Every electronic device has a display , which consists of 4 things: a touch screen, a layer of air or glue, a matrix, and a light source. The matrix determines how the graphics will be displayed, the brightness, the screen resolution, and its response time - this is how many milliseconds it will take to perform some action. It is inserted into screens so that it has pixels - dots that transmit colors to create an image.
Matrices are made using three technologies: TN, IPS, LTPS. The first one is outdated and not used, but the next 2 are popular. Here is information about them.
Differences and features of screens made using IPS and LTPS technology
Almost all smartphone manufacturers use two interactive display technologies - IPS and LTPS.
Currently, they have replaced the outdated and inferior NT in functionality. There are characteristic differences between the two LCD display technologies that make one superior to the other. Let's track all the differences point by point.
Differences
The technologies are similar in production principle. But there are differences between them that are reflected in their design, and, therefore, performance. Now about the difference between them:
Amount of elements
Manufacturers care about how their dies are made. They strive to make production easier. Therefore, the number of components is taken into account during development.
All IPS matrix circuits are located directly on the surface. From it there are 4 thousand contacts for connecting to the driver. And LTPS has less than 200 due to the fact that some of the circuits are located on glass. This made production easier and faster.
Comparing IPS and LTPS technologies
IPS is a method for producing matrices for liquid crystal monitors and displays, which includes four structural elements.
- Illumination matrix or lamp. Its function is to illuminate the display from the inside.
- Pixel and light filtering systems.
- Liquid based crystals.
- Microelectrodes over the entire surface of the matrix.
Innovation : Unlike the old TN - IPS has a 170-degree view.
LTPS - in turn, this technology is based on the use of crystalline silicon, which is capable of producing an induction current at low temperatures.
The size of the silicon crystal is no more than 0.1 microns. In order to obtain crystals of this size and quality, silicon is deposited with gas, and then fired at a plasma temperature of up to 1000 degrees Celsius.
A characteristic innovation is the use of a small amount of energy with the rapid transfer of electrons, but at the same time the system response is slower when pressing on the interactive display. Ping length – 0.15 s.
Why does my Samsung screen burn out?
Burnout occurs in areas where blue or white color is used heavily. Black color does not use the pixel backlight, so it does not cause burn-in. Burnt-in pixels become dark and visible on the screen. The lighter the image, the better they are visible.
Interesting materials:
Does a girl need to undergo military service in order to serve under a contract? Do I need to prime painted walls before wallpapering? Should you eat after cardio? Does latex paint need to be diluted with water? Do you need to wash your refrigerator? Do I need to wash store-bought champignons? Do I need to wash carrots for storage? Do I need to wash disposable tableware before use? Do I need to wash champignons before cooking? Do irises need to be pruned in spring?
Pros and cons of IPS displays
The positive characteristics of IPS displays include:
- The technique has been improved and has reduced the base cost of the display to $9.5. This makes the technology accessible to an absolute number of buyers.
- The display is capable of showing videos and photos with maximum quality, which is close to the real world. Displays can transmit images at maximum resolution.
- Low energy consumption. Liquid crystals consume practically no energy; all the charge goes to the LEDs of the backlight matrix.
- The liquid-based chip display allows you to perform all types of manipulations designed for interactive monitors and displays.
- Durable. If we compare IPS displays with analogues, then it provides the longest “life” period for displays. The very first thing that is susceptible to defects is the backlight diodes, as well as the polymer surface of the matrix.
Currently, the technology has the highest rating in the sales markets.
Disadvantages of IPS matrices
Characteristic disadvantages are the following criteria:
- Low contrast and color gradient when working with dark shades. This will be noticeable when working with the display at night, when the images are dominated by black. The picture may reflect, and the black color may have a gray tint.
- Small ping when the display is in touchpad mode. And also anticipation when watching VR content.
- The displays have a thickness that is greater than that of all similar products. This is due to the need to layer the 4 components described above.
The shortcomings are leveled out, since they practically do not affect the functionality and are absolutely invisible to customers.
Which technology to choose
LTPS has fixed the shortcomings of IPS. They are faster, simpler in design, and easier to manufacture. The technology consumes less energy. But their cost starts from 5 thousand rubles.
IPS matrices are inferior to LTPS, but this does not mean that they are bad. Apart from the response speed, they are similar. They have the same brightness. Moreover, they are produced with the same resolutions. And they cost from 1.5 thousand.
Displays with these technologies are practically no different, except for the price.
Electronics and technologyComment
Pros and cons of LTPS displays
LTPS displays have the following pros and cons.
Advantages of LTPS matrices
Before introducing the products, LTPS manufacturers analyzed all possible negative nuances that were observed in LCD monitors on silicon crystals.
Benefits include:
- All pixels light up individually. Each crystal has individual control and backlighting, allowing for better color rendering and clearer image boundaries. Compared to IPS, image contrast is significantly improved.
- Fast reaction speed. Thanks to the design, which contains an LED matrix, there is practically no even the slightest wait when changing frames in regular videos and VR content, as well as games.
- Since image saturation depends on the backlight of the diode matrix, when viewing dark images the backlight reduces its activity. This allows you to reduce energy costs.
- Since there is no liquid crystal spacer in the “interlayer”, the matrices are thinner.
Disadvantages of LTPS matrices
The disadvantages compared to LCD monitors were completely eliminated, but in turn new disadvantages were identified:
- The image may have a slight blue tint. This is because the silicon crystals themselves have a bluish tint. This sets off the green and red shades of the color scheme (color rendering based on three colors - blue, green, red). This phenomenon can be mitigated by increasing the contrast in the screen settings, but this may cause additional strain on the eyes when looking.
- Low service life of blue LEDs. The color rendering of the display is based on them, so they “burn out” a little earlier. If this happens, the screen will begin to distort colors with a gradient of green or red.
- Memory effect. The image may remain motionless in areas where pixels have become “burnt out” due to time or mechanical damage.
- PenTile. It is used to reduce the negative effect of “burning out” of blue pixels using red and green pixels. But at the same time, the quality of visualization deteriorates.
Important! All product shortcomings are related only to the blue pixels and the color of the silicon crystals. If this circumstance is not considered fundamental for users, then the technology is recommended as the most functional at a given time.
Advantages and disadvantages of AMOLED
Pros and cons
Low screen response time (about 0.01 ms, which is achieved due to the absence of an air gap and the merging of the touch layer with the screen)
Less power consumption (for dark colors LEDs are less bright and require less power)
Better color rendition and viewing angles
The screen is thinner (this makes it possible to place various sensors under the screen itself)
Better brightness and high contrast
The richest and deepest black color
Shorter service life (especially if the screen is used frequently at high brightness levels)
Greater harm to human eyes
Less screen reliability (easier to damage the display)
Which is better LTPS or IPS
To determine the superiority of one matrix over another, it is necessary to understand in more detail the design parameters of both products.
First, let's look at the general features and technological parameters of the matrices, and then move on to the differences.
Common parameters
Essentially, both manufacturers use silicon to make displays, with one caveat: IPS uses silicon-based liquid crystals, and LTPS uses low-temperature silicon crystals with a polymer shell.
Crystals made from silicon derivatives operate in the following technical conditions and have the following properties:
- Temperature during operation does not exceed 200 degrees
- Great resistance to damage by cold.
- When ionized, they are capable of conducting current.
- They are simply processed and integrated into microcircuits.
- Silicon is easily mined, unlike other semiconductors such as tantalum and vanadium.
Both technologies provide monitors and displays with a wide viewing angle, using almost the same operating principle, based on the illumination of pixels through which induction is passed.
Differences
The most characteristic differences include the following comparative parameters:
- Both products use different numbers of design elements, aiming to increase functionality and reduce frame transmission response time. Currently, LTPS goes one step further by reducing the number of elements by eliminating the additional backlight matrix.
- The IPS display bus is routed at the top of the display. The driver and bus combine almost 4500 contacts. In LTPS, the bus is located on the glass under a microscopic polymer film; in this case, there are 5 times fewer contacts than in IPS. Accordingly, production is easier.
- LTPS has a significantly smaller standard size.
- In terms of response speed, LTPS is also 2-3 times faster than the alternative.
Important! What sets LTPS apart is its more expensive price, which is increased due to the unique technology of placing contacts on the glass surface.
Common features
These matrices are made using different technologies and there are differences between them. But there are similarities. Here they are:
Main material: silicon
Liquid crystals are made from silicon. They are turned by a control electrode, which supplies electrons to the crystal and turns it. This is the main part of any LCD display.
Manufacturers chose silicon because:
- It has an operating temperature of up to 200 degrees.
- It is cold-resistant.
- Conducts current well if impurities are added.
- There is more silicon in nature than other semiconductors.
- It's easy to handle
In 2015, smartphones with an indium gallium zinc oxide matrix were released. But the phones turned out to be expensive without any difference in quality.
Wide viewing angle
When a phone has a small viewing angle, it is not convenient for the user to look at it. It is difficult for him to hold the smartphone perpendicular to his eyes, because his physiological characteristics do not allow him to do this.
LCD screens have a viewing angle of 170 degrees . This is enough to comfortably look at the phone screen, looking at text or pictures. A large viewing angle is especially necessary for monitors.
Similar structure
These technologies have approximately the same device design: filters, liquid crystals, control electrodes. LEDs.
The only difference is how polycrystals are produced from silicon. In PTLS it polymerizes at a temperature of 400 degrees . This way the glass, which melts at 650 degrees, .
Different names of technologies do not mean that they are manufactured differently. They are designed according to the same principle; they have one semiconductor - silicon. They even use the same technique.
Smartphone matrix type
The technologies presented for comparison took their origins from their predecessors:
- TN+film
- AMOLED
The first took liquid crystals as a basis, and the second used silicon crystals. Currently, IPS is considered not a separate technology, but a modification of TN+film. But in what ways have the products developed? This question should be answered to track the full package of innovations in IPS technology in order to compare it with LTPS.
Innovation : Thin film transistors (TFTs) were used for the first time in IPS. They are necessary to illuminate subpixels - micro-inclusions located around the circumference of the main pixel. Subpixel backlighting allows you to create a backlight gradient for the main pixel, which multiplies color rendition and image clarity.
The same technology is used in LTPS, but more compactly, since the backlight is provided not by the backlight matrix, but by working with each pixel individually.
Amoled display - what is it?
AMOLED is a special manufacturing technology based on organic light-emitting diodes, where each of them is an independent part of the entire matrix. That is, each LED is illuminated independently. Unlike other manufacturing technologies, AMOLED does not have a special backlight layer that would make the part itself much thicker. Here, each “particle” is highlighted independently and, in fact, is independent. The technology is mainly used to create displays for computers, mobile devices and televisions. AMOLED technology is a kind of breakthrough, since displays with this technology are very bright and colorful, with fairly realistic color reproduction. But it didn’t end with AMOLED, and the technology began to develop further. AMOLED displays have become especially famous thanks to devices from Samsung, which have been using and improving this technology for many years.
What is Super AMOLED
AMOLED (Active Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Mode) displays are very bright, which makes them a good option for use in mobile devices (smartphones, tablets, smartwatches). Super AMOLED is an improved version of standard AMOLED technology. Its difference lies in the fact that now the touch layer (or Touchscreen - “touchscreen”) is located in the screen itself. This makes it possible to achieve smaller part sizes and remove the layer of air that previously appeared between the screen and the touch layer itself. Thus, the display becomes even thinner and lighter, and the picture is brighter and more contrasty.
Here are the differences between the improved Super version and the standard technology:
- Brightness increased by 20%;
- Reflection of sunlight rays is significantly less (by about 80%);
- Energy consumption is 20% lower;
- Newton's rings are now less likely to appear on screen;
- No dust between the screen and display (due to the absence of an air gap).
The design itself looks something like this:
- The first layer is the cathode.
- The second layer is active organic matter. They are used precisely as the very pixels that “burn” on the screen.
- The third is a layer of TFT thin film transistors. Used to control the layer of active organic matter. Transistors regulate the current, setting the brightness and a specific color to each pixel (organic light-emitting diode).
- The fourth is the anode layer.
- The last layer is the substrate.
Nothing ended with Super AMOLED, and the technology began to develop even further. Next, the world saw Super AMOLED Plus. This is a slightly improved version of Super AMOLED, which slightly improved image quality and color reproduction using special Real-Stripe technology. This technology has made it possible to change the way images are drawn. If earlier in Super AMOLED the picture might have seemed grainy, now this drawback was absent due to the fact that the image began to be drawn with full-fledged RGB subpixels.
The latest stage in AMOLED development is Dynamic AMOLED. This is the name given to Super AMOLED matrices with maximum color rendition.
Let's describe the upgrade of the IPS matrix from its TN+film source
TN+film
The most typical matrix is LCD, that is, its technology uses liquid-based crystals. Light passing through the filter is polarized and acquires the required color.
For another ten years, these products were considered an innovation, but the requirements for smartphones to increase their interactivity and functionality created the prerequisites for upgrading TN matrices. TN cannot boast of good viewing angles or contrast, and has poor color rendering.
The modification is irrevocably outdated.
IPS
This technology has replaced, logically, it is more than ten years old. If we look at the displays of second and third generation smartphones, they all use this matrix. The technical parameters and operating conditions of the matrix are described above; let’s mention its creator - the South Korean Samsung Corporation.
Improvements (upgrades) are based on the appearance of the following criteria:
- The viewing angle is at least 160 degrees.
- High pixel density, upgrading picture quality to full HD.
Energy consumption remained at the same level.
Important! There are many modifications of IPS, they all differ somewhat in quality, since they use components of different quality. These factors ultimately affect the cost of smartphones.
Next, we will present flagship smartphones that use IPS and LTPS.
“Which smartphone screen is better?” – Yandex.Q
M.Video experts are always ready to find not only answers to your questions, but also... · mvideo.ruSubscribe
As already answered earlier, today the most common types of smartphone screens are IPS and AMOLED. After all, in fact, LCD, LTPS, PLS, SFT are types of IPS matrix; like OLED, Super AMOLED, P-OLED and others are just varieties of light-emitting diode (LED) technology. The advantages of IPS displays include: - Availability and low cost even with... Read more
13 Good answer14
The most important thing is probably forgotten. Which screen is better, safer for eyesight?
2 more comments
Write a comment
We help solve user problems related to modern gadgets and... · mob-mobile.ruSubscribe
The quality of a smartphone's display is generally related to its price category. For example, the ultra-budget segment is characterized by **NT matrices**, which are still incorrectly called TFT in the specifications. Poor viewing angles, mediocre brightness, but fast response time, low cost and low (compared to IPS) power consumption. In the budget, and often in the middle segment, more often... Read more
2 Good answer
Write a comment
System administrator, a little blogger at lifeservice.me
Subscribe
The eternal debate is IPS or LED (Amoled). One has better color rendition, the other has true black, plus features that allow you to save battery power, because black color does not waste energy. There is no winner in this debate, as in music, everyone chooses what they like. Technology will certainly resolve this debate and someone will undoubtedly leave.
3 Good answer1
Yes, only a year later Amoled picked up phantoms (((
Write a comment
Basically, most phones have IPS and LED. This difference and debate, as for me, is useless. Everyone installs good, normally working OLED screens (you can look at the full article about this if you are of course interested - https://texnoblogger.com/oled-ekrany-razbor/). But! You won't notice the difference. You can see the difference if you put 2 phones next to each other and look closely, then maybe. In… Read more
1 Good answer8
“But it’s common knowledge that iPhones have the best screens,” how is this possible if they don’t produce their own matrices, but use... Read more
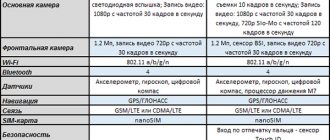
The best smartphones with IPS and LTPS screens
Apple iPhone 11
Apple is currently a generally recognized global flagship whose displays use an IPS matrix.
Main advantages of iPhone 11:
- Highest resolution IPS display.
- Excellent cameras that allow you to capture images with a delay of a thousandth of a microsecond.
- Biometrics via display.
- Moisture protection according to IP68 standard.
- Processor generation A13 Bionic (7 nm+)
- Fast charging, power - 18 watts.
The main disadvantages of the iPhone 11:
- The memory card cannot be used.
- There is no 3.5 mm jack provided.
- The design provides a “light” connector.
Honor 20
Honor 20 uses an LTPS screen in its design, which provides instant biometric scanning and improved color reproduction in rich colors.
Main advantages of Honor 20:
- The best LTPS display sold in 2020.
- Instant scanner.
- No staffing waiting.
- Advanced contrast settings to level out the “blue” in the color gradient.
Main disadvantages of Honor 20:
- Inconvenient macro camera.
- Ping when working with a proximity sensor.
These two smartphones are flagships that use two competing technologies in their display design, but at the same time provide customers with convenient functionality and excellent image quality.
If we look at the flagship smartphones for 2022 and 2022, they are an order of magnitude inferior to those named. Technologies are constantly evolving, various production methods are being sought and new capabilities are being introduced.
Trends in display development will be discussed below.
Global development prospects
Both products may well be replaced by the creation of QLED displays. It is based on the physical concept of a quantum inclusion or quantum dot - a hundredth part of a microscopic semiconductor that can produce light if an induction current is applied to it.
Quantum dot has an unlimited color range, allowing it to deliver the highest quality images with no frame-by-frame ping.
This is a completely new branch for the production of displays, much like amoled was once unique and inimitable until it was replaced by LPTS.
Important! QLED is the most expensive technology, the implementation of which increases the cost of smartphones by 1.3–1.5 times. But at the same time, the quality of the picture increases exponentially.
Currently, LPTS, when compared to QLED in percentage terms, can provide 45% of the functionality of the latter. As for IPS, the possibilities do not exceed 30%.