that the data transfer speed will be the same as 2.0.
But there is one exception. Bus-powered USB 3.0 and 3.1 devices that consume more power than USB 2.0 will likely fail to turn on. After all, they will not have enough energy. This does not apply to flash drives, keyboards and all ordinary devices. But it may apply to various USB video cameras, etc. Carefully read on the packaging what is required for such gadgets.
What's the difference when using USB 2.0 and 3.0 on a computer?
Due to the fact that a large number of external devices are connected via the USB port, the mechanical stress on these connectors has increased many times over. Frequent connection of flash drives, headsets, and all kinds of chargers leads to mechanical abrasion of parts and weakening of electrical contacts. Moreover, the consumer may accidentally hit the cable connector or flash drive, which will damage the port and require repair. If the connector is installed on a separate printed circuit board connected to the main board via a cable, then this is not so bad. If the USB connector is soldered directly into the motherboard, then repairs will be expensive.
To avoid trouble, the consumer should be careful and evenly use all USB connectors available on the computer. In addition to the built-in connectors, you can purchase an additional PCI expansion card with USB ports. It is installed in the corresponding PCI slot on the motherboard and provides additional connectors for connecting external devices to the outside of the case.
Also, as an option, you can purchase a USB port splitter (external hub). It will increase the number of connectors and secure the computer itself.
However, you need to take into account that through such a splitter it will not be possible to connect energy-intensive devices, for example, an external hard drive without additional power. In addition, the consumer sometimes allows powerful loads to be connected to the main port, such as an external hard drive or several loads that together exceed the energy capabilities of the power bus. This can lead to burnout of the protective elements of the circuit and failure of the interface to operate.
To prevent this from happening, you need to remember that USB 2.0 can supply a maximum of 500 mA of current to the power line, and USB 3.0 - 900 mA. For more powerful loads, it is recommended to use external power supplies.
Another danger lies in incorrectly turning on/off, for example, a flash drive in “hot” mode, as well as the action of static electricity. Although the developers guarantee the safety of this mode, it is advisable to carry out all communications with the computer and external device turned off. As for static electricity, it is the number one enemy of dry heated rooms. A dangerous charge accumulates on a person’s body and clothing, and in order to remove it, it is necessary to touch the grounding bus, water pipe or water heating radiator.
Now the user has the necessary knowledge about the correct operation of the USB 2.0 and USB 3.0 ports of the computer, and the recommendations given will allow you to solve the tasks without problems and successfully.