The iPhone 6S, as well as its phablet version Plus, have become a worthy continuation of the “six” predecessors that created a universal sensation. They both pleased and disappointed some of the high expectations. We were pleased to finally have an improved filling. And the main disappointment stems from the fact that at first glance, nothing seems to have changed, and it is not clear what to pay the increased price for.
But, despite the minimal external differences, the next flagships are technically much more advanced than the iPhone 6. And, of course, the issue of iPhones meeting the high title of market leaders has long been overdue. The constantly increasing technical parameters and capabilities of competing models inexorably demanded further technical improvements from Apple smartphones.
The time has come for drastic changes . This time, the engineers took into account most of the wishes of customers and critics. The capabilities of the camera, processor and system have finally expanded, and display controls have also undergone significant improvements. So the outrage is unfounded.
New dimensions
As for the dimensions of the updated Apple phone, they have changed little, as has its “appearance” itself. This is absolutely in the spirit of the thrifty Cupertino people - why spend money ahead of time on reconfiguring the flow line, if you can still use last year’s developments? So far, this housing design is quite relevant; all the components necessary for operation are placed.
Now the length of the smartphones is 138.3 mm (or 158.2 mm for the Plus version), width is 67.1 mm (or 77.9 mm), thickness is 7.1 mm and 7.3 mm, respectively.
If we compare the parameters of the s-series with the sizes of the previous flagships - iPhone 6 (and 6 Plus), we can see that the new iPhones have added a millimeter in width, and in length - the compact version has grown by 2 mm, and by 1 mm – Plus model. The thickness of the case for both sizes has increased equally - by 2 mm.
By and large, the visual difference between the models is practically invisible to the eye. The dimensions and location of the ports and antenna frames remain the same, there is nothing to start from. The differences barely appear only when two smartphones are placed next to each other.
See for yourself - iPhones placed in close proximity show minimal differences.
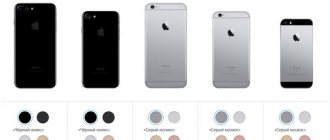
Purely externally, the s-series is given away only by the modified factory markings printed on the back panel. Now there is a postscript S. And, of course, a new popular color - metallic pink. Both the first and the second are hidden without a trace behind the case, which you will probably use, given the explosive combination of large sizes and a slippery body (and, of course, considerable cost). So no one will guess that you own the latest, ultra-modern modification of iPhones.
The main intrigue is that, despite the almost unchanged size, the 6 S and 6 S Plus weigh much more than the previous series. The excess is almost 20 grams for the Plus version (192 g instead of 172 g), and 14 grams for the simple version (143 g versus 129 g). Still, the weight of the new Plus modification, equal to two chocolate bars, will clearly weigh heavily on your pocket. So what is the reason?
As it turned out, all this is due to the use of a more durable aluminum alloy, with the addition of zinc, 7000 series. With its use, Apple saved itself from the flood of potential complaints about iPhones bending in pockets that occurred last year. It is thicker and therefore stronger than the previously used 6000 series.
An additional touch layer, consisting of tiles of sensors that enable 3D Touch, also contributed.
Apple also announced the use of a new generation of glass - Ion X. It undergoes a special two-stage hardening, thanks to which the iPhone display coating has become one of the most durable on the market. His sensitivity also increased.
And finally, an improved camera (with an expansion of 12 megapixels, instead of 8 megapixels), which buyers had long been asking to be brought up to modern standards, had to be placed somewhere.
Detailed technical specifications
Make and model
Make and model of the device, and alternative names (if any).
| Brand Device manufacturer company. | Apple |
| Model Device name. | iPhone 6s |
| Alternative names Other model names, if available. Sometimes the model is called differently, depending on the country or because of popular nicknames. | A1634 A1688 A1690 A1699 |
Design
Appearance of the device including dimensions, weight, volume, colors and materials.
| Width The horizontal side of the device when used in standard orientation. | 67.1 mm (millimeters) |
| Height The vertical side of the device when used in standard orientation. | 138.3 mm (millimeters) |
| Thickness The cross-sectional size of the device. | 7.1 mm (millimeters) |
| Weight How much does the device weigh excluding the case, SIM and memory cards and other additional elements. | 143 g (grams) |
| Volume Approximate value calculated using the formula: length times width times height. | 65.89 cm³ (cubic centimeters) |
| Colors What colors is the device available in? | Gray Silver Golden Rose gold |
| Housing materials What materials is the body made of? | Aluminium alloy |
System on a Chip (SoC)
A system on a chip, a single-chip system (System on a Chip, SoC) is when several systems performing different device functions are connected on one chip.
| System on a Chip (SoC) A single-chip system that contains components such as a processor, graphics accelerator, memory units, communication interfaces, etc., as well as software for the operation of the system. | Apple A9 APL0898 |
Central processing unit (CPU)
| Central processing unit (CPU) The main component of the device is responsible for calculations and data processing. | Apple Twister |
| Technical process What technological process is used to make the chip? The smaller the process technology, the better - the chips consume less power and generate less heat. | 14 nm (nanometers) |
| Processor size Processor capacity is a parameter that indicates how many bits of data a processor register processes in 1 clock cycle. This is usually 32 or 64 bits. | 64 bit |
| Instruction Set Architecture Instruction set architecture (ISA) is a programmable part of the microprocessor core used by software to control the operation of the processor. | ARMv8-A |
| Number of processor cores The processor can be either single-core or multi-core. The performance of the processor depends on the number of cores (threads). The more cores working simultaneously, the higher the power consumption, so in mobile devices all cores are used only under high load. | 2 |
| CPU clock speed Clock speed is the number of operations per second that a processor or its core can achieve. The higher the frequency, the higher the overall performance of the device, but performance also depends on the processor architecture and the number of cores. | 1840 MHz (megahertz) |
Graphics Processing Unit (GPU)
| Graphics Processing Unit (GPU) The graphics processing unit (GPU) is used to process and display graphics - 3D effects, games, interfaces and other visual elements. Due to the pipeline architecture, the GPU is many times more efficient in graphics processing than the processor. | PowerVR GT7600 |
| Number of GPU cores Similar to a processor, a GPU can have one core or several. The number of cores (threads) determines the performance and amount of information processed. The more cores, the better. | 6 |
Random access memory (RAM)
| Amount of random access memory (RAM) RAM (Random Access Memory, RAM, RAM) is temporary memory (works only while the device is running), which stores data and code for the operational operation of programs and applications. The more RAM, the more programs you can run simultaneously without loss of performance (there will be fewer “brakes”). | 2 GB (gigabytes) |
| Type of random access memory (RAM) Information about the type of RAM used by the device. | LPDDR4 —- M9 motion coprocessor Samsung N71AP — 14 nm TSMC N71mAP — 16 nm |
Built-in memory
Most mobile devices have built-in Flash memory, which is used as a storage for system data, the operating system, as well as user data - photos, videos, recordings and much more.
| Built-in memory capacity The higher the amount of built-in memory, the more games, programs, music, videos and your other files will fit in the device, especially the amount of memory is important when the device does not support memory cards. | 16 GB (gigabytes) 64 GB (gigabytes) 128 GB (gigabytes) |
Operating system
A mobile operating system (OS) is pre-installed software with a well-thought-out interface for user control of device functions.
| Operating system (OS) The operating system installed by default by the device manufacturer, as well as its version. | iOS 9 iOS 10 iOS 11.4 iOS 12.3 |
Battery
To operate autonomously, a mobile device requires a battery that powers all its components.
| Battery capacity The main characteristic of a battery is its maximum capacity, that is, the charge it can store. Capacity is measured in mAh (mAh, milliamp-hour). The higher the capacity, the longer the mobile device can work. | 1715 mAh (milliamp-hours) |
| Battery type Many types of batteries have been used in portable devices, but NiCd (nickel-cadmium), NiMH (nickel-metal hydride), and even more so SLA (lead-acid) batteries are already considered obsolete. Instead, modern mobile devices use Li-Ion (lithium-ion) and Li-Pol, Li-Poly (lithium-polymer) batteries. | Li-polymer |
| Call duration on 3G network (WCDMA, UMTS, CDMA2000) About how long a fully charged battery will be discharged during a call on third generation networks. Approximate time because it is influenced by various factors, including ambient temperature. | 14 h (hours) 840 min (minutes) 0.6 days |
| Waiting time on 3G network (WCDMA, UMTS, CDMA2000) About how long a fully charged battery will be discharged if the mobile device is in standby mode and connected to third generation networks. | 240 h (hours) 14400 min (minutes) 10 days |
Screen
The screen (display) is the main element for displaying graphic information.
| Technology The technology used to make the screen. There are many types of display manufacturing with their pros and cons. | IPS |
| Diagonal The screen diagonal of a device is measured in inches (inch, in or simply ″), and 1″ is equal to 2.54 cm. | 4.7 in (inches) 119.38 mm (millimeters) 11.94 cm (centimeters) |
| Width Approximate screen width | 58.51 mm (millimeters) 5.85 cm (centimeters) |
| Height Approximate screen height | 104.06 mm (millimeters) 10.41 cm (centimeters) |
| Aspect Ratio Aspect ratio is the ratio of the shorter side of the screen, which is considered to be 1, to the longer side, which is denoted by a decimal fraction indicating the ratio to the short side. | 1.779:1 |
| Screen resolution Screen resolution is the number of horizontal pixels (dots) multiplied by the number of vertical pixels. The higher the resolution, the more detailed the image will be. | 750 x 1334 pixels |
| Pixel Density The number of pixels per inch or PPI (pixels per inch) indicates the density of pixels per 1 inch (2.54 cm) of the screen. The higher the PPI, the sharper the image, and the less visible or even invisible “squares and dots” (pixels). | 326 ppi (pixels per inch) 128 ppcm (pixels per centimeter) |
| Color depth Color depth means how many bits are used in 1 pixel to display color (bits per pixel). | 24 bit 16777216 colors |
| Screen area Approximate usable area occupied by the screen on the front of the device. The higher the percentage, the narrower the frames around the display or the smaller the “chin with bangs.” | 65.82% (percent) |
| Touch screen A touch screen is a device that usually covers the display and is a touch input tool. In fact, in mobile devices, the touchscreen is a replacement for the keyboard and mouse. | Yes |
| Touch screen type There are many types of touch screens, with their pros and cons. Mobile devices often use capacitive touchscreens, but technology does not stand still and new types of sensors are appearing. | Capacitive |
| Multi-touch Touch screen support for two or more touches. For example, zooming photos with two fingers. | Yes |
| Impact-resistant protective glass of the display The screen and touchscreen of a mobile device are usually covered with protective tempered glass (sometimes plastic or film is used instead of glass) to protect the display from impacts and scratches. Many companies are engaged in the production of such protection, but the most famous are Corning - Gorilla Glass and Asahi - Dragontrail. | Yes |
| Display Contrast Ratio Contrast ratio is the ratio of display brightness in the white area to the black area. For example, 1000:1 means that white is 1000 times brighter than black. The higher the ratio, the deeper the blacks and the overall better image. | 1400:1 |
| Brightness Screen brightness is measured in candelas per square meter (cd/m2, cd/m2). The higher this indicator, the brighter the screen luminosity will be and the less it will be affected by ambient lighting. Comfortable brightness for videos and games is considered to be 300 cd/m2 or more. | 500 cd/m² |
Main camera
The main camera, usually built into the rear of the device, is designed for creating photo and video content.
| Photomatrix model An image sensor (matrix) is a light-sensitive sensor that converts an optical image into electrical signals that the device can subsequently process. | Sony IMX315 Exmor RS |
| Maximum image resolution This is the maximum number of pixels (dots) horizontally and vertically. The higher the resolution, the more detailed the image will be. Resolution can also be indicated in megapixels - this is the total number of pixels that can be in the image, calculated by the formula: vertical pixels multiplied by the number of horizontal pixels and divide the resulting amount by 1 million. | 4032 x 3024 pixels 12.19 MP (megapixels) |
| Matrix type There are two main types of photomatrix, CCD (Charge-Coupled Device) and CMOS (Complimentary Metal-Oxide Semiconductor). Mobile devices mainly use a CMOS matrix - it requires less space, has low power consumption and heating. Recently, new types of sensors have begun to appear, for example PureCel from OmniVision. | CMOS (complementary metal-oxide semiconductor) |
| Matrix size The larger the physical dimensions of the sensor, the larger pixels can be installed there or the greater their number, increasing the luminous flux and exposure. That is, the larger the size, the better. | 4.8 x 3.6 mm (millimeters) 0.24 in (inches) |
| Matrix pixel size Pixel size is one of the matrix parameters that determines what size pixels are used in the matrix. The larger the size, the better - less noise and a larger light-sensitive area. | 1.19 µm (micrometers) 0.00119 mm (millimeters) |
| Crop factor The crop factor is the ratio between the dimensions of a small format 35 mm matrix (36 x 24mm) and the size of the device matrix. That is, how much is our matrix smaller than the 35 mm matrix. Almost all cameras have smaller matrices, and the indicator itself is more of a reference value. | 7.21 |
| Focal length Focal length is the distance from the center of the lens to the image sensor. | 4.02 mm (millimeters) 29 mm (millimeters) *(35 mm / full frame) |
| Diaphragm Aperture (f-number, f) is used to control the light flux passing through the lens. The aperture is indicated by a fraction, and the smaller the fractional number, the higher the aperture passing through the lens. The more light that passes through the lens, the better overall, less noise in your photos and better night photography. | f/2.2 |
| Flash type Most mobile devices are equipped with light-emitting diode (LED) flashes, but there are also xenon flashes. As a flash, xenon is better - it is more powerful, but LED is more versatile (can work as a flashlight) and consumes less electricity. | Double LED |
| Maximum video resolution This is the maximum number of pixels (dots) horizontally and vertically. The higher the resolution, the more detailed the image will be. | 3840 x 2160 pixels 8.29 MP (megapixels) |
| FPS video recording at maximum resolution FPS (Frames per Second, frame rate) is the number of frames that changes in 1 second. The higher the number of frames per second, the smoother the image will be. In this case, we mean the number of frames that the camera can achieve at its maximum resolution; the lower the resolution, the higher the FPS can be. | 30 fps (frames per second) |
| Presence of flash Incorporating a flash into a mobile device allows you to take pictures in low light conditions. Creates the necessary lighting and compensates for the lack of natural light. | Yes |
| Digital zoom With digital zoom (zoom, enlargement), the subject is brought closer due to software image algorithms. The higher the magnification with digital zoom, the worse the image quality (noise, blur) will be compared to a non-zoomed one. | Yes |
| Number of lenses in the lens This is the number of optical elements (lenses) that are contained in the optical circuit of a camera lens. | 5 |
| Focus on face Function of auto-detection of living objects and autofocus on their face or head. | Yes |
| Panoramic shooting mode Panoramic photography is a series of frames where each subsequent frame is a continuation of the previous one; at the end of the shooting, all frames are stitched together at the software level to create a panoramic photograph. Frames can be shot both vertically and horizontally, and their width can be up to 360 degrees. This type of shooting is used when the camera's viewing angle is not enough to capture the entire scene. | Yes |
| HDR shooting mode HDR photography takes a quick series of shots with highlights, midtones, and shadows, then combines them into a single frame with high dynamic range. | Yes |
| Electronic (digital) image stabilizer EIS (Electronic Image Stabilizer - digital image stabilization) is performed using software algorithms and is needed to reduce blurring when the camera shakes. | Yes |
| Additional Information Additional information about the functions and characteristics of cameras. | Autofocus Continuous shooting Geo-tagging Touch focusing Exposure compensation Self-timer |
Front-camera
The front camera of a mobile device (selfie camera, rear camera) is a camera on the front part, which is usually used for video communication, recognition of gestures or faces, and selfie photographs.
| Photo resolution The maximum image resolution that the camera can produce. As resolution increases, image detail increases. Resolution can also be indicated in megapixels (the total number of pixels that an image can consist of) - these are vertical pixels multiplied by horizontal pixels and divided by 1 million. | 2560 x 1920 pixels 4.92 MP (megapixels) |
| Face unlock This is a new way to unlock your phone using facial recognition | Yes |
| Matrix type There are not many types of matrices, the main ones are CCD, PureCel and the most popular in mobile devices due to low power consumption and compact size - CMOS. | CMOS (complementary metal-oxide semiconductor) |
| Diaphragm An aperture (or aperture) is essentially an adjustable baffle to control the amount of light passing through the lens. The aperture is indicated by a fraction, and the smaller it is, the more light passes through the lens, which has a positive effect on photographs - there will be less noise and better night photography. While the main cameras also come with an adjustable aperture, most front cameras have a fixed aperture. | f/2.2 |
| Video resolution This is the maximum resolution the camera can record video at. The higher the resolution, the better. | 1920 x 1080 pixels 2.07 MP (megapixels) |
| Frame rate (FPS) of video shooting This is talking about FPS at maximum video resolution; at lower resolutions, the frame rate per second can be higher. FPS determines the smoothness of the video, as well as the ability to speed up or slow down it. | 30 fps (frames per second) —- Retina flash HDR Exposure compensation Self-timer |
| Camera focal length Focal length is the distance from the center of the lens to the sensor. The focal length determines the viewing angle, scale and degree of blur. | 31 mm (millimeters) |
SIM card
Subscriber Identification Module (SIM) used in mobile devices to identify subscribers in cellular networks.
| Type, size of SIM card A regular (mini SIM) card has dimensions of 25x15 mm. Micro SIM - 15x12 mm. Nano SIM - 12.3x8.8 mm. The sizes of SIM cards are different and not interchangeable. There is also an eSIM (virtual, electronic SIM card), it is built into the device and does not take up space. | Nano-SIM (4FF - fourth form factor, since 2012, 12.30 x 8.80 x 0.67 mm) |
| Number of SIM cards How many SIM cards does the device support? | 1 |
Mobile networks
This is a system in which communication and data transfer is carried out between subscribers, the location of one or more of which changes. This section lists the supported mobile communication standards and frequencies.
| GSM GSM (Global System for Mobile Communications) is a standard for digital mobile cellular communications of the second generation 2G with time and frequency division of channels. GSM came to replace analog cellular communications 1G (first generation). | GSM 850 MHz GSM 900 MHz GSM 1800 MHz GSM 1900 MHz |
| CDMA CDMA (Code Division Multiple Access) - this mobile communication standard can be classified as a 2.5G network (generation), unlike 2G, CDMA has higher speech quality, higher cellular network capacity and increased data transfer speed. | CDMA 800 MHz CDMA 1700/2100 MHz CDMA 1900 MHz |
| UMTS UMTS (Universal Mobile Telecommunications System), also called 3GSM, is a third generation (3G) mobile communications standard based on the WCDMA air interface. | UMTS 850 MHz UMTS 900 MHz UMTS 1700/2100 MHz UMTS 1900 MHz UMTS 2100 MHz |
| LTE LTE (Long-Term Evolution, often referred to as 4G LTE) is a standard for wireless high-speed data transmission, which, although it belongs to fourth generation networks (4G), is essentially a transitional stage from 3G to 4G, greatly accelerating data transfer speeds. The standard has an improved version, LTE Advanced (LTE-A), which can already be considered a full-fledged 4th generation network. | LTE 700 MHz Class 13 LTE 700 MHz Class 17 LTE 800 MHz LTE 850 MHz LTE 900 MHz LTE 1800 MHz LTE 1900 MHz LTE 2100 MHz LTE 2600 MHz LTE-TDD 1900 MHz (B39) LTE-TDD 2300 MHz (B40) LTE-TDD 2500 MHz (B41) LTE-TDD 2600 MHz (B38) LTE AWS (B4) LTE 700 MHz (B12) LTE 800 MHz (B18) LTE 800 MHz (B19) LTE 800 MHz (B20) LTE 1900+ MHz (B25) LTE 800 MHz (B26) LTE 800 MHz SMR (B27) LTE 700 MHz APT (B28) LTE 700 MHz de (B29) LTE 2300 MHz (B30) |
| CDMA2000 CDMA2000 (Code Division Multiple Access) is a third generation (3G) mobile communications standard that is based on CDMA to improve it. Compared to CDMA One, it is distinguished by network reliability, data transfer speed and high voice quality. | 1xEV-DO Rev. A |
Mobile network data standards
What data transfer standards in cellular networks are supported by the device, as well as their speed.
| Data transmission technologies Technologies for receiving and transmitting data, as well as their maximum speed. | UMTS (384 kbit/s) EDGE GPRS HSPA+ (HSUPA 5.76 Mbit/s, HSDPA 42 Mbit/s) LTE Cat 6 (51.0 Mbit/s, 301.5 Mbit/s) EV-DO Rev. A (1.8 Mbit/s, 3.1 Mbit/s) |
WiFi
Wi-Fi (Wireless Fidelity) is a technology for wireless data transmission over a local network among devices based on IEEE 802.11 standards.
| Wi-Fi Hot-Spot A hotspot is a Wi-Fi access point. In a mobile device, Hot-Spot turns the smartphone into a Wi-Fi access point, essentially turning it into a router capable of distributing the Internet. | Yes |
| Dual-band Wi-Fi DUAL-BAND (dual-band) Wi-Fi is the ability of a device to immediately receive or broadcast wireless signals in two frequency bands 2.4 and 5 GHz. 5GHz is a less congested frequency, due to which the connection will be of better quality. | Yes |
| WiFi MIMO MIMO is a spatial encoding method for a signal that increases the bandwidth of the channel in which data is transmitted and received by systems from multiple antennas. It is usually denoted as number (number of transmitters) x number (number of antennas). For example, 2x2 MIMO means that a WI-FI system consists of 2 transmitters and 2 receive antennas, while 1x1 is a traditional single antenna design. The more systems, the higher the throughput. | Yes |
| WiFi Supported WIFI wireless network standards. | 802.11a (IEEE 802.11a-1999) 802.11b (IEEE 802.11b-1999) 802.11g (IEEE 802.11g-2003) 802.11n (IEEE 802.11n-2009) 802.11n 5GHz 802.11ac (IEEE 802.11ac) —- |
Bluetooth
Bluetooth (BT, bluetooth (z), “blue tooth”) is a short-range wireless network (up to 10, sometimes 100 meters) operating on radio waves to transmit voice and data between devices.
| Bluetooth version Bluetooth technology is actively developing and, since 1998, has been constantly updating versions of the standard. Each subsequent version introduces one or several improvements in data exchange speed, range, facilitates pairing, reduces power consumption, or introduces some new protocols and operating profiles. The higher the Bluetooth version, the better. The technology is also backward compatible, for example, if your mobile device has version 5.0, then it will work with accessories version 4.2 and lower, but the improvements introduced in version 5.0 will not work; they will work only if both the device and accessories are version 5. | 4.2 |
| Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) Bluetooth LE is a low energy BT protocol specification. | Yes |
| A2DP profile The A2DP Bluetooth profile is designed to transmit a high-quality two-channel stereo signal via Bluetooth to wireless headphones, speakers and other acoustics. | Yes |
Sensors
Modern devices have many sensors that help in measurements, trigger functions, and make using the device more pleasant.
| Light sensor The light sensor reacts to the light level and is able to adjust the screen brightness automatically based on this. This is necessary to reduce power consumption and ease of use of the device. | Yes |
| Proximity sensor The proximity sensor reacts to the proximity of the mobile device to some object. For example, the sensor is used when talking on the phone to turn off the screen, which saves energy and prevents you from pressing buttons with your ear or cheek. | Yes |
| Gyroscope Gyroscope (gyroscope, gyro sensor) is a sensor for orientation in space that tracks the angle of inclination of even a stationary device along three coordinate axes. The sensor is mainly used in conjunction with an accelerometer in games and applications. | Yes |
| Accelerometer An accelerometer is a sensor that measures apparent acceleration, that is, it determines the position and distance at which a mobile device moves in space. Based on the data from this sensor, the screen orientation change, pedometer, control using tilts and gestures in games and applications, etc. work. | Yes |
| Barometer A barometer is a sensor capable of measuring atmospheric pressure. Used in weather forecasting, displaying altitude above sea level. | Yes |
| Fingerprint's scanner The scanner is responsible for authorization using a previously saved fingerprint, as a result of which the device is unlocked, payment is made, some action is confirmed - just put your finger on the scanner. Scanners can be either built into the body or built into a button or screen. | Yes |
| Digital compass This is software that displays data from a magnetic sensor or GPS in the form of a compass on the screen of a mobile device. If there are no sensors or GPS, then the digital compass will not work. | Yes |
| Additional sensors |
Audio
Audio - characteristics and capabilities of a mobile device in terms of sound.
| Music speaker There are two types of speakers in mobile devices - auditory and musical. The auditory speaker (speaker) is used for conversation, the music speaker (buzzer) is used to play music and sounds. | Loudspeaker Earphone —- Cirrus Logic 338S00105 Cirrus Logic 338S1285 HAC (M3/T4) — Hearing Aid Compatibility |
Radio
The radio in a mobile device can be built-in by the manufacturer (catch local radio channels, no internet required, often works only with headphones (as an antenna), but not always) or installed as an online application (requires internet, but more channels and often better quality) .
| Built-in radio Is a radio tuner integrated into the mobile device? | No |
Navigation and location
The location is determined by satellite navigation systems that track the device's autonomous geospatial location at multiple points. The most common satellite navigation systems are GPS, GLONASS, and the Chinese BeiDou.
| GPS GPS (Global Positioning System) is a global satellite navigation system that can determine the position of a mobile device, build routes and find the desired object on the map with an accuracy of several meters. | Yes |
| A-GPS A-GPS (Assisted GPS) is an assistive technology that will help you quickly find the location of your cellular device without waiting for satellite data, which is especially important in indoors and cities. Location is determined in various ways, for example, Wi-Fi access points, mobile towers, bluetooth and others. | Yes |
| GLONASS GLONASS is a Russian Global Navigation Satellite System, which is similar to GPS and works in tandem with it, increasing the accuracy and speed of navigation. | Yes |
| Additional navigation systems | Wi-Fi Cell ID |
USB connector
USB (Universal Serial Bus) is a serial interface for connecting peripherals to computers, smartphones, laptops and much more. The interface allows you to exchange data and power a peripheral device with energy, as well as connect several peripheral devices to one USB connector at once.
| USB standard The higher the standard, the faster the throughput, or more precisely the data exchange rate. With version 3.0 of the standard, the current was increased to 0.9A, eliminating the need for additional power for some devices. | 2.0 |
| USB Mass Storage Connecting a mobile device via USB as a data storage device. That is, when you enable this mode, your device can be used as a flash drive. | Yes |
| Additional characteristics Additional features of the USB connector, for example, OTG, whether the connection is supported, peripheral devices and additional memory. | Charging via USB Own cable/interface |
Headphone jack
A TRS headphone jack (or jack) is a common standard of connectors used for transmitting audio signals. By diameter there are jack (6.5 mm), mini-jack (3.5 mm) and micro-jack (2.5 mm). In mobile devices, the 3.5mm jack was considered the most popular and widespread, but recently they began to be removed, leaving only USB connectors, through which headphones are connected with a corresponding plug or using adapters.
| 3.5mm headphone jack Does the device have a 3.5 mm audio jack? | Yes |
Connection and synchronization
Options for synchronizing your mobile device and connecting it to other devices.
| NFC NFC (Near field communication, near contactless communication) is a technology for contactless communication between devices over a short distance. Widely used for contactless payment, in the form of a travel card or pass, and is also used for reading and interacting with NFC tags and for exchanging data between devices. | Yes |
| Connection, synchronization Types of synchronization and connection technologies supported by the device. | Computer sync OTA sync Tethering TV-Out UMA VoLTE |
Browser
A browser is a browser program for viewing sites and their content on the Internet. Through the browser, you can open websites, search for information, download necessary files, watch streaming videos, play browser games, etc.
| Technologies Markup and programming languages supported by the built-in (standard) browser. For mobile devices, you can install additional browser applications if the standard one does not suit you. | HTML HTML5 CSS 3 |
Audio file formats/codecs
Mobile devices support many audio file formats, as well as codecs for playing them.
| Default formats The formats that the mobile device supports out of the box are indicated. But if the device does not support the format you need, then you can try adding support for it. Sometimes support depends on the technical characteristics of the device (“hardware”) and nothing can be added here, but often the ability to process a particular audio format depends on the software part. You can install another audio player or codec set separately. | AAC (Advanced Audio Coding) eAAC+ / aacPlus v2 / HE-AAC v2 M4A (MPEG-4 Audio, .m4a) MP3 (MPEG-2 Audio Layer II, .mp3) WAV (Waveform Audio File Format, .wav, .wave) Apple Lossless AAX+ AAX |
Video file formats/codecs
Video file formats that the device supports and is capable of decoding and playing.
| Default formats Video file formats that the device is capable of playing with standard firmware and a standard (built-in) set of programs. Not all formats are supported by default, but you can install a third-party video player and/or set of codecs. | 3GPP (3rd Generation Partnership Project, .3gp) H.263 H.264 / MPEG-4 Part 10 / AVC video H.265 / MPEG-H Part 2 / HEVC QuickTime (.mov, .qt) MPEG-4 |
Screen
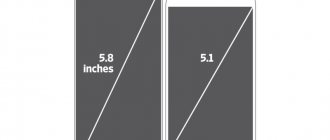
Despite the introduction of a fundamentally new smart touch technology - 3D Touch, the screen dimensions have not changed. Still the same familiar 4.7 inches for the simple “six” or 5.5 inches for the Plus version. The pixel density of the iPhone matrix remained at the same level. In fact, the outside is still the same branded Retina HD, which, thanks to the TapticEngine engine, has become a completely new interesting brainchild of Apple. Probably, the possibility of increasing image detail was postponed in order to reduce the energy costs required to ensure the operation of the updated display. After all, the fewer dots per inch, the less charge is consumed by the matrix. Still, the grain is barely noticeable. Surely users will not agree to a more contrasting screen on a smartphone, which will last much less time on a single charge.
Battery
As for the operating time, unfortunately, the increased size of the iPhone 6S did not in any way affect the expansion of battery capacity. On the contrary, Apple developers partially reduced the battery capacity to free up enough space for an additional touch layer. For example, the 6S now has a 1715 mAh battery at its disposal. The Plus version, in accordance with the size, also has a more powerful battery - 2750 mAh. And this is 95-165 mAh less than before. However, the good news is that compared to its predecessors, there are no significant changes in the duration of work. Except that it began to charge a little faster.
It turns out that the increased energy loads from the screen with the new progressive 3 DTouch technology are again compensated by the vaunted optimization of the hardware and system. In general, according to the manufacturer, who conducted tests in laboratory conditions, the operating time of the new iPhone remained at the same level. Although many users noted that s-series smartphones in full-scale tests are still slightly inferior, even to their not very “tenacious” predecessors. After all, their capacity parameters were a little more - 1810 mAh or 2915 mAh, respectively, which is also far from a standard to be compared to.
Display
To be honest, I don’t have much to write about the screen: it’s exactly the same as last year’s iPhone 6. The screen resolution is 1334x750 pixels with a diagonal of 4.7″, the pixel density is 326 ppi, which today is far from a record figure (according to For this reason, the iPhone 6S screen does not look as smooth as competing screens that have a pixel density of more than 400 ppi). If you don't chase resolution numbers, there are no complaints about the screen; it has excellent brightness and contrast, as well as visibility in the sun. Let me demonstrate this last statement with a photo from last year's iPhone 6 review:
Framework
The dimensions of the frames around the display have also not undergone any significant changes. And this fact is often cited as a reproach to Apple engineers, saying that everyone else has been making almost frameless smartphones for a long time. But in practice it turns out that they are much more convenient, since a confident grip in the hand involves placing your fingers on the front panel. The frames also eliminate the possibility of accidental clicks that redirect anywhere - when you hold the phone in your hand - when viewing web pages or videos. Those. and here the Apple ideology is thoroughly adhered to – everything is for the convenience of the user. Agree, the absence of frames is a very dubious superiority, rather of a purely aesthetic nature than a necessary condition for comfortable use. This innovation does not carry any “payload”. Therefore, it is confidently (for now) neglected by the development team.
In addition , the frames provide an additional stiffening rib, which significantly enhances the overall strength of the body. If you wanted a rigid gadget in metal “armor” - get it. Now the iPhone will definitely not bend or crumble into parts when dropped on the asphalt, like its plastic counterparts. After all, no matter how much you take care of your smartphone, sooner or later it will fall, and it’s better for the massive metal end to be scratched than for the display glass to shatter into pieces, damaging the expensive matrix. This is common sense!
Accessories
So if you still have soft leather or silicone cases from your previous iPhone, they will probably be suitable for S-version gadgets. Considering the sufficient elasticity of these materials, they will easily diverge by the required couple of millimeters. All ports and buttons remain in the same places, so there should be no problems when using the cases. This is true for both the 4.7-inch 6s and the Plus modification.
The only thing is that the increased thickness of the new model may let us down a little - after all, two extra millimeters (for the sake of the improved screen) make themselves felt. Expensive plastic cases that promise comprehensive protection against dirt, water and dust are likely to be small. You may also want to have an additional “window” in the case - in place of the marking with the letter S, to let others know that you own a new and improved flagship. After all, iPhones are also a fashion brand. Although you won’t find such cases from the manufacturer itself.
But this is all nothing compared to the mass of opportunities that the iPhone s series opens up for users. They gave a new powerful round of development to the glorious Apple smartphones. Impressive sales levels are an excellent confirmation of this, and the company’s natural increase in profits speaks volumes!
Camera
Apple has a very conservative approach to cameras in its smartphones. Suffice it to say that the company used 8-megapixel modules for four years (from 2011 to 2015). And now the iPhone 6S finally brought the long-awaited increase in resolution, which again turned out to be conservative - up to 12 MP. At the same time, the lens remains the same, its aperture is f/2.2, which is not bad in itself, but worse than competitors who already use optics in their smartphones with a maximum aperture of f/2.0 and even f/1.8.
Overall, I would characterize the camera in the iPhone 6S as very good, even excellent, but overall it is inferior in quality to cameras in smartphones such as the Samsung Galaxy S6 or LG G4. True, the iPhone takes its toll on the speed of the camera, its simple and friendly interface, the ability to record slow-motion video (up to 120 fps in FullHD resolution and up to 240 fps in 720p) and built-in interval shooting mode.
Examples of photos taken with the iPhone 6S camera: